Intramuscular Versus Intravenous SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab for Treatment of COVID-19 (COMET-TAIL): A Randomized Non-inferiority Clinical Trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410, COMET-TAIL, NCT04913675, Mar 2023
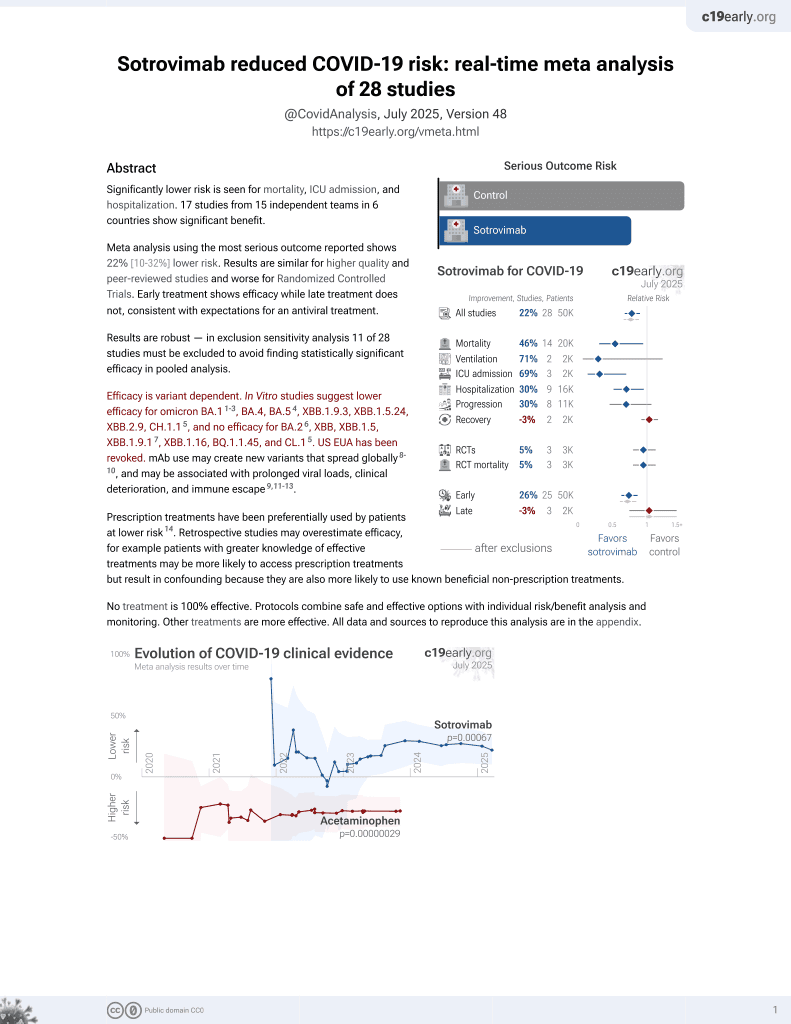
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
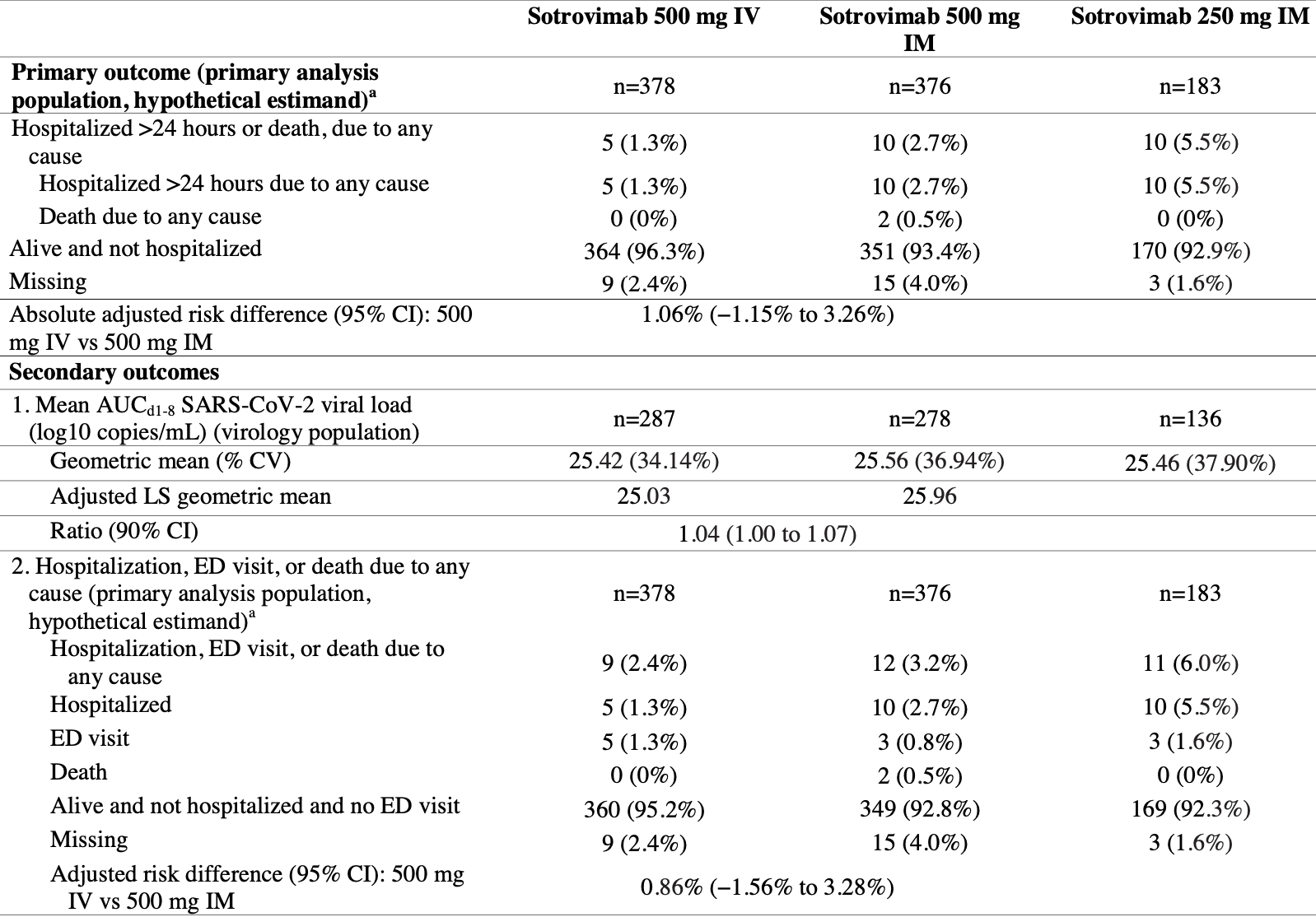
RCT 982 high risk outpatients in the USA reporting that intramuscular sotrovimab was non-inferior to intravenous administration. Death and hospitalization was more frequent with intramuscular administration, without statistical significance due to the small number of events.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments8.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 401.1% higher, RR 5.01, p = 0.25, treatment 2 of 376 (0.5%), control 0 of 378 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 101.1% higher, RR 2.01, p = 0.20, treatment 10 of 376 (2.7%), control 5 of 378 (1.3%).
|
|
risk of progression, 503.2% higher, RR 6.03, p = 0.07, treatment 6 of 376 (1.6%), control 1 of 378 (0.3%), progression to severe.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
6.
Zhou et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 Variant Evades Neutralization by Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.15.480166.
Shapiro et al., 24 Mar 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, preprint, 28 authors, study period August 2020 - March 2021, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo, trial NCT04913675 (history) (COMET-TAIL).
Contact: akohli@azliver.com, lgaffney@vir.bio.
Intramuscular Versus Intravenous SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab for Treatment of COVID-19 (COMET-TAIL): A Randomized Non-inferiority Clinical Trial
doi:10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410
Sotrovimab 500-mg IM was non-inferior to sotrovimab 500-mg IV for treatment of mild/moderate COVID-19 in high-risk patients, measured by all-cause hospitalization >24h or death through day 29, and was well-tolerated. Sotrovimab IM should provide easier outpatient access to COVID-19 treatment.
Funding The study was supported by Vir Biotechnology, Inc. in collaboration with GSK.
Author Contributions PSP, DKH, EA, WWY, EM, JES, DA, SC, and AP conceptualized and designed the study. All authors acquired, analyzed and/or interpreted the data. DI and DC conducted the statistical analyses. AK, LAG, and DI accessed and verified the data. All authors drafted the manuscript and critically reviewed and revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors had full access to all the data in the study, take responsibility for the accuracy of the analysis, and had authority over manuscript preparation and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures
References
Agostini, Schnell, Di Iulio, Resistance analysis in the COMET-TAIL study: participants with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 treated with intramuscular or intravenous sotrovimab, Open Forum Infect Dis
Atique, Ghafoor, Javed, Fatima, Yousaf et al., Correlation of viral load with the clinical and biochemical profiles of COVID-19 patients, Cureus
Cameroni, Bowen, Rosen, Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature
Cathcart, Havenar-Daughton, Lempp, The dual function monoclonal antibodies VIR-7831 and VIR-7832 demonstrate potent in vitro and in vivo activity against SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.09.434607
Chen, Nirula, Heller, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cheng, Reyes, Satram, Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 during SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron waves in the USA, Infect Dis Ther
Dougan, Azizad, Chen, Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Goldstein, Walensky, The challenges ahead with monoclonal antibodies: from authorization to access, JAMA
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early COVID-19 treatment with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Harman, Nash, Webster, Comparison of the risk of hospitalization among BA.1 and BA.2 COVID-19 cases treated with sotrovimab in the community in England. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.10.21.22281171
Martin-Blondel, Marcelin, Soulie, Sotrovimab to prevent severe COVID-19 in high-risk patients infected with Omicron BA.2, J Infect
Park, Pinto, Walls, Imprinted antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Science
Sager, El-Zailik, Passarell, Population pharmacokinetics and exposureresponse analysis of sotrovimab in the early treatment of COVID-19, CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol, doi:10.1002/psp4.12958
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Wu, Carr, Harvey, WHO's therapeutics and COVID-19 living guideline on mAbs needs to be reassessed, Lancet
Zheng, Green, Tazare, Comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab and molnupiravir for prevention of severe covid-19 outcomes in patients in the community: observational cohort study with the OpenSAFELY platform, BMJ
Zheng, Tazare, Nab, Comparative effectiveness of Paxlovid versus sotrovimab and molnupiravir for preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes in nonhospitalised patients: observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.20.23284849
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Convenient administration of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment in community settings is desirable. Sotrovimab is a pan-sarbecovirus dual-action monoclonal antibody formulated for intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) administration for early treatment of mild/moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This phase 3, randomized, multicenter, open-label study tested non-inferiority of IM to IV administration using a 3.5% absolute non-inferiority margin. From June to August 2021, patients aged ≥12 years with COVID-19, not hospitalized or receiving supplemental oxygen, and at high risk for progression were randomized 1:1:1 to a single 500-mg IV sotrovimab infusion or 500-mg or 250-mg IM sotrovimab injection. The primary composite endpoint was progression to all-cause hospitalization for >24 hours for acute management of illness or all-cause death through day 29.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Sotrovimab 500 mg IM was non-inferior to 500 mg IV: 10/376 (2.7%) participants in the sotrovimab 500-mg IM group versus 5/378 (1.3%) in the sotrovimab 500-mg IV group met the primary endpoint (absolute adjusted risk difference: 1.06% [95% confidence interval [CI]: −1.15%, 3.26%]). The CI upper limit was lower than the prespecified non-inferiority margin of 3.5%. 250-mg IM group enrollment was discontinued early because a greater proportion of hospitalizations was seen in that group versus the 500-mg groups. Serious adverse events occurred in <1% to 2% of participants across groups. Four participants experienced serious disease related events and died (500 mg IM: 2/393 [<1%]; 250 mg IM: 2/195 [1%]).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Sotrovimab 500-mg IM injection was well tolerated and non-inferior to IV administration. IM administration could expand outpatient treatment access for COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Registration</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"http://ClinicalTrials.gov\">ClinicalTrials.gov</jats:ext-link>Identifier:<jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04913675\">NCT04913675</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Key Points</jats:title><jats:p>Sotrovimab 500-mg IM was non-inferior to sotrovimab 500-mg IV for treatment of mild/moderate COVID-19 in high-risk patients, measured by all-cause hospitalization >24h or death through day 29, and was well-tolerated. Sotrovimab IM should provide easier outpatient access to COVID-19 treatment.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3106-1258",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Shapiro",
"given": "Adrienne E.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkis",
"given": "Elias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acloque",
"given": "Jude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Free",
"given": "Almena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonzalez-Rojas",
"given": "Yaneicy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "Rubaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juarez",
"given": "Erick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moya",
"given": "Jaynier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parikh",
"given": "Naval",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inman",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cebrik",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nader",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noormohamed",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Qianwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skingsley",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "Daren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peppercorn",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agostini",
"given": "Maria L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parra",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chow",
"given": "Sophia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mogalian",
"given": "Erik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pang",
"given": "Phillip S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hong",
"given": "David K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sager",
"given": "Jennifer E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeh",
"given": "Wendy W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "Elizabeth L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaffney",
"given": "Leah A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kohli",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T22:45:20Z",
"timestamp": 1679697920000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-27T14:25:25Z",
"timestamp": 1679927125000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-28T04:25:20Z",
"timestamp": 1679977520454
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with covid-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med@",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.2",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2108163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"article-title": "Early COVID-19 treatment with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.4",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.09.434607",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.7"
},
{
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.8",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. NIH OpenData Portal SARS-CoV-2 Variants & Therapeutics. Available at: https://opendata.ncats.nih.gov/variant/activity. Accessed 10 February 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2",
"article-title": "Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "664",
"issue": "7898",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.9",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"article-title": "An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.10",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-022-00755-0",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 during SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron waves in the USA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.11",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.10.21.22281171",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.12"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab and molnupiravir for prevention of severe covid-19 outcomes in patients in the community: observational cohort study with the OpenSAFELY platform",
"first-page": "071932",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.13",
"volume": "379:e",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.01.20.23284849",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.06.033",
"article-title": "Sotrovimab to prevent severe COVID-19 in high-risk patients infected with Omicron BA.2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e104",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.15",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.adc9127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.21872",
"article-title": "The challenges ahead with monoclonal antibodies: from authorization to access",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2151",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "JAMA. Dec 1",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.17",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.18",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. Available at: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed 13 January 2022."
},
{
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.19",
"unstructured": "Infectious Diseases Society of America. IDSA guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Overview of IDSA COVID-19 treatment guidelines, version 5.5.0 – October 27. 2021. Available at: https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/. Accessed 3 November 2021."
},
{
"article-title": "Correlation of viral load with the clinical and biochemical profiles of COVID-19 patients",
"first-page": "e16655",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"article-title": "Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.21",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/psp4.12958",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.22"
},
{
"article-title": "1150. Resistance analysis in the COMET-TAIL study: participants with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 treated with intramuscular or intravenous sotrovimab",
"first-page": "ofac492.",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.24",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 14 March 2023."
},
{
"article-title": "WHO’s therapeutics and COVID-19 living guideline on mAbs needs to be reassessed",
"first-page": "2194",
"issue": "10369",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2023032707250644000_2023.03.21.23287410v1.25",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2023.03.21.23287410"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Intramuscular Versus Intravenous SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab for Treatment of COVID-19 (COMET-TAIL): A Randomized Non-inferiority Clinical Trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}