Effectiveness of REGEN-COV combination monoclonal antibody infusion to reduce risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in pregnancy: A retrospective cohort study
et al., American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.017, Sep 2022
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
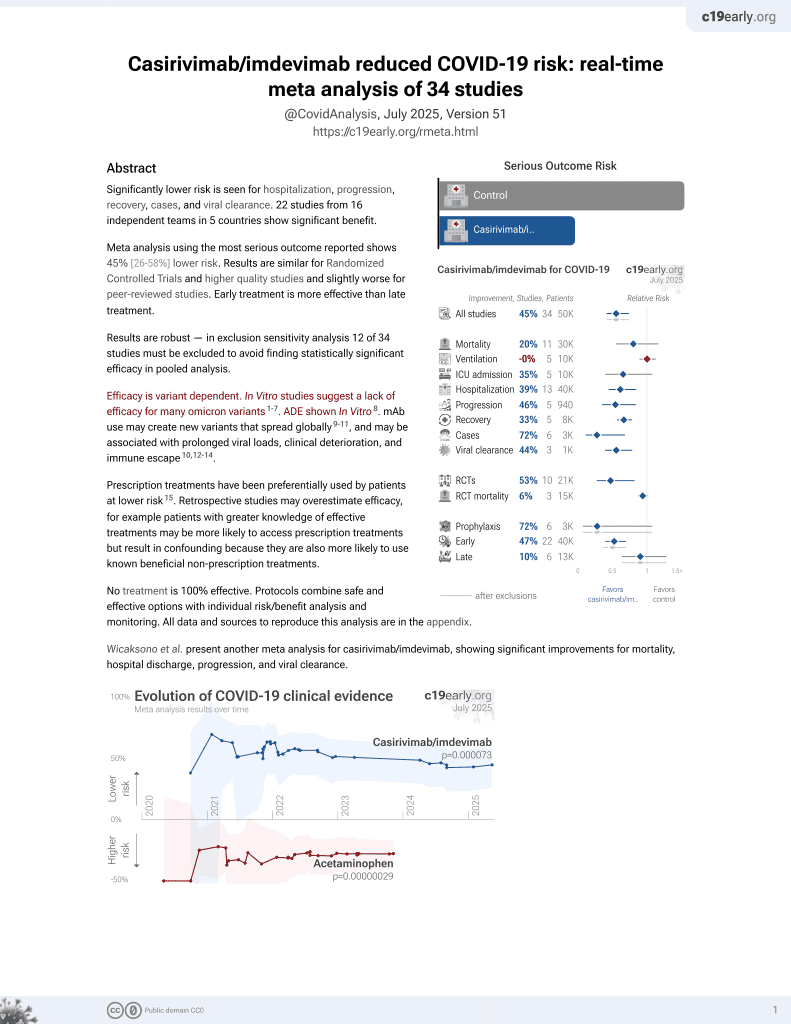
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
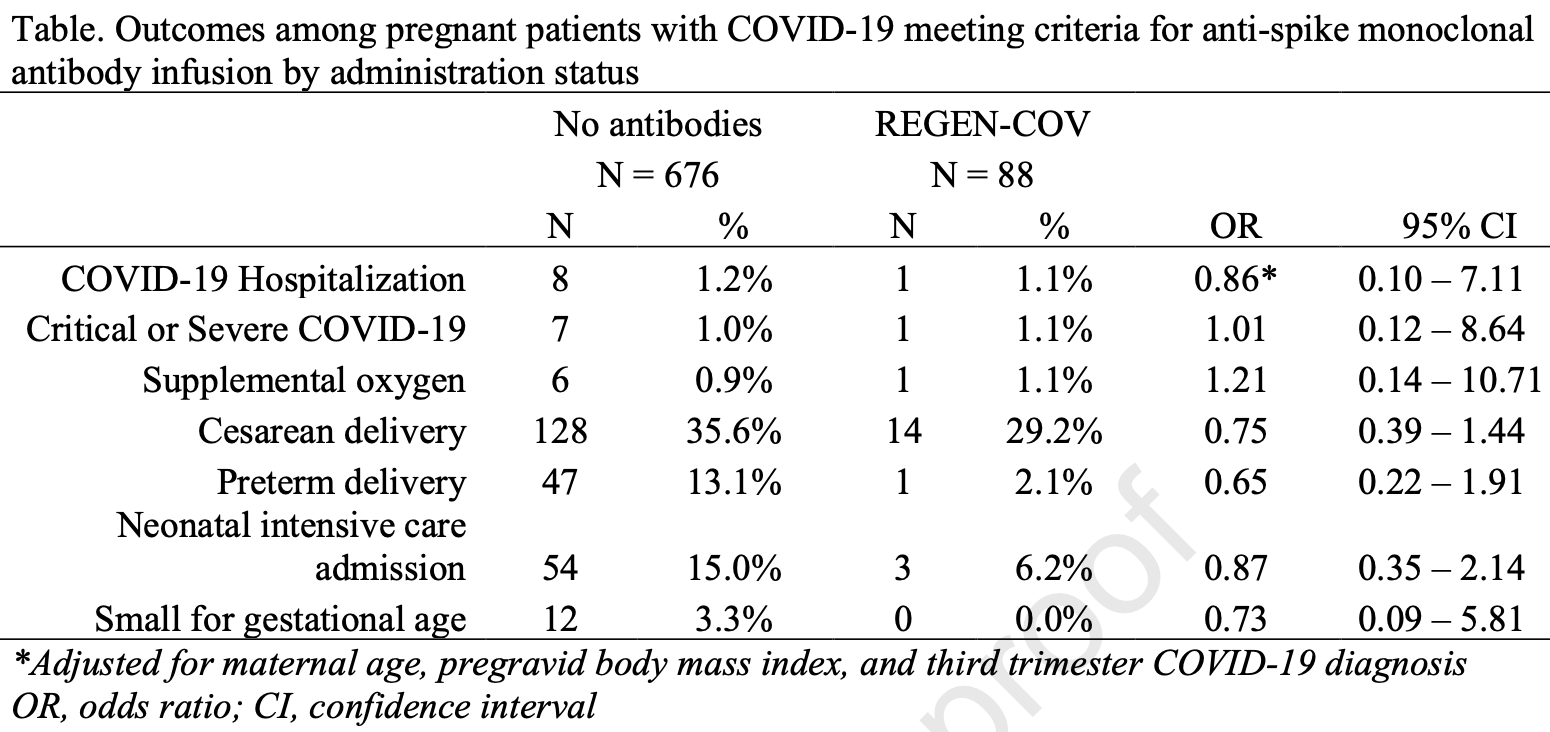
Retrospective 764 pregnant patients with COVID-19 in the USA, 88 treated with casirivimab/imdevimab, showing no significant difference in outcomes.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments8.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 20.8% higher, RR 1.21, p = 0.87, treatment 1 of 88 (1.1%), control 6 of 676 (0.9%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of severe case, 1.0% higher, RR 1.01, p = 0.99, treatment 1 of 88 (1.1%), control 7 of 676 (1.0%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 13.9% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.90, treatment 1 of 88 (1.1%), control 8 of 676 (1.2%), NNT 2125, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
6.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Williams et al., 12 Sep 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: frank.williams2@ochsner.org.
Effectiveness of REGEN-COV combination monoclonal antibody infusion to reduce the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in pregnancy: a retrospective cohort study
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.017
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
Halalau, Imam, Karabon, External validation of a clinical risk score to predict hospital admission and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2020.1828616
Jamieson, Rasmussen, An update on COVID-19 and pregnancy, Am J Obstet Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2021.08.054
Kalafat, Prasad, Birol, An internally validated prediction model for critical COVID-19 infection and intensive care unit admission in symptomatic pregnant women, Am J Obstet Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2021.09.024J
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.017",
"ISSN": [
"0002-9378"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.017",
"alternative-id": [
"S0002937822007414"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effectiveness of REGEN-COV combination monoclonal antibody infusion to reduce risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in pregnancy: A retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.017"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Frank B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "John A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elmayan",
"given": "Ardem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Jane K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mussarat",
"given": "Naiha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biggio",
"given": "Joseph R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology",
"container-title-short": "American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"ajog.org",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-12T05:41:25Z",
"timestamp": 1662961285000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-12T14:24:59Z",
"timestamp": 1662992699000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-12T14:50:04Z",
"timestamp": 1662994204650
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661990400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0002937822007414?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0002937822007414?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0002937822007414"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Obstetrics and Gynecology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of REGEN-COV combination monoclonal antibody infusion to reduce risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in pregnancy: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}