Vitamin D levels associate with blood glucose and BMI in COVID-19 patients predicting disease severity
et al., The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab599, Aug 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
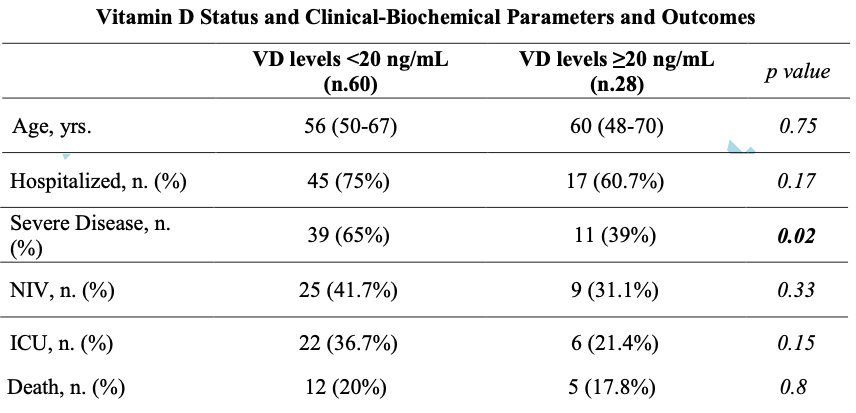
Retrospective 88 patients in Italy, showing vitamin D deficiency associated with severe cases, blood glucose, and BMI.
This is the 88th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 10.7% lower, RR 0.89, p = 1.00, high D levels 5 of 28 (17.9%), low D levels 12 of 60 (20.0%), NNT 47, >20ng/mL.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 41.6% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.22, high D levels 6 of 28 (21.4%), low D levels 22 of 60 (36.7%), NNT 6.6, >20ng/mL.
|
|
risk of severe case, 39.6% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.04, high D levels 11 of 28 (39.3%), low D levels 39 of 60 (65.0%), NNT 3.9, >20ng/mL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
di Filippo et al., 12 Aug 2021, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Vitamin D levels associate with blood glucose and BMI in COVID-19 patients predicting disease severity
doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab599/6349205
Context: High prevalence of Vitamin-D (VD) deficiency in COVID-19 patients was reported and hypothesized to increase COVID-19 severity likely due to its negative impact on immune and inflammatory responses. Furthermore, clear associations between hypovitaminosis-D and fat body-mass excess and diabetes, factors associated with COVID-19 severity, have been widely recognized. Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate in COVID-19 patients the relationship between VD levels and inflammatory response, BMI, blood glucose and disease severity. Design: Patients admitted to San Raffaele-Hospital for COVID-19 were enrolled in this study, excluding those with comorbidities and therapies influencing VD-metabolism. 25(OH)VD levels, plasma glucose levels, BMI and inflammatory parameters were evaluated at admission.
Results: A total of 88 patients were included. Median VD level was 16.3 ng/mL and VDdeficiency was found in 68.2% of patients. VD-deficiency was found more frequently in male patients and in those affected by severe COVID-19. Regression analyses showed a positive correlation between VD and PaO2/FiO2 ratio, and negative correlations between VD and plasma glucose, BMI, Neutrophil/Lymphocyte ratio, CRP and IL-6.
References
Afzal, Bojesen, Nordestgaard, Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study and metaanalysis, Clin Chem, doi:10.1373/clinchem.2012.193003
Akbar, Wibowo, Pranata, Setiabudiawan, Low Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated With Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.660420
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, Zein, Rahme et al., The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis
Biesalski, Obesity, vitamin D deficiency and old age a serious combination with respect to coronavirus disease-2019 severity and outcome, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000700
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Bischoff-Ferrari, Dietrich, Orav, Hughes, Positive association between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and bone mineral density: a population-based study of younger and older adults, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.12.029
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions, Endocr Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Brandi, Giustina, Filippo, Frara, Giustina, Sexual Dimorphism of Coronavirus 19 Morbidity and Lethality, doi:10.1016/j.tem.2020.09.00310
Burton, Fort, Seoane, Hospitalization and Mortality among Black Patients and White Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsa2011686
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19
Cereda, Bogliolo, Klersy, Vitamin D 25OH deficiency in COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary referral hospital
Chen, Chu, Doebis, Baehr, Hocher, Sex Dependent Association of Vitamin D with Insulin Resistance
Ciceri, Castagna, Rovere-Querini, Early predictors of clinical outcomes of COVID-19 outbreak in Milan, Italy, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108509
Coppelli, Giannarelli, Aragona, Hyperglycemia at Hospital Admission Is Associated With Severity of the Prognosis in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: The Pisa COVID-19 Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1380
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
Di Filippo, Doga, Frara, Giustina, Hypocalcemia in COVID-19: Prevalence, clinical significance and therapeutic implications
Di Filippo, Formenti, Doga, Hypocalcemia is a distinctive biochemical feature of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02541-9
Di Filippo, Formenti, Doga, Pedone, Rovere-Querini et al., Radiological Thoracic Vertebral Fractures are Highly Prevalent in COVID-19 and Predict Disease Outcomes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa738
Di Filippo, Formenti, Giustina, Hypocalcemia: the quest for the cause of a major biochemical feature of COVID-19, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02525-9
Diabetes, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-S002
Ding, Gao, Wilding, Trayhurn, Bing, Vitamin D signalling in adipose tissue, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114512003285
Dossari, Ahmad, Aljowair, Association of vitamin d with glycemic control in Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective chart review study in an emerging university hospital, J. Clin. Lab. Anal, doi:10.1002/jcla.23048
Favre, Legueult, Pradier, Raffaelli, Ichai et al., Visceral fat is associated to the severity of COVID-19, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154440
Ferrari, Locatelli, Briguglio, Lombardi, Is there a link between vitamin D status, SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and COVID-19 severity?, Cell Biochem Funct, doi:10.1002/cbf.3597
Filippo, Formenti, Rovere-Querini, Hypocalcemia is highly prevalent and predicts hospitalization in patients with COVID-19, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02383-5
Filippo, Lorenzo, Cinel, Weight trajectories and abdominal adiposity in COVID-19 survivors with overweight/obesity
Formenti, Tecilazich, Frara, Giubbini, Luca et al., Body mass index predicts resistance to active vitamin D in patients with hypoparathyroidism, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-019-02105-6
Formenti, Volta, Di Filippo, Berruti, Giustina, Effects of Medical Treatment of Prostate Cancer on Bone Health, Trends Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1016/j.tem.2020.12.004
Gerstein, Miller, Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0802743
Giustina, Adler, Binkley, Consensus statement from 2nd International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D, Rev Endocr Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-019-09532-w
Giustina, Bouillon, Binkley, Controversies in Vitamin D: A Statement From the Third International Conference, JBMR Plus, doi:10.1002/jbm4.10417
Giustina, Formenti, Preventing a covid-19 pandemic Can high prevalence of severe hypovitaminosis D play a role in the high impact of Covid infection in Italy?, BMJ
Giustina, Hypovitaminosis D and the endocrine phenotype of COVID-19
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Hough, Sonn, Birge, Avioli, Vitamin D metabolism in the chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Endocrinology, doi:10.1210/endo-113-2-790
Hu, Chen, Sun, Wang, Wang, Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: A meta-analysis of interventional studies, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014970
Hussain, Mahawar, Xia, Yang, El-Hasani, Obesity and mortality of COVID-19. Meta analysis [published correction appears, Obes Res Clin Pract
Hutchings, Babalyan, Baghdasaryan, Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7
Isaia, Giorgino, Adami, High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in female type 2 diabetic population, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/diacare.24.8.1496
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of Vitamin D Status with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Krul-Poel, Wee, Lips, Simsek, Management et al., DISEASE: The effect of vitamin D supplementation on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-16-0391
Li, Guan, Wu, Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316
Li, Liu, Mao, Predictive values of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Lima-Martínez, Boada, Madera-Silva, Marín, Contreras, COVID-19 and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship, Clin Investig Arterioscler, doi:10.1016/j.arteri.2020.10.001
Maddaloni, Cavallari, Napoli, Conte, Vitamin D and Diabetes Mellitus, Front Horm Res, doi:10.1159/000486083
Mancini, Mazziotti, Doga, Vertebral fractures in males with type 2 diabetes treated with rosiglitazone, Bone, doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.06.006
Manson, A Cluster-Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Vitamin D3 Supplementation to Reduce Disease Severity in Persons With Newly Diagnosed COVID-19
Marazuela, Giustina, Puig-Domingo, Endocrine and metabolic aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic [published correction appears, Rev Endocr Metab Disord
Mariani, Tajer, Antonietti, Inserra, Ferder et al., High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (CARED-TRIAL), Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05073-3
Martins, Boavida, Raposo, Diabetes hinders community-acquired pneumonia outcomes in hospitalized patients, BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2015-000181
Mazziotti, Bilezikian, Canalis, Cocchi, Giustina, New understanding and treatments for osteoporosis, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-011-9570-2
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Migliaccio, Nisio, Mele, Obesity and hypovitaminosis D: causality or casualty?, Int J Obes Suppl, doi:10.1038/s41367-019-0010-8
Monteverdi, Pedersini, Gallo, The Interaction of Lean Body Mass With Fat Body Mass Is Associated With Vertebral Fracture Prevalence in Women With Early Breast Cancer Undergoing Aromatase Inhibitor Therapy, JBMR Plus
Pereira-Santos, Costa, Assis, Santos, Santos, Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Obes Rev, doi:10.1111/obr.12239
Pietschmann, Schernthaner, Woloszczuk, Serum osteocalcin levels in diabetes mellitus: analysis of the type of diabetes and microvascular complications, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/BF00265373
Pittas, Hughes, Sheehan, Vitamin D Supplementation and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1900906
Pizzini, Aichner, Sahanic, Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on COVID-19-A Prospective Analysis from the CovILD Registry, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092775
Ponti, Maccaferri, Ruini, Tomasi, Ozben, Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression, Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, doi:10.1080/10408363.2020.1770685
Pramono, Jocken, Essers, Goossens, Blaak, Vitamin D and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity in Humans With Overweight/Obesity, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00995
Puig-Domingo, Marazuela, Giustina, COVID-19 and endocrine diseases. A statement from the European Society of Endocrinology, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02294-5
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area [published correction appears, JAMA
Rousseau, Vitamin D Supplementation and Covid-19: a Randomised, Double-Blind, Controlled Study
Rovere-Querini, Tresoldi, Conte, Biobanking for COVID-19 research
Sempos, Heijboer, Bikle, Vitamin D assays and the definition of hypovitaminosis D: results from the First International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.13652
Smet, Smet, Herroelen, Gryspeerdt, Martens, Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality, Am J Clin Pathol, doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252
Tecilazich, Formenti, Giustina, Role of vitamin D in diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological and clinical aspects
Tsuprykov, Buse, Skoblo, Haq, Hocher, Reference intervals for measured and calculated free 25-hydroxyvitamin D in normal pregnancy, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.03.005
Tsur, Feldman, Feldhammer, Hoshen, Leibowitz et al., Decreased serum concentrations of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol are associated with increased risk of progression to impaired fasting glucose and diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc12-1050
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China [published correction appears, JAMA
Zeng, Chu, Doebis, Baehr, Hocher, Reference values for free 25-hydroxy-vitamin D based on established total 25-hydroxy-vitamin D reference values, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105877
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Wang, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab599",
"ISSN": [
"0021-972X",
"1945-7197"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgab599",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Context</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A high prevalence of vitamin D (VD) deficiency in COVID-19 patients has been reported and hypothesized to increase COVID-19 severity likely because of its negative impact on immune and inflammatory responses. Furthermore, clear associations between hypovitaminosis D and fat body mass excess and diabetes, factors associated with COVID-19 severity, have been widely recognized.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The aim of this study was to evaluate in COVID-19 patients the relationship between VD levels and inflammatory response, body mass index (BMI), blood glucose (GLU), and disease severity.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Patients admitted to San Raffaele-Hospital for COVID-19 were enrolled in this study, excluding those with comorbidities and therapies influencing VD metabolism. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels, plasma GLU levels, BMI, and inflammatory parameters were evaluated at admission.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 88 patients were included. Median VD level was 16.3 ng/mL and VD deficiency was found in 68.2% of patients. VD deficiency was found more frequently in male patients and in those affected by severe COVID-19. Regression analyses showed a positive correlation between VD and PaO2/FiO2 ratio, and negative correlations between VD and plasma GLU, BMI, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein, and interleukin 6. Patients with both hypovitaminosis D and diabetes mellitus, as well those with hypovitaminosis D and overweight, were more frequently affected by a severe disease with worse inflammatory response and respiratory parameters, compared to those without or just one of these conditions.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We showed, for the first-time, a strict association of VD levels with blood GLU and BMI in COVID-19 patients. VD deficiency might be a novel common pathophysiological mechanism involved in the detrimental effect of hyperglycemia and adiposity on disease severity.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "di Filippo",
"given": "Luigi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Allora",
"given": "Agnese",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Doga",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Formenti",
"given": "Anna Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory Medicine Service, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Locatelli",
"given": "Massimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2615-3649",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vita-Salute San Raffaele University and Division of Transplantation, Immunology and Infectious Diseases, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rovere Querini",
"given": "Patrizia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Frara",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6783-3398",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Giustina",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T16:34:17Z",
"timestamp": 1628786057000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-18T23:15:30Z",
"timestamp": 1639869330000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-07T20:59:41Z",
"timestamp": 1709845181473
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 30,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1628726400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/jcem/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1210/clinem/dgab599/40302452/dgab599.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-pdf/107/1/e348/41819314/dgab599.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-pdf/107/1/e348/41819314/dgab599.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "80",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e348-e360",
"prefix": "10.1210",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "The Endocrine Society",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"article-title": "Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0001",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China [published correction appears in JAMA. 2021;325(11):1113]",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0002",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1017",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0003",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-020-09569-2",
"article-title": "Endocrine and metabolic aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic [published correction appears in Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021;22(1):145]",
"author": "Marazuela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "495",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocr Metab Disord",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0004",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02294-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and endocrine diseases. A statement from the European Society of Endocrinology",
"author": "Puig-Domingo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0005",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0006",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108509",
"article-title": "Early predictors of clinical outcomes of COVID-19 outbreak in Milan, Italy",
"author": "Ciceri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108509",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0007",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tem.2020.09.003",
"article-title": "Sexual dimorphism of coronavirus 19 morbidity and lethality",
"author": "Brandi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "918",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Trends Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0009",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00516-y",
"article-title": "The emerging osteo-metabolic phenotype of COVID-19: clinical and pathophysiological aspects",
"author": "di Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0010",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02383-5",
"article-title": "Hypocalcemia is highly prevalent and predicts hospitalization in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Di Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0011",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02541-9",
"article-title": "Hypocalcemia is a distinctive biochemical feature of hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "di Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0012",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"article-title": "Mechanisms in endocrinology: vitamin D and COVID-19",
"author": "Bilezikian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R133",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0013",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-021-02671-8",
"article-title": "Hypovitaminosis D and the endocrine phenotype of COVID-19",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0014",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa738",
"article-title": "Radiological thoracic vertebral fractures are highly prevalent in COVID-19 and predict disease outcomes",
"author": "di Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e602",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0015",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02525-9",
"article-title": "Hypocalcemia: the quest for the cause of a major biochemical feature of COVID-19",
"author": "di Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0016",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hypocalcemia in COVID-19: Prevalence, clinical significance and therapeutic implications",
"author": "di Filippo",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocr Metab Disord",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D’Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1359",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0018",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hernández",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1343-",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0019",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"article-title": "Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers",
"author": "Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20191",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0020",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092775",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19—a prospective analysis from the CovILD Registry",
"author": "Pizzini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2775",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0021",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0022",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.055",
"article-title": "Vitamin D 25OH deficiency in COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary referral hospital",
"author": "Cereda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2469",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0023",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7",
"article-title": "Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D",
"author": "Hutchings",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0024",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbf.3597",
"article-title": "Is there a link between vitamin D status, SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and COVID-19 severity?",
"author": "Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem Funct.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0025",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41367-019-0010-8",
"article-title": "Obesity and hypovitaminosis D: causality or casualty?",
"author": "Migliaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Obes Suppl.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0026",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2018-00995",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in humans with overweight/obesity",
"author": "Pramono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "49",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0027",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00265373",
"article-title": "Serum osteocalcin levels in diabetes mellitus: analysis of the type of diabetes and microvascular complications",
"author": "Pietschmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "892",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0028",
"volume": "31",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000486083",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Maddaloni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "Front Horm Res.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0029",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endo-113-2-790",
"article-title": "Vitamin D metabolism in the chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat",
"author": "Hough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0030",
"volume": "113",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcla.23048",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D with glycemic control in Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective chart review study in an emerging university hospital",
"author": "Al Dossari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e23048",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Lab Anal.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0031",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1373/clinchem.2012.193003",
"article-title": "Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study and metaanalysis",
"author": "Afzal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0032",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc12-1050",
"article-title": "Decreased serum concentrations of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol are associated with increased risk of progression to impaired fasting glucose and diabetes",
"author": "Tsur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1361",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0033",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1900906",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Pittas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "520",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0034",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Biobanking for COVID-19 research",
"author": "Rovere-Querini",
"journal-title": "Panminerva Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0035"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.13652",
"article-title": "Vitamin D assays and the definition of hypovitaminosis D: results from the First International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D",
"author": "Sempos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2194",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0036",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0037",
"volume": "854",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-S002",
"article-title": "2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2020",
"author": "American Diabetes Association.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S14",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0038",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Preventing a covid-19 pandemic: can high prevalence of severe hypovitaminosis D play a role in the high impact of Covid infection in Italy?",
"author": "Giustina",
"first-page": "m810",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0039",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"article-title": "Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Endocr Rev.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0040",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"article-title": "The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154753",
"journal-title": "Metabolism.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0041",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Kazemi",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0042"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.660420",
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (vitamin D) level is associated with susceptibility to COVID-19, severity, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Akbar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660420",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0043",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition",
"author": "ARDS Definition Task Force;",
"first-page": "2526",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0044",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0045",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408363.2020.1770685",
"article-title": "Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression",
"author": "Ponti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0046",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03374-8",
"article-title": "Predictive values of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0047",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252",
"article-title": "Serum 25(OH)D level on hospital admission associated with COVID-19 stage and mortality",
"author": "De Smet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Pathol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0048",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: a bidirectional relationship",
"author": "Lima-Martínez",
"first-page": "151",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Investig Arterioscler.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0049",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1380",
"article-title": "Hyperglycemia at hospital admission is associated with severity of the prognosis in patients hospitalized for COVID-19: the Pisa COVID-19 Study",
"author": "Coppelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2345",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0050",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa0802743",
"article-title": "Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2545",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0051",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.24.8.1496",
"article-title": "High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in female type 2 diabetic population",
"author": "Isaia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1496",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0052",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-011-9570-2",
"article-title": "New understanding and treatments for osteoporosis",
"author": "Mazziotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0053",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2009.06.006",
"article-title": "Vertebral fractures in males with type 2 diabetes treated with rosiglitazone",
"author": "Mancini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "784",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Bone.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0054",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiological and clinical aspects",
"author": "Tecilazich",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocr Metab Disord",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0055"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000014970",
"article-title": "Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: a meta-analysis of interventional studies",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14970",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore).",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0056",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-16-0391",
"article-title": "Management of endocrine disease: the effect of vitamin D supplementation on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Krul-Poel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0057",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Sex-dependent association of vitamin D with insulin resistance in humans",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0058"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsa2011686",
"article-title": "Hospitalization and mortality among Black patients and White patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Price-Haywood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2534",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0059",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"article-title": "Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19)",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0060",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154440",
"article-title": "Visceral fat is associated to the severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Favre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154440",
"journal-title": "Metabolism.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0061",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.12239",
"article-title": "Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira-Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Obes Rev.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0062",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tem.2020.12.004",
"article-title": "Effects of medical treatment of prostate cancer on bone health",
"author": "Formenti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Trends Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0063",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbm4.10440",
"article-title": "The interaction of lean body mass with fat body mass is associated with vertebral fracture prevalence in women with early breast cancer undergoing aromatase inhibitor therapy",
"author": "Monteverdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e10440",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "jbmr Plus.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0064",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-019-02105-6",
"article-title": "Body mass index predicts resistance to active vitamin D in patients with hypoparathyroidism",
"author": "Formenti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "699",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0065",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.12.029",
"article-title": "Positive association between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and bone mineral density: a population-based study of younger and older adults",
"author": "Bischoff-Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "634",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Am J Med.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0066",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114512003285",
"article-title": "Vitamin D signalling in adipose tissue",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1915",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0067",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0000000000000700",
"article-title": "Obesity, vitamin D deficiency and old age a serious combination with respect to coronavirus disease-2019 severity and outcome",
"author": "Biesalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0068",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Weight trajectories and abdominal adiposity in COVID-19 survivors with overweight/obesity",
"author": "Di Filippo",
"journal-title": "Int J Obes (Lond)",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0069"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-019-09532-w",
"article-title": "Consensus statement from 2nd International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocr Metab Disord.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0070",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbm4.10417",
"article-title": "Controversies in Vitamin D: a statement from the Third International Conference",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e10417",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "jbmr Plus.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0071",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105877",
"article-title": "Reference values for free 25-hydroxy-vitamin D based on established total 25-hydroxy-vitamin D reference values",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105877",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0072",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.03.005",
"article-title": "Reference intervals for measured and calculated free 25-hydroxyvitamin D in normal pregnancy",
"author": "Tsuprykov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0073",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Manson",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0074",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Rousseau",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0075",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05073-3",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (CARED-TRIAL)",
"author": "Mariani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0076",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0077",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjdrc-2015-000181",
"article-title": "Diabetes hinders community-acquired pneumonia outcomes in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Martins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e000181",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "bmj Open Diabetes Res Care.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0078",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-021-02734-w",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and endocrine and metabolic diseases. An updated statement from the European Society of Endocrinology",
"author": "Puig-Domingo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "301",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrine.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0079",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-21-0397",
"article-title": "One year of the pandemic—how European endocrinologists responded to the crisis: a statement from the European Society of Endocrinology",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "C1",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol.",
"key": "2021121823131290400_CIT0080",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 80,
"references-count": 80,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/107/1/e348/6349205"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Biochemistry (medical)",
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology",
"Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Blood Glucose and BMI in COVID-19 Patients, Predicting Disease Severity",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "107"
}
