Evaluation of the recovery rate and prevention of hospitalization among covid-19 outpatients: a randomized clinical trial comparing N-acetylcysteine with Bromhexine
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v2, IRCT20220302054167N1, Jan 2023
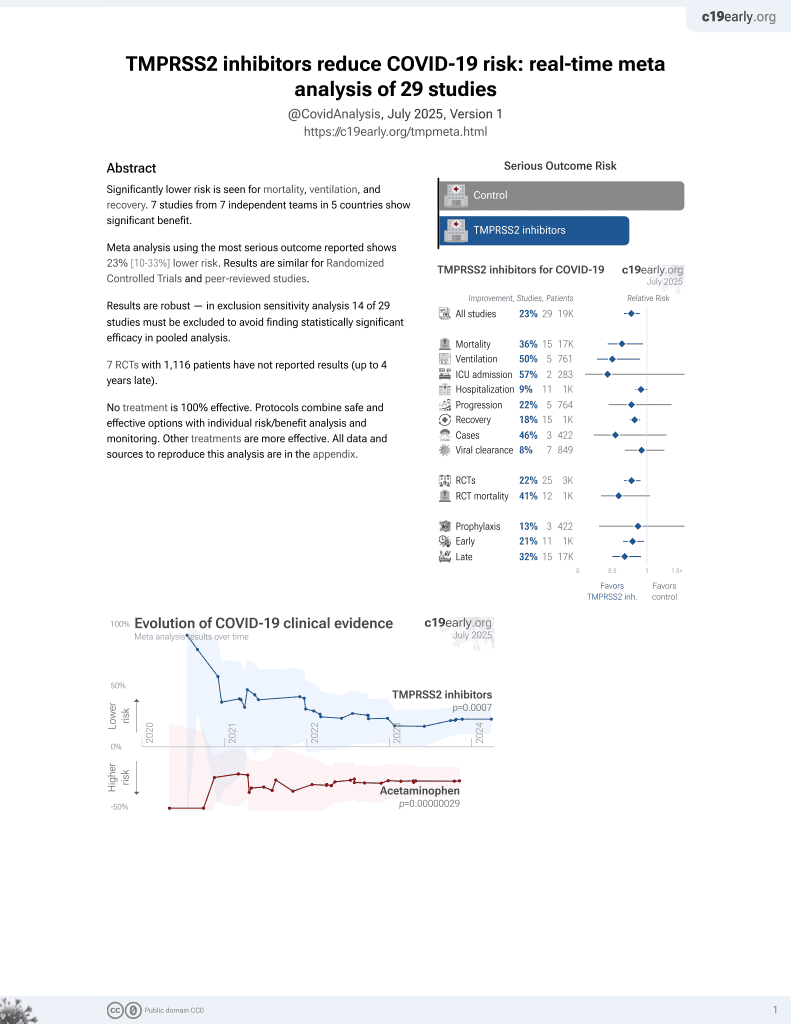
22nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.00063 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 225 outpatients in Iran showing lower mortality and hospitalization, and faster recovery with N-acetylcysteine and bromhexine. Baseline information per group is not provided, Figure 1 has the control group hospitalization status switched and the totals do not match, and the registration and previous version of this paper do not include the control group. N-acetylcysteine 600mg daily for 5 days, bromhexine 8mg tid for 5 days.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
inconsistent data, no baseline group details, control group not in previous version.
Study covers N-acetylcysteine, TMPRSS2 inhibitors, and bromhexine.
|
risk of death, 93.3% lower, RR 0.07, p = 0.01, treatment 0 of 75 (0.0%), control 7 of 75 (9.3%), NNT 11, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 88.0% lower, RR 0.12, p < 0.001, treatment 6 of 75 (8.0%), control 50 of 75 (66.7%), NNT 1.7.
|
|
recovery time, 28.5% lower, relative time 0.72, p < 0.001, treatment mean 10.76 (±0.64) n=75, control mean 15.04 (±8.56) n=75.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ghayour et al., 3 Jan 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, preprint, mean age 58.6, 4 authors, study period April 2022 - September 2022, trial IRCT20220302054167N1.
Contact: anahitaeslami1995@gmail.com.
Evaluation of the recovery rate and prevention of hospitalization among covid-19 outpatients: a randomized clinical trial comparing N-acetylcysteine with Bromhexine
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v2
Objectives: Due to the referral of COVID-19 patients to outpatient centers in the early stages, the aim of the present study is to compare the effect of N-acetylcysteine and Bromhexine on the recovery rate and prevention of hospitalization in outpatients with Methodology: This study was conducted from April 2022 to September 2022. First, PCR-con rmed COVID-19 patients were divided into tree groups, one of these groups received N-acetylcysteine while the other received bromhexine and One of these groups did not receive any medication. The patients were followed up on the seventh and fourteenth days of the disease in terms of the duration of changes in oxygen saturation and recovery. The hospitalization and death of the patients were also evaluated after one month. Results: Out of 225 studied patients, oxygen saturation was increased by 1.33% in the third visit of the patients who received N-acetylcysteine compared to their rst visit. This percentage was 1.19% in the patients who received bromhexine.29.77% of the patients were admitted to the hospital and 70.23% of them had no history of hospitalization within 14 day and their mortality rate was 9.33% in control group and it was zero in both groups of patients who received drug. Conclusions: The results of this study showed that early initiation of Bromhexine and N-acetylcysteine can effectively reduce the hospitalization rate and mortality and shorten the duration of hospitalization.
However, more studies are still needed to prove their bene ts Declarations 6.1. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committees of Hamadan University of Medical Scienece with the ethics code: IR.UMSHA.REC.1400.957 and this study was approved by the judges of the International Center for Registration of Clinical Trials of Iran, a member of the international centers approved by the World Health Organization and with the code: IRCT20220302054167N1 Con rmed. Informed consent was obtained from all participating patients/their legal guardians in this study after fully explaining the study method, side effects of drugs and other necessary matters. All patients were rst examined in terms of drug allergy history, and then the study was fully explained to the patients, and the questions and doubts of the patients were fully answered, and it was also explained to the patients that for any reason, they wanted to continue participating in the study. do not have, they can withdraw, and this study will not interfere with their treatment. Also, all patients are assured that all their information is con dential and only collective information of the entire study is available. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Availability data and materials All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Competing..
References
Ansarin, Tolouian, Ardalan, Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial, Bioimpacts, doi:10.34172/bi.2020.27
Hesni, Sayad, Khosravi Shadmani, Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of 27,256 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Kermanshah Province, Iran: a retrospective one-year cohort study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07312-7
Huang, Su, Theron, An interferon-gamma-related cytokine storm in SARS patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.20255
Izquierdo, Soriano, González, Use of N-Acetylcysteine at high doses as an oral treatment for patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Sci Prog, doi:10.1177/00368504221074574
Lee, Hong, Jang, N-acetylcysteine decreases airway in ammation and responsiveness in asthma by modulating claudin 18 expression, Korean J Intern Med, doi:10.3904/kjim.2019.105
Marchetti, Lodola, Licciardello, Colombo, Use of N-acetylcysteine in the management of coronary artery diseases, Cardiologia
Mccarty, Dinicolantonio, Nutraceuticals have potential for boosting the type 1 interferon response to RNA viruses including in uenza and coronavirus, Prog Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.02.007
Poppe, Wittig, Jurida, The NF-κB-dependent and -independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006286
Rumack, Bateman, Acetaminophen and acetylcysteine dose and duration: past, present and future [published correction appears, Clin Toxicol
Schulte-Schrepping, Reusch, Paclik, Severe COVID-19 Is Marked by a Dysregulated Myeloid Cell Compartment, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.001
Shi, Puyo, N-Acetylcysteine to Combat COVID-19: An Evidence Review, Ther Clin Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/TCRM.S273700
Stegelmeier, Van Vloten, Mould, Myeloid Cells during Viral Infections and In ammation, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11020168
Sun, Zhang, Li, Xu, A systematic review of chest imaging ndings in COVID-19, Quant Imaging Med Surg, doi:10.21037/qims-20-564
Suter, Domenighetti, Schaller, Laverrière, Ritz et al., N-acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.105.1.190
Taher, Lashgari, Sedighi, Rahimi-Bashar, Poorolajal et al., A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2
Wu, Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002
Šalamon, Kramar, Marolt, Poljšak, Milisav, Medical and Dietary Uses of N-Acetylcysteine, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox8050111
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v2",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Objectives: Due to the referral of COVID-19 patients to outpatient centers in the early stages, the aim of the present study is to compare the effect of N-acetylcysteine and Bromhexine on the recovery rate and prevention of hospitalization in outpatients with COVID-19\nMethodology: This study was conducted from April 2022 to September 2022. First, PCR-confirmed COVID-19 patients were divided into tree groups, one of these groups received N-acetylcysteine while the other received bromhexine and One of these groups did not receive any medication. The patients were followed up on the seventh and fourteenth days of the disease in terms of the duration of changes in oxygen saturation and recovery. The hospitalization and death of the patients were also evaluated after one month.\nResults: Out of 225 studied patients, oxygen saturation was increased by 1.33% in the third visit of the patients who received N-acetylcysteine compared to their first visit. This percentage was 1.19% in the patients who received bromhexine.29.77% of the patients were admitted to the hospital and 70.23% of them had no history of hospitalization within 14 day and their mortality rate was 9.33% in control group and it was zero in both groups of patients who received drug.\nConclusions: The results of this study showed that early initiation of Bromhexine and N-acetylcysteine can effectively reduce the hospitalization rate and mortality and shorten the duration of hospitalization.\nClinical trial code: IRCT20220302054167N1 and ethics code: IR.UMSHA.REC.1400.957</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hamedan University of medical science"
}
],
"family": "Ghayour",
"given": "Anahita Eslami",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hamedan University of medical science"
}
],
"family": "Nazari",
"given": "Sasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hamedan University of medical science"
}
],
"family": "Keramat",
"given": "Fariba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hamedan University of medical science"
}
],
"family": "Shahbazi",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-03T19:54:07Z",
"timestamp": 1680551647000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-23T18:44:17Z",
"timestamp": 1684867457000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-03T12:57:56Z",
"timestamp": 1709470676470
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680480000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2309373/v2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2309373/v2.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0709-x",
"article-title": "The new scope of virus taxonomy: partitioning the virosphere into 15 hierarchical ranks",
"author": "International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses Executive Committee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "668",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses Executive Committee. The new scope of virus taxonomy: partitioning the virosphere into 15 hierarchical ranks. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5(5):668–74. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0709-x.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S273700",
"article-title": "N-Acetylcysteine to Combat COVID-19: An Evidence Review",
"author": "Shi Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1047",
"journal-title": "Ther Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Shi Z, Puyo CA. N-Acetylcysteine to Combat COVID-19: An Evidence Review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:1047–55. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S273700. Published 2020 Nov 2.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/qims-20-564",
"article-title": "A systematic review of chest imaging findings in COVID-19",
"author": "Sun Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1058",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Quant Imaging Med Surg",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Sun Z, Zhang N, Li Y, Xu X. A systematic review of chest imaging findings in COVID-19. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020;10(5):1058–79. doi:10.21037/qims-20-564.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.20255",
"article-title": "An interferon-gamma-related cytokine storm in SARS patients",
"author": "Huang KJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "185",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Huang KJ, Su IJ, Theron M, et al. An interferon-gamma-related cytokine storm in SARS patients. J Med Virol. 2005;75(2):185–94. doi:10.1002/jmv.20255.",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11020168",
"article-title": "Myeloid Cells during Viral Infections and Inflammation",
"author": "Stegelmeier AA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "168",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Stegelmeier AA, van Vloten JP, Mould RC, et al. Myeloid Cells during Viral Infections and Inflammation. Viruses. 2019;11(2):168. doi:10.3390/v11020168. Published 2019 Feb 19.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.001",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 Is Marked by a Dysregulated Myeloid Cell Compartment",
"author": "Schulte-Schrepping J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1419",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Schulte-Schrepping J, Reusch N, Paclik D, et al. Severe COVID-19 Is Marked by a Dysregulated Myeloid Cell Compartment. Cell. 2020;182(6):1419–40.e23. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.001.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2020.02.007",
"article-title": "Nutraceuticals have potential for boosting the type 1 interferon response to RNA viruses including influenza and coronavirus",
"author": "McCarty MF",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "383",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Prog Cardiovasc Dis",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "McCarty MF, DiNicolantonio JJ. Nutraceuticals have potential for boosting the type 1 interferon response to RNA viruses including influenza and coronavirus. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):383–5. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.02.007.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002",
"article-title": "Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19",
"author": "Wu J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Wu J. Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19. Nitric Oxide. 2020;102:39–41. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002.",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006286",
"article-title": "The NF-κB-dependent and -independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells",
"author": "Poppe M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1006286",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Poppe M, Wittig S, Jurida L, et al. The NF-κB-dependent and -independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13(3):e1006286. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006286. Published 2017 Mar 29.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/15563650.2012.659252",
"author": "Rumack BH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Rumack BH, Bateman DN. Acetaminophen and acetylcysteine dose and duration: past, present and future [published correction appears in Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021 Apr;59(4):359] [published correction appears in Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021 Dec;59(12):1195]. ClinToxicol(Phila).2012; 50(2):91–98. doi:10.3109/15563650.2012.659252.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3904/kjim.2019.105",
"article-title": "N-acetylcysteine decreases airway inflammation and responsiveness in asthma by modulating claudin 18 expression",
"author": "Lee PH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1229",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Korean J Intern Med",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Lee PH, Hong J, Jang AS. N-acetylcysteine decreases airway inflammation and responsiveness in asthma by modulating claudin 18 expression. Korean J Intern Med. 2020;35(5):1229–37. doi:10.3904/kjim.2019.105.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox8050111",
"author": "Šalamon Š",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Šalamon Š, Kramar B, Marolt TP, Poljšak B, Milisav I. Medical and Dietary Uses of N-Acetylcysteine. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(5):111. Published 2019 Apr 28. doi:10.3390/antiox8050111.",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Use of N-acetylcysteine in the management of coronary artery diseases",
"author": "Marchetti G",
"first-page": "633",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cardiologia",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Marchetti G, Lodola E, Licciardello L, Colombo A. Use of N-acetylcysteine in the management of coronary artery diseases. Cardiologia. 1999;44(7):633–7.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.105.1.190",
"article-title": "N-acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study",
"author": "Suter PM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "190",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Suter PM, Domenighetti G, Schaller MD, Laverrière MC, Ritz R, Perret C. N-acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Chest. 1994;105(1):190–4. doi:10.1378/chest.105.1.190.",
"volume": "105",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-022-07312-7",
"article-title": "Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of 27,256 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Kermanshah Province, Iran: a retrospective one-year cohort study",
"author": "Hesni E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Hesni E, Sayad B, Shadmani K. F. et al. Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of 27,256 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Kermanshah Province, Iran: a retrospective one-year cohort study. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22:319. doi.org/10.1186/s12879-022-07312-7.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00368504221074574",
"article-title": "Use of N-Acetylcysteine at high doses as an oral treatment for patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Izquierdo JL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "368504221074574",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Prog",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Izquierdo JL, Soriano JB, González Y, et al. Use of N-Acetylcysteine at high doses as an oral treatment for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Sci Prog. 2022;105(1):368504221074574. doi:10.1177/00368504221074574.",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/bi.2020.27",
"article-title": "Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Ansarin K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "209",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Bioimpacts",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Ansarin K, Tolouian R, Ardalan M, et al. Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial. Bioimpacts. 2020;10(4):209–15. doi:10.34172/bi.2020.27.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "JohnsHopkins Coronavirus Resource Center (CRC). (2022) Https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/mortality."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2",
"article-title": "A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Taher A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1650",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Taher A, Lashgari M, Sedighi L, Rahimi-Bashar F, Poorolajal J, Mehrpooya M. A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Dec;73(6):1650–9. doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2. Epub 2021 Jun 10. PMID: 34114174; PMCID: PMC8191712.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {
"has-version": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v3",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v4",
"id-type": "doi"
}
],
"is-version-of": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v3",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2309373/v4",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2309373/v2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Evaluation of the recovery rate and prevention of hospitalization among covid-19 outpatients: a randomized clinical trial comparing N-acetylcysteine with Bromhexine",
"type": "posted-content"
}