Inhaled beclomethasone in the treatment of early COVID-19: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, hospital-based trial in Sri Lanka
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803, Dec 2023
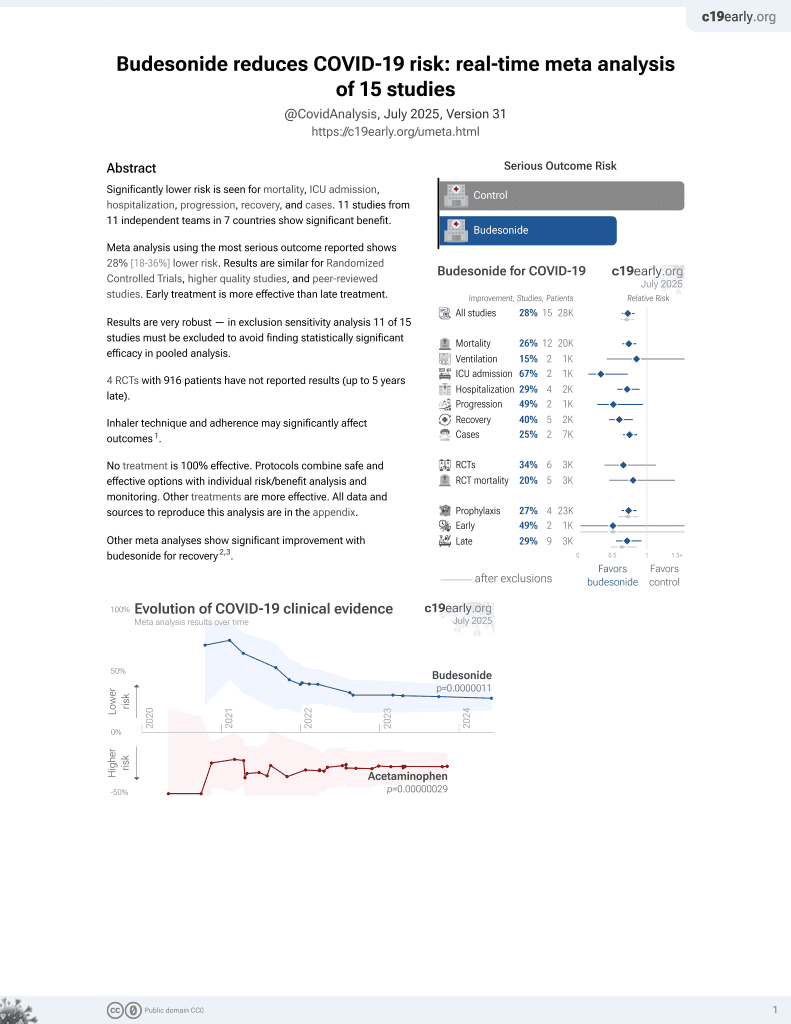
Budesonide for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2021, now with p = 0.0000042 from 14 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 385 asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 patients in Sri Lanka showing no significant difference in progression to severe disease with inhaled beclomethasone. There was a reduction in time to clinical recovery in patients initially presenting with moderate COVID-19 symptoms.
Mettananda et al., 14 Dec 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Sri Lanka, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 13 July, 2021 - 25 October, 2021.
Contact: chamila@kln.ac.lk.
Inhaled beclomethasone in the treatment of early COVID-19: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, hospital-based trial in Sri Lanka
BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803
Objectives To study if early initiation of inhaled beclomethasone 1200 mcg in patients with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 reduces disease progression to severe COVID-19. Design Double-blinded, parallel-groups, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Setting A hospital-based study in Sri Lanka. Participants Adults with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19, presenting within the first 7 days of symptom onset or laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19, admitted to a COVID-19 intermediate treatment centre in Sri Lanka between July and November 2021. Interventions All participants received inhaled beclomethasone 600 mcg or placebo two times per day, for 10 days from onset of symptoms/COVID-19 test becoming positive if asymptomatic or until reaching primary endpoint, whichever is earlier. Primary outcome measure Progression of asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 to severe COVID-19. Secondary outcome measures The number of days with a temperature of 38°C or more and the time to selfreported clinical recovery. Results A total of 385 participants were randomised to receive beclomethasone(n=193) or placebo(n=192) stratified by age (≤60 or >60 years) and sex. One participant from each arm withdrew from the study. All participants were included in final analysis. Primary outcome occurred in 24 participants in the beclomethasone group and 26 participants in the placebo group (RR 0.90 ; p=0.763). The median time for selfreported clinical recovery in all participants was 5 days (95% CI 3 to 7) in the beclomethasone group and 5 days (95% CI 3 to 8) in the placebo group (p=0.5). The median time for self-reported clinical recovery in patients with moderate COVID-19 was 5 days (95% CI 3 to 7) in the beclomethasone group and 6 days (95% CI 4 to 9) in the placebo group (p=0.05). There were no adverse events. Conclusions Early initiation of inhaled beclomethasone in patients with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 did not reduce disease progression to severe COVID-19. Trial registration number Sri Lanka Clinical Trials Registry; SLCTR/2021/017. ⇒ This is a randomised double-blind adequately powered placebo-controlled trial. ⇒ This study brings evidence from low-middle-income countries and South Asians. ⇒ Patients were recruited irrespective of having symptoms or not. ⇒ Patients were recruited irrespective of their risk of developing complications. ⇒ Patients were randomised irrespective of their vaccination status.
Competing interests None declared. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
Bafadhel, Faner, Taillé, Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19, Eur Respir Rev, doi:10.1183/16000617.0099-2022
Beasley, Harper, Bird, Inhaled corticosteroid therapy in adult asthma. time for a new therapeutic dose terminology, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.201810-1868CI
Brodin, Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01202-8
Campbell, Julious, Altman, Estimating sample sizes for binary, ordered categorical, and continuous outcomes in two group comparisons, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.311.7013.1145
Clemency, Varughese, Gonzalez-Rojas, Efficacy of inhaled Ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of adolescents and adults with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6759
Duvignaud, Lhomme, Onaisi, Inhaled Ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in adults at risk of adverse outcomes: a randomised controlled trial (COVERAGE), Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.02.031
Ezer, Belga, Daneman, Inhaled and intranasal Ciclesonide for the treatment of COVID-19 in adult outpatients: CONTAIN phase II randomised controlled trial, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068060
Gomes, Jeewandara, Jayadas, Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern by identification of single nucleotide Polymorphisms in the spike protein by a Multiplex real-time PCR, J Virol Methods, doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114374
Griesel, Wagner, Mikolajewska, Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015125
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Lee, Bortolussi-Courval, Belga, Inhaled corticosteroids for outpatients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02921-2021
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Efficacy and safety of Baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallelgroup, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3
Mariette, Hermine, Tharaux, Effectiveness of Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A follow-up of the CORIMUNO-TOCI-1 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2209
Nice, Inhaled corticosteroid doses for NICE's asthma guideline2018 05.06
Powell, Smart, Wood, Validity of the common cold questionnaire (CCQ) in asthma exacerbations, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001802
Powers, Bacci, Leidy, Performance of the inFLUenza patient-reported outcome (FLU-PRO) diary in patients with influenzalike illness (ILI), PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0194180
Ramakrishnan, Nicolau, Langford, Inhaled Budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
Song, Yoon, Seo, Ciclesonide Inhaler treatment for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: A randomized, open-label, phase 2 trial, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10163545
The, Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Thorlund, Dron, Park, A real-time dashboard of clinical trials for COVID-19, Lancet Digit Health, doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30086-8
Wu, Daouk, Kebbe, Low-dose versus high-dose dexamethasone for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275217
Yu, Bafadhel, Dorward, Inhaled Budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X
Yu, Bafadhel, Dorward, Inhaled Budesonide for COVID-19 in people at higher risk of adverse outcomes in the community: interim analyses from the PRINCIPLE trial, medRxiv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803",
"ISSN": [
"2044-6055",
"2044-6055"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>To study if early initiation of inhaled beclomethasone 1200 mcg in patients with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 reduces disease progression to severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Double-blinded, parallel-groups, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Setting</jats:title><jats:p>A hospital-based study in Sri Lanka.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Participants</jats:title><jats:p>Adults with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19, presenting within the first 7 days of symptom onset or laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19, admitted to a COVID-19 intermediate treatment centre in Sri Lanka between July and November 2021.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>All participants received inhaled beclomethasone 600 mcg or placebo two times per day, for 10 days from onset of symptoms/COVID-19 test becoming positive if asymptomatic or until reaching primary endpoint, whichever is earlier.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Primary outcome measure</jats:title><jats:p>Progression of asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 to severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Secondary outcome measures</jats:title><jats:p>The number of days with a temperature of 38°C or more and the time to self-reported clinical recovery.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 385 participants were randomised to receive beclomethasone(n=193) or placebo(n=192) stratified by age (≤60 or >60 years) and sex. One participant from each arm withdrew from the study. All participants were included in final analysis. Primary outcome occurred in 24 participants in the beclomethasone group and 26 participants in the placebo group (RR 0.90 ; p=0.763). The median time for self-reported clinical recovery in all participants was 5 days (95% CI 3 to 7) in the beclomethasone group and 5 days (95% CI 3 to 8) in the placebo group (p=0.5). The median time for self-reported clinical recovery in patients with moderate COVID-19 was 5 days (95% CI 3 to 7) in the beclomethasone group and 6 days (95% CI 4 to 9) in the placebo group (p=0.05). There were no adverse events.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Early initiation of inhaled beclomethasone in patients with asymptomatic, mild or moderate COVID-19 did not reduce disease progression to severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial registration number</jats:title><jats:p>Sri Lanka Clinical Trials Registry; SLCTR/2021/017.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3328-1553",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mettananda",
"given": "Chamila",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peiris",
"given": "Chathura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abeyrathna",
"given": "Dharani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunasekara",
"given": "Aloka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Egodage",
"given": "Thimira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dantanarayana",
"given": "Channaka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4065-2639",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pathmeswaran",
"given": "Arunasalam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ranasinha",
"given": "Channa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMJ Open",
"container-title-short": "BMJ Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T07:08:28Z",
"timestamp": 1702624108000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T07:08:52Z",
"timestamp": 1702624132000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"N/A"
],
"name": "COVID-related research fund set up by the Faculty of Medicine, University of Kelaniya, Sri Lanka"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-16T00:45:26Z",
"timestamp": 1702687526297
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 13,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1702512000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e075803",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30086-8",
"article-title": "A real-time dashboard of clinical trials for COVID-19",
"author": "Thorlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e286",
"journal-title": "Lancet Digit Health",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.1",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-01202-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0275217",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.4",
"unstructured": "Wu H , Daouk S , Kebbe J , et al . Low-dose versus high-dose dexamethasone for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial. PLOS ONE 2022;17:e0275217. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275217"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0",
"article-title": "Inhaled Budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Ramakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.6",
"unstructured": "Yu L-M , Bafadhel M , Dorward J , et al . Inhaled Budesonide for COVID-19 in people at higher risk of adverse outcomes in the community: interim analyses from the PRINCIPLE trial. medRxiv 2021;2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10163545",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.7",
"unstructured": "Song J-Y , Yoon J-G , Seo Y-B , et al . Ciclesonide Inhaler treatment for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: A randomized, open-label, phase 2 trial. J Clin Med 2021;10:3545. doi:10.3390/jcm10163545"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-068060",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.8",
"unstructured": "Ezer N , Belga S , Daneman N , et al . Inhaled and intranasal Ciclesonide for the treatment of COVID-19 in adult outpatients: CONTAIN phase II randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2021;375:e068060. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068060"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6759",
"article-title": "Efficacy of inhaled Ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of adolescents and adults with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Clemency",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.9",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02921-2021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.10",
"unstructured": "Lee TC , Bortolussi-Courval É , Belga S , et al . Inhaled corticosteroids for outpatients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 2022;59:2102921. doi:10.1183/13993003.02921-2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.02.031",
"article-title": "Inhaled Ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in adults at risk of adverse outcomes: a randomised controlled trial (COVERAGE)",
"author": "Duvignaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.11",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.12",
"unstructured": "Insufficient data on use of inhaled corticosteroids to treat COVID-19. 2022. Available: www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/insufficient-data-use-inhaled-corticosteroids-treat-covid-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015125",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.13",
"unstructured": "Griesel M , Wagner C , Mikolajewska A , et al . Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2022;3:CD015125. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015125"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/16000617.0099-2022",
"article-title": "Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Bafadhel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir Rev",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.14",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.15",
"unstructured": "Worldometer . Sri Lanka Population 2020, Available: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/sri-lanka-population"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/circ.106.25.3143",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.16",
"unstructured": "Third report of the National cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III) final report. Circulation 2002;106:3143. doi:10.1161/circ.106.25.3143"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114374",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.17",
"unstructured": "Gomes L , Jeewandara C , Jayadas TP , et al . Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern by identification of single nucleotide Polymorphisms in the spike protein by a Multiplex real-time PCR. J Virol Methods 2022;300:S0166-0934(21)00313-X. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114374"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.18",
"unstructured": "COVID-19_Treatment_Guidelines_Panel . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. 2021. Available: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.19",
"unstructured": "WHO . Sri Lanka - WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard 2021, Available: https://covid19.who.int/region/searo/country/lk"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.311.7013.1145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0001802",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.21",
"unstructured": "Powell H , Smart J , Wood LG , et al . Validity of the common cold questionnaire (CCQ) in asthma exacerbations. PLoS One 2008;3:e1802. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001802"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0194180",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.22",
"unstructured": "Powers JH , Bacci ED , Leidy NK , et al . Performance of the inFLUenza patient-reported outcome (FLU-PRO) diary in patients with influenza-like illness (ILI). PLoS ONE 2018;13:e0194180. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0194180"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.24"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.25",
"unstructured": "NICE . Inhaled corticosteroid doses for NICE’s asthma guideline2018 05.06.2021, Available: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng80/resources/inhaled-corticosteroid-doses-pdf-4731528781"
},
{
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.26",
"unstructured": "GINA . Global strategy for asthma management and prevention; online appendix2019 05.06.2021, Available: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/GINA-2019-Appendix-wms.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201810-1868CI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2209",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A follow-up of the CORIMUNO-TOCI-1 randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Mariette",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1241",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.28",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial",
"author": "Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023121423051900000_13.12.e075803.29",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-075803"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Inhaled beclomethasone in the treatment of early COVID-19: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, hospital-based trial in Sri Lanka",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "13"
}