Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir for COVID-19 Treatment: An Analysis of Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531
, Jun 2020
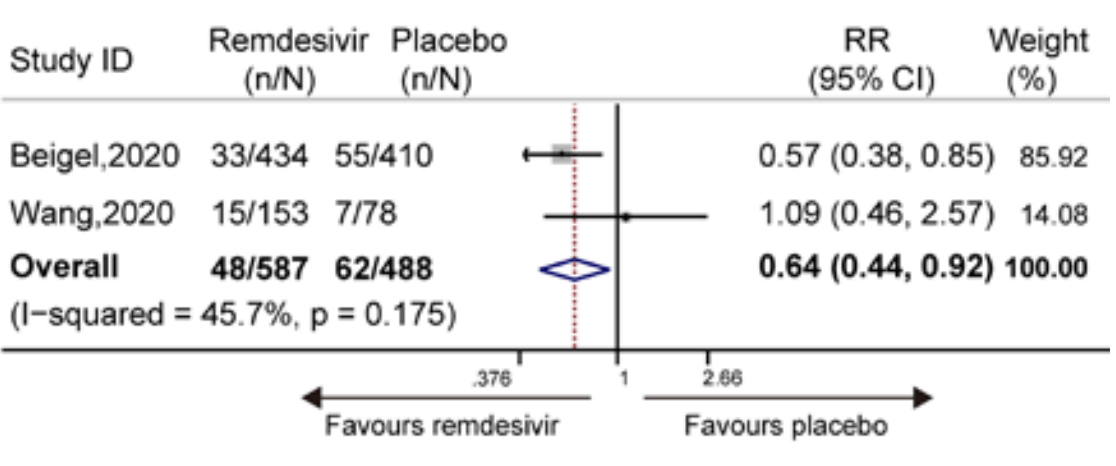
Meta analysis of Beigel and Wang RCTs showing remdesivir significantly decreased mortality (8.18% vs. 12.70%, RR 0.64 [0.44-0.92], p = 0.175).
Remdesivir efficacy disappears with longer
followup. Mixed-effects meta-regression of efficacy as a function of
followup duration across all remdesivir studies shows decreasing efficacy with
longer followup1. This may reflect
antiviral efficacy being offset by serious adverse effects of treatment.
Currently there are 84 remdesivir studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 1% lower [-9‑10%] |
| Ventilation | 11% higher [-11‑38%] |
| ICU admission | 119% higher [33‑259%] |
| Hospitalization | 21% higher [-4‑52%] |
|
risk of death, 36.0% lower, RR 0.64, p = 0.02.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhu et al., 29 Jun 2020, preprint, 11 authors.
Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir for COVID-19 Treatment: An Analysis of Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials
doi:10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531
BACKGROUND Remdesivir, an inhibitor of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, has been identified as a candidate for COVID-19 treatment. However, the therapeutic effect of remdesivir is controversial.
METHODS We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, from inception to June 11, 2020 for randomized controlled trials on the clinical efficacy of remdesivir. The main outcomes were discharge rate, mortality, and adverse events. This study is registered at INPLASY (INPLASY202060046). RESULTS Data of 1075 subjects showed that remdesivir significantly increased the discharge rate of patients with COVID-19 compared with the placebo (50.4% vs. 45.29%; relative risk [RR] 1.19 [95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05-1.34], I 2 = 0.0%, P = 0.754). It also significantly decreased mortality (8.18% vs. 12.70%; RR 0.64 [95% CI, 0.44-0.92], I 2 = 45.7%, P = 0.175) compared to the placebo. Data of 1296 subjects showed that remdesivir significantly decreased the occurrence of serious adverse events (RR 0.77 [95% CI, 0.63-0.94], I 2 = 0.0%, P = 0.716). CONCLUSION Remdesivir is efficacious and safe for the treatment of COVID-19. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER 2 .
Efficacy and Safety of
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Covid-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region -case series, N Engl J Med
Dersimonian, Laird, Meta-analysis in clinical trials, Control Clin Trials
Eastman, Roth, Brimacombe, Remdesivir: A review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19, ACS Cent Sci
Goldman, Lye, Hui, Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015301
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Higgins, Thompson, Deeks, Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses, BMJ
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Jadad, Moore, Carroll, Assessing the quality of reports of randomised clinical trials: is blinding necessary?, Control Clin Trials
Mahase, Covid-19: Remdesivir is helpful but not a wonder drug, say researchers, BMJ
Or, )) OR (Novel coronavirus pneumonia)
Patel, Jernigan, Ncdcr, Initial public health response and interim clinical guidance for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak -United States, December 31, 2019-February 4, 2020, Am J Transplant
Sheahan, Sims, Graham, Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses, Sci Transl Med
Sheahan, Sims, Leist, Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV, Nat Commun
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5
Woolf, On estimating the relation between blood group and disease, Ann Hum Genet
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>BACKGROUND</jats:title><jats:p>Remdesivir, an inhibitor of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, has been identified as a candidate for COVID-19 treatment. However, the therapeutic effect of remdesivir is controversial.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>METHODS</jats:title><jats:p>We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, from inception to June 11, 2020 for randomized controlled trials on the clinical efficacy of remdesivir. The main outcomes were discharge rate, mortality, and adverse events. This study is registered at INPLASY (INPLASY202060046).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>RESULTS</jats:title><jats:p>Data of 1075 subjects showed that remdesivir significantly increased the discharge rate of patients with COVID-19 compared with the placebo (50.4% vs. 45.29%; relative risk [RR] 1.19 [95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05–1.34], I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0.0%, P = 0.754). It also significantly decreased mortality (8.18% vs. 12.70%; RR 0.64 [95% CI, 0.44–0.92], I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 45.7%, P = 0.175) compared to the placebo. Data of 1296 subjects showed that remdesivir significantly decreased the occurrence of serious adverse events (RR 0.77 [95% CI, 0.63–0.94], I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0.0%, P = 0.716).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>CONCLUSION</jats:title><jats:p>Remdesivir is efficacious and safe for the treatment of COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER</jats:title><jats:p>This study is registered at the International Platform of Registered Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (INPLASY202060046).</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
29
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teng",
"given": "Zhaowei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Lirong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Shuanglan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teng",
"given": "Yirong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hao",
"given": "Qinggang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Dake",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xiaolan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Sheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-29T20:15:13Z",
"timestamp": 1593461713000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-05T22:27:20Z",
"timestamp": 1609885640000
},
"group-title": "Epidemiology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-12T12:21:28Z",
"timestamp": 1710246088757
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
29
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
29
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.15805",
"article-title": "Team nCDCR. Initial public health response and interim clinical guidance for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak - United States, December 31, 2019-February 4, 2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "889",
"journal-title": "Am J Transplant",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NE-JMoa2007016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.0c00489",
"article-title": "Remdesivir: A review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "ACS Cent Sci",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1798",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021010507151271000_2020.06.22.20136531v1.19"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.06.22.20136531"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir for COVID-19 Treatment: An Analysis of Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials",
"type": "posted-content"
}