Ursodeoxycholic acid may protect from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant by reducing angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2
et al., Pharmacology Research & Perspectives, doi:10.1002/prp2.1194, Apr 2024
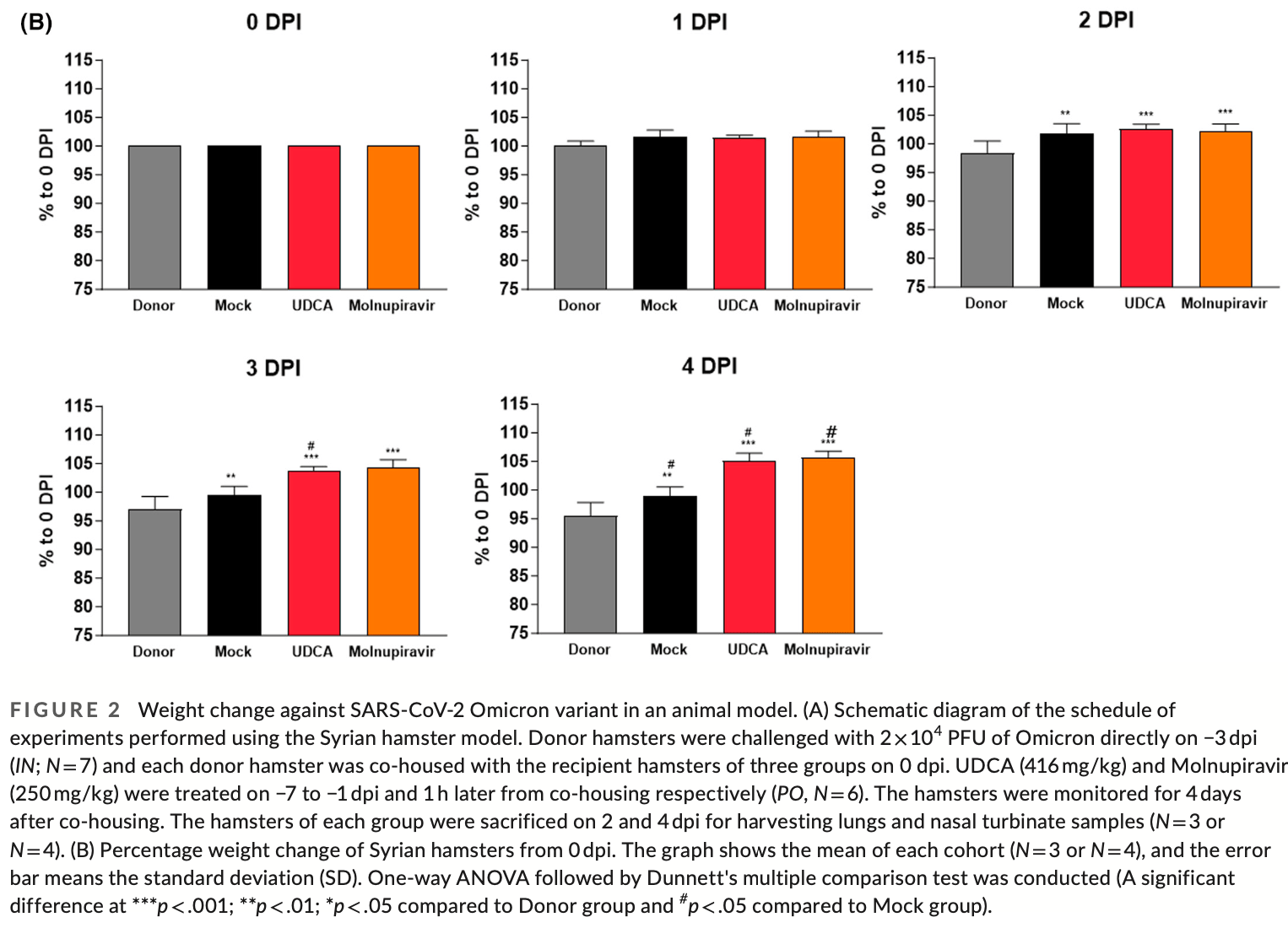
Syrian hamster study showing ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) may protect against SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant transmission and infection. Hamsters treated prophylactically with oral UDCA had significantly less weight loss compared to untreated animals after exposure to infected hamsters. UDCA treatment also reduced viral RNA levels of the E and RdRp genes in the nasal turbinates. Immunohistochemistry showed UDCA decreased ACE2 expression in the nasal cavity, which was confirmed by RT-PCR. The protective effects of UDCA were comparable to or better than post-exposure treatment with molnupiravir. Authors propose that UDCA downregulates ACE2 expression by antagonizing the farnesoid X receptor and impairs SARS-CoV-2's ability to enter cells.
4 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid for COVID-19:
Ursodeoxycholic acid reduced ACE2 expression and blocked pseudovirus
infection in Calu-3 cells2, protected against Omicron infection in hamsters by
downregulating ACE2 expression via FXR inhibition, leading to reduced
viral load in the upper respiratory tract and prevention of weight
loss4, may reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection by interfering with
spike protein binding to ACE2 receptors on B cells1, and inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating
ACE2 expression via FXR inhibition in multiple tissues (respiratory,
biliary, and intestinal), reduced viral transmission in a hamster model,
and decreased viral replication in human organ perfusion models3.
1.
Park et al., Ursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates B Cell Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Interfering Its Binding to ACE2, Biomolecules & Therapeutics, doi:10.4062/biomolther.2025.149.
2.
Tong et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces ACE-2 activity in COVID-19 patients and Calu- 3 cells, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-5317838/v1.
Lee et al., 4 Apr 2024, USA, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: minsookim@pusan.ac.kr.
Ursodeoxycholic acid may protect from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant by reducing angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2
Pharmacology Research & Perspectives, doi:10.1002/prp2.1194
The SARS-CoV-2 caused COVID-19 pandemic has posed a global health hazard. While some vaccines have been developed, protection against viral infection is not perfect because of the urgent approval process and the emergence of mutant SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we employed UDCA as an FXR antagonist to regulate ACE2 expression, which is one of the key pathways activated by SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant infection. UDCA is a well-known reagent of liver health supplements and the only clinically approved bile acid. In this paper, we investigated the protective efficacy of UDCA on Omicron variation, since it has previously been verified for protection against Delta variant. When co-housing with an Omicron variant-infected hamster group resulted in spontaneous airborne transmission, the UDCA pre-supplied group was protected from weight loss relative to the non-treated group at 4 days post-infection by more than 5%-10%. Furthermore, UDCA-treated groups had a 3-fold decrease in ACE2 expression in nasal cavities, as well as reduced viral expressing genes in the respiratory tract. Here, the data show that the UDCA serves an alternative option for preventive drug, providing SARS-CoV-2 protection against not only Delta but also Omicron variant. Our results of this study will help to propose drug-repositioning of UDCA from liver health supplement to preventive drug of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
compared to the mock group (Figure 3B ; Figure S2C ). Since ACE2 functions as a receptor, interactions with viruses or other stimuli may alter the ACE2 expression by ACE2 shedding or ACE2-expressing cell death during Omicron infection. 36 Besides, in Syrian hamsters, ACE2 expression is relatively low in the lung samples. 37 Confirming the reduction in expression brought on by UDCA may be challenging given the low level of ACE2 expression in the lungs of Syrian hamsters. We found that UDCA treatment lowered lung damage caused by viral infection on 4 dpi (Figure S1 ). Directly infected hamsters showed a relatively higher inflammation score of 2.00 ± 0.41 points at 2 dpi and 1.75 ± 1.19 points at 4 dpi. In the mock group, the score was similarly boosted to 0.67 ± 0.58 points on 4 dpi within the histological investigation on the lung lesions. At both time points, there were no pathological changes in UDCA and Molnupiravir groups. Similarly, whereas no plaque was found in UDCA-treated group, the mock group had significant viral replication on 4 dpi (Figure S3C ). The donor group had the highest viral RNA level and titer at 2 dpi, while the mock group had the highest at 4 dpi. Since 5 or 7 days after infection, the viral load may have been lowered by spontaneous recovery in the donor group. In contrast, viral replication might be started in the early stages of infection by airborne transmission in the mock group. Viral replication of the Omicron variant is higher in the..
References
Abadi, Jeshvaghani, Fathalipour, Dehghan, Sirjani et al., Therapeutic strategies in the fight against COVID-19: from bench to bedside, Iran J Med Sci, doi:/10.30476/IJMS.2021.92662.2396
Alexander, Christopoulos, Davenport, The concise guide to pharmacology 2019/20: G protein-coupled receptors, Br J Pharmacol, doi:/10.1111/bph.14748
Brevini, Maes, Webb, FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2, Nature, doi:/10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0
Carino, Moraca, Fiorillo, Hijacking SARS-CoV-2/ACE2 receptor interaction by natural and semi-synthetic steroidal agents acting on functional pockets on the receptor binding domain, Front Chem, doi:/10.3389/fchem.2020.572885
Claudel, Staels, Kuipers, The Farnesoid X receptor: a molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, doi:/10.1161/01.ATV.0000178994.21828.a7
Colombo, Battezzati, Podda, Bettinardi, Giunta, Ursodeoxycholic acid for liver disease associated with cystic fibrosis: a double-blind multicenter trial. The Italian Group for the Study of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Cystic Fibrosis, Hepatology, doi:/10.1002/hep.510230627
Crosignani, Battezzati, Setchell, Tauroursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. A dose-response study, Dig Dis Sci, doi:/10.1007/BF02213140
Dhawan, Saied, Mitra, Alhumaydhi, Emran et al., Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) and its sublineages: what do we know so far amid the emergence of recombinant variants of SARS-CoV-2?, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113522
Dolgin, Pan-coronavirus vaccine pipeline takes form, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:/10.1038/d41573-022-00074-6
Fan, Li, Zhang, Wan, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: recent progress and future perspectives, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:/10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x
Gattinger, Ohradanova-Repic, Valenta, Importance, applications and features of assays measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Int J Mol Sci, doi:/10.3390/ijms24065352
Gaziano, Giambartolomei, Pereira, Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repurposing opportunities for COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:/10.1038/s41591-021-01310-z
Ghoshal, Vasanth, Tejan, A guide to laboratory diagnosis of Corona Virus Disease-19 for the gastroenterologists, Indian J Gastroenterol, doi:/10.1007/s12664-020-01082-3
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:/10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Hanafi, Mohamed, Sheikh, Kadir, Othman, Overview of bile acids signaling and perspective on the signal of ursodeoxycholic acid, the most hydrophilic bile acid, in the heart, Biomolecules, doi:/10.3390/biom8040159
Harding, Sharman, Faccenda, The IUPHAR/BPS guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2018: updates and expansion to encompass the new guide to IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:/10.1093/nar/gkx1121
Ikegami, Matsuzaki, Ursodeoxycholic acid: mechanism of action and novel clinical applications, Hepatol Res, doi:/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00297.x
Imai, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Hatta, Syrian hamsters as a small animal model for SARS-CoV-2 infection and countermeasure development, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:/10.1073/pnas.2009799117
Islam, Dhawan, Nafady, Understanding the omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: mutational impacts, concerns, and the possible solutions, Ann Med Surg (Lond), doi:/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103737
Lee, Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea, Ewha Med J, doi:/10.12771/emj.2021.44.1.1
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, De Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:/10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y
Long, Carius, Chavez, Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency clinician: presentation and evaluation, Am J Emerg Med, doi:/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.01.028
Markov, Ghafari, Beer, The evolution of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:/10.1038/s41579-023-00878-2
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:/10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x
Niu, Li, Xu, Sun, Gan et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid protects against lung injury induced by fat embolism syndrome, J Cell Mol Med, doi:/10.1111/jcmm.15985
Park, Kim, Lee, Rapid emergence of the Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Korea, Ann Lab Med, doi:/10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.211
Sackmann, Pauletzki, Aydemir, Efficacy and safety of ursodeoxycholic acid for dissolution of gallstone fragments: comparison with the combination of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, Hepatology, doi:/10.1002/hep.1840140630
Shuai, Chan, Hu, Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron, Nature, doi:/10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5
Vaughan, Omicron emerges, New Sci, doi:/10.1016/S0262-4079(21)02140-0
Willett, Grove, Maclean, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron is an immune escape variant with an altered cell entry pathway, Nat Microbiol, doi:/10.1038/s41564-022-01241-6
Willett, Grove, Maclean, The hyper-transmissible SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant exhibits significant antigenic change, vaccine escape and a switch in cell entry mechanism, medRxiv, doi:/10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111
Zhao, Lu, Peng, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant shows less efficient replication and fusion activity when compared with Delta variant in TMPRSS2-expressed cells, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:/10.1080/22221751.2021.2023329
Zhou, Mohlenberg, Thakor, Sensitivity to vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and viral entry inhibitors and advances to counter the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:/10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Zhou, Yang, Wang, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:/10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prp2.1194",
"ISSN": [
"2052-1707",
"2052-1707"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prp2.1194",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>The SARS‐CoV‐2 caused COVID‐19 pandemic has posed a global health hazard. While some vaccines have been developed, protection against viral infection is not perfect because of the urgent approval process and the emergence of mutant SARS‐CoV‐2 variants. Here, we employed UDCA as an FXR antagonist to regulate ACE2 expression, which is one of the key pathways activated by SARS‐CoV‐2 Delta variant infection. UDCA is a well‐known reagent of liver health supplements and the only clinically approved bile acid. In this paper, we investigated the protective efficacy of UDCA on Omicron variation, since it has previously been verified for protection against Delta variant. When co‐housing with an Omicron variant‐infected hamster group resulted in spontaneous airborne transmission, the UDCA pre‐supplied group was protected from weight loss relative to the non‐treated group at 4 days post‐infection by more than 5%–10%. Furthermore, UDCA‐treated groups had a 3‐fold decrease in ACE2 expression in nasal cavities, as well as reduced viral expressing genes in the respiratory tract. Here, the data show that the UDCA serves an alternative option for preventive drug, providing SARS‐CoV‐2 protection against not only Delta but also Omicron variant. Our results of this study will help to propose drug‐repositioning of UDCA from liver health supplement to preventive drug of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/prp2.1194"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-01-05"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-03-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-04-04"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0001-2382-2854",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Technology Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
},
{
"name": "College of Pharmacy, Pusan National University Busan Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Kyungmin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0008-4507-7438",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Technology Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Na",
"given": "Yujeong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0009-3380-1828",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Drug Discovery Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Minjin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0007-4042-4720",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Technology Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Dongjin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0000-4360-6641",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Technology Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Jongseo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0006-4528-2816",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Technology Center Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Yongin‐si Gyeonggi‐do Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Gwanyoung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9426-5015",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Pharmacy, Pusan National University Busan Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Min‐Soo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmacology Research & Perspectives",
"container-title-short": "Pharmacology Res & Perspec",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T13:31:27Z",
"timestamp": 1712237487000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T13:31:32Z",
"timestamp": 1712237492000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T00:52:50Z",
"timestamp": 1712278370634
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 3,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/prp2.1194",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24065352",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.30476/IJMS.2021.92662.2396",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-023-00878-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0262-4079(21)02140-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113522",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103737",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/cmr.00014-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01310-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.ATV.0000178994.21828.a7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2020.572885",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom8040159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02213140",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.510230627",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.1840140630",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.15985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00297.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2009799117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkx1121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.14748",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41573-022-00074-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01241-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_12_28_1",
"unstructured": "WillettBJ GroveJ MacLeanOA et al.The hyper‐transmissible SARS‐CoV‐2 Omicron variant exhibits significant antigenic change vaccine escape and a switch in cell entry mechanism.medRxiv. 2022:2022.01.03.21268111. doi:10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.01.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.2023329",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12664-020-01082-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12771/emj.2021.44.1.1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.0c02624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.579330",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02012-06",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_39_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 38,
"references-count": 38,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/prp2.1194"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics",
"Neurology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid may protect from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant by reducing angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}