COVID-19 Biomarkers Comparison: Children, Adults and Elders
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina59050877, May 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 1,376 patients in Romania, showing vitamin D levels inversely related to COVID-19 symptoms, severity, ICU admission, and death.
Capraru et al., 3 May 2023, retrospective, Romania, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 1 March, 2021 - 1 March, 2022.
Contact: bagiu.iulia@umft.ro (corresponding author), ionut.capraru@umft.ro, irina.stefan@umft.ro, baditoiu.luminita@umft.ro, dan.vulcanescu@umft.ro, horhat.florin@umft.ro, muntean.delia@umft.ro, licker.monica@umft.ro, radulescu.matilda@umft.ro, cristianmotz@yahoo.com, diaconu.mircea@umft.ro, cmarian@umft.ro.
COVID-19 Biomarkers Comparison: Children, Adults and Elders
Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina59050877
Background and Objectives: this study aimed to research links between C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinekinase (CK), 25-OH vitamin D (25-OHD), ferritin (FER), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL)cholesterol and clinical severity in patients from the western part of Romania, and compare their potential use as biomarkers for intensive care units (ICU) admission and death in children, adults and elders. Materials and Methods: this study is a retrospective cohort study, performed on patients positively diagnosed with COVID-19. Available CRP, LDH, CK 25-OH vitamin D, ferritin, HDL cholesterol and clinical severity were recorded. The following were assessed: median group differences, association, correlation and receiver operating characteristic. Results: 381 children, 614 adults and 381 elders were studied between 1 March 2021 and 1 March 2022. Most children and adults presented mild symptomatology (53.28%, 35.02%, respectively), while most elders presented severe symptomatology (30.04%). ICU admission was 3.67% for children, 13.19% for adults and 46.09% for elders, while mortality was 0.79% for children, 8.63% for adults and 25.1% for elders. With the exception of CK, all other biomarkers showed some significant associations with clinical severity, ICU admission and death. Conclusions: CRP, LDH, 25-OH vitamin D, ferritin and HDL are important biomarkers for COVID-19 positive patients, especially in the pediatric population, while CK was mostly within normal ranges.
Risk for ICU Admission Details from the testing using the ROC curve analysis with regard to ICU admission are shown in Table 18 . CK was excluded from this analysis, as, across all testing, its AUC (area under curve) was not statically significant. Graphically, this data can be seen in Supplementary Material, Figures S1-S6 . Observed differences are between the 25-OH vitamin D AUC of elders and both adults and children, being significantly smaller (0.631 vs. 0.838, 0.778, respectively) and ferritin where the AUC of children was significantly higher than both adults and elders (0.949 vs. 0.807, 0.735, respectively). Regarding 25-OH vitamin D, this might be due to lower levels in elders overall, considering that their median was also lower than that of both adults and children (19.21 vs. 25.96, 23.44, respectively). Ferritin might be a better marker in children than in adults or elders, due to its high AUC.
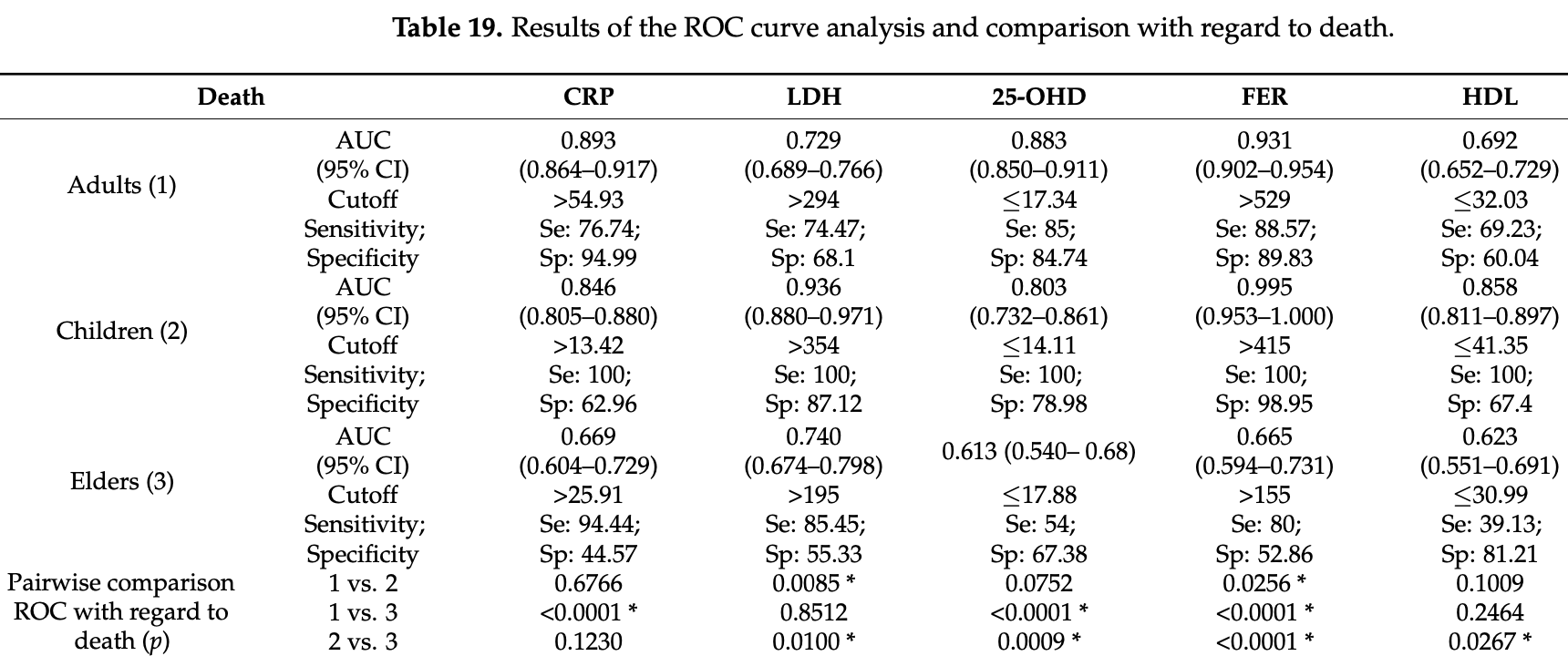
Risk for Death Details from the testing using the ROC curve analysis with regard to death are shown in Table 19 . CK was excluded from this analysis, as, across all testing, its AUC was not statically significant. Graphically, this data can be seen in Supplementary Material, Figures S7-S12 . Observed differences are between the CRP AUC of adults and elders (0.893 vs. 0.669); the LDH AUC of children with both adults and elders (0.936 vs. 0.729, 0.740, respectively); the 25-OH vitamin D AUC of elders with both adults and children (0.613 vs. 0.883, 0.803, respectively);..
References
Akdogan, Guzel, Tosun, Akpinar, Diagnostic and early prognostic value of serum CRP and LDH levels in patients with possible COVID-19 at the first admission, J. Infect. Dev. Ctries, doi:10.3855/jidc.14072
Alpcan, Tursun, Kandur, 25-OH vitamin D levels in children with COVID-19: A report from Turkey, Epidemiol. Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268821001825
Bagiu, Scurtu, Horhat, Mot, Horhat et al., COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and 25-OH vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients, Life, doi:10.3390/life13010091
Baycan, Bölen, Atalay, Agirbasli, Prognostic significance of HDL-C on long-term mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the Turkish population: A potential mechanism for population differences, Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci, doi:10.17305/bjbms.2022.7545
Bayramo Glu, Akkoç, Akgün, Yurdakul, Selçuk Duru et al., The association between 25-OH vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: Single-center experience from a pandemic hospital, Eur. J. Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1
Chen, Xu, Ma, Shi, Li et al., Clinical laboratory evaluation of COVID-19, Clin. Chim. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2021.04.022
Danta, SARS-CoV-2, Hypoxia, and Calcium Signaling: The Consequences and Therapeutic Options, ACS Pharm. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00219
De Rosa, Verrengia, Merlo, Rea, Siciliano et al., Muscle manifestations and CK levels in COVID infection: Results of a large cohort of patients inside a Pandemic COVID-19 Area, Acta Myol, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.119838
Del Giudice, Indolfi, Dinardo, Decimo, Decimo et al., 25-OH vitamin D status can affect COVID-19 outcomes also in pediatric population, Pharma Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.phanu.2022.100319
Di Filippo, Allora, Doga, Formenti, Locatelli et al., Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Blood Glucose and BMI in COVID-19 Patients, Predicting Disease Severity, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab599
Di Filippo, Uygur, Locatelli, Nannipieri, Frara et al., Low vitamin D levels predict outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with both severe and non-severe disease at hospitalization, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-023-03331-9
Erman, Boyuk, Sertbas, Ozdemir, Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome Components and COVID-19 Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients: A Pilot Study, Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol, doi:10.1155/2022/9682032
Fernandes, Oliveira, Guerguis, Eisenberg, Choi et al., Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Clinical Syndromes and Predictors of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Children and Youth, J. Pediatr, doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016
Gefen, Palumbo, Nathan, Singer, Castellanos-Reyes et al., Pediatric COVID-19-associated rhabdomyolysis: A case report, Pediatr Nephrol, doi:10.1007/s00467-020-04617-0
Gjuzelova, Nakova, Nanovic, Metodieva, Stojkoska et al., Association of Inflammatory Markers with Disease Severity and Outcome in Covid-19 Patients, Prilozi, doi:10.2478/prilozi-2023-0010
Goian, Vlaicu, Moţăţeanu, Bălăuţă, Popovici, The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Children with Special Educational Needs in Rural Areas from Mehedinţi County, Soc. Work. Rev
Gradinaru, Rolul Lactat Dehidrogenazei în Evaluarea Clinico-Evolutiva a Infecţiilor Virale date Preliminare, Atmos. Meas. Tech
Güllü, Güngör, ˙ipek, Yurttutan, Dilber, Predictive value of cardiac markers in the prognosis of COVID-19 in children, Am. J. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2021.06.075
Han, Zhang, Mu, Wei, Jin et al., Lactate dehydrogenase, an independent risk factor of severe COVID-19 patients: A retrospective and observational study, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103372
Henry, Aggarwal, Wong, Benoit, Vikse et al., Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis, Am. J. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073
Heyl, Hardy, Tucker, Hopper, Marchã et al., Frailty, Comorbidity, and Associations With In-Hospital Mortality in Older COVID-19 Patients: Exploratory Study of Administrative Data. Interact, J. Med. Res, doi:10.2196/41520
Hoang, Chorath, Moreira, Evans, Burmeister-Morton et al., COVID-19 in 7780 pediatric patients: A systematic review, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100433
Jat, Sankar, Das, Ratageri, Choudhary et al., Clinical Profile and Risk Factors for Severe Disease in 402 Children Hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 from India: Collaborative Indian Pediatric COVID Study Group, J. Trop, doi:10.1093/tropej/fmab048
Karacaer, Yaylacı, Demirci, Cekic, Suner et al., Association of mortality and endothelial dysfunction with serum ADMA level in COVID-19 patients. Pak, J. Med. Sci, doi:10.12669/pjms.38.7.5327
Kurian, Mathews, Paul, Viswam, Shivashankar et al., Association of serum ferritin with severity and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients: An observational study in a tertiary healthcare facility, Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101295
Lam, Celcilia, Levels Of C-Reactive Protein, D-Dimer, And Lactate Dehydrogenase As Predictors Of Covid-19 Outcome In Children: A Systematic Review, Jimki, doi:10.53366/jimki.v9i2.446
Liu, Wang, Wang, Li, Yuan et al., Biomarkers for Lipid and Albumin Metabolism in Hospitalized Patients with Underlying Diseases and Community-Acquired Pneumonia Caused by Bacterial or SARS-CoV-2 Infection, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S399921
Liu, Zhang, Zhang, Hu, Liu, CRP and ALB predict nucleic acid turn negative within 14 days in symptomatic patients with COVID-19, Scott Med. J, doi:10.1177/0036933021994243
Magdy, Saad, El Khateeb, Ahmed, Gamal El-Din, Comparative evaluation of semi-quantitative CT-severity scoring versus serum lactate dehydrogenase as prognostic biomarkers for disease severity and clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients, Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med, doi:10.1186/s43055-021-00493-2
Mamishi, Olfat, Pourakbari, Eshaghi, Abdolsalehi et al., Multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in children: Update and new insights from the second report of an Iranian referral hospital, Epidemiol, doi:10.1017/S0950268822001522
Marhaeni, Felicia, Sumadi Jap, Hartoyo, Andayani, Comparing serum ferritin levels during COVID-19 infection and recovery period in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia, a single-center study, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1056599
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Michael, Couture, Swedlund, Hampton, Eglash et al., An Evidence-Based Review of vitamin D for Common and High-Mortality Conditions, J. Am. Board Fam. Med, doi:10.3122/jabfm.2022.220115R1
Mohammadshahi, Ghobadi, Matinfar, Boskabady, Aslani, FBG/HDL-C) on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality COVID-19, doi:10.1155/2023/6329873
Parra, Saballs, Dinubile, Feliu, Iftimie et al., Low HDL-c levels at admission are associated with greater severity and worse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 disease, Atheroscler. Plus, doi:10.1016/j.athplu.2023.01.002
Peng, Huang, Liu, Gao, Liu, Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: A longitudinal cohort study, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.960859
Say, Crawford, Mcnab, Wurzel, Steer et al., Post-acute COVID-19 outcomes in children with mild and asymptomatic disease, Lancet Child Adolesc. Health, doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00124-3
Serrano-Lorenzo, Coya, López-Jimenez, Blázquez, Delmiro et al., Plasma LDH: A specific biomarker for lung affectation in COVID-19? Pract, Lab. Med, doi:10.1016/j.plabm.2021.e00226
Soheilirad, Karimian, Aghajani Delvar, COVID-19 in Pediatric Patients: An update on Features and Treatment Options, Tanaffos
Song, Effect of serum LDH and CK levels on condition and prognosis of COVID-patients, Med. J. Wuhan Univ. 2021
Stadler, Mangge, Rani, Curcic, Herrmann et al., Low HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity Indicates a Fatal Course of COVID-19, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11101858
Vulcănescu, Vlaicu, Bălăuţă, Jivanov, Loneliness and Social Isolation of the Elderly from Drobeta-Turnu Severin during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Soc. Work. Rev. 2021
Wang, Hu, Chen, Characteristics of abnormal serum creatine kinase-MB levels in children with COVID-19, World J. Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s12519-020-00402-z
Wang, Wu, Guo, Liu, Yang et al., Elevated Serum Creatine Kinase as an Independent Prognostic Factor for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
Wang, Zhong, Li, Fu, Su et al., Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Biochem. Res Int, doi:10.1155/2021/5596727
Yılmaz, Şen, Is 25-OH vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?, Pediatr. Pulmonol
Zhou, Ding, Yang, Peng, Tang et al., Serum lactate dehydrogenase level may predict acute respiratory distress syndrome of patients with fever infected by SARS-CoV-2, Ann. Transl. Med, doi:10.21037/atm-20-2411
Zurita-Cruz, Fonseca-Tenorio, Villasís-Keever, López-Alarcón, Parra-Ortega et al., Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 pediatric patients: A randomized controlled trial, doi:10.3389/fped.2022.943529
Çakırca, Çakırca, Torun, Bindal, Üstünel et al., Comparing the predictive values of procalcitonin/albumin ratio and other inflammatory markers in determining COVID-19 severity, Pak J. Med. Sci, doi:10.12669/pjms.39.2.6856
Ştulea, Goian, Vlaicu, The Impact Of The Covid-19 Pandemic On The Social Life Of The Staff And Beneficiaries Of The Gătaia Psychiatric Hospital
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina59050877",
"ISSN": [
"1648-9144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050877",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and Objectives: this study aimed to research links between C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinekinase (CK), 25-OH vitamin D (25-OHD), ferritin (FER), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL)cholesterol and clinical severity in patients from the western part of Romania, and compare their potential use as biomarkers for intensive care units (ICU) admission and death in children, adults and elders. Materials and Methods: this study is a retrospective cohort study, performed on patients positively diagnosed with COVID-19. Available CRP, LDH, CK 25-OH vitamin D, ferritin, HDL cholesterol and clinical severity were recorded. The following were assessed: median group differences, association, correlation and receiver operating characteristic. Results: 381 children, 614 adults and 381 elders were studied between 1 March 2021 and 1 March 2022. Most children and adults presented mild symptomatology (53.28%, 35.02%, respectively), while most elders presented severe symptomatology (30.04%). ICU admission was 3.67% for children, 13.19% for adults and 46.09% for elders, while mortality was 0.79% for children, 8.63% for adults and 25.1% for elders. With the exception of CK, all other biomarkers showed some significant associations with clinical severity, ICU admission and death. Conclusions: CRP, LDH, 25-OH vitamin D, ferritin and HDL are important biomarkers for COVID-19 positive patients, especially in the pediatric population, while CK was mostly within normal ranges.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"medicina59050877"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Capraru",
"given": "Ionut Dragos",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1046-7272",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Laboratory, Emergency Hospital for Children “Louis Turcanu”, 300011 Timișoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vulcanescu",
"given": "Dan Dumitru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3099-8249",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Laboratory, Emergency Hospital for Children “Louis Turcanu”, 300011 Timișoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bagiu",
"given": "Iulia Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6133-0204",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Laboratory, Emergency Hospital for Children “Louis Turcanu”, 300011 Timișoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Horhat",
"given": "Florin George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Popescu",
"given": "Irina Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1572-1196",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baditoiu",
"given": "Luminita Mirela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9100-4530",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
},
{
"name": "Microbiology Laboratory, “Pius Brinzeu” County Clinical Emergency Hospital, No. 156 L. Rebreanu, 300723 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Muntean",
"given": "Delia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9245-5883",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
},
{
"name": "Microbiology Laboratory, “Pius Brinzeu” County Clinical Emergency Hospital, No. 156 L. Rebreanu, 300723 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Licker",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Multidisciplinary Research Center on Antimicrobial Resistance, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Radulescu",
"given": "Matilda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "ENT Department, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. No. 2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Mot",
"given": "Ion Cristian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"family": "Diaconu",
"given": "Mircea Mihai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7749-1384",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Eftimie Murgu Sq. Nr.2, 300041 Timisoara, Romania"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Marian",
"given": "Catalin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina",
"container-title-short": "Medicina",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-04T06:03:18Z",
"timestamp": 1683180198000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-04T08:34:57Z",
"timestamp": 1683189297000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-05T04:35:10Z",
"timestamp": 1683261310872
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683072000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/59/5/877/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "877",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43055-021-00493-2",
"article-title": "Comparative evaluation of semi-quantitative CT-severity scoring versus serum lactate dehydrogenase as prognostic biomarkers for disease severity and clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Magdy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.14072",
"article-title": "Diagnostic and early prognostic value of serum CRP and LDH levels in patients with possible COVID-19 at the first admission",
"author": "Akdogan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dev. Ctries.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm-20-2411",
"article-title": "Serum lactate dehydrogenase level may predict acute respiratory distress syndrome of patients with fever infected by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1118",
"journal-title": "Ann. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.0c00219",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, Hypoxia, and Calcium Signaling: The Consequences and Therapeutic Options",
"author": "Danta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "400",
"journal-title": "ACS Pharm. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103372",
"article-title": "Lactate dehydrogenase, an independent risk factor of severe COVID-19 patients: A retrospective and observational study",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11245",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0036933021994243",
"article-title": "CRP and ALB predict nucleic acid turn negative within 14 days in symptomatic patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Scott Med. J.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Rolul Lactat Dehidrogenazei în Evaluarea Clinico-Evolutiva a Infecţiilor Virale date Preliminare",
"author": "Gradinaru",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Atmos. Meas. Tech.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of serum LDH and CK levels on condition and prognosis of COVID-patients",
"author": "Song",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Med. J. Wuhan Univ.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25106",
"article-title": "Is 25-OH vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3595",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Pulmonol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S399921",
"article-title": "Biomarkers for Lipid and Albumin Metabolism in Hospitalized Patients with Underlying Diseases and Community-Acquired Pneumonia Caused by Bacterial or SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1135",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12519-020-00402-z",
"article-title": "Characteristics of abnormal serum creatine kinase-MB levels in children with COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "326",
"journal-title": "World J. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Elevated Serum Creatine Kinase as an Independent Prognostic Factor for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Immunogenet. Open Access",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268821001825",
"article-title": "25-OH vitamin D levels in children with COVID-19: A report from Turkey",
"author": "Alpcan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e180",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1",
"article-title": "The association between 25-OH vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: Single-center experience from a pandemic hospital",
"author": "Yurdakul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2699",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268822001522",
"article-title": "Multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in children: Update and new insights from the second report of an Iranian referral hospital",
"author": "Mamishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e179",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "25-OH vitamin D status can affect COVID-19 outcomes also in pediatric population",
"author": "Indolfi",
"first-page": "100319",
"journal-title": "Pharma Nutr.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101295",
"article-title": "Association of serum ferritin with severity and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients: An observational study in a tertiary healthcare facility",
"author": "Kurian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101295",
"journal-title": "Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1056599",
"article-title": "Comparing serum ferritin levels during COVID-19 infection and recovery period in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia, a single-center study",
"author": "Marhaeni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1056599",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11101858",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Stadler, J.T., Mangge, H., Rani, A., Curcic, P., Herrmann, M., Prüller, F., and Marsche, G. (2022). Low HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity Indicates a Fatal Course of COVID-19. Antioxidants, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.athplu.2023.01.002",
"article-title": "Low HDL-c levels at admission are associated with greater severity and worse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Parra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Atheroscler. Plus",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17305/bjbms.2022.7545",
"article-title": "Prognostic significance of HDL-C on long-term mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the Turkish population: A potential mechanism for population differences",
"author": "Baycan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1016",
"journal-title": "Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Pediatric Patients: An update on Features and Treatment Options",
"author": "Soheilirad",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Tanaffos",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Loneliness and Social Isolation of the Elderly from Drobeta-Turnu Severin during the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Vlaicu",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Soc. Work. Rev.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Children with Special Educational Needs in Rural Areas from Mehedinţi County",
"author": "Goian",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Soc. Work. Rev.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The Impact Of The Covid-19 Pandemic On The Social Life Of The Staff And Beneficiaries Of The Gătaia Psychiatric Hospital, In Timiş County",
"author": "Goian",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "Bull. Transilv. Univ. Brasov. Ser. VII Soc. Sci. Law",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/41520",
"article-title": "Frailty, Comorbidity, and Associations With In-Hospital Mortality in Older COVID-19 Patients: Exploratory Study of Administrative Data",
"author": "Heyl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e41520",
"journal-title": "Interact. J. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00124-3",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 outcomes in children with mild and asymptomatic disease",
"author": "Say",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e22",
"journal-title": "Lancet Child Adolesc. Health",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/tropej/fmab048",
"article-title": "Clinical Profile and Risk Factors for Severe Disease in 402 Children Hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 from India: Collaborative Indian Pediatric COVID Study Group",
"author": "Jat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "fmab048",
"journal-title": "J. Trop. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100433",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in 7780 pediatric patients: A systematic review",
"author": "Hoang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100433",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016",
"article-title": "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Clinical Syndromes and Predictors of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Children and Youth",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "J. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "230",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2021.04.022",
"article-title": "Clinical laboratory evaluation of COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chim. Acta",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "519",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life13010091",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Bagiu, I.C., Scurtu, I.L., Horhat, D.I., Mot, I.C., Horhat, R.M., Bagiu, R.V., Capraru, I.D., Diaconu, M.M., Adam, O., and Ciornei, B. (2022). COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and 25-OH vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients. Life, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.53366/jimki.v9i2.446",
"article-title": "Levels Of C-Reactive Protein, D-Dimer, And Lactate Dehydrogenase As Predictors Of Covid-19 Outcome In Children: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Lam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Jimki",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparing the predictive values of procalcitonin/albumin ratio and other inflammatory markers in determining COVID-19 severity",
"author": "Torun",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Pak J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.plabm.2021.e00226",
"article-title": "Plasma LDH: A specific biomarker for lung affectation in COVID-19?",
"author": "Coya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00226",
"journal-title": "Pract. Lab. Med.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073",
"article-title": "Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis",
"author": "Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1722",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/5596727",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5596727",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Res Int.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Muscle manifestations and CK levels in COVID infection: Results of a large cohort of patients inside a Pandemic COVID-19 Area",
"author": "Verrengia",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Myol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00467-020-04617-0",
"article-title": "Pediatric COVID-19-associated rhabdomyolysis: A case report",
"author": "Gefen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1517",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Nephrol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2021.06.075",
"article-title": "Predictive value of cardiac markers in the prognosis of COVID-19 in children",
"author": "Yurttutan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.960859",
"article-title": "Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: A longitudinal cohort study",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "960859",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3122/jabfm.2022.220115R1",
"article-title": "An Evidence-Based Review of vitamin D for Common and High-Mortality Conditions",
"author": "Michael",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1217",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Board Fam. Med.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2022.943529",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 pediatric patients: A randomized controlled trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "943529",
"journal-title": "Front. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab599",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Blood Glucose and BMI in COVID-19 Patients, Predicting Disease Severity",
"author": "Allora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e348",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-023-03331-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Di Filippo, L., Uygur, M., Locatelli, M., Nannipieri, F., Frara, S., and Giustina, A. (Endocrine, 2023). Low vitamin D levels predict outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with both severe and non-severe disease at hospitalization, Endocrine, ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/prilozi-2023-0010",
"article-title": "Association of Inflammatory Markers with Disease Severity and Outcome in Covid-19 Patients",
"author": "Gjuzelova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Prilozi",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12669/pjms.38.7.5327",
"article-title": "Association of mortality and endothelial dysfunction with serum ADMA level in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Karacaer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1808",
"journal-title": "Pak. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/9682032",
"article-title": "Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome Components and COVID-19 Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients: A Pilot Study",
"author": "Erman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9682032",
"journal-title": "Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/6329873",
"article-title": "Role of Lipid Profile and Its Relative Ratios (Cholesterol/HDL-C, Triglyceride/HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C, WBC/HDL-C, and FBG/HDL-C) on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality COVID-19",
"author": "Mohammadshahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6329873",
"journal-title": "J. Lipids.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "2023",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/59/5/877"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 Biomarkers Comparison: Children, Adults and Elders",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "59"
}
