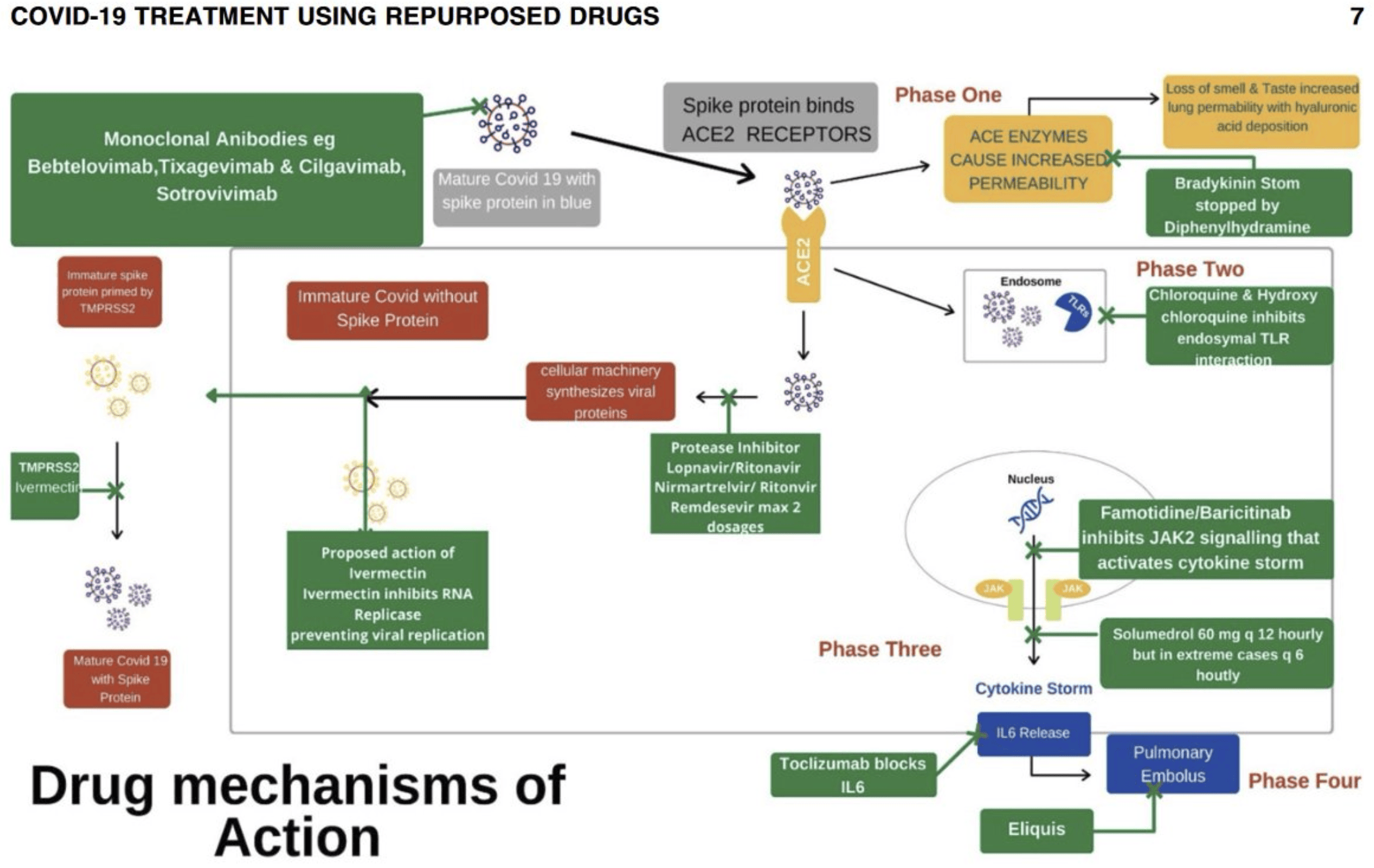
Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports
et al., Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034, Aug 2024
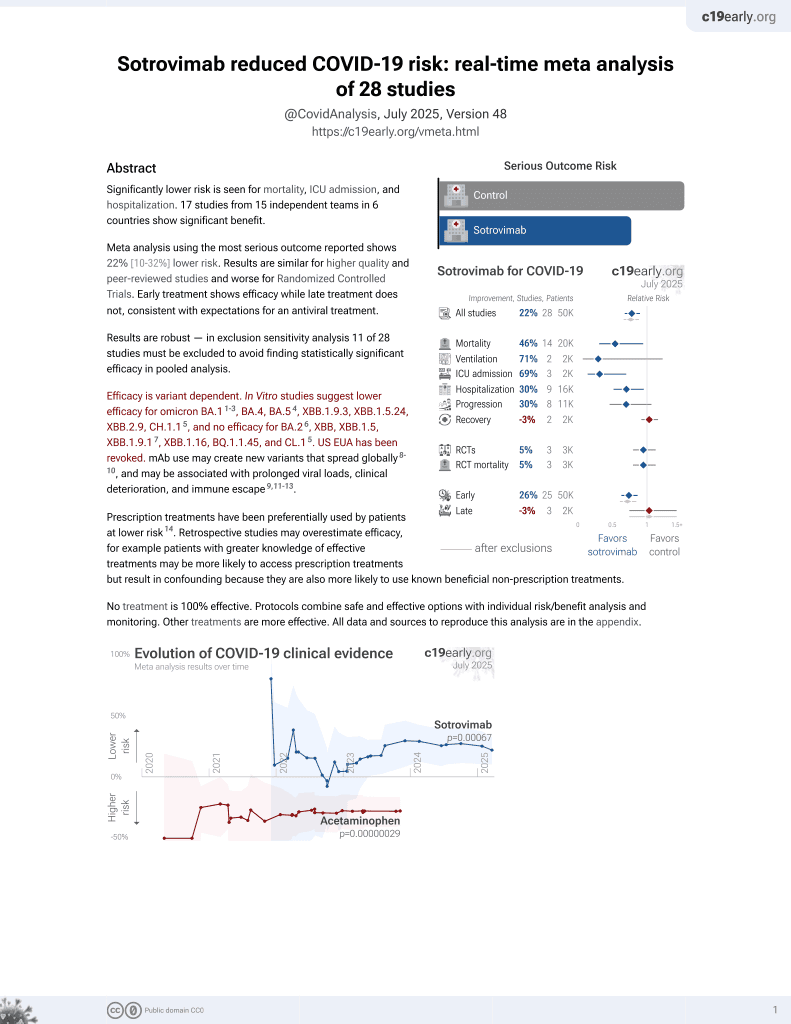
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the successful treatment of COVID-19 using existing medications including HCQ, AZ, ivermectin, famotidine, monoclonal antibodies, and others. Authors note that the typical treatment of severe viral infections with multiple therapeutic agents has generally not been done in COVID-19 clinical trials, that different mechanisms of action from multiple treatments can minimize the emergence of drug-resistant SARS-CoV-2 strains, and that early treatment disrupts viral replication, avoids progression to cytokine storm, and is critical to avoid long-term complications.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
6.
Zhou et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 Variant Evades Neutralization by Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.15.480166.
7.
Uraki et al., Antiviral efficacy against and replicative fitness of an XBB.1.9.1 clinical isolate, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108147.
8.
Focosi et al., The Emergence of Escape Mutations in COVID-19 Following Anti-Spike Monoclonal Antibody Treatment: How Do We Tackle It?, Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S540928.
9.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
10.
Focosi (B), D., Monoclonal Antibody Therapies Against SARS-CoV-2: Promises and Realities, Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1007/82_2024_268.
Enyeji et al., 5 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2024.0034",
"ISSN": [
"0882-8245",
"1557-8976"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/vim.2024.0034",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1089/vim.2024.0034"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2653-8605",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Community Medicine, Mercer University School of Medicine, Columbus, Georgia, 31901, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Enyeji",
"given": "Abraham M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Georgetown University, Data Science and Analytics Washington, DC 20057, USA."
}
],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "Amit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Germantown Medical Health Center, Germantown, Maryland, 20876 USA."
}
],
"family": "Mangat",
"given": "Harpal S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viral Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Viral Immunology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-03T11:03:52Z",
"timestamp": 1722683032000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T14:00:56Z",
"timestamp": 1722866456000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T00:25:30Z",
"timestamp": 1722903930363
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/nv/resources-tools/text-and-data-mining-policy/121/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722816000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1089/vim.2024.0034",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/pdf/10.1089/vim.2024.0034",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "278",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1089",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Mary Ann Liebert Inc",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-88863-3_14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13016/i1wo-er4h",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac663",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rce.2020.05.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1922",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.59177",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22115438",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B8"
},
{
"author": "Mangat HS",
"first-page": "1088",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Health Sci J",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.29121/granthaalayah.v8.i7.2020.678",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/head.14006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.109754",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/jrip.2020.19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/SCIADV.ABD4049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B15"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/vim.2024.0034"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports",
"type": "journal-article"
}
enyeji