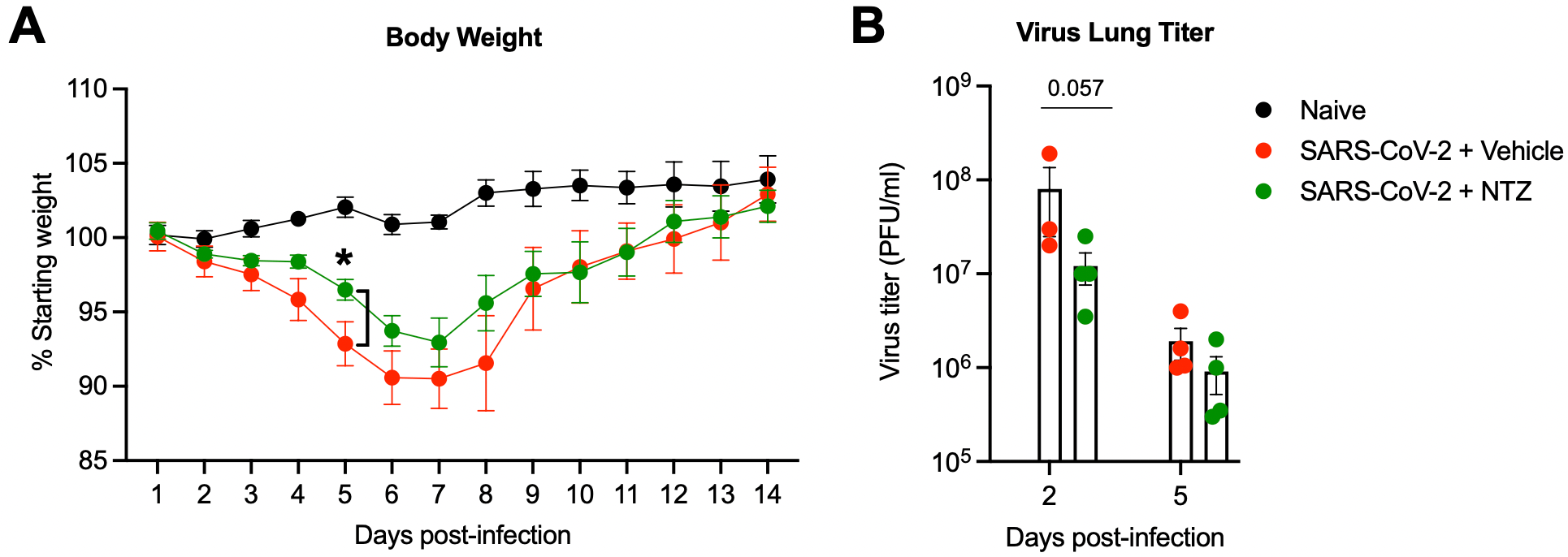
The oral drug nitazoxanide restricts SARS-CoV-2 infection and attenuates disease pathogenesis in Syrian hamsters
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.08.479634, Feb 2022
Syrian hamster study showing improvements in SARS-CoV-2 related weight loss, inflammation, viral load, and lung synctia formation with nitazoxanide, and an in vitro study showing that nitazoxanide inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in H9, iAT2, Vero E6, Vero TMPRSS2, and Ace2-A549 cells.
6 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nitazoxanide for COVID-19:
1.
Xu et al., Two-way pharmacodynamic modeling of drug combinations and its application to pairs of repurposed Ebola and SARS-CoV-2 agents, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/aac.01015-23.
2.
Rajoli et al., Dose prediction for repurposing nitazoxanide in SARS‐CoV‐2 treatment or chemoprophylaxis, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.14619.
Miorin et al., 9 Feb 2022, preprint, 35 authors.
The oral drug nitazoxanide restricts SARS-CoV-2 infection and attenuates disease pathogenesis in Syrian hamsters
doi:10.1101/2022.02.08.479634
A well-tolerated and cost-effective oral drug that blocks SARS-CoV-2 growth and dissemination would be a major advance in the global effort to reduce COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Here, we show that the oral FDA-approved drug nitazoxanide (NTZ) significantly inhibits SARS-CoV-2 viral replication and infection in different primate and human cell models including stem cell-derived human alveolar epithelial type 2 cells. Furthermore, NTZ synergizes with remdesivir, and it broadly inhibits growth of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 (beta), P.1 (gamma), and B.1617.2 (delta) and viral syncytia formation driven by their spike proteins. Strikingly, oral NTZ treatment of Syrian hamsters significantly inhibits SARS-CoV-2-driven weight loss, inflammation, and viral dissemination and syncytia formation in the lungs. These studies show that NTZ is a novel host-directed therapeutic that broadly inhibits SARS-CoV-2 dissemination and pathogenesis in human and hamster physiological models, which supports further testing and optimization of NTZ-based therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection alone and in combination with antiviral drugs.
Microscopy Shared Resource Facility at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. We are grateful to Gail Cassell for helpful discussions through the years. Finally, we are indebted to Wallis Annenberg, Jeanne Sullivan, and the founders of Fast Grants for their critical and early support.
Conflict of interest The
References
Alwan, Dieppe, Elson, Bradfield, Amanat et al., Bone resorbing activity in synovial fluids in destructive osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, Curr Protoc Microbiol
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -final report, N Engl J Med
Blum, Cimerman, Hunter, Tierno, Lacerda et al., Nitazoxanide superiority to placebo to treat moderate COVID-19 -A Pilot prove of concept randomized double-blind clinical trial, eClinicalMedicine
Bobrowski, Chen, Eastman, Itkin, Shinn et al., Synergistic and antagonistic drug combinations against SARS-CoV-2, Mol Ther
Braga, Ali, Secco, Chiavacci, Neves et al., Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia, Nature
Caputo, Caci, Ferrera, Pedemonte, Barsanti et al., TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity, Science
Cardenas, Loo, Gale, Jr, Hartman et al., Ebola virus VP35 protein binds double-stranded RNA and inhibits alpha/beta interferon production induced by RIG-I signaling, J Virol
Chan, Zhang, Yuan, Poon, Chan et al., Simulation of the clinical and pathological manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in golden Syrian hamster model: implications for disease pathogenesis and transmissibility, Clin Infect Dis
Daniloski, Jordan, Wessels, Hoagland, Kasela et al., Identification of required host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection in human cells, Cell
Doan, Vorobjev, Rees, Filby, Wolkenhauer et al., An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, Trends Biotechnol
Doumbo, Rossignol, Pichard, Traore, Dembele et al., Nitazoxanide in the treatment of cryptosporidial diarrhea and other intestinal parasitic infections associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in tropical Africa, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Emeny, Morgan, Regulation of the interferon system: evidence that Vero cells have a genetic defect in interferon production, J Gen Virol
Escalera, Gonzalez-Reiche, Aslam, Mena, Pearl et al., The VP35 protein of Ebola virus inhibits the antiviral effect mediated by double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR, N Engl J Med
Haffizulla, Hartman, Hoppers, Resnick, Samudrala et al., Effect of nitazoxanide in adults and adolescents with acute uncomplicated influenza: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Haridas, Ranjbar, Vorobjev, Goldfeld, Barteneva, Imaging flow cytometry analysis of intracellular pathogens, Methods
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat Rev Microbiol
Hou, Okuda, Edwards, Martinez, Asakura et al., SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract, Cell
Huang, Hume, Abo, Werder, Villacorta-Martin et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of pluripotent stem cell-derived human lung Alveolar Type 2 cells elicits a rapid epithelial-intrinsic inflammatory response, Cell Stem Cell
Hussar, New drugs of 2003, J Am Pharm Assoc
Ianevski, Giri, Aittokallio, SynergyFinder 2.0: visual analytics of multidrug combination synergies, Nucleic Acids Res
Imai, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Hatta, Loeber, Halfmann et al., Syrian hamsters as a small animal model for SARS-CoV-2 infection and countermeasure development, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Jacob, Vedaie, Roberts, Thomas, Villacorta-Martin et al., Derivation of self-renewing lung alveolar epithelial type II cells from human pluripotent stem cells, Nat Protoc
Jasenosky, Cadena, Mire, Borisevich, Haridas et al., The FDA-Approved Oral Drug Nitazoxanide Amplifies Host Antiviral Responses and Inhibits Ebola Virus. iScience 19, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Leung, Prins, Borek, Farahbakhsh, Tufariello et al., Structural basis for dsRNA recognition and interferon antagonism by Ebola VP35, Nat Struct Mol Biol
Leventhal, Clancy, Erasmus, Feldmann, Hawman, An Intramuscular DNA Vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 Decreases Viral Lung Load but Not Lung Pathology in Syrian Hamsters, Microorganisms
Loewe, Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells, Arzneimittelforschung
Miner, Labitzke, Liu, Wang, Henckels et al., Drug repurposing: the anthelmintics niclosamide and nitazoxanide are potent TMEM16A antagonists that fully bronchodilate airways, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Piacentini, La Frazia, Riccio, Pedersen, Topai et al., Nitazoxanide inhibits paramyxovirus replication by targeting the Fusion protein folding: role of glycoprotein-specific thiol oxidoreductase ERp57, Cell Rep
Ranjbar, Haridas, Nambu, Jasenosky, Sadhukhan et al., Cytoplasmic RNA Sensor Pathways and Nitazoxanide Broadly Inhibit Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth, iScience
Reid, Valmas, Martinez, Sanchez, Basler, Ebola virus VP24 proteins inhibit the interaction of NPI-1 subfamily karyopherin proteins with activated STAT1, J Virol
Riva, Yuan, Yin, Martin-Sancho, Matsunaga et al., Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing, Nature
Rossignol, Hidalgo, Feregrino, Higuera, Gomez et al., A double-'blind' placebo-controlled study of nitazoxanide in the treatment of cryptosporidial diarrhoea in AIDS patients in Mexico, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg
Rossignol, La Frazia, Chiappa, Ciucci, Santoro, Thiazolides, a new class of anti-influenza molecules targeting viral hemagglutinin at the post-translational level, J Biol Chem
Rossignol, Matthew, Oaks, Bostick, Vora et al., Early treatment with nitazoxanide prevents worsening of mild and moderate COVID-19 and subsequent hospitalization
Rossignol, Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent, Antiviral Res
Sampaio, Chauveau, Hertzog, Bridgeman, Fowler et al., The RNA sensor MDA5 detects SARS-CoV-2 infection, Sci Rep
Schroeder, Cheng, Jan, Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride channel subunit, Cell
Schumann, Gantke, Muhlberger, Ebola virus VP35 antagonizes PKR activity through its C-terminal interferon inhibitory domain, J Virol
Sia, Yan, Chin, Fung, Poon et al., Pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 virus in golden Syrian hamsters, Nature
Stachulski, Rossignol, Pate, Taujanskas, Robertson et al., Synthesis, antiviral activity, preliminary pharmacokinetics and structural parameters of thiazolide amine salts, Future Med Chem
White, Rosales, Yildiz, Kehrer, Miorin et al., Plitidepsin has potent preclinical efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the host protein eEF1A, Science
Xie, Muruato, Lokugamage, Narayanan, Zhang et al., An Infectious cDNA Clone of SARS-CoV-2, Cell Host Microbe
Xu, Edwards, Borek, Feagins, Mittal et al., Ebola virus VP24 targets a unique NLS binding site on karyopherin alpha 5 to selectively compete with nuclear import of phosphorylated STAT1, Cell Host Microbe
Yang, Cho, Koo, Tak, Cho et al., TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance, Nature
Yin, Riva, Pu, Martin-Sancho, Kanamune et al., MDA5 governs the innate immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in lung epithelial cells, Cell Rep
Zhang, Bornholdt, Liu, Abelson, Lee et al., The ebola virus interferon antagonist VP24 directly binds STAT1 and has a novel, pyramidal fold, PLoS Pathog
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.02.08.479634",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.08.479634",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A well-tolerated and cost-effective oral drug that blocks SARS-CoV-2 growth and dissemination would be a major advance in the global effort to reduce COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Here, we show that the oral FDA-approved drug nitazoxanide (NTZ) significantly inhibits SARS-CoV-2 viral replication and infection in different primate and human cell models including stem cell-derived human alveolar epithelial type 2 cells. Furthermore, NTZ synergizes with remdesivir, and it broadly inhibits growth of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 (beta), P.1 (gamma), and B.1617.2 (delta) and viral syncytia formation driven by their spike proteins. Strikingly, oral NTZ treatment of Syrian hamsters significantly inhibits SARS-CoV-2-driven weight loss, inflammation, and viral dissemination and syncytia formation in the lungs. These studies show that NTZ is a novel host-directed therapeutic that broadly inhibits SARS-CoV-2 dissemination and pathogenesis in human and hamster physiological models, which supports further testing and optimization of NTZ-based therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection alone and in combination with antiviral drugs.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miorin",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mire",
"given": "Chad E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ranjbar",
"given": "Shahin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hume",
"given": "Adam J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Jessie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3873-9188",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Crossland",
"given": "Nicholas A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "Kris M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laporte",
"given": "Manon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kehrer",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haridas",
"given": "Viraga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moreno",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nambu",
"given": "Aya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jangra",
"given": "Sonia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cupic",
"given": "Anastasija",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1360-3260",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dejosez",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abo",
"given": "Kristine A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tseng",
"given": "Anna E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Werder",
"given": "Rhiannon B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rathnasinghe",
"given": "Raveen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutetwa",
"given": "Tinaye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramos",
"given": "Irene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sainz de Aja",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garcia de Alba Rivas",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schotsaert",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corley",
"given": "Ronald B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Falvo",
"given": "James V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez-Sesma",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rossignol",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Andrew A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zwaka",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kotton",
"given": "Darrell N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mühlberger",
"given": "Elke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Sastre",
"given": "Adolfo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldfeld",
"given": "Anne E",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T22:35:12Z",
"timestamp": 1644446112000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T22:35:13Z",
"timestamp": 1644446113000
},
"group-title": "Immunology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T23:11:27Z",
"timestamp": 1644448287896
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "bioRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.02.08.479634",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"The oral drug nitazoxanide restricts SARS-CoV-2 infection and attenuates disease pathogenesis in Syrian hamsters"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}