The Association between Lifestyle Risk Factors and COVID-19 Hospitalization in a Healthcare Institution
et al., American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, doi:10.1177/15598276221135541, Oct 2022
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
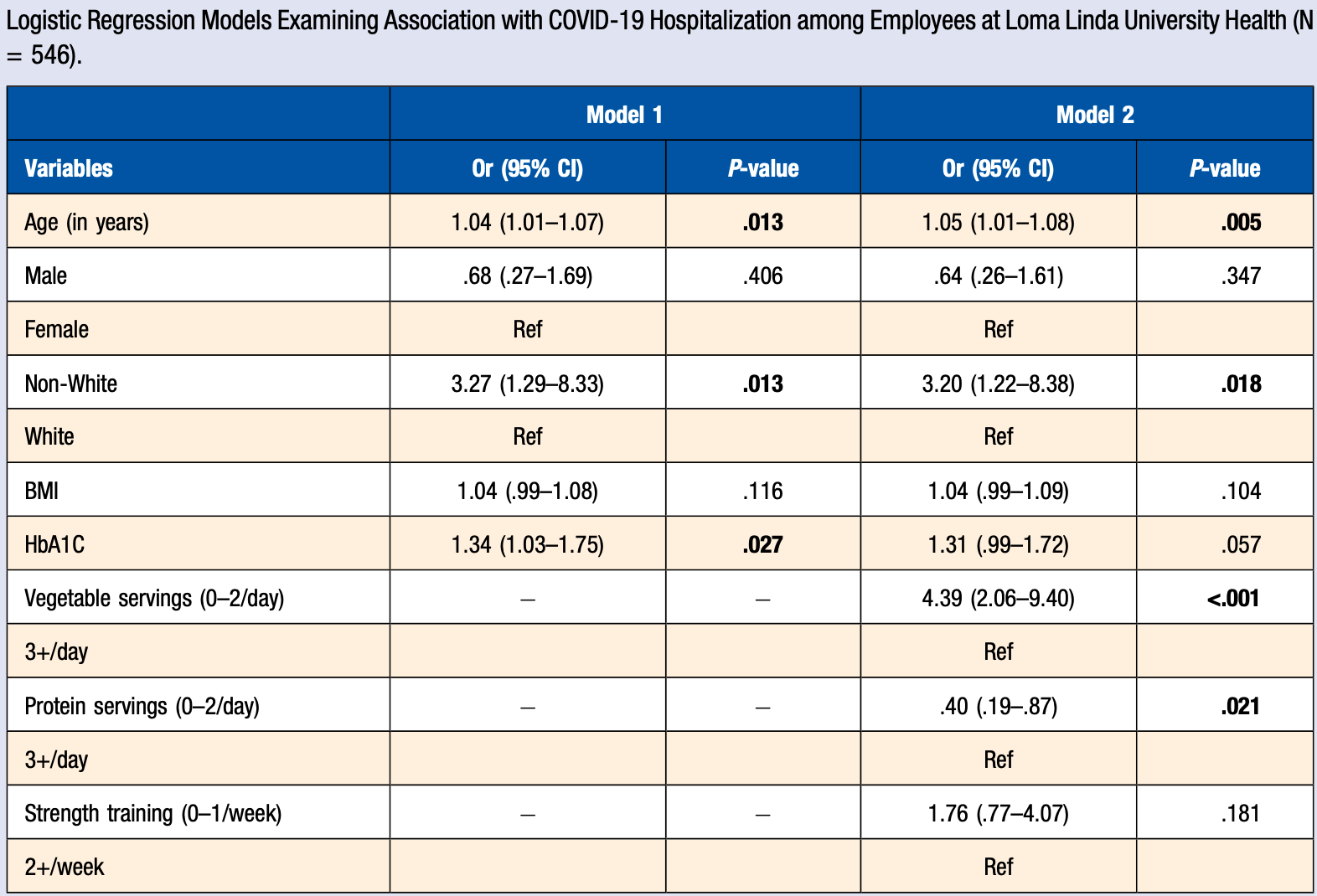
Retrospective 546 COVID+ patients in the USA, showing lower risk of hospitalization with higher frequency of strength training, without statistical significance.
Although the 41% lower hospitalization is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 33% lower hospitalization [25‑40%] from meta-analysis of the 20 hospitalization results to date.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers exercise and diet.
|
risk of hospitalization, 40.7% lower, RR 0.59, p = 0.18, high activity levels 9 of 241 (3.7%), low activity levels 29 of 305 (9.5%), adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor high activity levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, strength training 2+/week vs. <2, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Reis et al., 24 Oct 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, survey, 6 authors, study period December 2020 - February 2021.
Contact: hdossantos@llu.edu.
The Association between Lifestyle Risk Factors and COVID-19 Hospitalization in a Healthcare Institution
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, doi:10.1177/15598276221135541
COVID-19 is an acute infectious respiratory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, a subtype of the coronavirus. In addition to normal levels of biometric measures, a healthy lifestyle has been considered an indispensable element in preventing complications of coronavirus infection. Demographic characteristics are also critical in determining risk levels. Aim: Investigate potential significant associations between health behaviors, biometric screenings, demographics, and COVID-19 hospitalization in Loma Linda University Health employees. Methods: Participants are employees covered under the employersponsored health plan at
ORCID iDs Wenes Pereira Reis https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9983-2664 Jisoo Oh https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8905-7633
References
Acosta, Garg, Pham, Racial and ethnic disparities in rates of COVID-19-associated hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, and inhospital death in the United States from March 2020 to february 2021, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479
Alamgir, Shaikh, Recent Advances on the Ethnomedicinal Plants as Immunomodulatory Agents, Research Signpost
Azemati, Rajaram, Jaceldo-Siegl, Animal-protein intake is associated with insulin resistance in Adventist Health Study 2 (AHS-2) calibration substudy participants: a cross sectional analysis, Curr Dev Nutr
Baud, Qi, Nielsen-Saines, Musso, Pomar et al., Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30195-X
Bonyek-Silva, Machado, Cerqueira-Silva, LTB4-Driven inflammation and increased expression of ALOX5/ ACE2 during severe COVID-19 in individuals with diabetes, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db20-1260
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Dulebohn, Napoli, Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19)
Da Silveira, Da, Fagundes, Bizuti, Starck et al., Physical exercise as a tool to help the immune system against COVID-19: an integrative review of the current literature, Clin Exp Med, doi:10.1007/s10238-020-00650-3
Diabetes, Standards of medical care in diabetes-2014, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc14-S014
Elder, Sharma, Gulati, Michos, Identification of female-specific risk enhancers throughout the lifespan of women to improve cardiovascular disease prevention, Am J Prev Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpc.2020.100028
Erdem, Lucey, Healthcare worker infections and deaths due to COVID-19: a survey from 37 nations and a call for WHO to post national data on their website, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.064
González, Fuentes, Márquez, Physical inactivity, sedentary behavior and chronic diseases, Korean J Fam Med, doi:10.4082/kjfm.2017.38.3.111
Guasch-Ferré, Willett, The Mediterranean diet and health: A comprehensive overview, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13333
Haddad, Vegetarian diet and risk of cardiovascular disease
Hamer, Kivimäki, Gale, Batty, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: A community-based cohort study of 387, 109 adults in UK, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5
Iannelli, Favre, Frey, Obesity and COVID-19: ACE 2, the missing tile, Obes Surg, doi:10.1007/s11695-020-04734-7
Kim, Rebholz, Hegde, Plant-based diets, pescatarian diets and COVID-19 severity: A populationbased case-control study in six countries, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272
Lai, Wang, Ko, Society of Taiwan Long-term Care Infection Prevention and Control. COVID-19 in long-term care facilities: an upcoming threat that cannot be ignored, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Ley, Sun, Willett, Associations between red meat intake and biomarkers of inflammation and glucose metabolism in women, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.075663
Mattioli, Sciomer, Maffei, Gallina, Lifestyle and stress management in women during COVID-19 pandemic: impact on cardiovascular risk burden, Am J Lifestyle Med, doi:10.1177/1559827620981014
Narula, Yusuf, Chong, Plasma ACE2 and risk of death or cardiometabolic diseases: A casecohort analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31964-4
Nguyen, Drew, Joshi, Risk of COVID-19 Among Frontline Healthcare Workers and the General Community: A Prospective Cohort Study, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, doi:10.1101/2020.04.29.20084111
Nieman, Wentz, The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system, J Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009
Racine, Shah, Moore, Kenerly, Owens et al., Profound racial disparities in COVID-19 associated hospitalizations in rural southwest Georgia
Rodriguez, Solomon, De Lemos, Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes for patients hospitalized with COVID-19: findings from the American heart association's COVID-19 cardiovascular disease registry, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.052278
Rothan, Byrareddy, The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
Sattar, Mcinnes, Mcmurray, Obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19 infection: Multiple potential mechanisms, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047659
Scheffer, Latini, Exerciseinduced immune system response: Anti-inflammatory status on peripheral and central organs, Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Basis Dis, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165823
Simpson, Katsanis, The immunological case for staying active during the COVID-19 pandemic, American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.041
Sze, Pan, Nevill, Ethnicity and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100630
Tiruneh, Tesema, Azanaw, Angaw, The effect of age on the incidence of COVID-19 complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Syst Rev, doi:10.1186/s13643-021-01636-2
Vizheh, Qorbani, Arzaghi, Muhidin, Javanmard et al., The mental health of healthcare workers in the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review, J Diabetes Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s40200-020-00643-9
Yang, Hu, Zhu, Obesity aggravates COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26237
Zhi, The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China, Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi, doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/15598276221135541",
"ISSN": [
"1559-8276",
"1559-8284"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/15598276221135541",
"abstract": "<jats:p> COVID-19 is an acute infectious respiratory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, a subtype of the coronavirus. In addition to normal levels of biometric measures, a healthy lifestyle has been considered an indispensable element in preventing complications of coronavirus infection. Demographic characteristics are also critical in determining risk levels. Aim: Investigate potential significant associations between health behaviors, biometric screenings, demographics, and COVID-19 hospitalization in Loma Linda University Health employees. Methods: Participants are employees covered under the employer-sponsored health plan at Loma Linda University Health, Loma Linda, CA, who tested positive for COVID-19. Logistic regression models were applied to analyze demographics, biometric screenings, and lifestyle factors associated with COVID-19 hospitalization. In our study, 7% of participants required hospitalization. Variables independently associated with COVID-19 hospitalization included higher age (OR = 1.05 [1.01–1.08], P = .005), non-White race compared to the White race (OR = 3.2 [1.22–8.38], P = .018), higher HbA1C levels showing a marginal association (OR = 1.31 [.99–1.72], P = .057), and lower vegetable consumption (OR = 4.39 [2.06–9.40], P < .001). Lower protein consumption decreased the Odds of hospitalization (OR = .40 [.19–.87], P = .021). Our results suggest that a diet that includes more vegetables and lower protein may confer some protection against COVID-19 hospitalization. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/15598276221135541"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9983-2664",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Reis",
"given": "Wenes Pereira",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"family": "Moses",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8905-7633",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Oh",
"given": "Jisoo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "April",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"family": "Gaio",
"given": "Josileide",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Public Health, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA (WPR, OM, JO, AW, JG, HDS)"
}
],
"family": "Dos Santos",
"given": "Hildemar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine",
"container-title-short": "American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T01:50:06Z",
"timestamp": 1666662606000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T01:50:18Z",
"timestamp": 1666662618000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T05:04:31Z",
"timestamp": 1666674271878
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/page/policies/text-and-data-mining-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1666569600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/15598276221135541",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/15598276221135541",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/15598276221135541",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "155982762211355",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Cascella M",
"key": "bibr1-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-15598276221135541"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "bibr3-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention",
"key": "bibr4-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "Symptoms of COVID-19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238-020-00650-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11695-020-04734-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31964-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26237",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc14-S014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30195-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-15598276221135541"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "bibr12-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "COVID-19: Vulnerable and High Risk Groups",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-15598276221135541"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "bibr14-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "Keep health workers safe to keep patients safe",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.064",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.29.20084111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-15598276221135541"
},
{
"author": "Loma Linda University Health",
"key": "bibr17-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "Living Whole Wellness Program",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40200-020-00643-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13643-021-01636-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-15598276221135541"
},
{
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention",
"key": "bibr21-15598276221135541",
"volume-title": "COVID-19 Risks and Vaccine Information for Older Adults",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc14-S014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db20-1260",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/cdn.116.000299",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1201/b22003-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.113.075663",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13333",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-15598276221135541"
},
{
"key": "bibr29-15598276221135541",
"unstructured": "Alamgir MK, Shaikh JU. 8. Recent Advances on the Ethnomedicinal Plants as Immunomodulatory Agents. Research Signpost; 2010: 227-244. ISBN978-81-308-0390-6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100630",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2021.10.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.052278",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1559827620981014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpc.2020.100028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4082/kjfm.2017.38.3.111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr37-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165823",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-15598276221135541"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-15598276221135541"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/15598276221135541"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Health Policy",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Association between Lifestyle Risk Factors and COVID-19 Hospitalization in a Healthcare Institution",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy"
}
reis6