A Retrospective Cohort Observational Study to Assess the Efficacy of Monoclonal Antibody in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients
et al., Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, doi:10.59556/japi.72.0646, Sep 2024
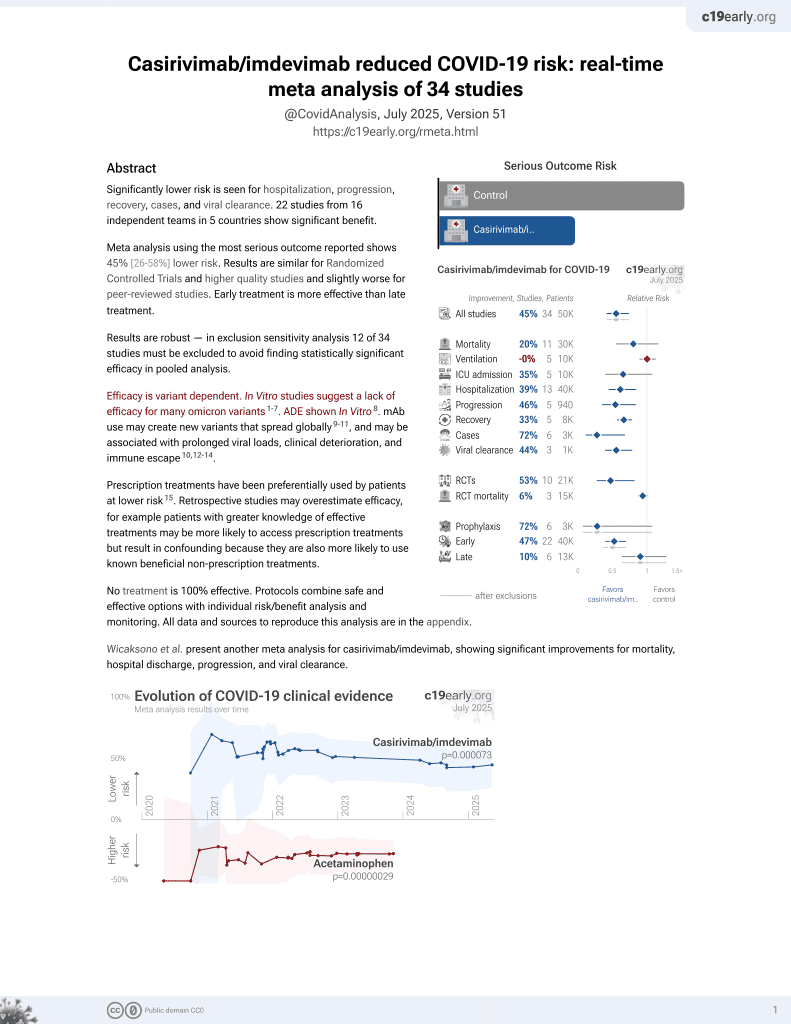
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
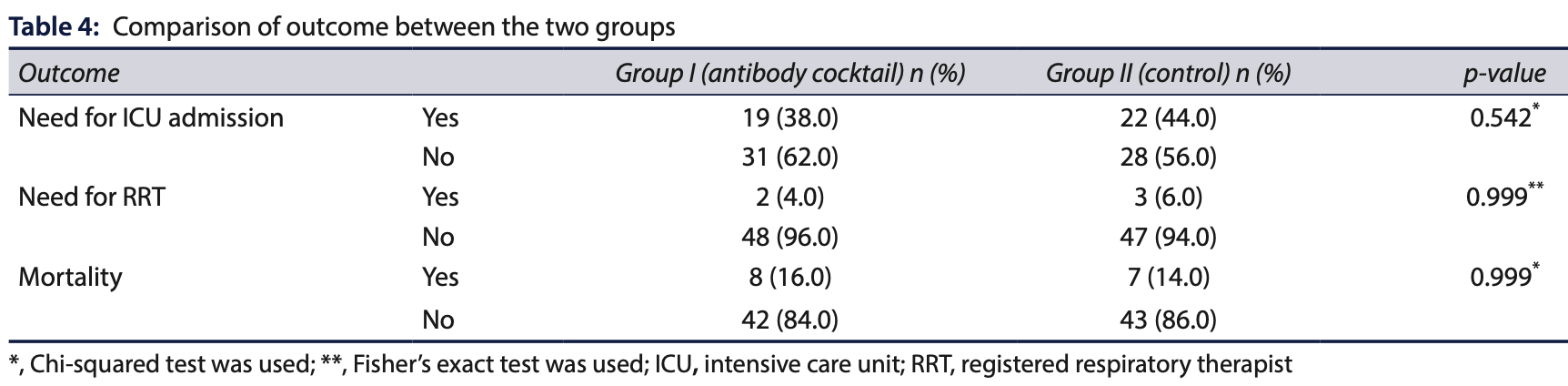
PSM retrospective 100 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in India showing no benefit with casirivimab/imdevimab treatment. There were no significant differences between groups in need for oxygen therapy, high-flow nasal cannula, noninvasive ventilation, invasive ventilation, ICU admission, hospital or ICU stay, or mortality.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
|
risk of death, 14.3% higher, RR 1.14, p = 1.00, treatment 8 of 50 (16.0%), control 7 of 50 (14.0%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 8 of 50 (16.0%), control 8 of 50 (16.0%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 13.6% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.68, treatment 19 of 50 (38.0%), control 22 of 50 (44.0%), NNT 17.
|
|
ICU time, 42.9% higher, relative time 1.43, p = 0.93, treatment 50, control 50.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 4.2% lower, RR 0.96, p = 1.00, treatment 23 of 50 (46.0%), control 24 of 50 (48.0%), NNT 50.
|
|
hospitalization time, 12.5% lower, relative time 0.88, p = 0.50, treatment 50, control 50.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Shah et al., 1 Sep 2024, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
A Retrospective Cohort Observational Study to Assess the Efficacy of Monoclonal Antibody in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients
doi:10.59556/japi.72.0646
Background: There are no studies examining the use of monoclonal antibodies in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients within the Indian population. Objectives: To determine the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Materials and methods: This retrospective cohort observational study was conducted from June 2021 to March 2022 in the Department of Critical Care Medicine at a tertiary care hospital in Pune, Maharashtra, India. The study included two cohorts of COVID-19 patients-a study group that received casirivimab/imdevimab infusion and a control group that did not receive monoclonal antibodies. The primary outcome measure was the assessment of the saturation of peripheral oxygen (SpO 2 ) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO 2 ) ratio. Secondary outcome measures included the need for the intensive care unit (ICU) admission and mechanical ventilation, duration of hospital stay, and inhospital mortality. Results: The mean SpO 2 on admission and discharge, as well as the mean SpO 2 /FiO 2 ratio, were comparable between the two groups. No significant differences were found in the requirements for oxygen therapy, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC), noninvasive ventilation (NIV), invasive ventilation, ICU admission, registered respiratory therapist (RRT) needs, or mortality rates between the two groups. Additionally, the median duration of hospital and ICU stay did not differ significantly between the groups. Conclusion: Casirivimab/imdevimab therapy did not show a beneficial effect on the outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
References
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19, Cell
Goyal, Choi, Pinheiro, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019-China, N Engl J Med
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med
Joy, Augustine, Karattuthodi, The impact of casirivimab-imdevimab antibody cocktail in patients amidst and post COVID 19 treatment: A retro-prospective comparative study in India, Clinic Epidemiol Glob Health
Lavezzo, Franchin, Ciavarella, Suppression of a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in the Italian municipality of Vo, Nature
Lee, Kim, Lee, Clinical course and molecular viral shedding among asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a community treatment center in the Republic of Korea, JAMA Intern Med
Ly-Cov555 Study, Group, Lundgren, Grund, A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Mutoh, Umemura, Ota, Effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapy for COVID-19 patients using a risk scoring system, J Infect Chemother
Oran, Topol, Prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: a narrative review, Ann Intern Med
Razonable, Pawlowski, Horo, Casirivimab-imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19, EClinicalMedicine
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19. In the New York City area, JAMA
Salama, Han, Yau, Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Stone, Frigault, Nj, Efficacy of Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Who, COVID-19: Symptoms and severity
Who, Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living guidelines
Wölfel, Corman, Guggemos, Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019, Nature