Vitamin C deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care unit
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001, Dec 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
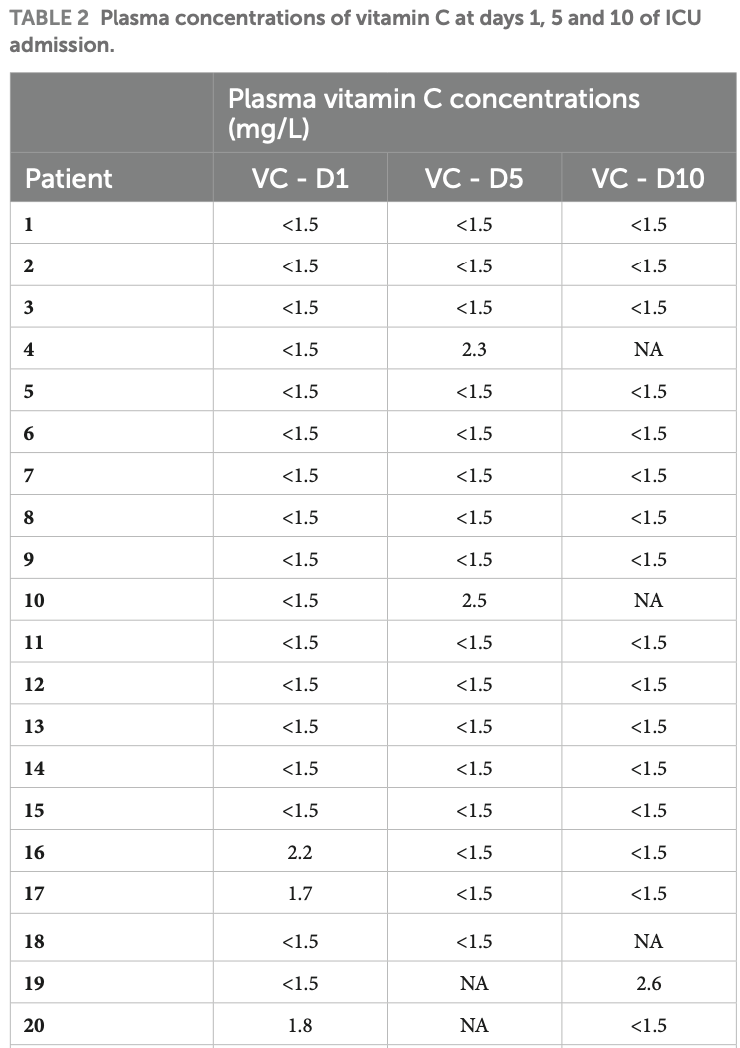
Observational study of 43 critically ill COVID-19 patients requiring respiratory support showing vitamin C deficiency present at ICU admission and persisting throughout ICU stay. 86% of patients had undetectable vitamin C levels (<1.5mg/L) on ICU admission, 83% on day 5, and 88% on day 10.
Chiscano-Camón et al., 20 Dec 2023, prospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, survey, mean age 62.0, 14 authors, study period 12 November, 2020 - 24 February, 2021.
Contact: luissilvestre.chiscano@vallhebron.cat.
Vitamin C deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care unit
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001
Objectives: To determine vitamin C plasma kinetics, through the measurement of vitamin C plasma concentrations, in critically ill Coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, identifying eventually the onset of vitamin C deficiency.
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CEIm) of Vall d'Hebron University Hospital [PR(AG)687/2020]. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/ institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin because the informed consent was waived due to epimediological situation, in between COVID-19 outbreak.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: a pilot study, Med Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064
Biancatelli, Berrill, Marik, The antiviral properties of vitamin C, Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2020.1706483
Bielsa-Berrocal, COVID-19: up to 82% critically ill patients had low vitamin C values, Nutr J, doi:10.1186/s12937-021-00727-z
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Uhl, Hoagland et al., Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19, Cells, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026
Blee, Cogbill, Lambert, Hemorrhage associated with vitamin C deficiency in surgical patients, Surgery, doi:10.1067/msy.2002.122373
Bosmann, Ward, The inflammatory response in sepsis, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.09.004
Bouadma, Lescure, Lucet, Yazdanpanah, Timsit, Severe SARS-CoV-2 infections: practical considerations and management strategy for intensivists, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05967-x
Brinkmann, Reichard, Goosmann, Fauler, Uhlemann et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1092385
Carr, Rosengrave, Bayer, Chambers, Mehrtens et al., Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1891-y
Carr, Shaw, Fowler, Natarajan, Ascorbate-dependent vasopressor synthesis: a rationale for vitamin C administration in severe sepsis and septic shock?, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-015-1131-2
Chen, Luo, Yuan, Wang, Yang et al., Vitamin C mitigates oxidative stress and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in severe community-acquired pneumonia and LPS-induced macrophages, Mediat Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2014/426740
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ferrer, Camós, Ruiz-Sanmartin et al., Pre-analytical and analytical procedures to avoid loss of vitamin C. Comment on: "COVID-19: up to 82% critically ill patients had low vitamin C values, Nutr J, doi:10.1186/s12937-022-00803-y
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Roca, Ferrer, Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y
Collie, Greaves, Jones, Eastwood, Bellomo, Vitamin C measurement in critical illness: challenges, methodologies and quality improvements, Clin Chem Lab Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2019-0912
De Melo, Homem-De-Mello, High-dose intravenous vitamin C may help in cytokine storm in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03228-3
Erol, Saglam, Saglam, Erol, Altun et al., The protection potential of antioxidant vitamins against acute respiratory distress syndrome: a rat trial, Inflammation, doi:10.1007/s10753-019-01020-2
Fisher, Kraskauskas, Martin, Farkas, Wegelin et al., Mechanisms of attenuation of abdominal sepsis induced acute lung injury by ascorbic acid, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00300.2011
Fisher, Seropian, Kraskauskas, Thakkar, Voelkel et al., Ascorbic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182120cb8
Fowler, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with Sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825
Frei, Stocker, England, Ames, Ascorbate: the most effective antioxidant in human blood plasma, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-5730-8_24
Fujii, Udy, Additional trials of vitamin C in septic shock: a bag of mixed fruit, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.030
Gan, Rosoman, Henshaw, Noble, Georgius et al., COVID-19 as a viral functional ACE2 deficiency disorder with ACE2 related multiorgan disease, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110024
Grommes, Soehnlein, Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury, Mol Med, doi:10.2119/molmed.2010.00138
Hafez, Osman, Gador, Khair, Aslam, Correlation between plasma vitamin C concentration and COVID-19 outcomes among patients seen at a major Hospital in the United Arab Emirates, Int J MCH AIDS, doi:10.21106/ijma.608
Hampl, Taylor, Johnston, Vitamin C deficiency and depletion in the United States: the third National Health and nutrition examination survey, 1988 to 1994, Am J Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.94.5.870
Hwang, Ryoo, Park, Jo, Jang et al., Combination therapy of vitamin C and thiamine for septic shock: a multi-Centre, double-blinded randomized, controlled study, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06191-3
Karlsen, Blomhoff, Gundersen, Stability of whole blood and plasma ascorbic acid, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602655
Khwaja, KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury, Nephron Clin Pract, doi:10.1159/000339789
Knaus, Draper, Wagner, Zimmerman, APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009
Knight, Ho, Pius, Buchan, Carson et al., Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO clinical characterisation protocol: development and validation of the 4C mortality score, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3339
Kumar, In silico virtual screening-based study of nutraceuticals predicts the therapeutic potentials of folic acid and its derivatives against COVID-19, Virusdisease, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-31775/v1
Lamontagne, Masse, Menard, Sprague, Pinto et al., Intravenous vitamin C in adults with Sepsis in the intensive care unit, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2200644
May, Harrison, Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2013.5205
May, Qu, Ascorbic acid prevents oxidant-induced increases in endothelial permeability, Biofactors, doi:10.1002/biof.134
Metnitz, Bartens, Fischer, Fridrich, Steltzer et al., Antioxidant status in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s001340050813
Mohammed, Fisher, Kraskauskas, Farkas, Brophy et al., Vitamin C: a novel regulator of neutrophil extracellular trap formation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5083131
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: a crosssectional comparative study in Jigawa, northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med, doi:10.1177/2050312121991246
Murthy, Gomersall, Fowler, Care for Critically ill Patients with COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3633
Oudemans-Van Straaten, Spoelstra-De Man, De Waard, Vitamin C revisited, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-014-0460-x
Pincemail, Cavalier, Charlier, Cheramy-Bien, Brevers et al., Oxidative stress status in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit for severe pneumonia. A pilot study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10020257
Polidori, Mecocci, Frei, Plasma vitamin C levels are decreased and correlated with brain damage in patients with intracranial hemorrhage or head trauma, Stroke, doi:10.1161/01.STR.32.4.898
Pullar, Bayer, Carr, Appropriate handling, processing and analysis of blood samples is essential to avoid oxidation of vitamin C to dehydroascorbic acid, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox7020029
Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson, Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5669
Rosengrave, Spencer, Williman, Mehrtens, Morgan et al., Intravenous vitamin C administration to patients with septic shock: a pilot randomised controlled trial, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-022-03900-w
Rozemeijer, Van Der Horst, De Man, Measuring vitamin C in critically ill patients: clinical importance and practical difficulties-is it time for a surrogate marker?, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03670-x
Schorah, Downing, Piripitsi, Gallivan, Hazaa et al., Total vitamin C, ascorbic acid, and dehydroascorbic acid concentrations in plasma of critically ill patients, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/63.5.760
Sevransky, Rothman, Hager, Bernard, Brown et al., Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator-and vasopressorfree days in patients with Sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24505
Singer, Deutschman, Seymour, Shankar-Hari, Annane et al., The third international consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3), JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0287
Sinnberg, Lichtensteiger, Hill-Mündel, Leischner, Niessner et al., Vitamin C deficiency in blood samples of COVID-19 patients, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11081580
Spoelstra-De Man, Elbers, Oudemans-Van Straaten, Making sense of early high-dose intravenous vitamin C in ischemia/reperfusion injury, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-018-1996-y
Stoppe, Preiser, De Backer, Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit: still LOV'IT?, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-022-04106-w
Vandenbroucke, Elm, Altman, Gøtzsche, Mulrow et al., Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0040297
Vincent, Moreno, Takala, Willatts, De Mendonça et al., The SOFA (Sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/ failure. On behalf of the working group on Sepsis-related problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/BF01709751
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Webb, Villamor, Update: effects of antioxidant and non-antioxidant vitamin supplementation on immune function, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.tb00298.x
Xing, Zhao, Yin, Guo, Shi et al., Vitamin C supplementation is necessary for patients with coronavirus disease: an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry finding, J Pharm Biomed Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2021.113927
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>To determine vitamin C plasma kinetics, through the measurement of vitamin C plasma concentrations, in critically ill Coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, identifying eventually the onset of vitamin C deficiency.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Prospective, observational, single-center study.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Setting</jats:title><jats:p>Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Vall d’Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona. Study period from November 12th, 2020, to February 24th, 2021.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Patients</jats:title><jats:p>Patients who had a severe hypoxemic acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 were included.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Plasma vitamin C concentrations were measured on days 1, 5, and 10 of ICU admission. There were no vitamin C enteral nor parenteral supplementation. The supportive treatment was performed following the standard of care or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Measurement</jats:title><jats:p>Plasma vitamin C concentrations were analyzed using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) system with a photodiode array detector (wavelength set to 245 nm). We categorized plasmatic levels of vitamin C as follows: undetectable: &lt; 1,5 mg/L, deficiency: &lt;2 mg/L. Low plasma concentrations: 2–5 mg/L; (normal plasma concentration: &gt; 5 mg/L).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main results</jats:title><jats:p>Forty-three patients were included (65% men; mean age 62 ± 10 years). The median Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score was 3 (1–4), and the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health disease Classification System (APACHE II) score was 13 (10–22). Five patients had shock. Bacterial coinfection was documented in 7 patients (16%). Initially all patients required high-flow oxygen therapy, and 23 (53%) further needed invasive mechanical ventilation during 21 (± 10) days. The worst PaO<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>/F<jats:sub>I</jats:sub>O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> registered was 93 (± 29). ICU and hospital survival were 77 and 74%, respectively. Low or undetectable levels remained constant throughout the study period in the vast majority of patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>This observational study showed vitamin C plasma levels were undetectable on ICU admission in 86% of patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 pneumonia requiring respiratory support. This finding remained consistent throughout the study period.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiscano-Camón",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruiz-Rodriguez",
"given": "Juan Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plata-Menchaca",
"given": "Erika P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bajaña",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin-Rodríguez",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmada",
"given": "Clara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrer-Costa",
"given": "Roser",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camos",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villena-Ortiz",
"given": "Yolanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ribas",
"given": "Vicent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruiz-Sanmartin",
"given": "Adolf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pérez-Carrasco",
"given": "Marcos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrer",
"given": "Ricard",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-20T08:59:00Z",
"timestamp": 1703062740000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-20T08:59:04Z",
"timestamp": 1703062744000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-21T00:22:02Z",
"timestamp": 1703118122719
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1703030400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-018-1996-y",
"article-title": "Making sense of early high-dose intravenous vitamin C in ischemia/reperfusion injury",
"author": "Spoelstra-de Man",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4684-5730-8_24",
"article-title": "Ascorbate: the most effective antioxidant in human blood plasma",
"author": "Frei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "264",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1706483",
"article-title": "The antiviral properties of vitamin C",
"author": "Colunga Biancatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-015-1131-2",
"article-title": "Ascorbate-dependent vasopressor synthesis: a rationale for vitamin C administration in severe sepsis and septic shock?",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.tb00298.x",
"article-title": "Update: effects of antioxidant and non-antioxidant vitamin supplementation on immune function",
"author": "Webb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2013.5205",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium",
"author": "May",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2068",
"journal-title": "Antioxid Redox Signal",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biof.134",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid prevents oxidant-induced increases in endothelial permeability",
"author": "May",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Biofactors",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/426740",
"article-title": "Vitamin C mitigates oxidative stress and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in severe community-acquired pneumonia and LPS-induced macrophages",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "426740",
"journal-title": "Mediat Inflamm",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10753-019-01020-2",
"article-title": "The protection potential of antioxidant vitamins against acute respiratory distress syndrome: a rat trial",
"author": "Erol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1585",
"journal-title": "Inflammation",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026",
"article-title": "Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19",
"author": "Blanco-Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1036",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110024",
"article-title": "COVID-19 as a viral functional ACE2 deficiency disorder with ACE2 related multi-organ disease",
"author": "Gan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110024",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-31775/v1",
"article-title": "In silico virtual screening-based study of nutraceuticals predicts the therapeutic potentials of folic acid and its derivatives against COVID-19",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Virusdisease",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/molmed.2010.00138",
"article-title": "Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury",
"author": "Grommes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Mol Med",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1092385",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria",
"author": "Brinkmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1532",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "303",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5083131",
"article-title": "Vitamin C: a novel regulator of neutrophil extracellular trap formation",
"author": "Mohammed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3131",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00300.2011",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of attenuation of abdominal sepsis induced acute lung injury by ascorbic acid",
"author": "Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L20",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "303",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-017-1891-y",
"article-title": "Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/63.5.760",
"article-title": "Total vitamin C, ascorbic acid, and dehydroascorbic acid concentrations in plasma of critically ill patients",
"author": "Schorah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "760",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "63",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.94.5.870",
"article-title": "Vitamin C deficiency and depletion in the United States: the third National Health and nutrition examination survey, 1988 to 1994",
"author": "Hampl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Am J Public Health",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.STR.32.4.898",
"article-title": "Plasma vitamin C levels are decreased and correlated with brain damage in patients with intracranial hemorrhage or head trauma",
"author": "Polidori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "898",
"journal-title": "Stroke",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/msy.2002.122373",
"article-title": "Hemorrhage associated with vitamin C deficiency in surgical patients",
"author": "Blee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "408",
"journal-title": "Surgery",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s001340050813",
"article-title": "Antioxidant status in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Metnitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "180",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.11825",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with Sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.3633",
"article-title": "Care for Critically ill Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Murthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05967-x",
"article-title": "Severe SARS-CoV-2 infections: practical considerations and management strategy for intensivists",
"author": "Bouadma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "579",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03228-3",
"article-title": "High-dose intravenous vitamin C may help in cytokine storm in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "de Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "500",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0460-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin C revisited",
"author": "Oudemans-van Straaten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182120cb8",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury",
"author": "Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1454",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009",
"article-title": "APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system",
"author": "Knaus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "818",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01709751",
"article-title": "The SOFA (Sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on Sepsis-related problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine",
"author": "Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "707",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3339",
"article-title": "Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO clinical characterisation protocol: development and validation of the 4C mortality score",
"author": "Knight",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m3339",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2012.5669",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition",
"author": "Ranieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000339789",
"article-title": "KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury",
"author": "Khwaja",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "c179",
"journal-title": "Nephron Clin Pract",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.0287",
"article-title": "The third international consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3)",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.0040297",
"article-title": "Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration",
"author": "Vandenbroucke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e297",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602655",
"article-title": "Stability of whole blood and plasma ascorbic acid",
"author": "Karlsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox7020029",
"article-title": "Appropriate handling, processing and analysis of blood samples is essential to avoid oxidation of vitamin C to dehydroascorbic acid",
"author": "Pullar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-022-00803-y",
"article-title": "Pre-analytical and analytical procedures to avoid loss of vitamin C. Comment on: \"COVID-19: up to 82% critically ill patients had low vitamin C values\"",
"author": "Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Nutr J",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2019-0912",
"article-title": "Vitamin C measurement in critical illness: challenges, methodologies and quality improvements",
"author": "Collie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem Lab Med",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2012.09.004",
"article-title": "The inflammatory response in sepsis",
"author": "Bosmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.030",
"article-title": "Additional trials of vitamin C in septic shock: a bag of mixed fruit",
"author": "Fujii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"article-title": "Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: a pilot study",
"author": "Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Med Drug Discov",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpba.2021.113927",
"article-title": "Vitamin C supplementation is necessary for patients with coronavirus disease: an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry finding",
"author": "Xing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113927",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Biomed Anal",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2050312121991246",
"article-title": "Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, northwestern Nigeria",
"author": "Muhammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "205031212199124",
"journal-title": "SAGE Open Med",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10020257",
"article-title": "Oxidative stress status in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit for severe pneumonia. A pilot study",
"author": "Pincemail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel).",
"key": "ref48",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-021-00727-z",
"article-title": "COVID-19: up to 82% critically ill patients had low vitamin C values",
"author": "Tomasa-Irriguible",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Nutr J",
"key": "ref49",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11081580",
"article-title": "Vitamin C deficiency in blood samples of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Sinnberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1580",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21106/ijma.608",
"article-title": "Correlation between plasma vitamin C concentration and COVID-19 outcomes among patients seen at a major Hospital in the United Arab Emirates",
"author": "Hafez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e608",
"journal-title": "Int J MCH AIDS",
"key": "ref51",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03670-x",
"article-title": "Measuring vitamin C in critically ill patients: clinical importance and practical difficulties-is it time for a surrogate marker?",
"author": "Rozemeijer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "310",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-03900-w",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C administration to patients with septic shock: a pilot randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Rosengrave",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref53",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06191-3",
"article-title": "Combination therapy of vitamin C and thiamine for septic shock: a multi-Centre, double-blinded randomized, controlled study",
"author": "Hwang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2015",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24505",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in patients with Sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Sevransky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "742",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref55",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2200644",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C in adults with Sepsis in the intensive care unit",
"author": "Lamontagne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2387",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref56",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-04106-w",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit: still LOV'IT?",
"author": "Stoppe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref57",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2023.1301001/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin C deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care unit",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "10"
}
