Course of inflammation and infection markers differ in ICU patients with severe COVID-19 under casirivimab- and/or tocilizumab application: an observational study
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4090027/v1, NCT06233357, Apr 2024
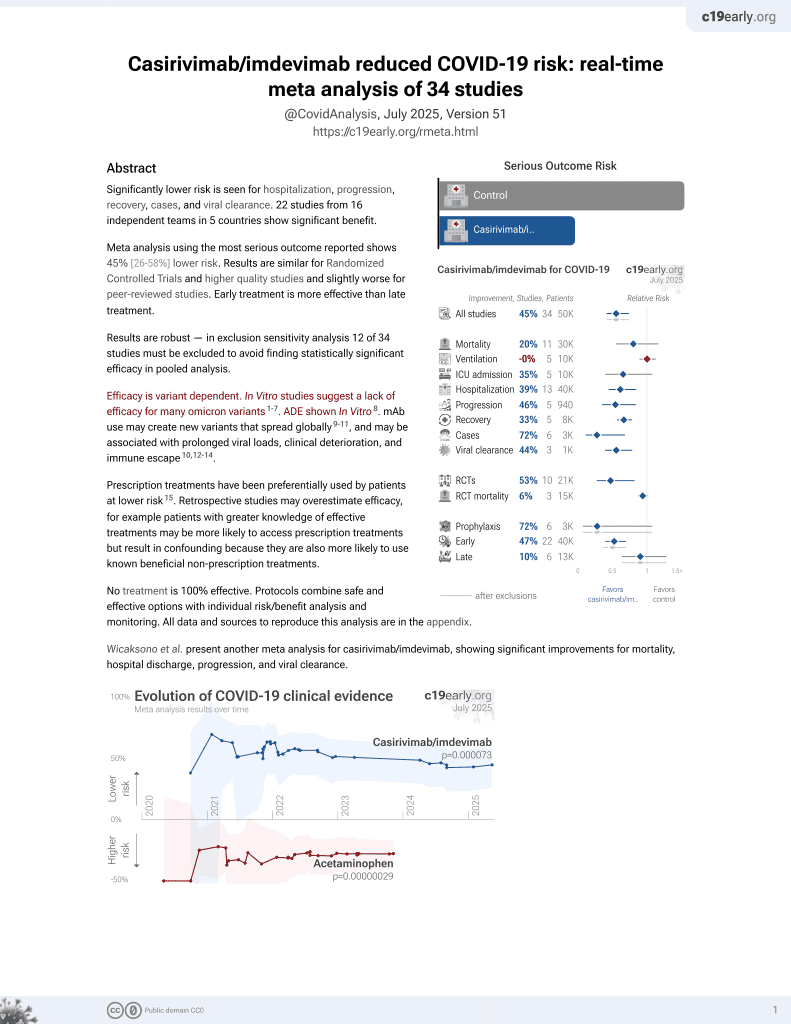
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
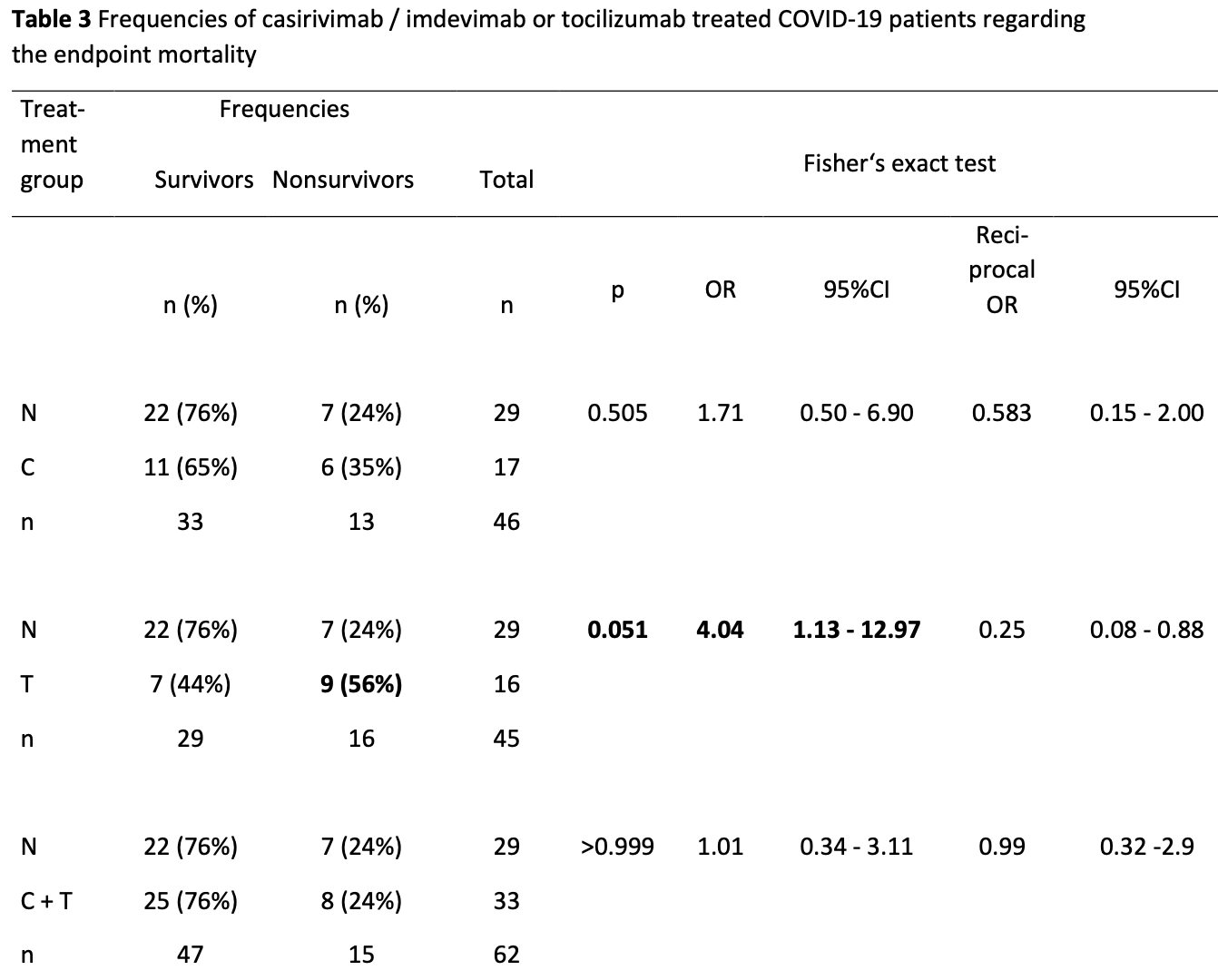
Retrospective 95 ICU patients showing no significant difference in mortality with casirivimab/imdevimab. There was significantly higher mortality with tocilizumab.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
|
risk of death, 16.0% higher, RR 1.16, p = 0.80, treatment 14 of 50 (28.0%), control 7 of 29 (24.1%), C or C+T vs. N.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Iustila-Maran et al., 5 Apr 2024, retrospective, Germany, preprint, 4 authors, study period August 2021 - February 2022, trial NCT06233357 (history).
Contact: manfred.weiss@uniklinik-ulm.de.
Course of inflammation and infection markers differ in ICU patients with severe COVID-19 under casirivimab- and/or tocilizumab application: an observational study
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4090027/v1
Background: The outcome and longitudinal course of inflammation and infection markers were unknown in COVID-19 patients on the ICU treated without (N) or with SARS-CoV-2 specific monoclonal antibodies (casirivimab / imdevimab, C) or antibodies against interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptors (tocilizumab, T), solely, or in combination of both (C + T).
Methods: In a retrospective observational study, in critically ill N, C, T, C+ T COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU with the CoV-2 delta-variant between August 2021 and February 2022, 28-day mortality and 30-day time course of infection and inflammation markers were evaluated. Results: Out of 95 patients with COVID-19, 29 patients were not treated (N), 17 with C, 16 with T, 33 with C + T. Mortality rates in N, C, T, and C + T, were 24%, 35%, 56%, and 24%, being higher in T compared to N and C + T (p = 0.05). Prolonged leukocyte, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) elevations were detected in nonsurvivors compared to survivors in C + T within the first two weeks, IL-6 in the first days in T. In N, higher PCT, CRP, IL-6 and ferritin occured in nonsurvivors in the first days.
Conclusion: Sporadically measured IL-6 and CRP in T is less useful. Longlasting IL-6 receptor blockade may be deleterious in COVID-19. High IL-6 may hint at poor prognosis within the first days in T, leukocytes, PCT, CRP and IL-6 in the first two weeks in C + T, and PCT, CRP, IL-6 and ferritin within the first days in N.
Abbreviations C: casirivimab / imdevimab; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; CoV-2: corona virus 2; C + T: casirivimab / imdevimab plus tocilizumab; CRP: C reactive protein; ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IL-6: interleukin 6; IL-6R: interleukin 6 receptor; LOS: length of stay; N: no casirivimab / imdevimab and no tocilizumab; NonSu: nonsurvivors; n. s.: not significant; Su: survivors; PCT: procalcitonin; T: tocilizumab; WHO: World Health Organization.
Authors' contributions MW, NM, AO and KT contributed to the conception and design of the study. AO, NM, KT and MW generated, collected and assembled the data. Data analysis and interpretation: MW and NM analyzed and interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Ethics approval has been given by the ethics commssion of the university Ulm, application nr. 129/22; NCT 06233357. Due to the fact, that clinical and laboratory data were gathered in routine care, no additional blood has been drawn, no diagnostic and no intervention in addition had been performed, the ethic's committe waived informed consent.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
Cantini, Goletti, Petrone, Fard, Niccoli et al., Immune Therapy, or Antiviral Therapy, or Both for COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Drugs
Catanzaro, Fagiani, Racchi, Corsini, Govoni et al., Immune response in COVID-19: addressing a pharmacological challenge by targeting pathways triggered by SARS-CoV-2, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Chen, Hu, Wei, Yuan, Wen et al., Systematic review and meta-analysis of tocilizumab in persons with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), Leukemia
Cox, Peacock, Harvey, Hughes, Wright et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies, Nat Rev Microbiol
Dodd, Follmann, Wang, Koenig, Korn et al., Endpoints for randomized controlled clinical trials for COVID-19 treatments, Clin Trials
Fu, Xu, Wei, Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?, J Transl Med
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Rowan, Nichol et al., Remap-Cap Investigators. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gustine, Jones, Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Am J Pathol
Hofmaenner, Garcia, Ganter, Brugger, Buehler et al., What every intensivist should know about Tocilizumab, Crit Care
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Recovery Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Huang, Mccreary, Bariola, Minnier, Wadas et al., Effectiveness of Casirivimab-Imdevimab and Sotrovimab During a SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant Surge: A Cohort Study and Randomized Comparative Effectiveness Trial, JAMA Netw Open
Keske, Tekin, Sait, Irkoren, Kapmaz et al., Appropriate use of tocilizumab in COVID-19 infection, Int J Infect Dis
Kluge, Janssens, Welte, Weber-Carstens, Schälte et al., S3-Leitlinie -Empfehlungen zur stationären Therapie von Patienten mit COVID-19
Lal, Erondu, Heymann, Gitahi, Yates, Fragmented health systems in COVID-19: rectifying the misalignment between global health security and universal health coverage, Lancet
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, J Clin Virol
Mcgonagle, Sharif, 'regan, Bridgewood, The Role of Cytokines including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease, Autoimmun Rev
Mikolajewska, Weber, S-S, Konik, Jensen et al., COVID-19 von leicht bis schwer richtig behandeln, Dtsch Artzebl
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Sarkar, Isa, Hou et al., Effect of Subcutaneous Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Combination vs Placebo on Development of Symptomatic COVID-19 in Early Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Pawar, Desai, Solomon, Ortiz, Gale et al., Risk of serious infections in tocilizumab versus other biologic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multidatabase cohort study, Ann Rheum Dis
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Razonable, Pawlowski, Horo, Arndt, Arndt et al., Casirivimab-Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19, EClinicalMedicine
Recovery, Group, Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Rosas, Brau, Waters, Go, Hunter et al., Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Sarmiento, Rojas, Jerez, Bertin, Campbell et al., Ruxolitinib for Severe COVID-19-Related Hyperinflammation in Nonresponders to Steroids, Acta Haematol
Shankar-Hari, Vale, Godolphin, Fisher, Higgins et al., WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies Working Group. Association Between Administration of IL-6 Antagonists and Mortality Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Meta-analysis, JAMA
Stone, Frigault, Serling-Boyd, Fernandes, Harvey et al., Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Vo, Mazur, Thai, The impact of COVID-19 economic crisis on the speed of adjustment toward target leverage ratio: An international analysis, Financ Res Lett
Wang, Knovich, Coffman, Torti, Torti, Serum ferritin: Past, present and future, Biochim Biophys Acta
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Zhao, Zhu, Zhang, Li, Wei et al., Tocilizumab combined with favipiravir in the treatment of COVID-19: A multicenter trial in a small sample size, Biomed Pharmacother
Zhou, Chen, Ji, He, Xue, Increased Serum Levels of Hepcidin and Ferritin Are Associated with Severity of COVID-19, Med Sci Monit
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-4090027/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4090027/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Background: The outcome and longitudinal course of inflammation and infection markers were unknown in COVID-19 patients on the ICU treated without (N) or with SARS-CoV-2 specific monoclonal antibodies (casirivimab / imdevimab, C) or antibodies against interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptors (tocilizumab, T), solely, or in combination of both (C + T). \nMethods: In a retrospective observational study, in critically ill N, C, T, C+ T COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU with the CoV-2 delta-variant between August 2021 and February 2022, 28-day mortality and 30-day time course of infection and inflammation markers were evaluated. \nResults: Out of 95 patients with COVID-19, 29 patients were not treated (N), 17 with C, 16 with T, 33 with C + T. Mortality rates in N, C, T, and C + T, were 24%, 35%, 56%, and 24%, being higher in T compared to N and C + T (p = 0.05). Prolonged leukocyte, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) elevations were detected in nonsurvivors compared to survivors in C + T within the first two weeks, IL-6 in the first days in T. In N, higher PCT, CRP, IL-6 and ferritin occured in nonsurvivors in the first days. \nConclusion: Sporadically measured IL-6 and CRP in T is less useful. Longlasting IL-6 receptor blockade may be deleterious in COVID-19. High IL-6 may hint at poor prognosis within the first days in T, leukocytes, PCT, CRP and IL-6 in the first two weeks in C + T, and PCT, CRP, IL-6 and ferritin within the first days in N. \nTrial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06233357, retrospectively registered, release date: January 31, 2024.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
13
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universitätsklinikum Ulm"
}
],
"family": "Iustila-Maran",
"given": "Stana-Nicoleta",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universitätsklinikum Ulm"
}
],
"family": "Orlet",
"given": "Amelie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universitätsklinikum Ulm"
}
],
"family": "Traeger",
"given": "Karl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universitätsklinikum Ulm"
}
],
"family": "Weiss",
"given": "Manfred",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T16:39:19Z",
"timestamp": 1712335159000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T16:39:19Z",
"timestamp": 1712335159000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-06T00:50:24Z",
"timestamp": 1712364624116
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712275200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4090027/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4090027/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4090027/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Course of inflammation and infection markers differ in ICU patients with severe COVID-19 under casirivimab- and/or tocilizumab application: an observational study",
"type": "posted-content"
}