Safety and Efficacy of Pemivibart, a Long-Acting Monoclonal Antibody, for Prevention of Symptomatic COVID-19: Interim Results From a Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial (CANOPY)
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaf265, CANOPY, NCT06039449, Nov 2024 (preprint)
Phase 3 trial of 306 immunocompromised adults and 484 non-immunocompromised adults showing pre-exposure prophylaxis with pemivibart was generally well-tolerated and provided protection against symptomatic COVID-19 through 6 months in immunocompromised individuals and 12 months in non-immunocompromised individuals.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research shows reduced efficacy against KP.3.1.1, KP.1.1, LB.1, KP.3.3, and XEC variants1-4.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments5.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
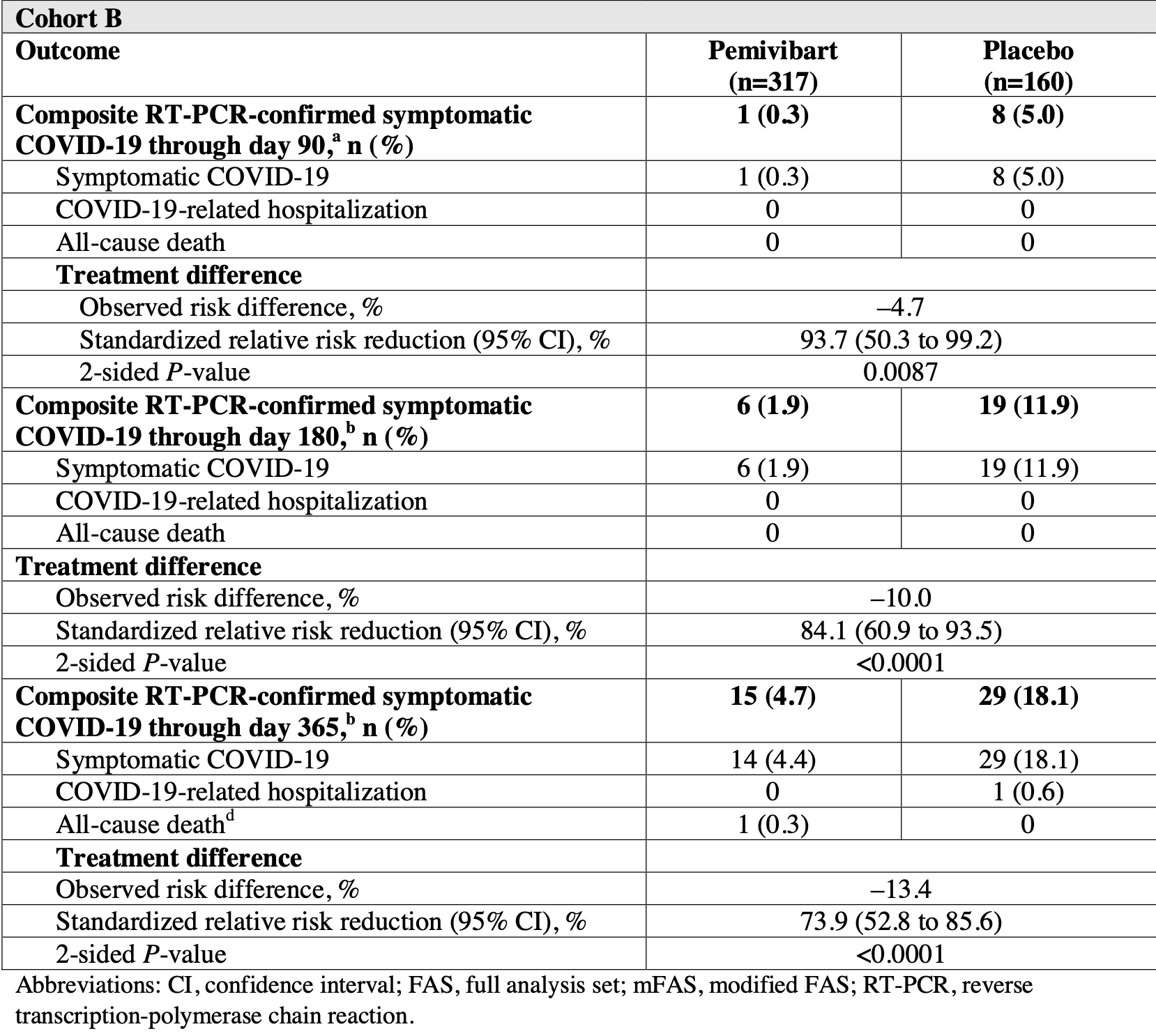
risk of death, 150.5% higher, RR 2.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 317 (0.3%), control 0 of 160 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 365.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 74.9% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.34, treatment 0 of 317 (0.0%), control 1 of 160 (0.6%), NNT 160, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 365.
|
|
case, hospitalization, death, 73.9% lower, RR 0.26, p < 0.001, treatment 15 of 317 (4.7%), control 29 of 160 (18.1%), NNT 7.5, day 365.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 75.6% lower, RR 0.24, p < 0.001, treatment 14 of 317 (4.4%), control 29 of 160 (18.1%), NNT 7.3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xie et al., Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250.
2.
Wang et al., Activity of Research-Grade Pemivibart against Recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 Sublineages, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2410203.
3.
Yao et al., Neutralizing Activity and Viral Escape of Pemivibart by SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.11.08.622746.
Wolfe et al., 13 Nov 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 59.0, 17 authors, study period November 2023 - December 2023, trial NCT06039449 (history) (CANOPY).
Contact: aholmes@invivyd.com, phawn@invivyd.com.
Safety and Efficacy of Pemivibart, a Long-Acting Monoclonal Antibody, for Prevention of Symptomatic COVID-19: Interim Results From the CANOPY Clinical Trial
doi:10.1101/2024.11.11.24317127
Key points: Pre-exposure prophylactic administration of 2 doses of pemivibart approximately 90 days apart was generally well-tolerated and provided protection against symptomatic COVID-19 through 6 months in individuals with immunocompromise and 12 months in individuals without immunocompromise, respectively.
Author contributions M.P., A.H., Y.L., I.Y., E.C., and K.N. contributed to study design. M.P., A.H., Y.L., I.Y., D.G., K.N., E.C., and A.P. were involved in protocol development. J.C. was a principal investigator. M.P., A.H., K.M., and N.B. were responsible for medical monitoring. All authors contributed to data interpretation and were involved in drafting and critically revising the manuscript, and all authors approved the final version and are accountable for the accuracy and integrity of the manuscript. All authors had full access to the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication. Y. L., D.G., and K.N. verified the data.
Potential conflicts of interest. Investigative sites and institutions were compensated by Invivyd, Inc. for all participant visits, including enrollment/baseline and follow-up. K.M., A.H., N.B., D.G., K.T., K.N., E.C., C.K., A.P., I.Y., M.W., P.H., P.S., Y.L., and M.P. were employees of Invivyd, Inc., at the time the study was conducted and may hold stock or shares in Invivyd, Inc.
Data availability As this trial is ongoing, data are not publicly available. Participants may have >1 immunocompromising condition or medication or risk factor for COVID-19 progression. c Taking high-dose corticosteroids (≥20 mg of prednisone or equivalent per day for at least 2 weeks), B-cell-depleting agents (within the past year), alkylating agents, antimetabolites, transplant-related immunosuppressive drugs, TNF blockers,..
References
Chary, Barbuto, Izadmehr, Tarsillo, Fleischer et al., COVID-19 therapeutics: use, mechanism of action, and toxicity (vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and immunotherapeutics), J Med Toxicol
Clinicaltrials, Gov, A study to investigate the prevention of COVID-19 withVYD222 in adults with immune compromise and in participants aged 12 years or older who are at risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2
Cohen, Nirula, Mulligan, Effect of Bamlanivimab vs Placebo on Incidence of COVID-19 Among Residents and Staff of Skilled Nursing and Assisted Living Facilities: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama
Corti, Purcell, Snell, Veesler, Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, Cell
Decuir, Payne, Self, Interim effectiveness of updated 2023-2024 (monovalent XBB.1.5) COVID-19 vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalization among immunocompetent adults aged ≥18 years -VISION and IVY Networks, September 2023-January 2024, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Dewolf, Laracy, Perales, Kamboj, Van Den Brink et al., SARS-CoV-2 in immunocompromised individuals, Immunity
Dougan, Azizad, Chen, Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19, medRxiv
Evans, Dube, Lu, Impact of COVID-19 on immunocompromised populations during the Omicron era: insights from the observational population-based INFORM study, Lancet Reg Health Eur
Ge, Durham, Meyer, Xie, Thomas, Covariate-adjusted difference in proportions from clinical trials using logistic regression and weighted risk differences, Drug Inf J
Group, Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): a randomised controlled trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Invivyd, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization of pemgarda (pemivibart)
Invivyd, Invivyd provides detailed virology data and analysis of SARS-CoV-2 structural biology predicting anticipated neutralization activity for PEMGARDA™ (pemivibart)
Ison, Popejoy, Evgeniev, Efficacy and safety of adintrevimab (ADG20) for the treatment of high-risk ambulatory patients with mild or moderate coronavirus disease 2019: results from a phase 2/3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (STAMP) conducted during Delta predominance and early emergence of Omicron, Open Forum Infect Dis
Ison, Weinstein, Dobryanska, Prevention of COVID-19 following a single intramuscular administration of adintrevimab: results from a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (EVADE), Open Forum Infect Dis
Ketkar, Willey, Pollack, Assessing the risk and costs of COVID-19 in immunocompromised populations in a large United States commercial insurance health plan: the EPOCH-US Study, Curr Med Res Opin
Kim, Garg, 'halloran, Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and inhospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the US Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), Clin Infect Dis
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimabcilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Link-Gelles, Rowley, Desilva, Interim effectiveness of updated 2023-2024 (monovalent XBB.1.5) COVID-19 vaccines against COVID-19-associated hospitalization among adults aged ≥18 years with immunocompromising conditions -VISION Network, September 2023-February 2024, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Mahoney, Gupta, Li, Preliminary safety results from a phase 1 first in human study of VYD222: an extended half-life monoclonal antibody (mAb) in development for COVID-19 prevention, ID Week
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature
Rappazzo, Tse, Kaku, Broad and potent activity against SARS-like viruses by an engineered human monoclonal antibody, Science
Razonable, Protecting the vulnerable: addressing the COVID-19 care needs of people with compromised immunity, Front Immunol
Rosas, Bräu, Waters, Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Sampson, Muñoz-Furlong, Campbell, Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report--Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Shoham, Batista, Amor, Vaccines and therapeutics for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19, EClinicalMedicine
Singson, Kirley, Pham, Factors associated with severe outcomes among immunocompromised adults hospitalized for COVID-19 -COVID-NET, 10 States, March 2020-February 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Wec, Wrapp, Herbert, Broad neutralization of SARS-related viruses by human monoclonal antibodies, Science
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaf265",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaf265",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We report an interim analysis of safety and efficacy of pemivibart in individuals with (cohort A) or without (cohort B) significant immunocompromise in the phase 3 CANOPY trial.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Eligible participants (≥18 years; negative for current SARS-CoV-2 infection) received 2 intravenous 4500-mg pemivibart infusions (cohort A) or were randomized 2:1 to receive blinded pemivibart or placebo (cohort B) 90 days apart. Safety was a primary endpoint for both cohorts. The primary immunobridging endpoint for cohort A has previously been reported. Composite incidence of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction-confirmed symptomatic COVID-19, COVID-19 hospitalization, and all-cause mortality was an exploratory endpoint.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In September-November 2023, 306 participants received pemivibart (cohort A); 317 received pemivibart and 162 placebo (cohort B). The most common study drug-related adverse events were infusion-related reactions (cohort A: 11/306 [3.6%]; cohort B: 7/317 [2.2%, pemivibart] and 0/162 [placebo]). Four of 623 (0.6%) participants who received pemivibart experienced anaphylactic reactions (2 serious). In cohort A, the composite COVID-19 incidence through month 6 was 11/298 (3.7%; 2 deaths). In cohort B, 6/317 (1.9%; no deaths) and 19/160 (11.9%; no deaths) pemivibart and placebo participants, respectively, met the endpoint through month 6 (84.1% standardized relative risk reduction [RRR; 95% CI, 60.9-93.5; nominal P&lt;.0001]), and 15/317 (4.7%; 1 death) and 29/160 (18.1%; no deaths) pemivibart and placebo participants, respectively, met the endpoint through month 12 (73.9% standardized RRR [95% CI, 52.8-85.6; nominal P&lt;.0001]). Twelve month protection was conferred with no additional dosing.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Pemivibart provided prophylactic efficacy against COVID-19 and was well-tolerated by most participants. Anaphylaxis was an important safety risk.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>NCT06039449</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5365-5030",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke University , Durham, North Carolina ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wolfe",
"given": "Cameron R",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jadestone Clinical Research , Silver Spring, Maryland ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Mahoney",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Holmes",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Betancourt",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Deepali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Tosh",
"given": "Kazima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Narayan",
"given": "Kristin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Campanaro",
"given": "Ed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Katz",
"given": "Chloe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Phelan",
"given": "Anne-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Yalcin",
"given": "Ilker",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Wingertzahn",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Hawn",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8664-3706",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schmidt",
"given": "Pete",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Invivyd, Inc. , Waltham, Massachusetts ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Popejoy",
"given": "Myra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-24T03:46:14Z",
"timestamp": 1748058374000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-24T03:46:15Z",
"timestamp": 1748058375000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-24T04:10:05Z",
"timestamp": 1748059805403,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1748044800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf265/63326958/ciaf265.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf265/63326958/ciaf265.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf265/8145246"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and Efficacy of Pemivibart, a Long-Acting Monoclonal Antibody, for Prevention of Symptomatic COVID-19: Interim Results From a Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial (CANOPY)",
"type": "journal-article"
}