Safety and Efficacy of Nebulised Anti-Inflammatory Solution of Alkaline Hypertonic Ibuprofen (AHI) for Treatment of SARS-Cov-2 Infection: A Compassionate Study with a Comparator Arms
et al., European Journal of Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.31488/EJRM.132, Dec 2022
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0000000039 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
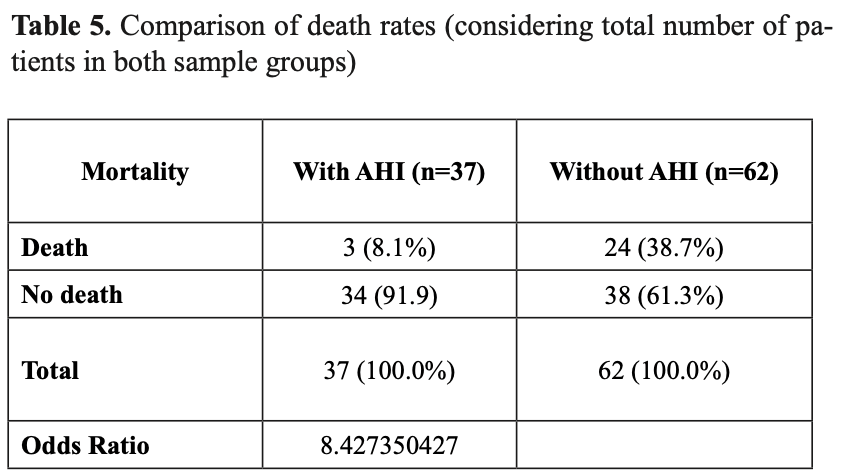
Retrospective 99 COVID-19 patients in Argentina showing significantly lower mortality with inhaled alkaline hypertonic ibuprofen (AHI) treatment. The treatment has a pH of 8.5. 3 times daily for 7-10 days.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
Study covers ibuprofen and alkalinization.
|
risk of death, 79.1% lower, RR 0.21, p < 0.001, treatment 3 of 37 (8.1%), control 24 of 62 (38.7%), NNT 3.3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kalayan et al., 31 Dec 2022, retrospective, Argentina, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period June 2020 - September 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with sodium ibuprofenate) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Safety and Efficacy of Nebulised Anti-Inflammatory Solution of Alkaline Hypertonic Ibuprofen (AHI) for Treatment of SARS-Cov-2 Infection: A Compassionate Study with a Comparator Arms
European Journal of Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.31488/ejrm.132
Background. This retrospective study evaluates the efficacy of inhalation therapy with alkaline hypertonic ibuprofen (AHI) in COVID-19 positive patients compared to a control group of patients who received conventional treatment. The study was carried out at the Orías Hospital in Jujuy Province, Argentina, from June to September 2020, with final follow-up on September 30. Methods. The study included 99 COVID-19 positive patients with moderate to severe disease (respiratory distress and/or hypoxemia). The control group of 62 patients were treated with the protocols in force at that time, oxygen, dexamethasone and enoxaparin. The group under evaluation comprised 37 patients treated with AH), in addition to standard treatment. Findings. Result shows that the treatment with AHI formulation is safe and effective. The mean respiratory rate (RR) of the patients went from 26.3 before treatment with AHI to 19.8 after treatment. On the other hand, the O2 saturation of patients before treatment with AHI showed a mean of 89.0%; at the end of treatment, the mean was 95.8%. In patients treated with AHI, on day 14, 85% had been discharged, while in patients not treated with AHI, only 36-37% were discharged on day 23. Patients with standard treatment, without AHI, show a mortality of 38.7%, distributed evenly in the 25 days of hospitalization. The mortality of patients treated with AHI was 8.1%, observed within the first 10 days of hospitalization. Interpretation. Results show that nebulization with AHI is an anti-inflammatory therapeutic alternative for the treatment of COVID-19 positive patients.
Declaration of Interests There are no conflicts of interest of the participants of this work to declare.
Contributorship Statement Galia Kalayan coordinated the development and data collection; Ana Carolina Arias Cau, Manuela del Valle Cabello, Mariela Nuñez, Romina Lumetto were the ones who collected the data and made their selection; Dante Beltramo, Roxana Alasino, Luis Argañaras, Néstor García and Nicolás Martinez Rios had the idea for the article; Dante Beltramo and Roxana Alasino wrote the article.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary Report, New Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Cao, Wnag, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Capellini, Restini, Bendhack, The Effect of Extracellular pH Changes on Intracellular pH and Nitric Oxide Concentration in Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells from Rat Aorta, PlosOne, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062887
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate Covid-19, New Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Clemente, Freiberger, Ravetti, An in silico analysis of Ibuprofen enantiomers in high concentrations of sodium chloride with SARS-CoV-2 main protease, J Biomo Structure & Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1872420
Elizur, Cannon, Ferkol, Airway inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.07-1631
Fang, Jiang, Su, The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies, Free Radic Biol Med
Freedman, Loscalzo, Nitric oxide and its relationship to thrombotic disorders, Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis
García, Porta, Alasino, Ibuprofen, a traditional drug that may impact the course of COVID-19 New effective formulation in nebulizable solution, Medical Hypotheses
Group, Horby, Estcourt, Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.09.21252736
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Huang, Lin, Chou, Ibuprofen protects ventilator-induced lung injury by downregulating Rho-kinase activity in rats, BioMed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/749097
Jiménez, Martin, Pozo, Mechanisms involved in protection afforded by L-arginine in ibuprofen-induced gastric damage: role of nitric oxide and prostaglandins, Dig Dis Sci, doi:10.1023/a:1013203217788
Landray, Recovery, Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 therapy) Colchicine arm stopped for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalised with COVID-19
Li, Song, Li, Ibuprofen attenuates interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and actin reorganization via modulation of RhoA signaling in rabbit chondrocytes, Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, doi:10.1093/abbs/gmz101
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of Convalescent Plasma Therapy on Time to Clinical Improvement in Patients With Severe and Life-threatening COVID-19 -A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10044
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Early High-Titer Plasma Therapy to Prevent Severe Covid-19 in Older Adults, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033700
Menzel, Kolarz, Modulation of nitric oxide synthase activity by ibuprofen, Inflammation, doi:10.1023/a:1027374605731
Monk, Marsden, Tear, Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30511-7
Muñoz, Alasino, Garro, High Concentrations of Sodium Chloride Improve Microbicidal Activity of Ibuprofen against Common Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens, Pharmaceuticals
Onischuk, Tolstikova, An´kov, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin and Diclofenac Sodium Nanoaerosol: Generation, Inhalation Delivery and Biological Effects in Mice and Rats, Journal of Aerosol Science, doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2016.05.005
Onischuk, Tolstikova, Sorokina, Analgesic Effect from Ibuprofen Nanoparticles Inhaled by Male Mice, J Aerosol Med Pulmonary Drug Delivery, doi:10.1089/jamp.2008.0721
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 -Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
Perlman, Malik, Ibuprofen prevents thrombin-induced lung vascular injury: mechanism of effect, The Am Physiol Soc. www.physiology.org/journal/ajpheart at Midwestern Univ Lib
Salva Oscar, Roxana, Celia, Nebulization with alkaline hipertonic ibuprofen induces a rapid increase in platelets circulating in COVID-19 patients but not in healthy subjects, Platelets, doi:10.1080/09537104.2021.1967918.-2021
Salva, Doreski, Rersal of SARS-CoV2-Induced Hypoxia by Nebulized Sodium Ibuprofenate in a Compassionate Use Program, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Plasmar, Group, A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
Veljkovic, Vergara-Alert, Egalés, Use of the informational spectrum methodology for rapid biological analysis of the novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: prediction of potential receptor, natural reservoir, tropism and therapeutic/vaccine target
Villanueva, Heckenberger, Strobach, Equipotent inhibition by R(-), S(+) and racemic ibuprofen of human polymorphonuclear cell function in vivo, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.31488/ejrm.132",
"ISSN": [
"2633-7452"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.31488/EJRM.132",
"container-title": "European Journal of Respiratory Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Eur J Respir Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T17:34:40Z",
"timestamp": 1669138480000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T17:34:46Z",
"timestamp": 1669138486000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-20T12:21:10Z",
"timestamp": 1705753270789
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"member": "16388",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.31488",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"publisher": "MAK Periodical Library",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://europeanjournalofrespiratorymedicine.com/safety-and-efficacy-of-nebulised-anti-inflammatory-solution-of-alkaline-hypertonic-ibuprofen-ahi-for-treatment-of-sars-cov-2-infection-a-compassionate-study-with-a-comparator-arms"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and Efficacy of Nebulised Anti-Inflammatory Solution of Alkaline Hypertonic Ibuprofen (AHI) for Treatment of SARS-Cov-2 Infection: A Compassionate Study with a Comparator Arms",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}
kalayan