Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces ACE-2 activity in COVID-19 patients and Calu- 3 cells
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1, Nov 2024
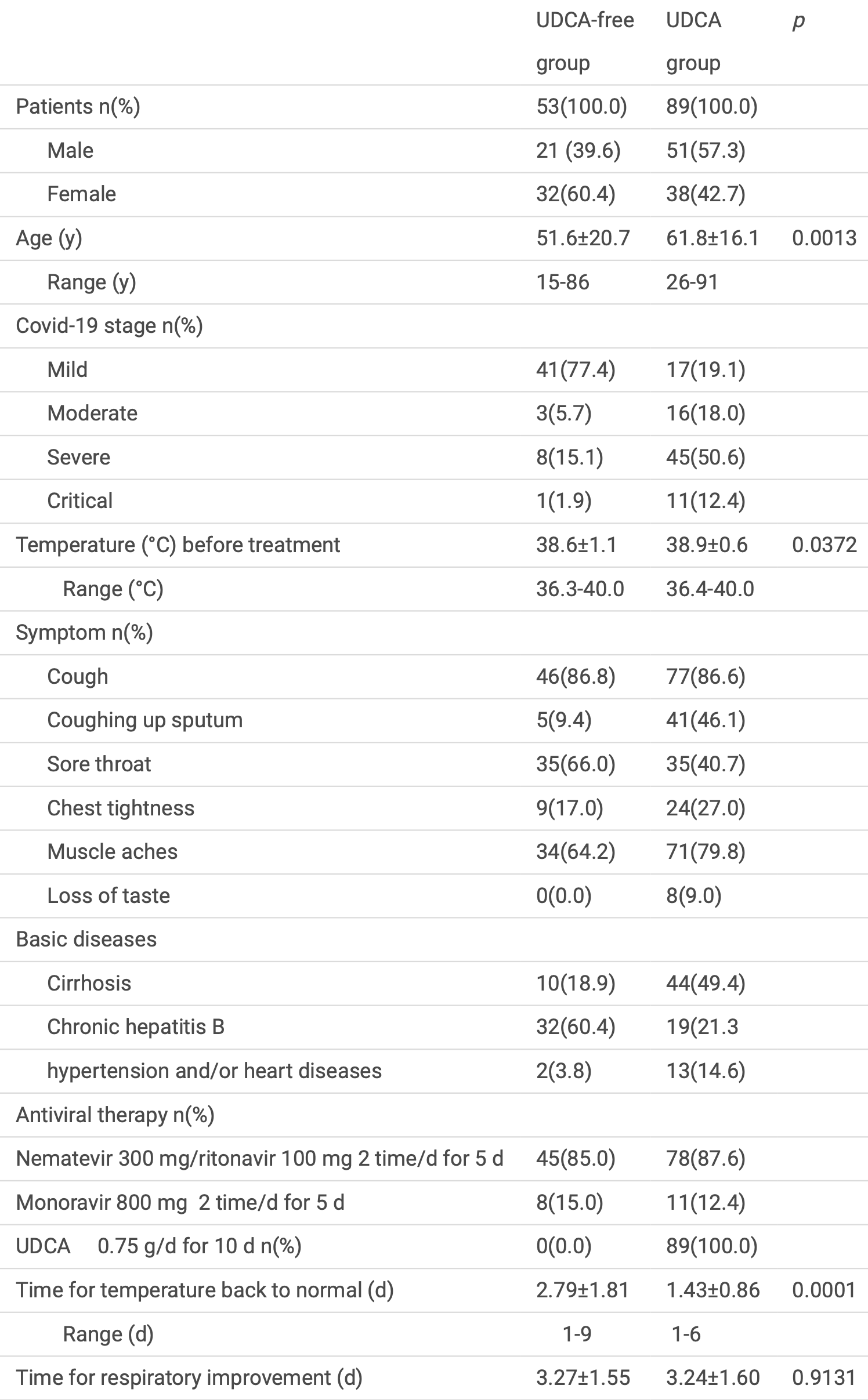
Retrospective 142 COVID-19 patients (89 treated with UDCA, 53 UDCA-free) showing reduced ACE2 levels in serum, plasma, and blood cells, a shorter time to fever resolution, and no significant difference in respiratory improvement with UDCA treatment. The groups are not comparable with 12% vs. 2% critical and 51% vs. 15% severe patients respectively, and no adjusted results are provided. Authors also include an in vitro study showing UDCA reduced ACE2 expression and blocked pseudovirus infection in Calu-3 lung cells.
4 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid for COVID-19:
Ursodeoxycholic acid reduced ACE2 expression and blocked pseudovirus
infection in Calu-3 cells2, protected against Omicron infection in hamsters by
downregulating ACE2 expression via FXR inhibition, leading to reduced
viral load in the upper respiratory tract and prevention of weight
loss4, may reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection by interfering with
spike protein binding to ACE2 receptors on B cells1, and inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating
ACE2 expression via FXR inhibition in multiple tissues (respiratory,
biliary, and intestinal), reduced viral transmission in a hamster model,
and decreased viral replication in human organ perfusion models3.
1.
Park et al., Ursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates B Cell Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Interfering Its Binding to ACE2, Biomolecules & Therapeutics, doi:10.4062/biomolther.2025.149.
2.
Tong et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces ACE-2 activity in COVID-19 patients and Calu- 3 cells, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1.
Tong et al., 20 Nov 2024, retrospective, China, preprint, 7 authors, study period January 2023 - May 2023.
Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces ACE-2 activity in COVID-19 patients and Calu- 3 cells
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1
Background Reportedly, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) decreases Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) activities by inhibiting FXR to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection. -19 patients (n=142, male=72, female=70) from January to May 2023 were divided into UDCA-free (n=53) and UDCA (n=89) groups and treated withnirmatasvir/ritonavir or molnupiravir for 5 days. Patients in the UDCA group were additionally given UDCA for 10 days. ACE2 was detected and clinical outcomes were assessed. Calu-3 cells were infected with the Covid-19 Spike (XBB.1.5) pseudovirusand incubated with or without UDCA.
Methods
Covid
Results On day 0 (before treatment), 3, 6, 9 (after anti-viral drug and/or UDCA treatment), ACE2 in serum and plasma in UDCA-free group was ~41 ng/ml (p=0.9962), and ~68ng/ml (p=0.6179); in UDCA group from 40.1±9.6 to 20.8±5.8 ng/ml (p=0.0000), and 68.8±15.6 to 30.2±7.7 ng/ml ( p=0.0000). In UDCA group, ACE2 mRNA in blood cells was from ~100% to 58.5±13.2% (p=0.000) on day 6 and time for fever return to normal shorter (p=0.0001). In Calu-3 cells, UDCA reduced ACE2 protein and mRNA, and blocked Covid-19 pseudovirus infection.
Conclusion UDCA reduces ACE2 activity in Covid-19 patients and Calu-3 cells, blocks Covid-19 pseudovirus infection in Calu-3 cells and improves the clinical outcomes. UDCA may be a potential drug for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The patient part of the study was conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Huzhou Central Hospital (Ethics No: 2023001-02). All human subjects and consent provided written informed consent.
Clinical Trial Clinical trial number: not applicable.
Consent for publication The Author con rms: that the work described has not been published before; that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that its publication has been approved by all co-authors; that its publication has been approved by the responsible authorities at Huzhou Central Hospital where the work is carried out. The author warrants that his/her contribution is original and that he/she has full power to make this consent. The author signs for and accepts responsibility for releasing this material on behalf of any and all co-authors. The copyright transfer covers the exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article. Author Contributions Z.T.: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing original draft, and project administration. J.Z.: methodology, formal analysis, resources. Q.W.: methodology, sample collection, formal analysis, investigation. F.Q.: validation, formal analysis, investigation. L. Z.: experiment operation, data analysis. W.W.: supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. K.Q.: methodology, formal analysis, supervision, project..
References
Brevini, Maes, Webb, John, Fuchs et al., FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2, Nature
Colapietro, Angelotti, Masetti, Shiffer, Pugliese et al., Ursodeoxycholic Acid Does Not Improve COVID-19 Outcome in Hospitalized Patients, Viruses
Corpechot, Verdoux, Frank-Soltysiak, Vallée, Grimaldi, Exploring the impact of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy on COVID-19 in a real-word setting, J Med Virol
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Li, Zhu, Cui, Lin, Li, Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Panahi, Gorabi, Talaei, Beiraghdar, Akbarzadeh et al., An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19, Virol J
Pozzi, Masselli, Gobbi, Mirandola, Taborda-Barata et al., Hydrogen Sul de Inhibits TMPRSS2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells: Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Biomedicines
Smyth, Truong, Rao, Lin, Foulke-Abel et al., Farnesoid X receptor enhances epithelial ACE2 expression and inhibits virally induced IL-6 secretion: implications for intestinal symptoms of SARS-CoV-2, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol
Talebian, Pl, Gruber, Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates the expression of proin ammatory cytokines in periodontal cells, J Periodontol
Thuy, Bao, Moon, Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells, Biomed Pharmacother
Wakabayashi, Nakayama, Yamamoto, Kitazawa, High D-glucose levels induce ACE2 expression via GLUT1 in human airway epithelial cell line Calu, BMC Mol Cell Bio
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1",
"abstract": "<title>Abstract</title>\n <p><bold>Background</bold>\nReportedly, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) decreases Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) activities by inhibiting FXR to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection.\n<bold>Methods</bold>\nCovid-19 patients (n=142, male=72, female=70) from January to May 2023 were divided into UDCA-free (n=53) and UDCA (n=89) groups and treated withnirmatasvir/ritonavir or molnupiravir for 5 days. Patients in the UDCA group were additionally given UDCA for 10 days. ACE2 was detected and clinical outcomes were assessed. Calu-3 cells were infected with the Covid-19 Spike (XBB.1.5) pseudovirusand incubated with or without UDCA.\n<bold>Results</bold>\nOn day 0 (before treatment), 3, 6, 9 (after anti-viral drug and/or UDCA treatment), ACE2 in serum and plasma in UDCA-free group was ~41 ng/ml (<italic>p</italic>=0.9962), and ~68ng/ml (<italic>p</italic>=0.6179); in UDCA group from 40.1±9.6 to 20.8±5.8 ng/ml (<italic>p</italic>=0.0000), and 68.8±15.6 to 30.2±7.7 ng/ml ( <italic>p</italic>=0.0000). In UDCA group, ACE2 mRNA in blood cells was from ~100% to 58.5±13.2% (<italic>p</italic>=0.000) on day 6 and time for fever return to normal shorter (<italic>p</italic>=0.0001). In Calu-3 cells, UDCA reduced ACE2 protein and mRNA, and blocked Covid-19 pseudovirus infection. \n<bold>Conclusion</bold>\nUDCA reduces ACE2 activity in Covid-19 patients and Calu-3 cells, blocks Covid-19 pseudovirus infection in Calu-3 cells and improves the clinical outcomes. UDCA may be a potential drug for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.</p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
23
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Zhaowei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Jianfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Qian",
"given": "Fuchu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Lili",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Weihong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Huzhou Central Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Qin",
"given": "Kefeng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-20T12:28:01Z",
"timestamp": 1732105681000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-20T12:28:14Z",
"timestamp": 1732105694000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-21T05:28:28Z",
"timestamp": 1732166908186,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1732060800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-5317838/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-5317838/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-01973-9",
"article-title": "An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19",
"author": "Panahi Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Panahi Y, Gorabi AM, Talaei S, Beiraghdar F, Akbarzadeh A, Tarhriz V, et al. An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19. Virol J. 2023;20(1):23.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "WHO. COVID-19 dashboard. 2024-08-13. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/variants"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S. el al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020; 181(2): 271 – 80.e8.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"article-title": "FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2",
"author": "Brevini T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"issue": "7950",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Brevini T, Maes M, Webb GJ, John BV, Fuchs CD, Buescher G, et al. FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2. Nature. 2023;615(7950):134–42.",
"volume": "615",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00099.2023",
"article-title": "Farnesoid X receptor enhances epithelial ACE2 expression and inhibits virally induced IL-6 secretion: implications for intestinal symptoms of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Smyth JS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "G446",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Smyth JS, Truong JK, Rao A, Lin R, Foulke-Abel J, Adorini L, et al. Farnesoid X receptor enhances epithelial ACE2 expression and inhibits virally induced IL-6 secretion: implications for intestinal symptoms of SARS-CoV-2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023;325(5):G446–52.",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9091273",
"article-title": "Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits TMPRSS2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells: Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Pozzi G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1273",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Pozzi G, Masselli E, Gobbi G, Mirandola P, Taborda-Barata L, Ampollini L, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits TMPRSS2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells: Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biomedicines. 2021;9(9):1273.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2023.1178590",
"article-title": "Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease",
"author": "Li Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1178590",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Zhu N, Cui X, Lin Y, Li X. Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1178590.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15081738",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic Acid Does Not Improve COVID-19 Outcome in Hospitalized Patients",
"author": "Colapietro F",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1738",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Colapietro F, Angelotti G, Masetti C, Shiffer D, Pugliese N, De Nicola S, et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Does Not Improve COVID-19 Outcome in Hospitalized Patients. Viruses. 2023;15(8):1738.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29418",
"article-title": "Exploring the impact of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy on COVID-19 in a real-word setting",
"author": "Corpechot C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29418",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Corpechot C, Verdoux M, Frank-Soltysiak M, Duclos-Vallée JC, Grimaldi L. Exploring the impact of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy on COVID-19 in a real-word setting. J Med Virol. 2024;96(1):e29418.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JPER.19-0013",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in periodontal cells",
"author": "Talebian RPL",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1098",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Periodontol",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Talebian RPL, Gruber R. Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in periodontal cells. J Periodontol. 2020;91(8):1098–104.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12860-022-00427-4",
"article-title": "High D-glucose levels induce ACE2 expression via GLUT1 in human airway epithelial cell line Calu",
"author": "Wakabayashi Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Mol Cell Bio",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Wakabayashi Y, Nakayama S, Yamamoto A, Kitazawa T. High D-glucose levels induce ACE2 expression via GLUT1 in human airway epithelial cell line Calu. BMC Mol Cell Bio. 2022;23(1):29.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113021",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells",
"author": "Thuy PX",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113021",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Thuy PX, Bao TDD, Moon EY. Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;150:113021.",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-5317838/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces ACE-2 activity in COVID-19 patients and Calu- 3 cells",
"type": "posted-content"
}