Feb 21 |
Sargramostim for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 4 studies | |
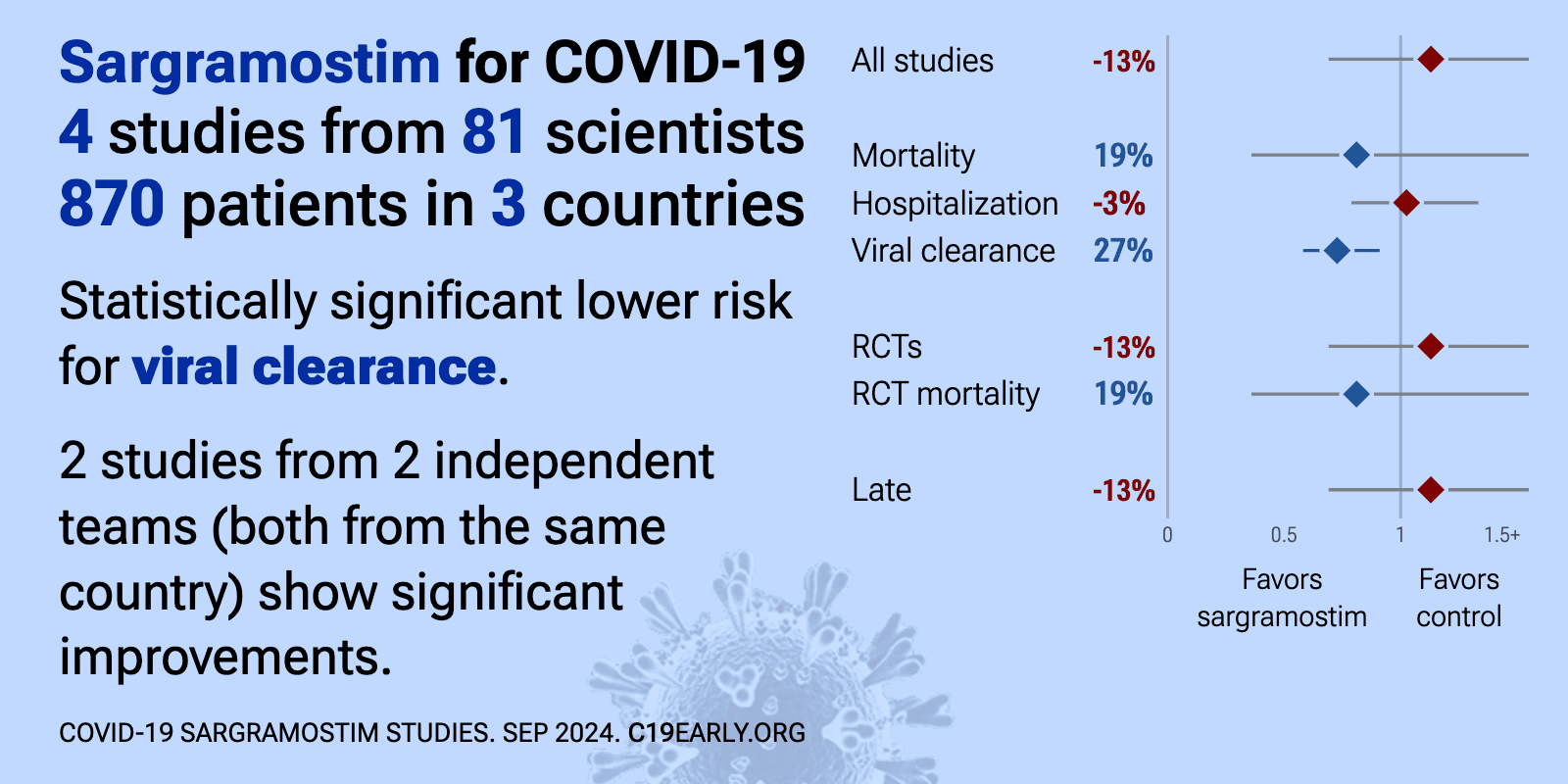
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 13% [-31‑85%] higher risk, without reaching statistical significance. Currently all studies are RCTs. Control Sargramostim Currently there is limited data, with only 8.. | ||
Nov 27 2023 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad500.351 | Inhaled Sargramostim (rhu GM-CSF) Leads to Enhanced SARS-CoV-2 Virus-Specific Immune Response and Viral Clearance: Results of the Biomarker Cohort of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2b Trial in Non-Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 |
| 30% higher progression (p=0.5) and 27% improved viral clearance (p=0.005). RCT 600 non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients at high risk for progression showing enhanced SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance by day 14 with inhaled sargramostim (rhu GM-CSF) compared to placebo. There was no significant difference in the primary e.. | ||
Sep 20 2023 |
et al., Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1080/23744235.2023.2254380 | Short-term inhalation of sargramostim with concomitant high-dose steroids does not hasten recovery in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial |
| 12% slower improvement (p=0.1) and 10% longer hospitalization. RCT 70 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with moderate pneumonia in Japan showing no significant difference in time to clinical improvement with inhaled sargramostim (GM-CSF) vs. placebo. Concomitant corticosteroid dose was not standardized... | ||
Dec 2 2022 |
et al., Military Medicine, doi:10.1093/milmed/usac362 | Inhaled Sargramostim (Recombinant Human Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor) for COVID-19-Associated Acute Hypoxemia: Results of the Phase 2, Randomized, Open-Label Trial (iLeukPulm) |
| 23% lower mortality (p=0.58), 27% lower ventilation (p=0.58), 56% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.04), and 3% longer hospitalization (p=0.86). RCT 122 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing improved oxygenation with inhaled sargramostim (GM-CSF) treatment. There was no significant difference in intubation rate, mortality, or adverse events. | ||
Oct 13 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-959220/v1 | Early treatment with inhaled GM-CSF improves oxygenation and anti-viral immunity in COVID-19 induced lung injury – a randomized clinical trial |
| 20% higher ventilation (p=0.77), 10% worse results (p=0.77), and 43% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.13). RCT 81 non-ventilated COVID-19 patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure showing improved oxygenation after 5 days of inhaled sargramostim (rhu-GM-CSF) compared to standard of care. More patients in the sargramostim group experienced at.. | ||