Metformin use before COVID-19 vaccination and the risks of COVID-19 incidence, medical utilization, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
et al., Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692, May 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
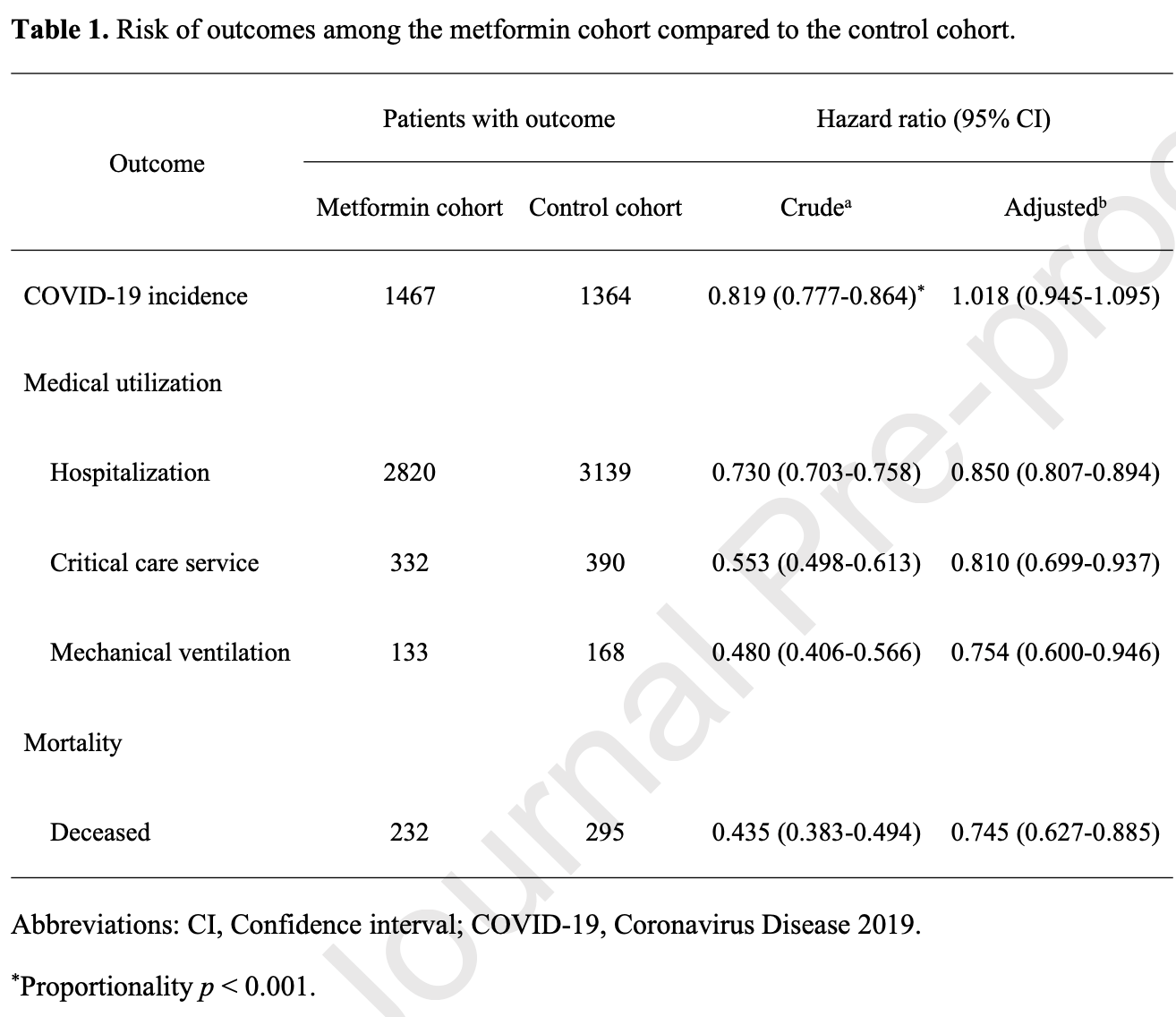
TriNetX retrospective 123,709 vaccinated patients with type 2 diabetes, showing significantly lower risk of COVID-19 mortality, mechanical ventilation, and hospitalization with metformin use. There was no significant difference for cases. The increasing benefit for more serious outcomes matches the results of studies to date.
|
risk of death, 25.0% lower, HR 0.75, p = 0.001, treatment 232 of 20,894 (1.1%), control 295 of 20,894 (1.4%), NNT 332, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 25.0% lower, HR 0.75, p = 0.01, treatment 133 of 20,894 (0.6%), control 168 of 20,894 (0.8%), NNT 597, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 19.0% lower, HR 0.81, p = 0.005, treatment 332 of 20,894 (1.6%), control 390 of 20,894 (1.9%), NNT 360, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 15.0% lower, HR 0.85, p < 0.001, treatment 2,820 of 20,894 (13.5%), control 3,139 of 20,894 (15.0%), NNT 65, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
risk of case, 2.0% higher, HR 1.02, p = 0.63, treatment 1,467 of 20,894 (7.0%), control 1,364 of 20,894 (6.5%), propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yen et al., 6 May 2023, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 1 January, 2020 - 22 November, 2022.
Contact: yenfushun@gmail.com, shiowing0107@gmail.com, sylin@vghtc.gov.tw, jccwei@gmail.com.
Metformin use before COVID-19 vaccination and the risks of COVID-19 incidence, medical utilization, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Authors' contribution FSY: study concept and design, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. SIW: data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; statistical analysis and drafting of the manuscript. SYL: study concept and design, data interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. JCCW: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, technical and material support, and study supervision.
Appendix A. Supplementary material Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/•••.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Barouch, Covid-19 vaccines -immunity, variants, boosters, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra2206573
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Mingrone, Hopkins et al., Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Mohan, Forteath et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
Diaz, Romero, Vazquez, Lechner, Blomberg et al., Metformin improves in vivo and in vitro B cell function in individuals with obesity and type-2 diabetes, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.078
Dispinseri, Lampasona, Secchi, Bazzigaluppi, Negri, Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 develop and persist in subjects with diabetes and COVID-19 pneumonia, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab055
Draznin, Aroda, Bakris, Benson, Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc22-S004
Edwards, Baric, Saphire, Ulmer, Stopping pandemics before they start: lessons learned from SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn1900
Kifle, Woldeyohanis, Demeke, A review on protective roles and potential mechanisms of metformin in diabetic patients diagnosed with COVID-19, Metabol Open, doi:10.1016/j.metop.2021.100137
Koelle, Martin, Antia, Lopman, Dean, The changing epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm4915
Kritas, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Mast cells contribute to coronavirus-induced inflammation: new anti-inflammatory strategy, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, doi:10.23812/20-Editorial-Kritas
Lampasona, Secchi, Scavini, Bazzigaluppi, Brigatti et al., Antibody response to multiple antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes: an observational cohort study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05284-4
Li, Wang, Kan, Wang, Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4
Li, Yang, Yan, Sun, Zeng et al., Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4
Mannick, Giudice, Lattanzi, Valiante, Praestgaard et al., mTOR inhibition improves immune function in the elderly, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3009892
Marfella, Onofrio, Sardu, Scisciola, Maggi et al., Does poor glycaemic control affect the immunogenicity of the COVID-19 vaccination in patients with type 2 diabetes: the CAVEAT study, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14547
Mbara, Mato, Driver, Nzuza, Mkhombo et al., Metformin turns 62 in pharmacotherapy: emergence of non-glycaemic effects and potential novel therapeutic applications, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173934
Pal, Bhadada, Misra, COVID-19 vaccination in patients with diabetes mellitus: current concepts, uncertainties and challenges, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.026
Polack, Thomas, Kitchin, Absalon, Gurtman et al., Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
Scarpello, Howlett, Metformin therapy and clinical uses, Diab Vasc Dis Res, doi:10.3132/dvdr.2008.027
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183
Wang, Wang, Wang, Wei, Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in COVID-19 survivors among non-vaccinated population: a retrospective cohort study from the TriNetX US collaborative networks, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101619
Watson, Barnsley, Toor, Hogan, Winskill et al., Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: a mathematical modelling study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00320-6
Yen, Wei, Shih, Hsu, Hsu et al., Metformin use before influenza vaccination may lower the risks of influenza and related complications, Vaccines (Basel), doi:10.3390/vaccines10101752
Yen, Wei, Shih, Hsu, Hwu, Metformin use and the risk of bacterial pneumonia in patients with type 2 diabetes, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-07294-1
Yen, Wei, Yip, Hsu, Hwu, Metformin use and the risks of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in patients with type 2 diabetes, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28278
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692",
"ISSN": [
"0168-8227"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692",
"alternative-id": [
"S0168822723004540"
],
"article-number": "110692",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Metformin use before COVID-19 vaccination and the risks of COVID-19 incidence, medical utilization, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yen",
"given": "Fu-Shun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shiow-Ing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Shih-Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng-Chung Wei",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice",
"container-title-short": "Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"diabetesresearchclinicalpractice.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-06T15:03:35Z",
"timestamp": 1683385415000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-06T15:03:50Z",
"timestamp": 1683385430000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-07T04:24:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683433440124
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0168822723004540?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0168822723004540?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "110692",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm4915",
"article-title": "The changing epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Koelle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1116",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0005",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0010",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard, https://covid19.who.int/table; 2022 [accessed 16 December 2022]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abn1900",
"article-title": "Stopping pandemics before they start: lessons learned from SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1133",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0015",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.026",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccination in patients with diabetes mellitus: current concepts, uncertainties and challenges",
"author": "Pal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0020",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2",
"article-title": "Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Bornstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "546",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0025",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra2206573",
"article-title": "Covid-19 vaccines - immunity, variants, boosters",
"author": "Barouch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1011",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0030",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-00435-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0035",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-S004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0040",
"unstructured": "American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, et al. 4. Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45:S46–59. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc22-S004."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14547",
"article-title": "Does poor glycaemic control affect the immunogenicity of the COVID-19 vaccination in patients with type 2 diabetes: the CAVEAT study",
"author": "Marfella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0045",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05284-4",
"article-title": "Antibody response to multiple antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes: an observational cohort study",
"author": "Lampasona",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2548",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0050",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab055",
"article-title": "Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 develop and persist in subjects with diabetes and COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Dispinseri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1472",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0055",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3132/dvdr.2008.027",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0060",
"unstructured": "Scarpello JH, Howlett HC. Metformin therapy and clinical uses. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2008;5:157–67. https://doi: 10.3132/dvdr.2008.027."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0065",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173934",
"article-title": "Metformin turns 62 in pharmacotherapy: emergence of non-glycaemic effects and potential novel therapeutic applications",
"author": "Mbara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0070",
"volume": "898",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-07294-1",
"article-title": "Metformin use and the risk of bacterial pneumonia in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Yen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3270",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0075",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4",
"article-title": "Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0080",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0085",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.078",
"article-title": "Metformin improves in vivo and in vitro B cell function in individuals with obesity and type-2 diabetes",
"author": "Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2694",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0090",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101752",
"article-title": "Metformin use before influenza vaccination may lower the risks of influenza and related complications",
"author": "Yen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1752",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0095",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in COVID-19 survivors among non-vaccinated population: a retrospective cohort study from the TriNetX US collaborative networks",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0100",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0105",
"unstructured": "Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2603–15. https://doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034577"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3009892",
"article-title": "mTOR inhibition improves immune function in the elderly",
"author": "Mannick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0110",
"year": "20146268179"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28278",
"article-title": "Metformin use and the risks of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Yen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28278",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0115",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metop.2021.100137",
"article-title": "A review on protective roles and potential mechanisms of metformin in diabetic patients diagnosed with COVID-19",
"author": "Kifle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Metabol Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0120",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0125",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00320-6",
"article-title": "Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: a mathematical modelling study",
"author": "Watson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1293",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0130",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0135",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "599",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0140",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Mast cells contribute to coronavirus-induced inflammation: new anti-inflammatory strategy",
"author": "Kritas",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "J Biol Regul Homeost Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110692_b0145",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168822723004540"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Metformin use before COVID-19 vaccination and the risks of COVID-19 incidence, medical utilization, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
