Neutralizing Activity and Viral Escape of Pemivibart by SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.11.08.622746, Nov 2024
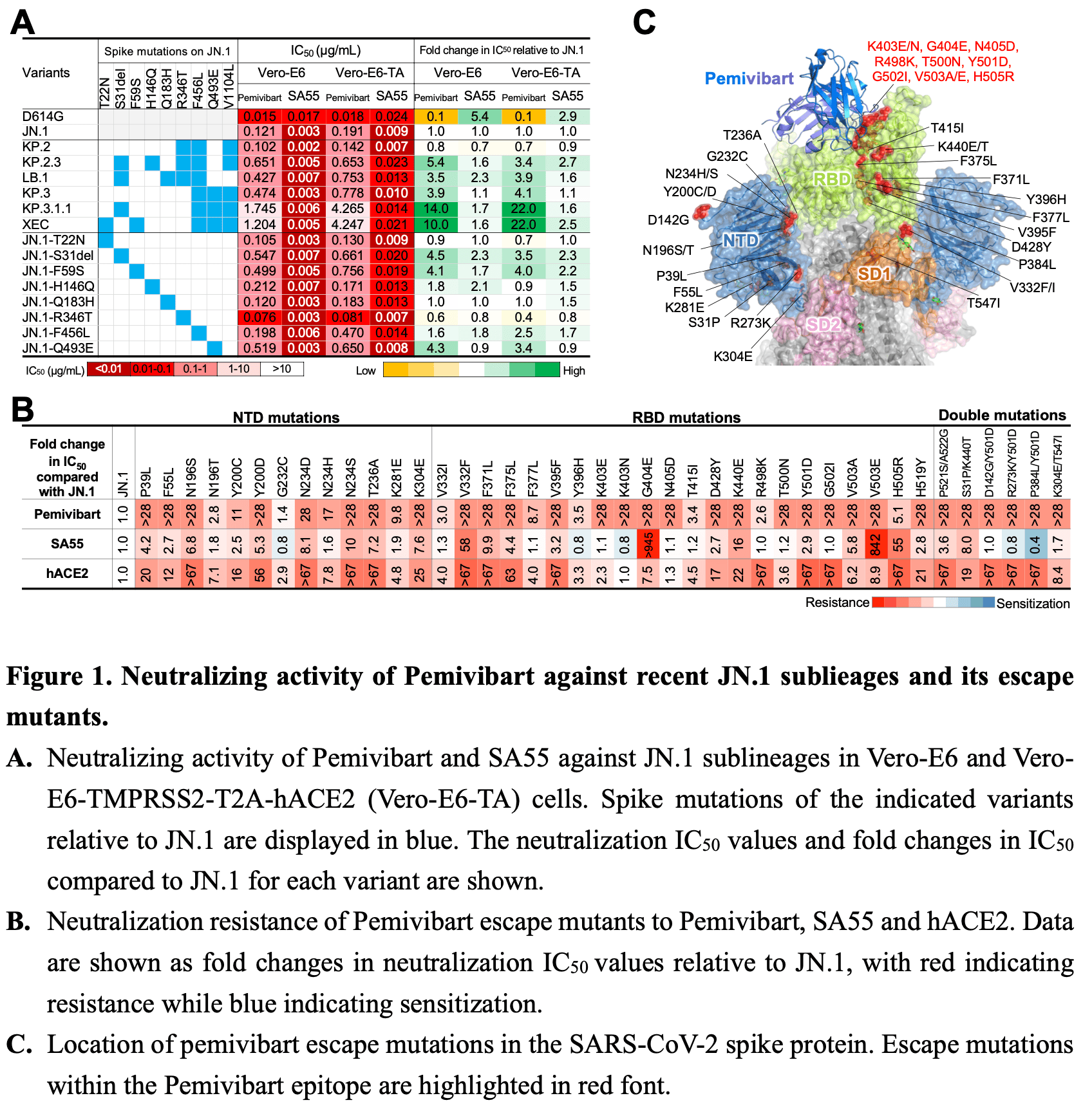
In vitro study showing that the monoclonal antibody pemivibart retains broad neutralizing activity against recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages but has reduced potency against KP.3.1.1 and XEC variants, with IC50 values ~22-fold higher than against JN.1. Authors found that S31 deletion, F59S, and Q493E mutations in the spike protein contributed to pemivibart resistance. Viral escape profiling revealed additional novel mutations across the N-terminal domain (NTD) and receptor-binding domain (RBD) that allow SARS-CoV-2 to evade pemivibart through multiple mechanisms beyond disrupting antibody binding.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research shows reduced efficacy against KP.3.1.1, KP.1.1, LB.1, KP.3.3, and XEC variants1-4.
1.
Xie et al., Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250.
2.
Wang et al., Activity of Research-Grade Pemivibart against Recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 Sublineages, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2410203.
3.
Yao et al., Neutralizing Activity and Viral Escape of Pemivibart by SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.11.08.622746.
4.
Planas et al., Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Variants KP.1.1, LB.1, and KP.3.3 From Approved Monoclonal Antibodies, Pathogens and Immunity, doi:10.20411/pai.v10i1.752.
Yao et al., 10 Nov 2024, preprint, 5 authors.
Contact: llh3411@whu.edu.cn, klan@whu.edu.cn, yg2521@cumc.columbia.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Neutralizing Activity and Viral Escape of Pemivibart by SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages
doi:10.1101/2024.11.08.622746
Pemivibart (Pemgarda™/VYD222) was granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 22, 2024, for COVID-19 pre-exposure prophylaxis in immunocompromised individuals. However, its efficacy and resistance against JN.1 sublineages have yet to be fully characterized. Here, we first assessed the neutralizing activity of Pemivibart against a panel of VSV-based pseudoviruses representing contemporary JN.1 sublineages, including XEC, the fastest-growing SARS-CoV-2 strain globally, in both Vero-E6 and Vero-E6-TMPRSS2-T2A-hACE2 (Vero-E6-TA) cells. We then engineered a replicationcompetent vesicular stomatitis virus with JN.1 spike (rVSVΔG-JN.1) to select for escape variants and performed structural analyses to comprehensively map Pemivibart's escape mutations. Our results demonstrated that Pemivibart exhibited comparable neutralization patterns in both cell lines and retains broad effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages tested. However, its potency was remarkably reduced against KP.3.1.1 and XEC, with IC50 values of approximately 4.2 µg/mL, about 22-fold higher than that for JN.1, as well as JN.1-derived Pemivibart-escape mutants harbouring low-frequency mutations across SARS-CoV-2 strains through mutiple antibody evasion mechanisms in Vero-E6-TA cells. Collectively, our findings underscored the importance of monitoring the clinical efficacy of Pemivibart as JN.1 sublineages continue to evolve. The escape profile of Pemivibart could provide valuable insights for forecasting and optimizing its effectiveness against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.
References
Bock, New Guidance Helps Clinicians Use Pemivibart to Protect Immunocompromised Patients From COVID-19, JAMA
Planas, Staropoli, Planchais, Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Variants KP.1.1, LB.1, and KP3.3 From Approved Monoclonal Antibodies, Pathog Immun
Wang, Guo, Ho, Ho, Pemivibart is less active against recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages, bioRxiv
Yisimayi, Song, Wang, Repeated Omicron exposures override ancestral SARS-CoV-2 immune imprinting, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.11.08.622746",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2024.11.08.622746",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Pemivibart (Pemgarda/VYD222) was granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 22, 2024, for COVID-19 pre-exposure prophylaxis in immunocompromised individuals. However, its efficacy and resistance against JN.1 sublineages have yet to be fully characterized. Here, we first assessed the neutralizing activity of Pemivibart against a panel of VSV-based pseudoviruses representing contemporary JN.1 sublineages, including XEC, the fastest-growing SARS-CoV-2 strain globally, in both Vero-E6 and Vero-E6-TMPRSS2-T2A-hACE2 (Vero-E6-TA) cells. We then engineered a replication-competent vesicular stomatitis virus with JN.1 spike (rVSVΔG-JN.1) to select for escape variants and performed structural analyses to comprehensively map Pemivibart's escape mutations. Our results demonstrated that Pemivibart exhibited comparable neutralization patterns in both cell lines and retains broad effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages tested. However, its potency was remarkably reduced against KP.3.1.1 and XEC, with IC50 values of approximately 4.2 μg/mL, about 22-fold higher than that for JN.1, as well as JN.1-derived Pemivibart-escape mutants harbouring low-frequency mutations across SARS-CoV-2 strains through mutiple antibody evasion mechanisms in Vero-E6-TA cells. Collectively, our findings underscored the importance of monitoring the clinical efficacy of Pemivibart as JN.1 sublineages continue to evolve. The escape profile of Pemivibart could provide valuable insights for forecasting and optimizing its effectiveness against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
10
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Tianjiao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Zhenghai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lan",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Yicheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Lihong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-11T03:05:17Z",
"timestamp": 1731294317000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-11T03:05:17Z",
"timestamp": 1731294317000
},
"group-title": "Microbiology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-11T03:40:10Z",
"timestamp": 1731296410173,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "bioRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
10
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1731196800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2024.11.08.622746",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
10
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2024.11.08.622746"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Neutralizing Activity and Viral Escape of Pemivibart by SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages",
"type": "posted-content"
}