Effect of Higher-Dose Ivermectin for 6 Days vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.1650, NCT04885530, Feb 2023
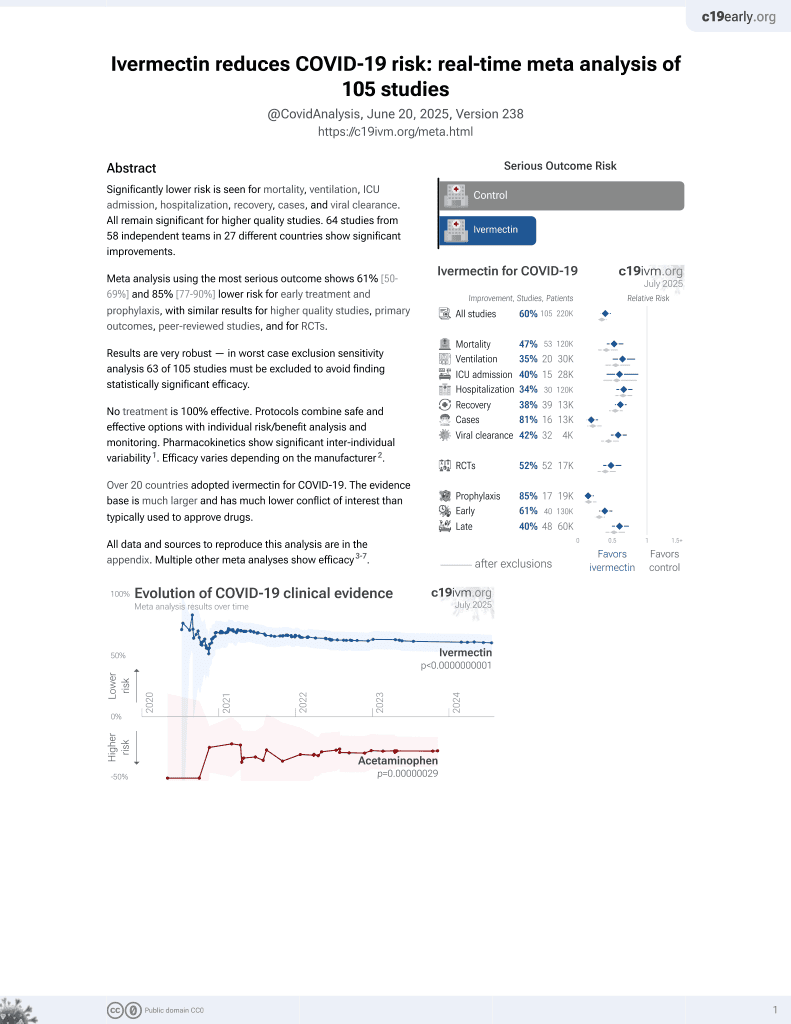
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
600µg/kg arm of ACTIV-6. Results of this trial are unreliable, with multiple critical anomalies, and no response from the authors. For details see1.
Naggie et al., 20 Feb 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 31 authors, trial NCT04885530 (history).
Contact: susanna.naggie@duke.edu.
Effect of Ivermectin 600 μg/kg for 6 days vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
doi:10.1101/2022.12.15.22283488
Background: Whether ivermectin, with a maximum targeted dose of 600 µg/kg, shortens symptom duration or prevents hospitalization among outpatients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains unknown. Our objective was to evaluate the effectiveness of ivermectin, dosed at 600 µg/kg, daily for 6 days compared with placebo for the treatment of early mild to moderate COVID-19. Methods: ACTIV-6, an ongoing, decentralized, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, platform trial, was designed to evaluate repurposed therapies in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. A total of 1206 participants age ≥30 years with confirmed COVID-19, experiencing ≥2 symptoms of acute infection for ≤7 days, were enrolled from February 16, 2022,
Author Contributions Drs Naggie and Hernandez had full access to all of the blinded data in the study. Drs Lindsell and Stewart directly accessed and verified the underlying study data and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors contributed to the drafting and review of the manuscript and agreed to submit for publication.
Disclosures
Data Sharing Statement Available in the Supplement to the ACTIV-6 Statistical Analysis Plan (Supplement 4).
(C) Caption: Thick vertical lines denote the estimated mean of the posterior distribution. Density is the relative likelihood of posterior probability distribution. Outcomes with higher density are more likely than outcomes with lower density.
References
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19, Infectious Diseases Society of America
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Hill, Mirchandani, Pilkington, Ivermectin for COVID-19: addressing potential bias and medical fraud, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab645
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Kory, Meduri, Iglesias, Varon, Marik, Retracted article: Clinical and scientific rationale for the "MATH+" hospital treatment protocol for COVID-19, J Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1177/0885066620973585
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Corrigendum to Antiviral effect of highdose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: A proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071
Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Effect of Ivermectin vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Reis, Silva, Silva, Effect of Early Treatment with Ivermectin among Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Schilling, Jittamala, Watson, Pharmacometric assessment of the in vivo antiviral activity of ivermectin in early symptomatic COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.07.15.22277570
Square, Retraction, Elgazzar, A. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 pandemic, Preprint
Thorlund, Dron, Park, Hsu, Forrest et al., A real-time dashboard of clinical trials for COVID-19, Lancet Digit Health, doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30086-8
Yu, Bafadhel, Dorward, Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X