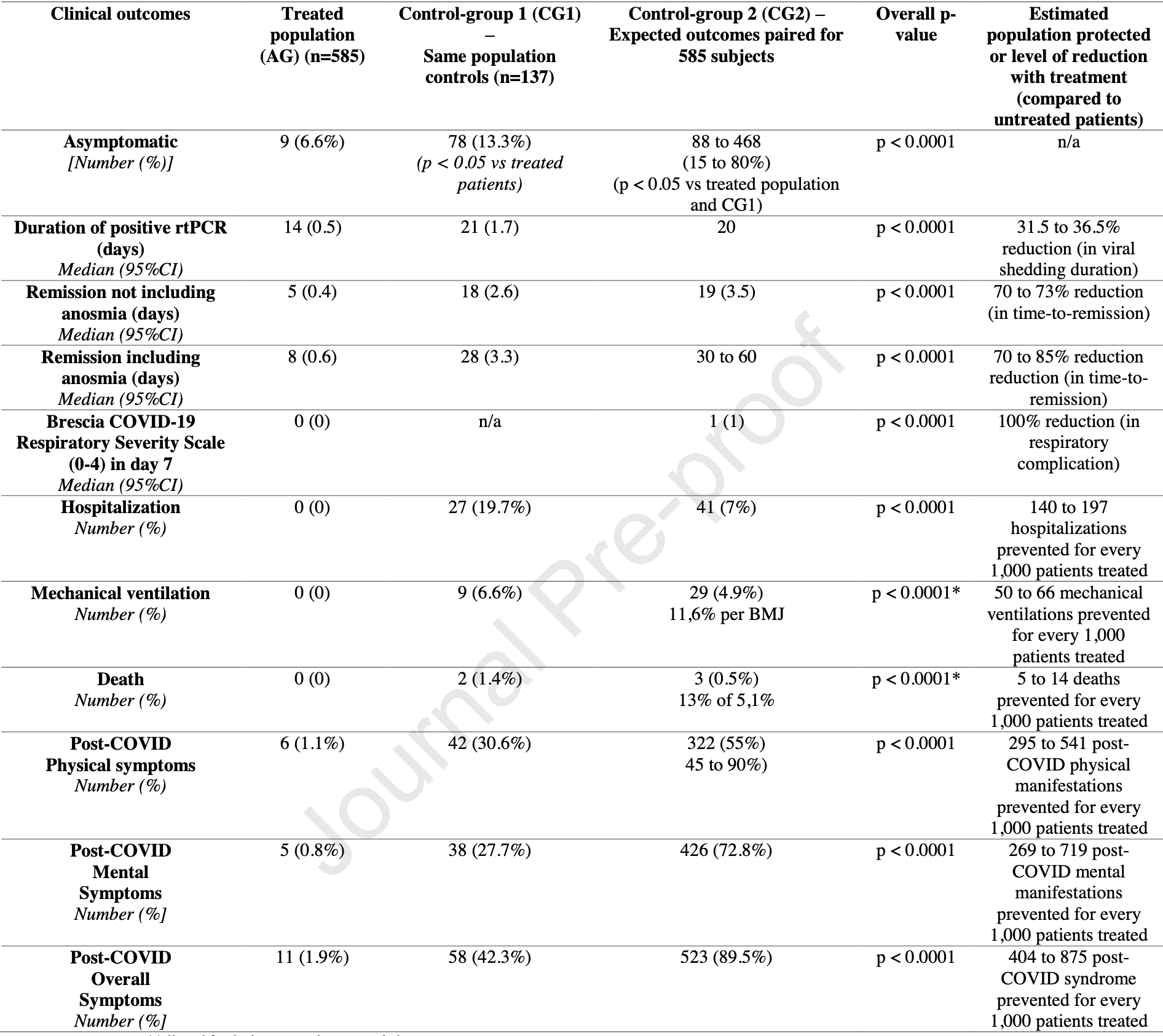
Early COVID-19 Therapy with azithromycin plus nitazoxanide, ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine in Outpatient Settings Significantly Improved COVID-19 outcomes compared to Known outcomes in untreated patients
et al., New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915, Nov 2020 (preprint)
Comparison of HCQ, nitazoxanide, and ivermectin showing similar effectiveness for overall clinical outcomes in COVID-19 when used before seven days of symptoms, and overwhelmingly superior compared to the untreated COVID-19 population, even for those outcomes not influenced by placebo effect, at least when combined with azithromycin, and vitamin C, D and zinc in the majority of the cases. 585 patients with mean treatment delay 2.9 days. There was no hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, or mortality with treatment. Control group 1 was a retrospectively obtained group of untreated patients of the same population.
Study covers nitazoxanide, ivermectin, and HCQ.
|
risk of death, 87.8% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.08, treatment 0 of 357 (0.0%), control 2 of 137 (1.5%), NNT 68, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), control group 1.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 97.0% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 357 (0.0%), control 9 of 137 (6.6%), NNT 15, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), control group 1.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 99.0% lower, RR 0.01, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 357 (0.0%), control 27 of 137 (19.7%), NNT 5.1, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), control group 1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cadegiani et al., 4 Nov 2020, prospective, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, average treatment delay 2.9 days.
Early COVID-19 therapy with azithromycin plus nitazoxanide, ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine in outpatient settings significantly improved COVID-19 outcomes compared to known outcomes in untreated patients
New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915
In a prospective observational study (pre-AndroCoV Trial), the use of nitazoxanide, ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine demonstrated unexpected improvements in COVID-19 outcomes when compared to untreated patients. The apparent yet likely positive results raised ethical concerns on the employment of further full placebo controlled studies in early-stage COVID-19. The present analysis aimed to elucidate, through a comparative analysis with two control groups, whether full placebo-control randomized clinical trials (RCTs) on early-stage COVID-19 are still ethically acceptable. The Active group (AG) consisted of patients enrolled in the Pre-AndroCoV-Trial (n = 585). Control Group 1 (CG1) consisted of a retrospectively obtained group of untreated patients of the same population (n = 137), and Control Group 2 (CG2) resulted from a precise prediction of clinical outcomes based on a thorough and structured review of indexed articles and official statements. Patients were matched for sex, age, comorbidities and disease severity at baseline. Compared to CG1 and CG2, AG showed reduction of 31.5-36.5% in viral shedding (p < 0.0001), 70-85% in disease duration (p < 0.0001), and 100% in respiratory complications, hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, deaths and post-COVID manifestations (p < 0.0001 for all). For every 1000 confirmed cases for COVID-19, at least 70 hospitalizations, 50 mechanical ventilations and five deaths were prevented. Benefits from the combination of early COVID-19 detection and early pharmacological approaches were consistent and overwhelming when compared to untreated groups, which, together with the well-established safety profile of the drug combinations tested in the Pre-AndroCoV Trial, precluded our study from continuing employing full placebo in early COVID-19.
Transparency declaration The authors declare no conflict of interest with any of the pharmacological interventions proposed by the present study.
Authorship statement Dr. Cadegiani was the principal investigator and contributed to the study conception and design, compiled and analyzed the data, and helped write the manuscript. Dr Goren contributed with the study design, analysis of the data, and review of the manuscript. Dr. Wambier performed the statistical analysis, analyzed the data, and helped write the manuscript. Dr. McCoy helped with the study design, helped to analyze the data, and reviewed the last version of the manuscript.
References
Afrin, Weinstock, Molderings, Covid-19 hyperinflammation and post-Covid-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Almubark, Memish, Tamim, Alenazi, Alabdulla et al., Natural history and clinical course of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients in the Kingdom of Saudi arabia, Saudi J Med Med Sci, doi:10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_853_20
Amdal, Pe, Falk, Piccinin, Bottomley et al., Healthrelated quality of life issues, including symptoms, in patients with active COVID-19 or post COVID-19; a systematic literature review, Qual Life Res, doi:10.1007/s11136-021-02908-z
Axfors, Schmitt, Janiaud, Van't Hooft, Abd-Elsalam et al., Mortality outcomes with hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 from an international collaborative meta-analysis of randomized trials, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22446-z
Bansal, Goyal, Cusick, Lahan, Dhaliwal et al., Hydroxychloroquine: a comprehensive review and its controversial role in coronavirus disease 2019, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2020.1839959
Bartoszko, Siemieniuk, Kum, Qasim, Zeraatkar et al., Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n949
Blum, Nitazoxanide superiority to placebo to treat moderate COVID-19 A Pilot prove of concept randomized double-blind clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100981
Booth, Reed, Ponzo, Yassaee, Aral et al., Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: a global systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247461
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402
Burton, Fort, Seoane, Hospitalization and mortality among black patients and white patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cadegiani, Can spironolactone be used to prevent COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with hypertension?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
Cadegiani, Goren, John, Wambier, Azithromycin with nitazoxanide, hydeoxychloroquine or ivermectin, with or without dutasteride, for early stage COVID-19: an open-label prospective observational study in males with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 (The Pre-AndroCoV Male Trial
Cadegiani, Goren, Mccoy, Wambier, Hydroxychloroquine, nitazoxanide and ivermectin have similar effects in early COVID-19: a head-to-head515 comparison of the Pre-AndroCoV Trial
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, John, An open-label prospective observational study of antiandrogen and non-antiandrogen early pharmacological approaches in females with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870v1.article-metrics
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, Spironolactone may provide protection from SARS-CoV-2: targeting androgens, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112
Cadegiani, Lim, Goren, Mccoy, Situm et al., Clinical symptoms of hyperandrogenic women diagnosed with COVID-19, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.17004
Cadegiani, Lin, Goren, Wambier, Potential risk for developing severe COVID-19 disease among anabolic steroid users, BMJ Case Rep, doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-241572
Cadegiani, Mccoy, Wambier, Goren, Early antiandrogen therapy with dutasteride reduces viral shedding, inflammatory responses, and time-to-remission in males with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional trial (EAT-DUTA AndroCoV trial -biochemical), Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.13047
Cadegiani, Mccoy, Wambier, Vaño-Galván, Shapiro et al., Proxalutamide significantly accelerates viral clearance and reduces time to clinical remission in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: results from a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.13492
Cadegiani, Repurposing existing drugs for COVID-19: an endocrinology perspective, BMC Endocr Disord, doi:10.1186/s12902-020-00626-0
Cadegiani, Wambier, Goren, Spironolactone: an antiandrogenic and anti-hypertensive drug that may provide protection against the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00453
Castelnuovo, Costanzo, Cassone, Cauda, Gaetano et al., Hydroxychloroquine and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials, Pathog Glob Health, doi:10.1080/20477724.2021.1936818
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Cohen, Hall, John, Rapoport, The 566 early natural history of SARS-CoV-2 infection: clinical observations from an urban, ambulatory COVID-19 clinic, Mayo Clin Proc
Donnelly, Post COVID Syndrome (PCS) and healthcare workers: who cares for the carers?, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcaa248
Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, Palacios-Ceña, Gómez-Mayordomo, Florencio, Cuadrado et al., Prevalence of post-COVID-19 symptoms in hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID-19 survivors: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Eur J Intern Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.06.009
Goren, Wambier, Herrera, Mccoy, Vaño-Galván et al., Anti-androgens may protect against severe COVID-19 outcomes: results from a prospective cohort study of 77 hospitalized men, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16953
Goyal, Choi, Pinheiro, Clinical characteristics of covid-19 in New York city, N Engl J Med
Grasselli, Pesenti, Cecconi, Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in lombardy, Italy: early experience and forecast during an emergency response, JAMA
Hickson, Margineantu, Hockenbery, Simon, Geballe, Inhibition of vaccinia virus replication by nitazoxanide, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.023
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Imai, Halfmann, Yamayoshi, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Chiba et al., Characterization of a new SARS-CoV-2 variant that emerged in Brazil, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2106535118
Iqbal, Lam, Sounderajah, Clarke, Ashrafian et al., Characteristics and predictors of acute and chronic post-COVID syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100899
Jans, Wagstaff, Ivermectin as a broad-spectrum host-directed antiviral: the real deal?, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells9092100
Kim, Kim, Ra, Lee, Bae et al., Clinical characteristics of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with mild COVID-19, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.040
Kragholm, Andersen, Gerds, Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) -a Danish nationwide, register553 based study, Clin Infect Dis
Li, Zhao, Zhan, Quantitative proteomics reveals a broadspectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment, J Cell Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.30055
Lyngbakken, Berdal, Eskesen, Kvale, Olsen et al., A pragmatic randomized controlled trial reports lack of efficacy of hydroxychloroquine on coronavirus disease 2019 viral kinetics, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19056-6
Mahmoud, Shitu, Mostafa, Drug repurposing of nitazoxanide: can it be an effective therapy for COVID-19?, J Genet Eng Biotechnol, doi:10.1186/s43141-020-00055-5
Massimo, Stefano, Elena, Vittorio, Nicolò et al., The humanitas COVID-19 task force, the humanitas gavazzeni COVID-19 task force, rodolfo hurle, alessandro nobili, maurizio cecconi, paolo casale, rosanna asselta impact of antiandrogen therapies on COVID-19 susceptibility: a case-control study in male population from two COVID-19 regional centers of lombardy, doi:10.1101/2020.04.20.20068056
Mccoy, Cadegiani, Wambier, Herrera, Vaño-Galván et al., 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are associated with reduced frequency of COVID-19 symptoms in males with androgenetic alopecia, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.17021
Mccoy, Wambier, Herrera, Vaño-Galván, Gioia et al., Androgen receptor genetic variant predicts COVID-19 disease severity: a prospective longitudinal study of hospitalized COVID-19 male patients, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16956
Meyerowitz-Katz, Merone, A systematic review and meta-analysis of published research data on COVID-19 infection-fatality rates, Int J Infect Dis
Millum, Grady, The ethics of placebo-controlled trials: methodological justifications, Contemp Clin Trial, doi:10.1016/j.cct.2013.09.00
Novak, Post COVID-19 syndrome associated with orthostatic cerebral hypoperfusion syndrome, small fiber neuropathy and benefit of immunotherapy: a case report, eNeurologicalSci, doi:10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100276
O Murchu, Spillane, Byrne, Neill, Harrington et al., Interventions in an ambulatory setting to prevent progression to severe disease in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, Ann Pharmacother, doi:10.1177/10600280211028242
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ
Rakedzon, Neuberger, Domb, Petersiel, Schwartz, From hydroxychloroquine to ivermectin: what are the anti-viral properties of anti-parasitic drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2?, J Travel Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taab005
Rocco, Silva, Cruz, Junior, Tierno et al., Early use of nitazoxanide in mild Covid-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.03725-2020
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Piscoya, Vidal et al., Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab591
Sawadogo, Dighero-Kemp, Ouédraogo, Hensley, Sakandé, How NETosis could drive "Post-COVID-19 syndrome" among survivors, Immunol Lett, doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.005
Son, Huang, Zeng, Bricker, Case et al., cell culture and coronavirus pathogenesis in a pig model
Stokes, Zambrano, Anderson, Coronavirus disease 2019 case surveillance -United States, january 22-may 30, 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Subramanian, Anand, Adderley, Okoth, Toulis et al., Increased COVID-19 infections in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a population-based study, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-1163
Tolba, Omirah, Hussein, Saeed, Assessment and characterization of post-COVID-19 manifestations, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13746
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis, Lancet Infect Dis
Wambier, Mehta, Goren, Cadegiani, COVID-19, androgens, and androgenic alopecia, Dermatol Rev, doi:10.1002/der2.50
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wijeratne, Crewther, 589 Post-COVID 19 Neurological Syndrome (PCNS); a novel syndrome with challenges for the global neurology community, J Neurol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2020.117179
Woolf, Chapman, Sabo, Excess deaths from COVID-19 and other causes, march-april 2020, JAMA
Wortham, Lee, Althomsons, Characteristics of persons who died with COVID-19 -United States, february 12-may, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Young, Ong, Kalimuddin, Low, Tan et al., Singapore 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak research team. Epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.3204
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective NMNI Cadegiani et al. Early drug therapy improves COVID-19 outcomes. cohort study, Lancet
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915",
"ISSN": [
"2052-2975"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915",
"alternative-id": [
"S2052297521000792"
],
"article-number": "100915",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cadegiani",
"given": "F.A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8190-2289",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Goren",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wambier",
"given": "C.G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCoy",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "New Microbes and New Infections",
"container-title-short": "New Microbes and New Infections",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-07T18:45:33Z",
"timestamp": 1625683533000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-08T10:48:12Z",
"timestamp": 1633690092000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-28T16:38:59Z",
"timestamp": 1711643939685
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 16,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630454400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625184000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2052297521000792?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2052297521000792?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100915",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"first-page": "30566",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib1",
"volume": "S0140–6736",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0247461",
"article-title": "Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: a global systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Booth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib2",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12902-020-00626-0",
"article-title": "Repurposing existing drugs for COVID-19: an endocrinology perspective",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Endocr Disord",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/der2.50",
"article-title": "COVID-19, androgens, and androgenic alopecia",
"author": "Gustavo Wambier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib4a",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.16956",
"article-title": "Androgen receptor genetic variant predicts COVID-19 disease severity: a prospective longitudinal study of hospitalized COVID-19 male patients",
"author": "McCoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e15",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib4b",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bcr-2021-241572",
"article-title": "Potential risk for developing severe COVID-19 disease among anabolic steroid users",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "BMJ Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.17004",
"article-title": "Clinical symptoms of hyperandrogenic women diagnosed with COVID-19",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e101",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib6",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-1163",
"article-title": "Increased COVID-19 infections in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a population-based study",
"author": "Subramanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "637",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib7",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine: a comprehensive review and its controversial role in coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Bansal",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19056-6",
"article-title": "A pragmatic randomized controlled trial reports lack of efficacy of hydroxychloroquine on coronavirus disease 2019 viral kinetics",
"author": "Lyngbakken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5284",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/20477724.2021.1936818",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Di Castelnuovo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pathog Glob Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis",
"author": "Bartoszko",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taab005",
"article-title": "From hydroxychloroquine to ivermectin: what are the anti-viral properties of anti-parasitic drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2?",
"author": "Rakedzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "taab005",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Travel Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib13",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Li",
"journal-title": "J Cell Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Ivermectin as a broad-spectrum host-directed antiviral: the real deal? Cells",
"author": "Jans",
"first-page": "E2100",
"issue": "9",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib15",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab591",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ciab591",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10600280211028242",
"article-title": "Interventions in an ambulatory setting to prevent progression to severe disease in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "O Murchu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharmacother",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.023",
"article-title": "Inhibition of vaccinia virus replication by nitazoxanide",
"author": "Hickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "398",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib19",
"volume": "518",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide and JIB-04 have broad-spectrum antiviral activity and inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in cell culture and coronavirus pathogenesis in a pig model",
"author": "Son",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03725-2020",
"article-title": "Early use of nitazoxanide in mild Covid-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Rocco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2003725",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43141-020-00055-5",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing of nitazoxanide: can it be an effective therapy for COVID-19?",
"author": "Mahmoud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Genet Eng Biotechnol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib22",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22446-z",
"article-title": "Mortality outcomes with hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 from an international collaborative meta-analysis of randomized trials",
"author": "Axfors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2349",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100981",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide superiority to placebo to treat moderate COVID-19 A Pilot prove of concept randomized double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Blum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00136.2020",
"article-title": "Can spironolactone be used to prevent COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with hypertension?",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E587",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib25",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112",
"article-title": "Spironolactone may provide protection from SARS-CoV-2: targeting androgens, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110112",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib26",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00453",
"article-title": "Spironolactone: an anti-androgenic and anti-hypertensive drug that may provide protection against the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib27",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.17021",
"article-title": "5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are associated with reduced frequency of COVID-19 symptoms in males with androgenetic alopecia",
"author": "McCoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e243",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib28",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.16953",
"article-title": "Anti-androgens may protect against severe COVID-19 outcomes: results from a prospective cohort study of 77 hospitalized men",
"author": "Goren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib29",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Lazzeri",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Early antiandrogen therapy with dutasteride reduces viral shedding, inflammatory responses, and time-to-remission in males with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional trial (EAT-DUTA AndroCoV trial - biochemical)",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib31",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Proxalutamide significantly accelerates viral clearance and reduces time to clinical remission in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: results from a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Cadegiani",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib32",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Cadegiani",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib33"
},
{
"author": "Cadegiani",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib34"
},
{
"author": "Cadegiani",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1966",
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study",
"author": "Petrilli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1966",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib36",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib38",
"series-title": "Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus DIsease 2019 (COVID-2019)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"article-title": "Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis",
"author": "Verity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib39",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib40",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy",
"author": "Onder",
"first-page": "1775",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib41",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4031",
"article-title": "Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in lombardy, Italy: early experience and forecast during an emergency response",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1545",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib42",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1464",
"article-title": "A systematic review and meta-analysis of published research data on COVID-19 infection-fatality rates",
"author": "Meyerowitz-Katz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.11787",
"article-title": "Excess deaths from COVID-19 and other causes, march-april 2020",
"author": "Woolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "510",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib44",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6924e2",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 case surveillance - United States, january 22-may 30, 2020",
"author": "Stokes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "759",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib45",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa924",
"article-title": "Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) - a Danish nationwide, register553 based study",
"author": "Kragholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsa2011686",
"article-title": "Hospitalization and mortality among black patients and white patients with covid-19",
"author": "Price-Haywood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2534",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib47",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6928e1",
"article-title": "Characteristics of persons who died with COVID-19 — United States, february 12–may 18, 2020",
"author": "Wortham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib49",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib50",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2010419",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of covid-19 in New York city",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2372",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib51",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.010",
"article-title": "The 566 early natural history of SARS-CoV-2 infection: clinical observations from an urban, ambulatory COVID-19 clinic",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1124",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib52",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib53",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib54",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.3204",
"article-title": "Singapore 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak research team. Epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore",
"author": "Young",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1488",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib56",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.040",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with mild COVID-19",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "948.e1",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib57",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_853_20",
"article-title": "Natural history and clinical course of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients in the Kingdom of Saudi arabia",
"author": "Almubark",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Saudi J Med Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib58",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2020.117179",
"article-title": "589 Post-COVID 19 Neurological Syndrome (PCNS); a novel syndrome with challenges for the global neurology community",
"author": "Wijeratne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117179",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib59",
"volume": "419",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.005",
"article-title": "How NETosis could drive \"Post-COVID-19 syndrome\" among survivors",
"author": "Sawadogo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Immunol Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib60",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Assessment and characterization of post-COVID-19 manifestations",
"author": "Tolba",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100276",
"article-title": "Post COVID-19 syndrome associated with orthostatic cerebral hypoperfusion syndrome, small fiber neuropathy and benefit of immunotherapy: a case report",
"author": "Novak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100276",
"journal-title": "eNeurologicalSci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib62",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016",
"article-title": "Covid-19 hyperinflammation and post-Covid-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome",
"author": "Afrin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib63",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcaa248",
"article-title": "Post COVID Syndrome (PCS) and healthcare workers: who cares for the carers?",
"author": "Donnelly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "611",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib64",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100899",
"article-title": "Characteristics and predictors of acute and chronic post-COVID syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Iqbal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100899",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib65",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of post-COVID-19 symptoms in hospitalized and non-hospitalized COVID-19 survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fernández-de-Las-Peñas",
"first-page": "208",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib66",
"volume": "S0953–6205",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Health-related quality of life issues, including symptoms, in patients with active COVID-19 or post COVID-19; a systematic literature review",
"author": "Amdal",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Qual Life Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib67",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cct.2013.09.003",
"article-title": "The ethics of placebo-controlled trials: methodological justifications",
"author": "Millum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "510",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Contemp Clin Trial.",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib68",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "International ethical guidelines for biomedical research involving human subjects.Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "182",
"journal-title": "Bull Med Ethics",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib69",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2106535118",
"article-title": "Characterization of a new SARS-CoV-2 variant that emerged in Brazil",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "27",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915_bib70",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 68,
"references-count": 68,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.10.31.20223883",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2052297521000792"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early COVID-19 therapy with azithromycin plus nitazoxanide, ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine in outpatient settings significantly improved COVID-19 outcomes compared to known outcomes in untreated patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "43"
}
cadegiani