Non-linear effects of meteorological factors on COVID-19: An analysis of 440 counties in the americas
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160, May 2024
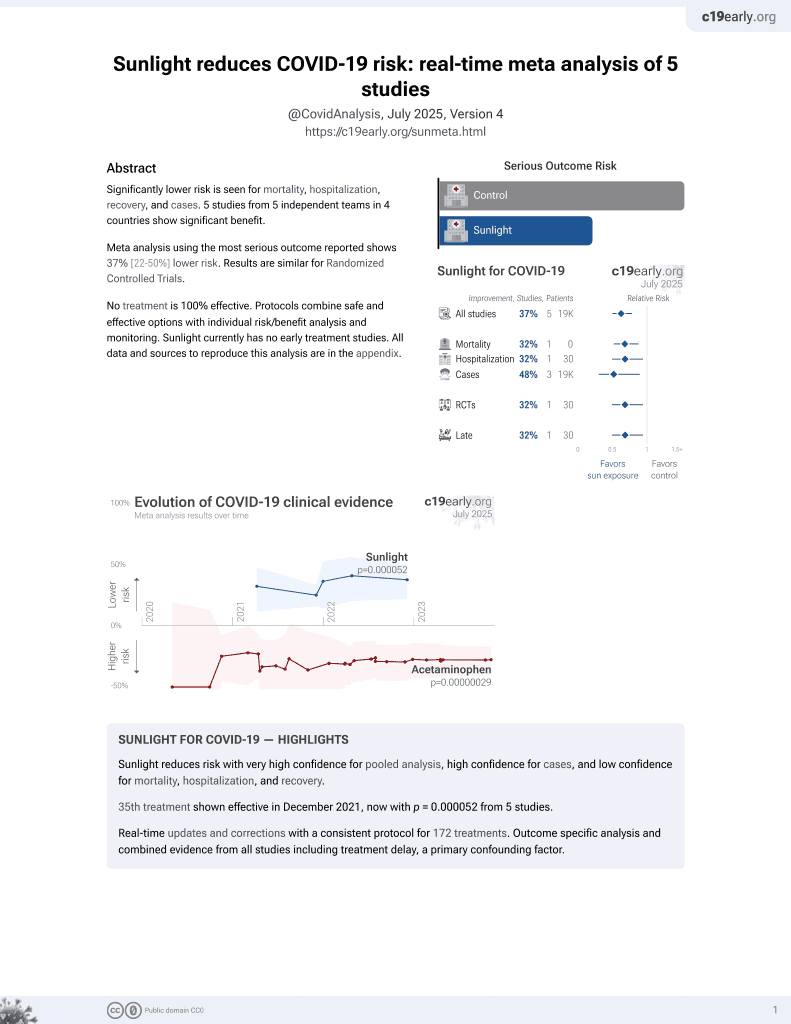
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
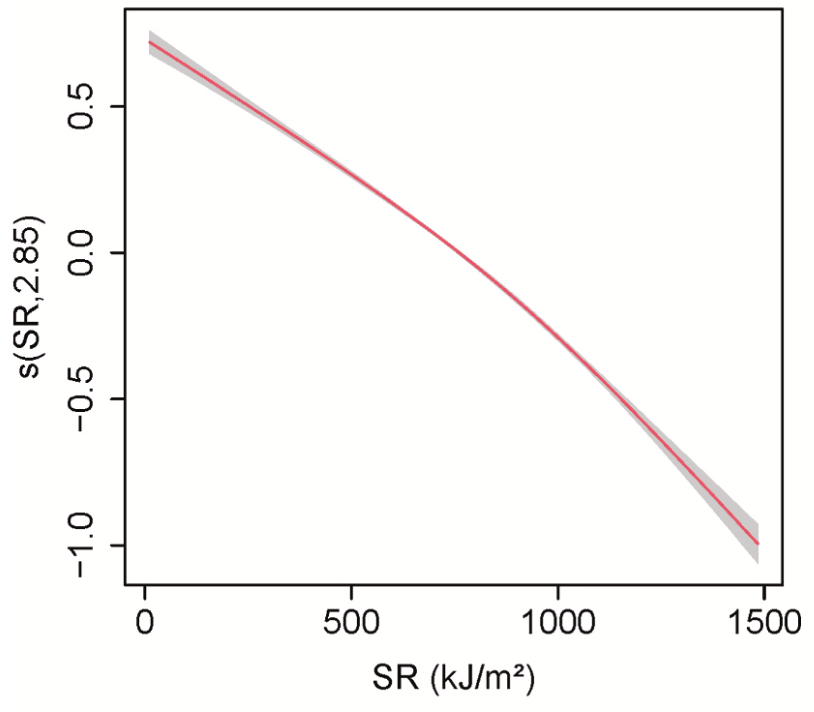
Retrospective 440 counties/districts across 7 countries in the Americas, showing solar radiation exhibited an overall negative association with daily new COVID-19 cases. The study used generalized additive models (GAM) and distributed lag nonlinear models (DLNM) to analyze the non-linear relationship and lag effects between daily new COVID-19 cases and meteorological factors. Increased infection risk was observed at low levels of solar radiation.
Zhang et al., 31 May 2024, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 1 January, 2020 - 31 December, 2021.
Contact: jwang169@vip.sina.com.
Non-linear effects of meteorological factors on COVID-19: An analysis of 440 counties in the americas
Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160
Background: In the last three years, COVID-19 has caused significant harm to both human health and economic stability. Analyzing the causes and mechanisms of COVID-19 has significant theoretical and practical implications for its prevention and mitigation. The role of meteorological factors in the transmission of COVID-19 is crucial, yet their relationship remains a subject of intense debate. Methods: To mitigate the issues arising from short time series, large study units, unrepresentative data and linear research methods in previous studies, this study used counties or districts with populations exceeding 100,000 or 500,000 as the study unit. The commencement of local outbreaks was determined by exceeding 100 cumulative confirmed cases. Pearson correlation analysis, generalized additive model (GAM) and distributed lag nonlinear model (DLNM) were used to analyze the relationship and lag effect between the daily new cases of COVID-19 and meteorological factors (temperature, relative humidity, solar radiation, surface pressure, precipitation, wind speed) across 440 counties or districts in seven countries of the Americas, spanning from January 1, 2020, to December 31, 2021. Results: The linear correlations between daily new cases and meteorological indicators such as air temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation were not significant. However, the non-linear correlations were significant. The turning points in the relationship for temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation were 5 • C and 23 • C, 74 % and 750 kJ/m 2 , respectively.
Conclusion: The influence of meteorological factors on COVID-19 is non-linear. There are two thresholds in the relationship with temperature: 5 • C and 23 • C. Below 5 • C and above 23 • C, there is a positive correlation, while between 5 • C and 23 • C, the correlation is negative. Relative humidity and solar radiation show negative correlations, but there is a change in slope at about 74 % and 750 kJ/m 2 , respectively.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Babu, Rao, Kumar, Paul, Pani, Plausible role of environmental factors on COVID-19 transmission in the megacity Delhi, India, Aerosol Air Qual. Res, doi:10.4209/aaqr.2020.06.0314
Badr, Zaitchik, Kerr, Nguyen, Chen et al., Unified real-time environmental-epidemiological data for multiscale modeling of the COVID-19 pandemic, doi:10.1101/2021.05.05.21256712
Bonilla, Lopez-Feldman, Pereda, Rivera, Ruiz-Tagle, Association between long-term air pollution exposure and COVID-19 mortality in Latin America, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0280355
Briz-Redón, Belenguer-Sapiña, Serrano-Aroca, A city-level analysis of PM2.5 pollution, climate and COVID-19 early spread in Spain, J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng, doi:10.1007/s40201-022-00786-2
Cai, Sun, Huang, Gamber, Wu et al., Indirect virus transmission in cluster of COVID-19 cases, wenzhou, China, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2606.200412
Carleton, Cornetet, Huybers, Meng, Proctor, Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S.A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2012370118
Chan, Peiris, Lam, Poon, Yuen et al., The effects of temperature and relative humidity on the viability of the SARS coronavirus, Adv. Virol, doi:10.1155/2011/734690
Cherrie, Clemens, Colandrea, Feng, Webb et al., Ultraviolet A radiation and COVID-19 deaths: a multi country study, doi:10.1101/2020.07.03.20145912
Chin, Chu, Perera, Hui, Yen et al., Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3
Colston, Hinson, Nguyen, Chen, Badr et al., Effects of hydrometeorological and other factors on SARS-CoV-2 reproduction number in three contiguous countries of tropical Andean South America: a spatiotemporally disaggregated time series analysis, IJID Regions, doi:10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.11.007
Dabisch, Schuit, Herzog, Beck, Wood et al., The influence of temperature, humidity, and simulated sunlight on the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols, Aerosol, Sci. Technol, doi:10.1080/02786826.2020.1829536
Ding, Gao, Shao, Non-linear link between temperature difference and COVID-19: excluding the effect of population density, The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, doi:10.3855/jidc.13926
Gardner, Kelton, Poljak, Van Kerkhove, Dobschuetz et al., A case-crossover analysis of the impact of weather on primary cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-019-3729-5
Gasparrini, Armstrong, Kenward, Distributed lag non-linear models, Stat. Med, doi:10.1002/sim.3940
Gasparrini, Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: the package dlnm, J. Stat. Softw
Greenhalgh, Jimenez, Prather, Tufekci, Fisman et al., Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00869-2
Guasp, Laredo, Urra, Higher solar irradiance is associated with a lower incidence of coronavirus disease 2019, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa575
Guo, Bo, Lin, Li, Zeng et al., Meteorological factors and COVID-19 incidence in 190 countries: an observational study, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143783
Hastie, Generalized additive models
Hastie, Tibshirani, Generalized additive models, stat, Sci, doi:10.1214/ss/1177013604
Hersbach, Bell, Berrisford, Hirahara, Horányi et al., The ERA5 global reanalysis, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc, doi:10.1002/qj.3803
Inagaki, Saito, Sugiyama, Okabayashi, Fujimoto, Rapid inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with deep-UV LED irradiation, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1796529
Iqbal, Fareed, Shahzad, He, Shahzad et al., The nexus between COVID-19, temperature and exchange rate in Wuhan city: new findings from partial and multiple wavelet coherence, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138916
Karim, Akter, Effects of climate variables on the COVID-19 mortality in Bangladesh, Theor. Appl. Climatol, doi:10.1007/s00704-022-04211-4
Kerr, Badr, Barbieri, Colston, Gardner et al., Evolving drivers of Brazilian SARS-CoV-2 transmission: a spatiotemporally disaggregated time series analysis of meteorology, policy, and human mobility, GeoHealth, doi:10.1029/2022GH000727
Khursheed, Mustafa, Akhtar, Investigating the roles of meteorological factors in COVID-19 transmission in Northern Italy, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1007/s11356-021-14038-7
Kim, Ramakrishnan, Raynor, Goyal, Effects of humidity and other factors on the generation and sampling of a coronavirus aerosol, Aerobiologia, doi:10.1007/s10453-007-9068-9
Li, Qian, Hang, Chen, Cheng et al., Probable airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in a poorly ventilated restaurant, Build. Environ, doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107788
Liu, Zhou, Yao, Zhang, Li et al., Impact of meteorological factors on the COVID-19 transmission: a multi-city study in China, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138513
Lowen, Mubareka, Steel, Palese, Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151
Lyu, Wang, Jiang, Ding, Zhai et al., Random forest regression on joint role of meteorological variables, demographic factors, and policy response measures in COVID-19 daily cases: global analysis in different climate zones, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1007/s11356-023-27320-7
Ma, Pei, Shaman, Dubrow, Chen, Role of meteorological factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23866-7
Marr, Tang, Van Mullekom, Lakdawala, Mechanistic insights into the effect of humidity on airborne influenza virus survival, transmission and incidence, J. R. Soc. Interface, doi:10.1098/rsif.2018.0298
Matson, Yinda, Seifert, Bushmaker, Fischer et al., Effect of environmental conditions on SARS-CoV-2 stability in human nasal mucus and sputum, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2609.202267
Merow, Urban, Seasonality and uncertainty in global COVID-19 growth rates, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2008590117
Moriyama, Hugentobler, Iwasaki, Seasonality of respiratory viral infections, Annu. Rev. Virol, doi:10.1146/annurev-virology-012420-022445
Morris, Yinda, Gamble, Rossine, Huang et al., Mechanistic theory predicts the effects of temperature and humidity on inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 and other enveloped viruses, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.65902
Nottmeyer, Armstrong, Lowe, Abbott, Meakin et al., The association of COVID-19 incidence with temperature, humidity, and UV radiationa global multi-city analysis, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158636
Orak, Effect of ambient air pollution and meteorological factors on the potential transmission of COVID-19 in Turkey, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.113646
Paireau, Charpignon, Larrieu, Calba, Hozé et al., Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1
Paireau, Charpignon, Larrieu, Calba, Hozé et al., Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1
Peng, Dominici, Louis, Model choice in time series studies of air pollution and mortality, J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc, doi:10.1111/j.1467-985X.2006.00410.x
Pequeno, Mendel, Rosa, Bosholn, Souza et al., Air transportation, population density and temperature predict the spread of COVID-19 in Brazil, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.9322
Prata, Rodrigues, De Queiroz Trevisan, Camargo, Frizzera et al., Climatic factors associated with economic determinants significantly affect the spread of COVID-19 in tropical Brazil, One Health, doi:10.1016/j.onehlt.2022.100375
Ratnesar-Shumate, Williams, Green, Krause, Holland et al., Simulated sunlight rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa274
Sabarathinam, Mohan Viswanathan, Senapathi, Karuppannan, Samayamanthula et al., SARS-CoV-2 phase I transmission and mutability linked to the interplay of climatic variables: a global observation on the pandemic spread, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1007/s11356-021-17481-8
Sagripanti, Lytle, Estimated inactivation of coronaviruses by solar radiation with special reference to COVID-19, Photochem. Photobiol, doi:10.1111/php.13293
Scapini, Torres, Rubilar-Torrealba, Meteorological, PM2.5 and PM10 factors on SARS-COV-2 transmission: the case of southern regions in Chile, Environ. Pollut, doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120961
Schuit, Ratnesar-Shumate, Yolitz, Williams, Weaver et al., Airborne SARS-CoV-2 is rapidly inactivated by simulated sunlight, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa334
Shahzad, Shahzad, Fareed, Iqbal, Hashmi et al., Asymmetric nexus between temperature and COVID-19 in the top ten affected provinces of China: a current application of quantile-on-quantile approach, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139115
Sobral, Duarte, Da Penha Sobral, Marinho, De Souza Melo, Association between climate variables and global transmission oF SARS-CoV-2, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138997
Sooryanarain, Elankumaran, Environmental role in influenza virus outbreaks, Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci, doi:10.1146/annurev-animal-022114-111017
Sun, Zhang, Yang, Wan, Wang, Impacts of geographic factors and population density on the COVID-19 spreading under the lockdown policies of China, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141347
Sweijd, Zaitchik, The 2020 WMO Symposium on Climatological, Meteorological and Environmental factors in the COVID-19 pandemic: a special issue from symposium presentations, One Health, doi:10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100243
Talmoudi, Bellali, Ben-Alaya, Saez, Malouche et al., Modeling zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis incidence in central Tunisia from 2009-2015: forecasting models using climate variables as predictors, PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0005844
Tamerius, Shaman, Alonso, Bloom-Feshbach, Uejio et al., Environmental predictors of seasonal influenza epidemics across temperate and tropical climates, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003194
Wood, Generalized Additive Models: an Introduction with R, doi:10.1201/9781315370279
Xie, Zhu, Association between ambient temperature and COVID-19 infection in 122 cities from China, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138201
Xiong, Li, Wu, Wolfson, Lawrence et al., The association between daily-diagnosed COVID-19 morbidity and short-term exposure to PM1 is larger than associations with PM2.5 and PM10, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.113016
Yin, Zhao, Pereira, Meteorological factors' effects on COVID-19 show seasonality and spatiality in Brazil, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.112690
Yuan, Wu, Jing, Liu, Du et al., Association between meteorological factors and daily new cases of COVID-19 in 188 countries: a time series analysis, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146538
Yuan, Wu, Jing, Liu, Du et al., Non-linear correlation between daily new cases of COVID-19 and meteorological factors in 127 countries, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110521
Zaitchik, Sweijd, Shumake-Guillemot, Morse, Gordon et al., A framework for research linking weather, climate and COVID-19, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19546-7
Zhang, None, Heliyon
Zhao, Qi, Luzzatto-Fegiz, Cui, Zhu, COVID-19: effects of environmental conditions on the propagation of respiratory droplets, Nano Lett, doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03331
Zoran, Savastru, Savastru, Tautan, Impacts of exposure to air pollution, radon and climate drivers on the COVID-19 pandemic in Bucharest, Romania: a time series study, Environ. Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.113437
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160",
"ISSN": [
"2405-8440"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405844024071913"
],
"article-number": "e31160",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Non-linear effects of meteorological factors on COVID-19: An analysis of 440 counties in the americas"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Heliyon"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0001-0795-1648",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Zhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Yuting",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Heliyon",
"container-title-short": "Heliyon",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T16:05:29Z",
"timestamp": 1715443529000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-24T03:14:57Z",
"timestamp": 1716520497000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-25T00:25:07Z",
"timestamp": 1716596707169
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714521600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 9,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715299200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405844024071913?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405844024071913?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e31160",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141347",
"article-title": "Impacts of geographic factors and population density on the COVID-19 spreading under the lockdown policies of China",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib4",
"volume": "746",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1029/2022GH000727",
"article-title": "Evolving drivers of Brazilian SARS-CoV-2 transmission: a spatiotemporally disaggregated time series analysis of meteorology, policy, and human mobility",
"author": "Kerr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "GeoHealth",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib5",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1",
"article-title": "Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France",
"author": "Paireau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib6",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10453-007-9068-9",
"article-title": "Effects of humidity and other factors on the generation and sampling of a coronavirus aerosol",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "Aerobiologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib7",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2011/734690",
"article-title": "The effects of temperature and relative humidity on the viability of the SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Adv. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib8",
"volume": "2011",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/annotation/df689228-603f-4a40-bfbf-a38b13f88147",
"article-title": "Environmental predictors of seasonal influenza epidemics across temperate and tropical climates",
"author": "Tamerius",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-animal-022114-111017",
"article-title": "Environmental role in influenza virus outbreaks",
"author": "Sooryanarain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib10",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-012420-022445",
"article-title": "Seasonality of respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Moriyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib11",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-019-3729-5",
"article-title": "A case-crossover analysis of the impact of weather on primary cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Gardner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib12",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa334",
"article-title": "Airborne SARS-CoV-2 is rapidly inactivated by simulated sunlight",
"author": "Schuit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib13",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/php.13293",
"article-title": "Estimated inactivation of coronaviruses by solar radiation with special reference to COVID-19",
"author": "Sagripanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"journal-title": "Photochem. Photobiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib14",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.65902",
"article-title": "Mechanistic theory predicts the effects of temperature and humidity on inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 and other enveloped viruses",
"author": "Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsif.2018.0298",
"article-title": "Mechanistic insights into the effect of humidity on airborne influenza virus survival, transmission and incidence",
"author": "Marr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. R. Soc. Interface.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib16",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2609.202267",
"article-title": "Effect of environmental conditions on SARS-CoV-2 stability in human nasal mucus and sputum",
"author": "Matson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2276",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib17",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100243",
"article-title": "The 2020 WMO Symposium on Climatological, Meteorological and Environmental factors in the COVID-19 pandemic: a special issue from symposium presentations",
"author": "Sweijd",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "One Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib18",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19546-7",
"article-title": "A framework for research linking weather, climate and COVID-19",
"author": "Zaitchik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5730",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib19",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4209/aaqr.2020.06.0314",
"article-title": "Plausible role of environmental factors on COVID-19 transmission in the megacity Delhi, India",
"author": "Babu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2075",
"journal-title": "Aerosol Air Qual. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib21",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00704-022-04211-4",
"article-title": "Effects of climate variables on the COVID-19 mortality in Bangladesh",
"author": "Karim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1463",
"journal-title": "Theor. Appl. Climatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib22",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2022.113646",
"article-title": "Effect of ambient air pollution and meteorological factors on the potential transmission of COVID-19 in Turkey",
"author": "Orak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib23",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.onehlt.2022.100375",
"article-title": "Climatic factors associated with economic determinants significantly affect the spread of COVID-19 in tropical Brazil",
"author": "Prata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "One Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib24",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-021-17481-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 phase I transmission and mutability linked to the interplay of climatic variables: a global observation on the pandemic spread",
"author": "Sabarathinam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72366",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib25",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0280355",
"article-title": "Association between long-term air pollution exposure and COVID-19 mortality in Latin America",
"author": "Bonilla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138513",
"article-title": "Impact of meteorological factors on the COVID-19 transmission: a multi-city study in China",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib27",
"volume": "726",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158636",
"article-title": "The association of COVID-19 incidence with temperature, humidity, and UV radiation – a global multi-city analysis",
"author": "Nottmeyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib28",
"volume": "854",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1",
"article-title": "Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France",
"author": "Paireau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib29",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj.9322",
"article-title": "Air transportation, population density and temperature predict the spread of COVID-19 in Brazil",
"author": "Pequeno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PeerJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib30",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120961",
"article-title": "Meteorological, PM2.5 and PM10 factors on SARS-COV-2 transmission: the case of southern regions in Chile",
"author": "Scapini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Pollut.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib31",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139115",
"article-title": "Asymmetric nexus between temperature and COVID-19 in the top ten affected provinces of China: a current application of quantile-on-quantile approach",
"author": "Shahzad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib32",
"volume": "736",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138997",
"article-title": "Association between climate variables and global transmission oF SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sobral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib33",
"volume": "729",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2022.112690",
"article-title": "Meteorological factors' effects on COVID-19 show seasonality and spatiality in Brazil",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib34",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2022.113437",
"article-title": "Impacts of exposure to air pollution, radon and climate drivers on the COVID-19 pandemic in Bucharest, Romania: a time series study",
"author": "Zoran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib35",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40201-022-00786-2",
"article-title": "A city-level analysis of PM2.5 pollution, climate and COVID-19 early spread in Spain",
"author": "Briz-Redón",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib36",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138916",
"article-title": "The nexus between COVID-19, temperature and exchange rate in Wuhan city: new findings from partial and multiple wavelet coherence",
"author": "Iqbal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib37",
"volume": "729",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138201",
"article-title": "Association between ambient temperature and COVID-19 infection in 122 cities from China",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib38",
"volume": "724",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.11.007",
"article-title": "Effects of hydrometeorological and other factors on SARS-CoV-2 reproduction number in three contiguous countries of tropical Andean South America: a spatiotemporally disaggregated time series analysis",
"author": "Colston",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "IJID Regions",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib39",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.13926",
"article-title": "Non-linear link between temperature difference and COVID-19: excluding the effect of population density",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib40",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-021-14038-7",
"article-title": "Investigating the roles of meteorological factors in COVID-19 transmission in Northern Italy",
"author": "Khursheed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48459",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib41",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2022.113016",
"article-title": "The association between daily-diagnosed COVID-19 morbidity and short-term exposure to PM1 is larger than associations with PM2.5 and PM10",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib42",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110521",
"article-title": "Non-linear correlation between daily new cases of COVID-19 and meteorological factors in 127 countries",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib43",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146538",
"article-title": "Association between meteorological factors and daily new cases of COVID-19 in 188 countries: a time series analysis",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib44",
"volume": "780",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143783",
"article-title": "Meteorological factors and COVID-19 incidence in 190 countries: an observational study",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib45",
"volume": "757",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23866-7",
"article-title": "Role of meteorological factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3602",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib46",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Badr",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/qj.3803",
"article-title": "The ERA5 global reanalysis",
"author": "Hersbach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1999",
"journal-title": "Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib48",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Generalized additive models, stat",
"author": "Hastie",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib49",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"author": "Wood",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib50",
"series-title": "Generalized Additive Models: an Introduction with R",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1467-985X.2006.00410.x",
"article-title": "Model choice in time series studies of air pollution and mortality",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "179",
"journal-title": "J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib51",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0005844",
"article-title": "Modeling zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis incidence in central Tunisia from 2009-2015: forecasting models using climate variables as predictors",
"author": "Talmoudi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib52",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Generalized additive models",
"author": "Hastie",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib53",
"series-title": "Statistical Models in S",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v043.i08",
"article-title": "Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: the package dlnm",
"author": "Gasparrini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Stat. Softw.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib54",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3940",
"article-title": "Distributed lag non-linear models",
"author": "Gasparrini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2224",
"journal-title": "Stat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib55",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-023-27320-7",
"article-title": "Random forest regression on joint role of meteorological variables, demographic factors, and policy response measures in COVID-19 daily cases: global analysis in different climate zones",
"author": "Lyu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "79512",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib56",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3",
"article-title": "Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions",
"author": "Chin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e10",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib57",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151",
"article-title": "Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature",
"author": "Lowen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib58",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00869-2",
"article-title": "Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Greenhalgh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1603",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib59",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2606.200412",
"article-title": "Indirect virus transmission in cluster of COVID-19 cases, wenzhou, China, 2020",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1343",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib60",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107788",
"article-title": "Probable airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in a poorly ventilated restaurant",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Build. Environ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib61",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03331",
"article-title": "COVID-19: effects of environmental conditions on the propagation of respiratory droplets",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7744",
"journal-title": "Nano Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib62",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012370118",
"article-title": "Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates",
"author": "Carleton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib63",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Cherrie",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa575",
"article-title": "Higher solar irradiance is associated with a lower incidence of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Guasp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2269",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib65",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2008590117",
"article-title": "Seasonality and uncertainty in global COVID-19 growth rates",
"author": "Merow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27456",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib66",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa274",
"article-title": "Simulated sunlight rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces",
"author": "Ratnesar-Shumate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib67",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The influence of temperature, humidity, and simulated sunlight on the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols, Aerosol",
"author": "Dabisch",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "Sci. Technol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib68",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1796529",
"article-title": "Rapid inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with deep-UV LED irradiation",
"author": "Inagaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1744",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31160_bib69",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 65,
"references-count": 65,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-3467952/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405844024071913"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Non-linear effects of meteorological factors on COVID-19: An analysis of 440 counties in the americas",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "10"
}