Higher Solar Irradiance Is Associated With a Lower Incidence of Coronavirus Disease 2019
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa575, May 2020
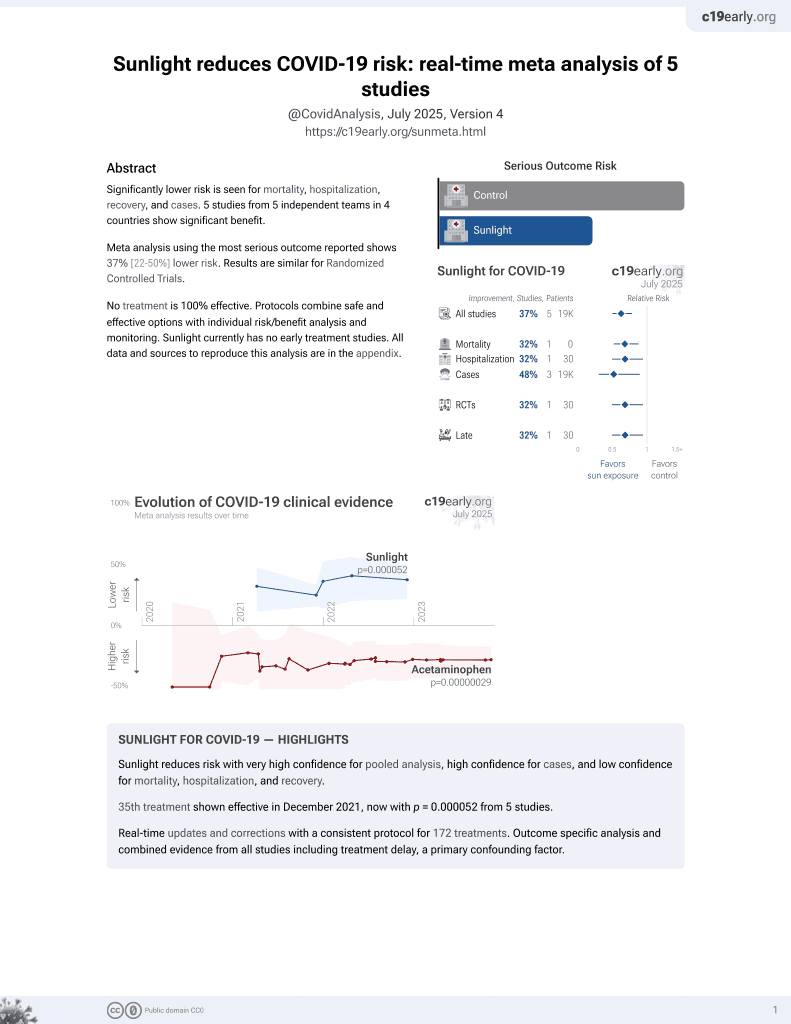
Sunlight for COVID-19
35th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
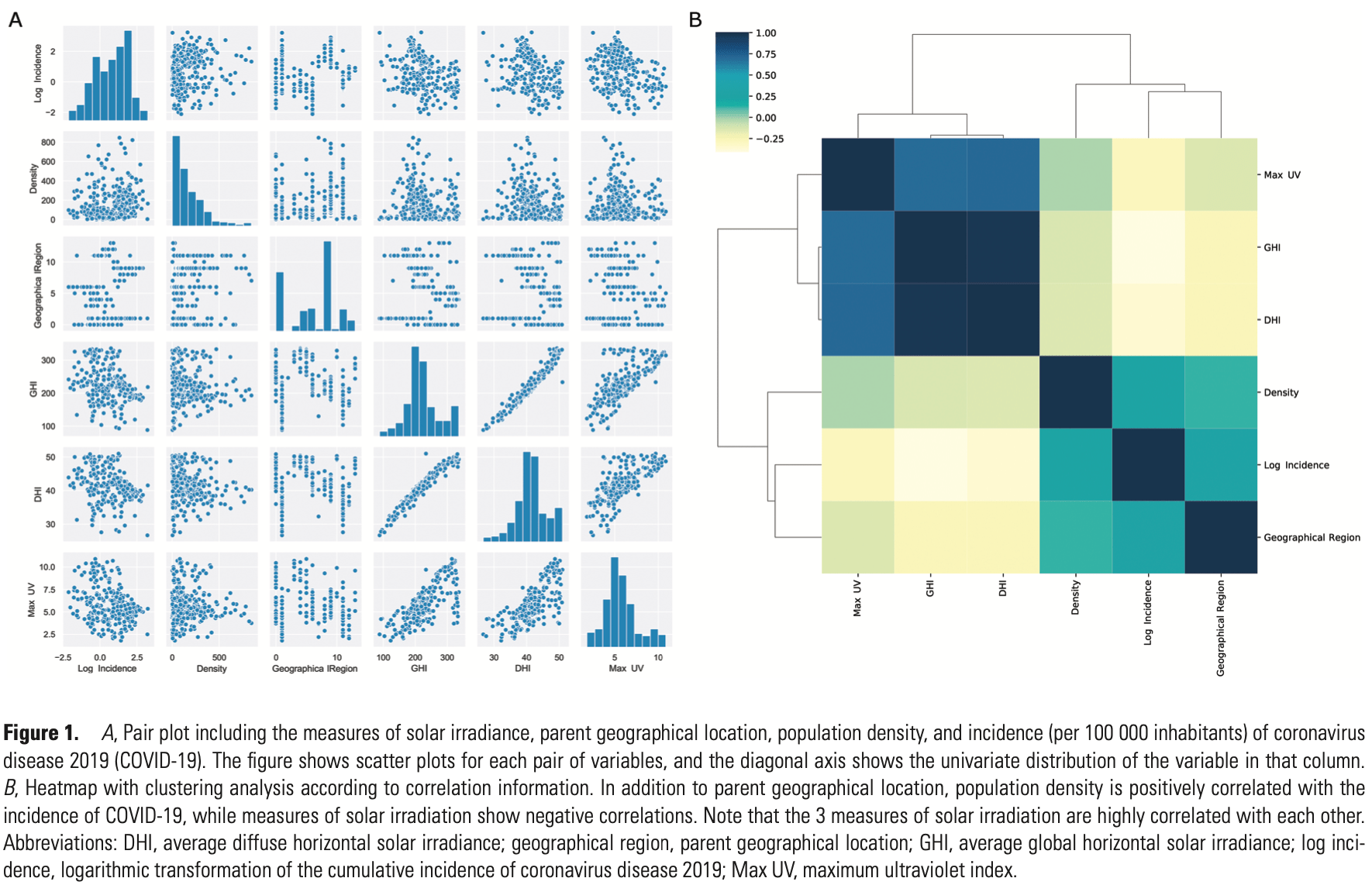
Analysis of 359 countries and regions showing COVID-19 cases associated with reduced solar irradiance.
Guasp et al., 19 May 2020, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: xurra@clinic.cat.
Higher Solar Irradiance Is Associated With a Lower Incidence of Coronavirus Disease 2019
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa575
We studied the relationship between the incidence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), demographical, and climatological measurements in different regions across the world. Lower solar irradiance and higher population density were independent predictors of greater COVID-19 outbreaks. Further studies on the potential protective effect of sunlight over COVID-19 are warranted.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Clinical Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Notes
References
Abhimanyu, Ak, The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease, Photochem Photobiol Sci
Anderson, Heesterbeek, Klinkenberg, Hollingsworth, How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?, Lancet
Dalziel, Kissler, Gog, Urbanization and humidity shape the intensity of influenza epidemics in U.S. cities, Science
Killerby, Biggs, Haynes, Human coronavirus circulation in the United States 2014-2017, J Clin Virol
Li, Guan, Wu, Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Lowen, Mubareka, Steel, Palese, Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature, PLoS Pathog
Luo, Majumder, Liu, The role of absolute humidity on transmission rates of the COVID-19 outbreak, doi:10.1101/2020.02.12.20022467
Neher, Dyrdak, Druelle, Hodcroft, Albert, Potential impact of seasonal forcing on a SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, Swiss Med Wkly
Rader, Scarpino, Nande, Crowding and the epidemic intensity of COVID-19 transmission, doi:10.1101/2020.04.15.20064980
Sagripanti, Lytle, Inactivation of influenza virus by solar radiation, Photochem Photobiol
Sutton, Aldous, Warren, Fuller, Alexander et al., Inactivation of the infectivity of two highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and a virulent Newcastle disease virus by ultraviolet radiation, Avian Pathol
Wu, Leung, Leung, Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa575",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa575",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We studied the relationship between the incidence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), demographical, and climatological measurements in different regions across the world. Lower solar irradiance and higher population density were independent predictors of greater COVID-19 outbreaks. Further studies on the potential protective effect of sunlight over COVID-19 are warranted.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0110-5213",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Neurosciences Unit, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer, Barcelona, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Guasp",
"given": "Mar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer, Barcelona, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Laredo",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Neurosciences Unit, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer, Barcelona, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Urra",
"given": "Xabier",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-18T19:44:42Z",
"timestamp": 1589831082000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-19T12:43:46Z",
"timestamp": 1605789826000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"INT19/00020"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004895",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "European Social Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-03T07:20:15Z",
"timestamp": 1670052015669
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 16,
"issue": "16",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "16",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
19
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1589846400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa575/33460193/ciaa575.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/71/16/2269/34393243/ciaa575.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/71/16/2269/34393243/ciaa575.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2269-2271",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"article-title": "Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1199",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0001",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5",
"article-title": "How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0002",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2018.01.019",
"article-title": "Human coronavirus circulation in the United States 2014–2017",
"author": "Killerby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0003",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151",
"article-title": "Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature",
"author": "Lowen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1470",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0004",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential impact of seasonal forcing on a SARS-CoV-2 pandemic",
"author": "Neher",
"first-page": "w20224",
"journal-title": "Swiss Med Wkly",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0005",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of absolute humidity on transmission rates of the COVID-19 outbreak",
"author": "Luo",
"journal-title": "medRxiv [Preprint]",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0006",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30260-9",
"article-title": "Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0007",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03079457.2013.853867",
"article-title": "Inactivation of the infectivity of two highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and a virulent Newcastle disease virus by ultraviolet radiation",
"author": "Sutton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "566",
"journal-title": "Avian Pathol",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0008",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00177.x",
"article-title": "Inactivation of influenza virus by solar radiation",
"author": "Sagripanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1278",
"journal-title": "Photochem Photobiol",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0009",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C6PP00355A",
"article-title": "The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease",
"author": "",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"journal-title": "Photochem Photobiol Sci",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0010",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Crowding and the epidemic intensity of COVID-19 transmission",
"author": "Rader",
"journal-title": "medRxiv [Preprint]",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0011",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aat6030",
"article-title": "Urbanization and humidity shape the intensity of influenza epidemics in U.S. cities",
"author": "Dalziel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2020111907071962200_CIT0012",
"volume": "362",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/71/16/2269/5840498"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Higher Solar Irradiance Is Associated With a Lower Incidence of Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "71"
}