COVID-19 Mortality in Europe, by Latitude and Obesity Status: A Geo-Spatial Analysis in 40 Countries
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030471, Jan 2022
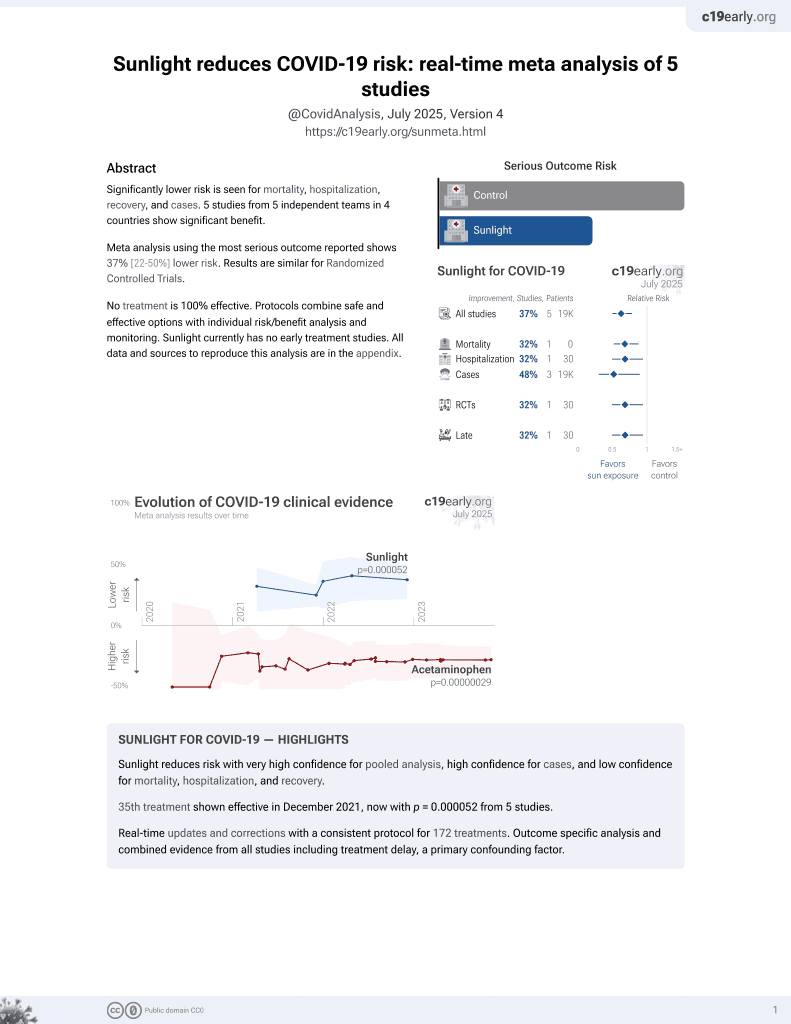
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
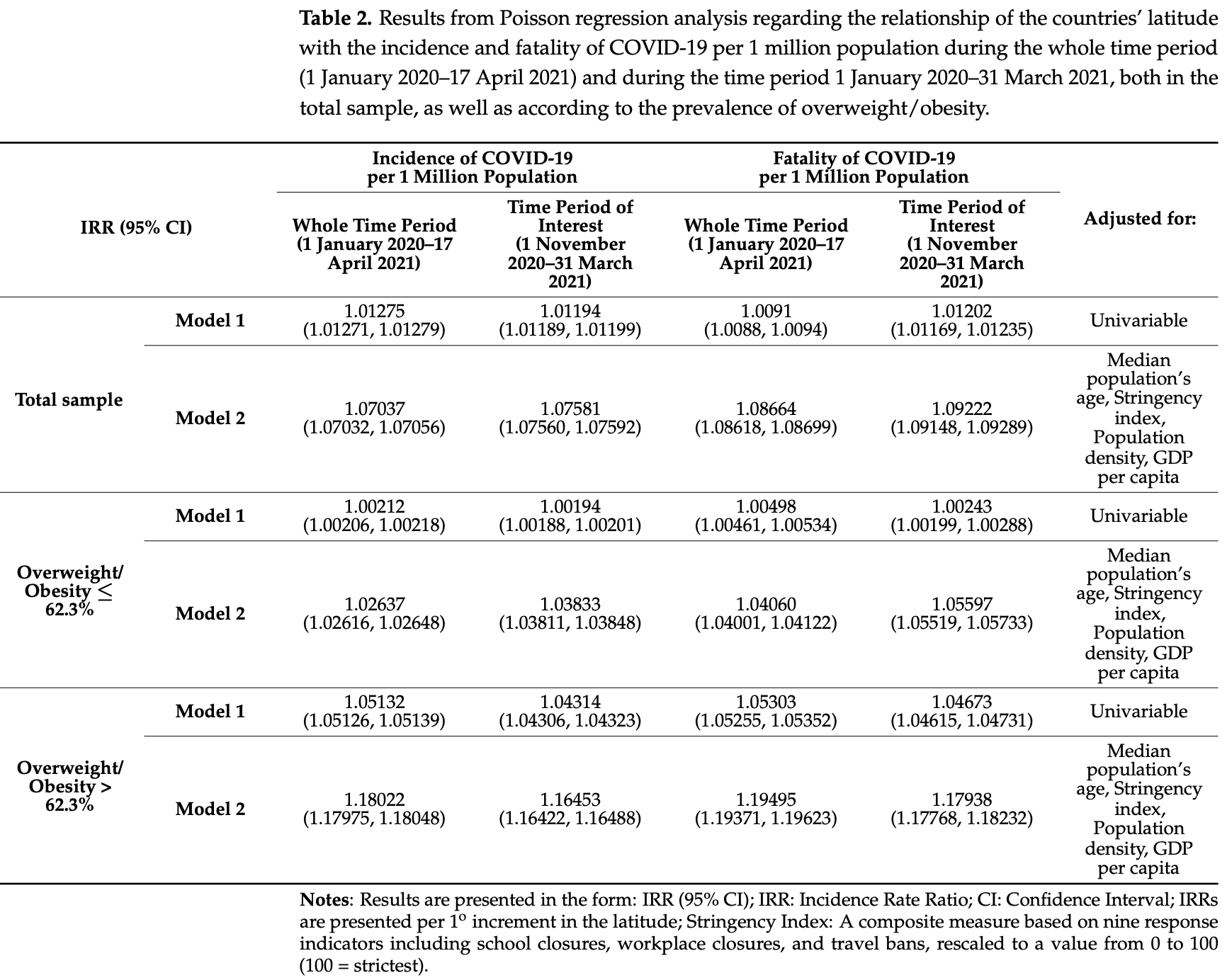
Ecological study of 40 European countries showing higher COVID-19 incidence and mortality associated with higher latitude (as a proxy for lower sunlight exposure and vitamin D synthesis). The association was stronger for countries with overweight/obesity prevalence above 62.3%.
Study covers sunlight and vitamin D.
Tyrovolas et al., 21 Jan 2022, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: dbpanag@hua.gr (corresponding author), stefanos.tyrovolas@polyu.edu.hk, ttsiam@hua.gr, angela.ym.leung@polyu.edu.hk, marianthi.morena@gmail.com, afaka@hua.gr, xalkias@hua.gr, sotirios.tsiodras@gmail.com.
COVID-19 Mortality in Europe, by Latitude and Obesity Status: A Geo-Spatial Analysis in 40 Countries
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030471
the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the current novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a public health emergency of international concern and later characterized it as a pandemic. New data show that excess body mass and vitamin D deficiency might be related to the disease severity and mortality. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether latitude, as a proxy of sunlight exposure and Vitamin D synthesis, and prevalent obesity among European populations, is related to COVID-19 spread and severity. European COVID-19 data (incidence and fatality), including information on the prevalence of obesity, social distancing, and others were obtained by the "Our World in Data" website on 17 April 2021. Adjusted analysis showed that higher COVID-19 incidence and fatality were pictured in countries being in higher latitude, both during the whole period, as well as, during the time period 1 November 2020-31 March 2021. Higher incidence and fatality of COVID-19 were observed where the prevalence of overweight/obesity was higher during the whole time period, whereas during the time period 1 November 2020-31 March 2021, only COVID-19 incidence was higher but not a fatality. The present results provide insights for targeted interventions and preventive strategies against COVID-19.
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The current paper is part of the approved study by Parc Sanitari's Sant Joan de Deu, Ethics Committee (PIC-67-20, Barcelona, Spain) and complies with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Akbar, Wibowo, Pranata, Setiabudiawan, Low Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated with Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.660420
Aranow, Vitamin D and the Immune System, J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res, doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006
Chen, Mei, Xie, Yuan, Ma et al., Low vitamin D levels do not aggravate COVID-19 risk or death, and vitamin D supplementation does not improve outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis and GRADE assessment of cohort studies and RCTs, Nutr. J, doi:10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y
Chowdhury, Alam, Rabbi, Rahman, Reza, Does higher Body Mass Index increase COVID-19 severity? A systematic review and meta-analysis, Obes. Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2021.100340
Dye, Cheng, Dagpunar, Williams, The scale and dynamics of COVID-19 epidemics across Europe, R. Soc. Open Sci, doi:10.1098/rsos.201726
Fernández, Giné-Vázquez, Liu, Yucel, Nai Ruscone et al., Are environmental pollution and biodiversity levels associated to the spread and mortality of COVID-19? A four-month global analysis, Environ. Pollut, doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116326
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001191
Hotamisligil, Inflammation and metabolic disorders, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature05485
Jin, Agarwala, Kundu, Harvey, Zhang et al., Individual and community-level risk for COVID-19 mortality in the United States, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01191-8
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus" or two related pandemics: Coronavirus disease and vitamin D deficiency, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114520001749
Kass, Duggal, Cingolani, Obesity could shift severe COVID-19 disease to younger ages, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31024-2
Liu, Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zhao et al., Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077
Mccarthy, O'donnell, Kelly, O'shea, Hogan, COVID-19 severity and obesity: Are MAIT cells a factor?, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00140-5
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Mendes, Hart, Lanham-New, Botelho, Exploring the Impact of Individual UVB Radiation Levels on Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Women Living in High Versus Low Latitudes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from the D-SOL Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123805
Muniyappa, Gubbi, COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020
O'shea, Hogan, Dysregulation of Natural Killer Cells in Obesity, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers11040573
O'sullivan, Laird, Kelly, Van Geffen, Van Weele et al., Ambient UVB Dose and Sun Enjoyment Are Important Predictors of Vitamin D Status in an Older Population, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.116.244079
Simonnet, Chetboun, Poissy, Raverdy, Noulette et al., High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22831
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Teshome, Adane, Girma, Mekonnen, The Impact of Vitamin D Level on COVID-19 Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559
Tian, Zhang, Hu, Jiang, Duan et al., Risk factors associated with mortality of COVID-19 in 3125 counties of the United States, Infect. Dis. Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00786-0
Tyrovolas, Giné-Vázquez, Fernández, Morena, Koyanagi et al., Estimating the COVID-19 spread through real-time population mobility patterns: Surveillance in Low-and Middle-income countries, J. Med. Internet Res, doi:10.2196/22999
Walrand, Autumn COVID-19 surge dates in Europe correlated to latitudes, not to temperature-humidity, pointing to vitamin D as contributing factor, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-81419-w
Walsh, Bowles, Evans, Vitamin D in obesity, Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes, doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000371
Woolf, Chapman, Lee, COVID-19 as the Leading Cause of Death in the United States, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24865
Woolf, Chapman, Sabo, Weinberger, Hill et al., Excess Deaths From COVID-19 and Other Causes, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.19545
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Yuan, Yang et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030471",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14030471",
"abstract": "<jats:p>On 30 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the current novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a public health emergency of international concern and later characterized it as a pandemic. New data show that excess body mass and vitamin D deficiency might be related to the disease severity and mortality. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether latitude, as a proxy of sunlight exposure and Vitamin D synthesis, and prevalent obesity among European populations, is related to COVID-19 spread and severity. European COVID-19 data (incidence and fatality), including information on the prevalence of obesity, social distancing, and others were obtained by the “Our World in Data” website on 17 April 2021. Adjusted analysis showed that higher COVID-19 incidence and fatality were pictured in countries being in higher latitude, both during the whole period, as well as, during the time period 1 November 2020–31 March 2021. Higher incidence and fatality of COVID-19 were observed where the prevalence of overweight/obesity was higher during the whole time period, whereas during the time period 1 November 2020–31 March 2021, only COVID-19 incidence was higher but not a fatality. The present results provide insights for targeted interventions and preventive strategies against COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14030471"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4797-7743",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Health Science and Education, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
},
{
"name": "Research, Innovation and Teaching Unit, Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, 08830 Sant Boi de Llobregat, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Salud Mental, CIBERSAM, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "School of Nursing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon GH506, Hong Kong"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tyrovolas",
"given": "Stefanos",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4625-460X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Health Science and Education, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsiampalis",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Environment, Geography, and Applied Economics, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Morena",
"given": "Marianthi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9836-1925",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Nursing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon GH506, Hong Kong"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Angela Y. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7552-0359",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Environment, Geography, and Applied Economics, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Faka",
"given": "Antigoni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Environment, Geography, and Applied Economics, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"family": "Chalkias",
"given": "Christos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0463-4321",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, 11527 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsiodras",
"given": "Sotirios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8583-153X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Health Science and Education, Harokopio University, 17671 Athens, Greece"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Panagiotakos",
"given": "Dimosthenes",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-23T20:34:40Z",
"timestamp": 1642970080000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-24T19:46:32Z",
"timestamp": 1721850392000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-28T05:16:24Z",
"timestamp": 1722143784671
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642723200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/3/471/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "471",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2020, April 11). WHO Announces COVID-19 Outbreak a Pandemic. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/news/news/2020/3/who-announces-covid-19-outbreak-a-pandemic."
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "(2020, June 21). Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov)."
},
{
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "(2020, April 11). Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Reports. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports."
},
{
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "(2020, April 11). Coronavirus: Newspaper Round-Up after COVID-19 Epicentre Shifts to Europe|Euronews. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/2020/03/20/coronavirus-newspaper-round-up-after-covid-19-epicentre-shifts-to-europe."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"article-title": "First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States",
"author": "Holshue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/22999",
"article-title": "Estimating the COVID-19 spread through real-time population mobility patterns: Surveillance in Low- and Middle- income countries",
"author": "Tyrovolas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e22999",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Internet Res.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116326",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Fernández, D., Giné-Vázquez, I., Liu, I., Yucel, R., Nai Ruscone, M., Morena, M., García, V.G., Haro, J.M., Pan, W., and Tyrovolas, S. (2021). Are environmental pollution and biodiversity levels associated to the spread and mortality of COVID-19? A four-month global analysis. Environ. Pollut., 271."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.26.20131144",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Dye, C., Cheng, R.C.H., Dagpunar, J.S., and Williams, B.G. (2020). The scale and dynamics of COVID-19 epidemics across Europe. R. Soc. Open Sci., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00786-0",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with mortality of COVID-19 in 3125 counties of the United States",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Poverty",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-01191-8",
"article-title": "Individual and community-level risk for COVID-19 mortality in the United States",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31024-2",
"article-title": "Obesity could shift severe COVID-19 disease to younger ages",
"author": "Kass",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1544",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Muniyappa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E736",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2021.100340",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Chowdhury, A.I., Alam, M.R., Rabbi, M.F., Rahman, T., and Reza, S. (2021). Does higher Body Mass Index increase COVID-19 severity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Med., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00140-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19 severity and obesity: Are MAIT cells a factor?",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the Immune System",
"author": "Aranow",
"first-page": "881",
"journal-title": "J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Teshome, A., Adane, A., Girma, B., and Mekonnen, Z.A. (2021). The Impact of Vitamin D Level on COVID-19 Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077",
"article-title": "Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Meltzer, D.O., Best, T.J., Zhang, H., Vokes, T., Arora, V., and Solway, J. (2020). Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results. JAMA Netw. Open, 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22831",
"article-title": "High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation",
"author": "Simonnet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Obesity",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "(2021, May 21). Our World in Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature05485",
"article-title": "Inflammation and metabolic disorders",
"author": "Hotamisligil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "860",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "444",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers11040573",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "O’Shea, D., and Hogan, A.E. (2019). Dysregulation of Natural Killer Cells in Obesity. Cancers, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114520001749",
"article-title": "“Scientific Strabismus” or two related pandemics: Coronavirus disease and vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Kara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "736",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.116.244079",
"article-title": "Ambient UVB Dose and Sun Enjoyment Are Important Predictors of Vitamin D Status in an Older Population",
"author": "Laird",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "858",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123805",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Mendes, M.M., Hart, K.H., Lanham-New, S.A., and Botelho, P.B. (2020). Exploring the Impact of Individual UVB Radiation Levels on Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Women Living in High Versus Low Latitudes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from the D-SOL Study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-021-00744-y",
"article-title": "Low vitamin D levels do not aggravate COVID-19 risk or death, and vitamin D supplementation does not improve outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis and GRADE assessment of cohort studies and RCTs",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Nutr. J.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.754539",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Akbar, M.R., Wibowo, A., Pranata, R., and Setiabudiawan, B. (2021). Low Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated with Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-81419-w",
"article-title": "Autumn COVID-19 surge dates in Europe correlated to latitudes, not to temperature-humidity, pointing to vitamin D as contributing factor",
"author": "Walrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1981",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0235.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Grant, W.B., Lahore, H., McDonnell, S.L., Baggerly, C.A., French, C.B., Aliano, J.L., and Bhattoa, H.P. (2020). Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the anti-viral state",
"author": "Beard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Eurostat (2016). European Health Interview Survey—Almost 1 Adult in 6 in the EU Is Considered Obese—Share of Obesity Increases with Age and Decreases with Education Level, Eurostat. Eurostat News Release, 20 October 2016."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MED.0000000000000371",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in obesity",
"author": "Walsh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.19545",
"article-title": "Excess Deaths From COVID-19 and Other Causes, March–July 2020",
"author": "Woolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24865",
"article-title": "COVID-19 as the Leading Cause of Death in the United States",
"author": "Woolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/3/471"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 Mortality in Europe, by Latitude and Obesity Status: A Geo-Spatial Analysis in 40 Countries",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}