Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Potential Role of Antidiabetic Therapy in the Evolution of COVID-19
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11010145, Jan 2023
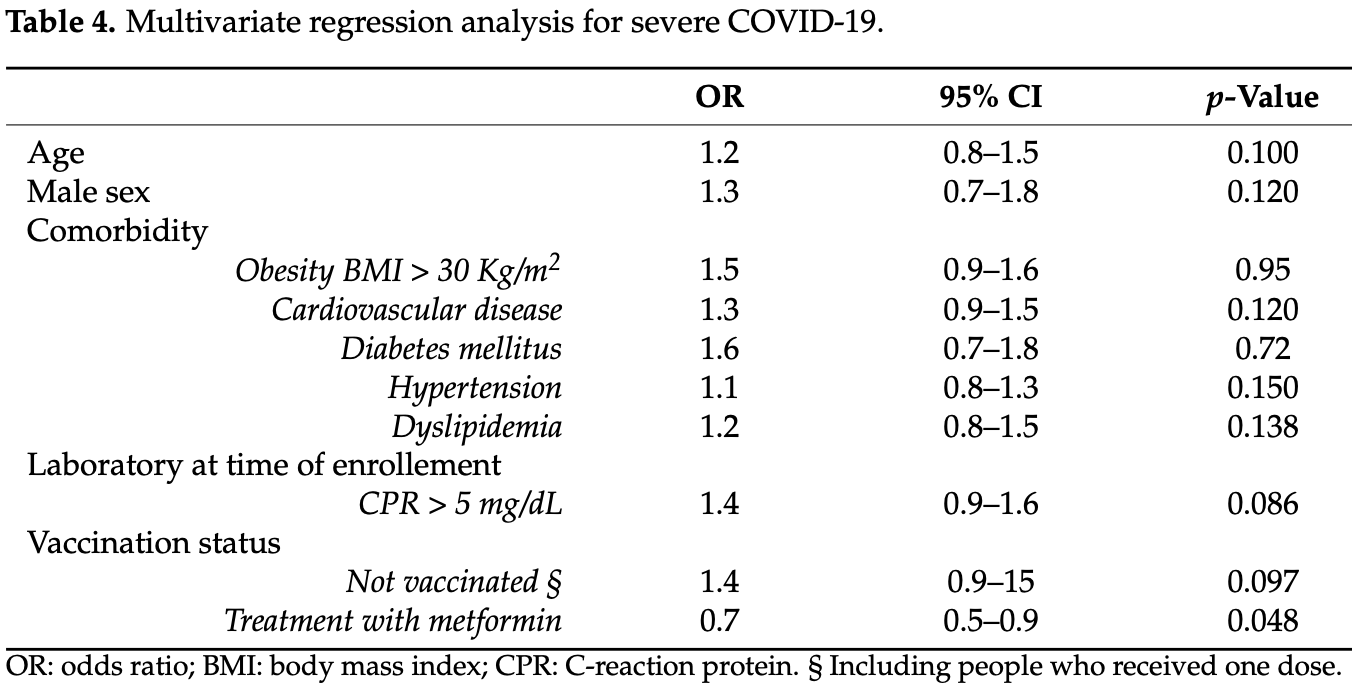
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 43 diabetes patients hospitalized for COVID-19 in Italy, showing lower risk of severe cases with metformin vs. insulin.
|
risk of severe case, 15.2% lower, RR 0.85, p = 0.048, treatment 5 of 19 (26.3%), control 14 of 24 (58.3%), NNT 3.1, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pinchera et al., 6 Jan 2023, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period November 2021 - May 2022, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Contact: biapin89@virgilio.it (corresponding author).
Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Potential Role of Antidiabetic Therapy in the Evolution of COVID-19
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11010145
Diabetes mellitus represents one of the most frequent comorbidities among patients with COVID-19, constituting a risk factor for a more severe prognosis than that of non-diabetic patients. However, the pathophysiological mechanism underlying this unfavorable outcome is still not completely clear. The goal of our study was to evaluate the potential role of antidiabetic therapy in the evolution of COVID-19.
Author Contributions: B.P. participated in substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work and the acquisition, analysis and interpretation data for the work. N.S.M. conceived idea with analysis and participated in interpreting the literature, drafting the article, approving the final version to be published, and being accountable for the accuracy/integrity of the content. A.R.B. participated in revising the initial draft of the article and approving the final version to be published. I.D.F. participated in drafting the article and approving the final version to be published. A.T. participated in analysis and interpretation of data for the work. G.B. participated in the acquisition and analysis of data for the work. R.V. conceived idea with analysis and participated in interpreting the literature, approving the final version to be published, and being accountable for the accuracy/integrity of the content. I.G. participated in substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work; the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data for the work; approval for the final version to be published. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Arnold, Scheurer, Dake, Hedgpeth, Hutto et al., Hospital Guidelines for Diabetes Management and the Joint Commission-American Diabetes Association Inpatient Diabetes Certification, Am. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2015.11.024
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bode, Garrett, Messler, Mcfarland, Crowe et al., Glycemic characteristics and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the United States, J. Diabetes Sci. Technol, doi:10.1177/1932296820924469
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: The CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Cdc Covid-, Preliminary estimates of the prevalence of selected underlying health conditions among patients with coronavirus disease 2019-United States, Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6913e2
Cho, Raybuck, Blagih, Kemboi, Haase et al., Hypoxia-inducible factors in CD4 + T cells promote metabolism, switch cytokine secretion, and T cell help in humoral immunity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1811702116
Di Castelnuovo, Bonaccio, Costanzo, Gialluisi, Antinori et al., Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: Survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study, Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc Dis
Hancock, Meyer, Mistry, Khetani, Wagschal et al., Insulin receptor as-sociates with promoters genome-wide and regulates gene ex-pression, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.030
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes. Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290
Inoki, Zhu, Guan, TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival, Cell
Isoda, Young, Zirlik, Macfarlane, Tsuboi et al., Metformin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB in human vascular wall cells, Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol, doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000201938.78044.75
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Yin, Yang et al., Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Know, Hasan, Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis, J. Med. Virol
Liu, Liu, Xiaoxing, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor MK-626 restores insulin secretion through enhancing autophagy in high fat diet-induced mice, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.116
Mancusi, Grassi, Borghi, Ferri, Muiesan et al., Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with COVID-19 Infection: The Results of the SARS-RAS Study of the Italian Society of Hypertension, High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev, doi:10.1007/s40292-020-00429-3
Musi, Hirshman, Nygren, Svanfeldt, Bavenholm et al., Metformin increases AMP-activated protein kinase activity in skeletal muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.7.2074
Niekerk, Merwe, Engelbrecht, Diabetes and susceptibility to infections: Implication for COVID-19, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13383
Pinchera, Scotto, Buonomo, Zappulo, Stagnaro et al., Diabetes and COVID-19: The potential role of mTOR, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109813
Pinchera, Spirito, Buonomo, Foggia, Carrano et al., mTOR Inhibitor Use Is Associated With a Favorable Outcome of COVID-19 in Patients of Kidney Transplant: Results of a Retrospective Study, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.852973
Radtke, Macdonald, Tacchini-Cottier, Regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by Notch, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri3445
Scheen, Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, Diabetes Metab
Shi, Zhang, Jiang, Zhang, Hu et al., Clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes in Wuhan, China: A two-center, retrospective study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0598
Singh, Gilles, Singh, Singh, Chudasama et al., Prevalence of comorbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and metaanalysis, Diabetes Obes. Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14124
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004
Singh, Singh, At-admission hyperglycemia is consistently associated with poor prognosis and early intervention can improve outcomes in patients with COVID-19, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.034
Singh, Singh, Hyperglycemia without diabetes and new-onset diabetes are both associated with poorer outcomes in COVID-19, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108382
Viollet, Guigas, Sanz, Garcia, Leclerc et al., Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview, Clin. Sci, doi:10.1042/CS20110386
Walrand, Guillet, Boirie, Vasson, Insulin differentially regulates monocyte and polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions in healthy young and elderly humans, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2005-1619
Xi, Zou, Ye, Huang, Chen et al., Pioglitazone protects tubular cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through enhancing autophagy via AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172695
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11010145",
"ISSN": [
"2076-2607"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010145",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Diabetes mellitus represents one of the most frequent comorbidities among patients with COVID-19, constituting a risk factor for a more severe prognosis than that of non-diabetic patients. However, the pathophysiological mechanism underlying this unfavorable outcome is still not completely clear. The goal of our study was to evaluate the potential role of antidiabetic therapy in the evolution of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"microorganisms11010145"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8685-5434",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pinchera",
"given": "Biagio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schiano Moriello",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4378-8366",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Buonomo",
"given": "Antonio Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Di Filippo",
"given": "Isabella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanzillo",
"given": "Anastasia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buzzo",
"given": "Giorgio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villari",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5199-8451",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gentile",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Federico II COVID Team",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microorganisms",
"container-title-short": "Microorganisms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T06:48:19Z",
"timestamp": 1672987699000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T08:04:23Z",
"timestamp": 1672992263000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-07T06:06:52Z",
"timestamp": 1673071612622
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672963200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/1/145/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "145",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"article-title": "Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: The CORONADO study",
"author": "Cariou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0598",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes in Wuhan, China: A two-center, retrospective study",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14124",
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1915",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes. Metab.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6913e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID-19 Response Team (2020). Preliminary estimates of the prevalence of selected underlying health conditions among patients with coronavirus disease 2019—United States, February 12–March 28 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep., 69, 382–386."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2020.07.031",
"article-title": "Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: Survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study",
"author": "Bonaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1899",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc Dis.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40292-020-00429-3",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with COVID-19 Infection: The Results of the SARS-RAS Study of the Italian Society of Hypertension",
"author": "Mancusi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.034",
"article-title": "At-admission hyperglycemia is consistently associated with poor prognosis and early intervention can improve outcomes in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1641",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108382",
"article-title": "Hyperglycemia without diabetes and new-onset diabetes are both associated with poorer outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108382",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1932296820924469",
"article-title": "Glycemic characteristics and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the United States",
"author": "Bode",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13383",
"article-title": "Diabetes and susceptibility to infections: Implication for COVID-19",
"author": "Niekerk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.030",
"article-title": "Insulin receptor as-sociates with promoters genome-wide and regulates gene ex-pression",
"author": "Hancock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "722",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3445",
"article-title": "Regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by Notch",
"author": "Radtke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2005-1619",
"article-title": "Insulin differentially regulates monocyte and polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions in healthy young and elderly humans",
"author": "Walrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2738",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1811702116",
"article-title": "Hypoxia-inducible factors in CD4+ T cells promote metabolism, switch cytokine secretion, and T cell help in humoral immunity",
"author": "Cho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8975",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109813",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: The potential role of mTOR",
"author": "Pinchera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109813",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20110386",
"article-title": "Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview",
"author": "Viollet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "253",
"journal-title": "Clin. Sci.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.852973",
"article-title": "mTOR Inhibitor Use Is Associated With a Favorable Outcome of COVID-19 in Patients of Kidney Transplant: Results of a Retrospective Study",
"author": "Pinchera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "852973",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00929-2",
"article-title": "TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival",
"author": "Inoki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diabetes.51.7.2074",
"article-title": "Metformin increases AMP-activated protein kinase activity in skeletal muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Musi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2074",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.ATV.0000201938.78044.75",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB in human vascular wall cells",
"author": "Isoda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "611",
"journal-title": "Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100290",
"journal-title": "Obes. Med.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172695",
"article-title": "Pioglitazone protects tubular cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through enhancing autophagy via AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway",
"author": "Xi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172695",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "863",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.116",
"article-title": "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor MK-626 restores insulin secretion through enhancing autophagy in high fat diet-induced mice",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "516",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "470",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"article-title": "Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2015.11.024",
"article-title": "Hospital Guidelines for Diabetes Management and the Joint Commission-American Diabetes Association Inpatient Diabetes Certification",
"author": "Arnold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "333",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "351",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"article-title": "Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108619",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Mortality risk with preadmission metformin use in patients with COVID-19 and diabetes: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Know",
"first-page": "695",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/1/145"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Potential Role of Antidiabetic Therapy in the Evolution of COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
