Efficacy and safety of Ixekizumab vs. low-dose IL-2 vs. Colchicine vs. standard of care in the treatment of patients hospitalized with moderate-to-critical COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical trial (STRUCK: Survival Trial Using Cytokine Inhibitors)
et al., Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical, doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0565-2022, STRUCK, NCT04724629, Apr 2022 (preprint)
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
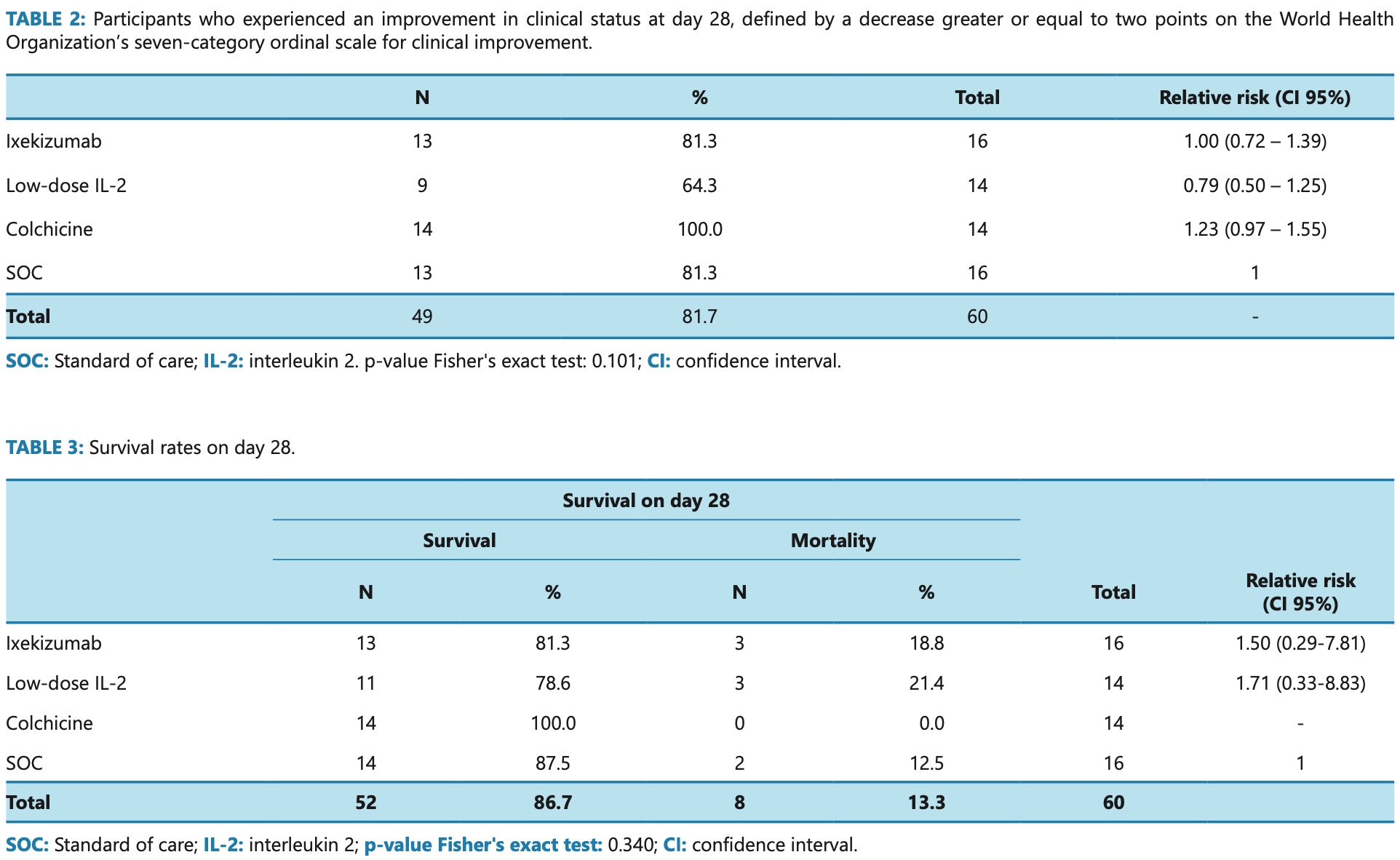
Open label RCT late stage hospitalized patients in Brazil with 14 colchicine and 16 SOC patients, showing lower mortality and improved recovery with treatment, without statistical significance. Authors note that the colchicine group had one patient with SOFA ≥7 vs. zero for SOC, however both groups had one patient intubated and SOC had more patients not requiring high-flow oxygen (12 vs. 8).
The journal version of this paper incorrectly states: "Ixekizumab, colchicine, and IL-2 were demonstrated to be safe but ineffective". The pre-print more accurately represents the improved but not statistically significant results:
"The colchicine arm presented the lowest mortality rate (0%), while the low dose IL-2 had the highest (21.4%) by day 28 post-enrollment. The frequency of adverse events was lowest in the colchicine group (7.3%). None of the differences observed was statistically significant. Interpretation: Colchicine added to SOC performed better than Ixekizumab, low-dose IL-2, or SOC alone for hospitalized patients with moderate to critical Covid-19 in this exploratory study. Larger studies are needed to confirm these findings."
Study covers interleukin-2, ixekizumab, and colchicine.
|
risk of death, 78.9% lower, RR 0.21, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 14 (0.0%), control 2 of 16 (12.5%), NNT 8.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of no improvement, 84.9% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.23, treatment 0 of 14 (0.0%), control 3 of 16 (18.8%), NNT 5.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pimenta Bonifácio et al., 28 Apr 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, mean age 48.9, 18 authors, study period 6 January, 2021 - 9 July, 2021, dosage 1.5mg days 1-3, 1mg days 4-28, trial NCT04724629 (history) (STRUCK).
Contact: fbellissimo@usp.br, livia_pb@usp.br.
Efficacy and safety of Ixekizumab vs. low-dose IL-2 vs. Colchicine vs. standard of care in the treatment of patients hospitalized with moderate-to-critical COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical trial (STRUCK: Survival Trial Using Cytokine Inhibitors)
Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical, doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0565-2022
data analysis; interpretation of results; critical revision of the final version for publication. FB-R -Study conception and design; study execution planning; supervision of the whole study team; interpretation of results; rewriting of the manuscript; critical analysis of the final version for publication. All authors reviewed the study, and approved the final version for publication. Authors hold themselves responsible for all aspects of the study, to ensure that all questions referring to accuracy and integrity are investigated and solved appropriately.
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 2: Plasma cytokine profiles (pg/mL) in COVID-19 patients at baseline (D 1) versus day 28 (D 28). SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Groups
References
Absalon-Aguilar, Rull-Gabayet, Perez-Fragoso, Mejia-Dominguez, Nunez-Alvarez et al., Colchicine Is Safe Though Ineffective in the Treatment of Severe COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial (COLCHIVID), J Gen Intern Med
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Annane, Arabi et al., Effect of Hydrocortisone on Mortality and Organ Support in Patients With Severe COVID-19: The REMAP-CAP COVID-19 Corticosteroid Domain Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Avdeev, Trushenko, Tsareva, Yaroshetskiy, Merzhoeva et al., Anti-IL-17 monoclonal antibodies in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: A pilot study, Cytokine
Beringer, Miossec, Systemic effects of IL-17 in inflammatory arthritis, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Bonifácio, Exploring new targets for COVID-19 treatment
Bryushkova, Skatova, Mutovina, Zagrebneva, Fomina et al., Tocilizumab, netakimab, and baricitinib in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: An observational study, PloS One
Bulat, Situm, Azdajic, Likic, Potential role of IL-17 blocking agents in the treatment of severe COVID-19?, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Caldrer, Mazzi, Bernardi, Prato, Ronzoni et al., Regulatory T Cells as Predictors of Clinical Course in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients, Front Immunol
Cecconi, Martinez-Vives, Vera, Olleros, Barrios et al., Efficacy of short-course colchicine treatment in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: a randomized clinical trial, Sci Rep
Choto, Makupe, Cakana, Sibanda, Mduluza, Excessive neutrophil recruitment promotes typical T-helper 17 responses in Coronavirus disease 2019 patients, PloS One
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Da, Roura-Piloto, Moral-Escudero, Bernal, Albendin-Iglesias et al., Colchicine in Recently Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial (COL-COVID), Int J Gen Med
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Siasos, Giotaki et al., Effect of Colchicine vs Standard Care on Cardiac and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease
Diaz, Orlandini, Castellana, Caccavo, Corral et al., Effect of Colchicine vs Usual Care Alone on Intubation and 28-Day Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open
Dupuis, Sirois, Rheaume, Nguyen, Clavet-Lanthier et al., Colchicine reduces lung injury in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome, PloS One
Fajgenbaum, June, Cytokine Storm, N Engl J Med
Giannakodimos, Gkountana, Lykouras, Karkoulias, Tsakas, The Role of Interleukin-6 in the Pathogenesis, Prognosis and Treatment of Severe COVID-19, Curr Med Chem
Gurczynski, Moore, IL-17 in the lung: the good, the bad, and the ugly, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Hirano, IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer, Int Immunol
Jafrin, Aziz, Islam, Elevated Levels of Pleiotropic Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Interleukin-10 (IL-10) are Critically Involved With the Severity and Mortality of COVID-19: An Updated Longitudinal Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on 147 Studies, Biomark Insights
Leforte, Hospital e Maternidade Christóvão da Gama
Lin, Fu, Yin, Li, Liu et al., ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway, iScience
Liu, Lu, Allan, Tang, Tetreault et al., Generation and characterization of ixekizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that neutralizes interleukin-17A, J Inflamm Res
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, Amaral, Menezes et al., Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial, RMD Open
Ma, Reynolds, Baker, Li, Benveniste et al., IL-17 enhancement of the IL-6 signaling cascade in astrocytes, J Immunol
Ma, Zhang, Ye, Chen, Yu et al., High Levels of Circulating IL-8 and Soluble IL-2R Are Associated With Prolonged Illness in Patients With Severe COVID-19, Front Immunol
Mareev, Orlova, Plisyk, Pavlikova, Akopyan et al., Proactive anti-inflammatory therapy with colchicine in the treatment of advanced stages of new coronavirus infection. The first results of the COLORIT study, Kardiologiia
Maslennikov, Ivashkin, Vasilieva, Chipurik, Semikova et al., Interleukin 17 antagonist netakimab is effective and safe in the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19), Eur Cytokine Netw
Mills, IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology, Nat Rev Immunol
Mulcahy, Hudson, Beggs, Reid, Roddam et al., High peripheral blood th17 percent associated with poor lung function in cystic fibrosis, PloS One
Pourdowlat, Saghafi, Mozafari, Sahebnasagh, Abedini et al., Efficacy and safety of colchicine treatment in patients with COVID-19: A prospective, multicenter, randomized clinical trial, Phytother Res: PTR
Pourgholaminejad, Pahlavanneshan, Basiri, COVID-19 immunopathology with emphasis on Th17 response and cell-based immunomodulation therapy: Potential targets and challenges, Scand J Immunol
Qian, Liu, Hartupee, Altuntas, Gulen, The adaptor Act1 is required for interleukin 17-dependent signaling associated with autoimmune and inflammatory disease, Nat Immunol
Ravelli, Gigant, Curmi, Jourdain, Lachkar et al., Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain, Nature
Resende, Da Cruz Lage, Lobe, Medeiros, Costa et al., Blockade of interleukin seventeen (IL-17A) with secukinumab in hospitalized COVID-19 patients -the BISHOP study, Infect Dis (Lond)
Ryzhakov, Lai, Blazek, To, Hussell et al., IL-17 boosts proinflammatory outcome of antiviral response in human cells, J Immunol
Sadeghi, Tahmasebi, Mahmood, Kuznetsova, Valizadeh et al., Th17 and Treg cells function in SARS-CoV2 patients compared with healthy controls, J Cell Physiol
Spolski, Li, Leonard, Biology and regulation of IL-2: from molecular mechanisms to human therapy, Nat Rev Immunol
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, Allier, Gaudet, Shah et al., Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet Respir Med
Van Eijk, Binkhorst, Bourgonje, Offringa, Mulder et al., COVID-19: immunopathology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment options, J Pathol
Who, COVID-19 Clinical management: living guidance
Who, R&D Blueprint novel Coronavirus COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis
Yang, Masters, Fortner, Champagne, Yanguas-Casas et al., IL-6 promotes the differentiation of a subset of naive CD8+ T cells into IL-21-producing B helper CD8+ T cells, J Exp Med
Zhang, Wang, Li, Xi, Mao et al., Potential contribution of increased soluble IL-2R to lymphopenia in COVID-19 patients, Cell Mol Immunol
Zhu, Wang, Zhou, Wang, Ke et al., Recombinant interleukin-2 stimulates lymphocyte recovery in patients with severe COVID-19, Exp Ther Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1590/0037-8682-0565-2022",
"ISSN": [
"1678-9849",
"0037-8682"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0565-2022",
"alternative-id": [
"S0037-86822023000100317"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4309-0304",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bonifácio",
"given": "Lívia Pimenta",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5735-1333",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Science Valley Research Institute, Brasil; Grupo Leforte, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramacciotti",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9655-4734",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Agati",
"given": "Leandro Barile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8232-5375",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vilar",
"given": "Fernando Crivelenti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8672-4453",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Silva",
"given": "Anna Christina Tojal da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2585-3870",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Louzada Júnior",
"given": "Paulo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3159-5687",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fonseca",
"given": "Benedito Antônio Lopes da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7970-5403",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Souza",
"given": "Hayala Cristina Cavenague de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0005-3588-3370",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Science Valley Research Institute, Brasil; Grupo Leforte, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Caroline Candida Carvalho de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0004-9950-0415",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Science Valley Research Institute, Brasil; Grupo Leforte, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aguiar",
"given": "Valéria Cristina Resende",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0006-2098-0706",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Grupo Leforte, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Quadros",
"given": "Carlos Augusto de Aguiar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6243-8855",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital do Rocio, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dusilek",
"given": "Cesar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9708-0294",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital do Rocio, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Itinose",
"given": "Kengi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0005-5583-6408",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital do Rocio, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Risson",
"given": "Ricardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0004-6049-7503",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital do Rocio, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Lucas Roberto Rivabem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2999-4961",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brazilian Clinical Research Institute, Brasil; Duke University Medical Center, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lopes",
"given": "Renato Delascio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2026-6925",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kallas",
"given": "Esper Georges",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3736-7127",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bellissimo-Rodrigues",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical",
"container-title-short": "Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-14T16:09:41Z",
"timestamp": 1681488581000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-14T16:10:01Z",
"timestamp": 1681488601000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-15T04:51:00Z",
"timestamp": 1681534260745
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_pdf&pid=S0037-86822023000100317&tlng=en",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "530",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1590",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"publisher": "FapUNIFESP (SciELO)",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"series-title": "COVID-19 Clinical management: living guidance",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra2026131",
"article-title": "Cytokine Storm",
"author": "Fajgenbaum DC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2255",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867328666201209100259",
"article-title": "The Role of Interleukin-6 in the Pathogenesis, Prognosis and Treatment of Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Giannakodimos I",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5328",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "Curr Med Chem",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.5642",
"article-title": "COVID-19: immunopathology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment options",
"author": "van Eijk LE",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/11772719221106600",
"article-title": "Elevated Levels of Pleiotropic Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Interleukin-10 (IL-10) are Critically Involved With the Severity and Mortality of COVID-19: An Updated Longitudinal Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on 147 Studies",
"author": "Jafrin S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11772719221106600",
"journal-title": "Biomark Insights",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxaa078",
"article-title": "IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer",
"author": "Hirano T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int Immunol",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.789735",
"article-title": "Regulatory T Cells as Predictors of Clinical Course in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Caldrer S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "789735",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0273186",
"article-title": "Excessive neutrophil recruitment promotes typical T-helper 17 responses in Coronavirus disease 2019 patients",
"author": "Choto TA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology",
"author": "Mills KHG",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "ref9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/sji.13131",
"article-title": "COVID-19 immunopathology with emphasis on Th17 response and cell-based immunomodulation therapy: Potential targets and challenges",
"author": "Pourgholaminejad A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Scand J Immunol",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.30047",
"article-title": "Th17 and Treg cells function in SARS-CoV2 patients compared with healthy controls",
"author": "Sadeghi A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2829",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Cell Physiol",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "236",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-018-0046-y",
"article-title": "Biology and regulation of IL-2: from molecular mechanisms to human therapy",
"author": "Spolski R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "648",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.626235",
"article-title": "High Levels of Circulating IL-8 and Soluble IL-2R Are Associated With Prolonged Illness in Patients With Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Ma A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626235",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0484-x",
"article-title": "Potential contribution of increased soluble IL-2R to lymphopenia in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "878",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1000142",
"article-title": "IL-17 enhancement of the IL-6 signaling cascade in astrocytes",
"author": "Ma X",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4898",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni1439",
"article-title": "The adaptor Act1 is required for interleukin 17-dependent signaling associated with autoimmune and inflammatory disease",
"author": "Qian Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102293",
"article-title": "ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway",
"author": "Lin X",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102293",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00344.2017",
"article-title": "IL-17 in the lung: the good, the bad, and the ugly",
"author": "Gurczynski SJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L6",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0120912",
"article-title": "High peripheral blood th17 percent associated with poor lung function in cystic fibrosis",
"author": "Mulcahy EM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1100917",
"article-title": "IL-17 boosts proinflammatory outcome of antiviral response in human cells",
"author": "Ryzhakov G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5357",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.14437",
"article-title": "Potential role of IL-17 blocking agents in the treatment of severe COVID-19?",
"author": "Bulat V",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1578",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S100940",
"article-title": "Generation and characterization of ixekizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that neutralizes interleukin-17A",
"author": "Liu L",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "J Inflamm Res",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00435-5",
"article-title": "Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1419",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17022",
"article-title": "Effect of Hydrocortisone on Mortality and Organ Support in Patients With Severe COVID-19: The REMAP-CAP COVID-19 Corticosteroid Domain Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Angus DC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1317",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0242318",
"article-title": "Colchicine reduces lung injury in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Dupuis J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455",
"article-title": "Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Lopes MI",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02393",
"article-title": "Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain",
"author": "Ravelli RB",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198",
"issue": "6979",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "428",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00222-8",
"article-title": "Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Tardif JC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "924",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20160417",
"article-title": "IL-6 promotes the differentiation of a subset of naive CD8+ T cells into IL-21-producing B helper CD8+ T cells",
"author": "Yang R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2281",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of Colchicine vs Standard Care on Cardiac and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The GRECCO-19 Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Deftereos SG",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328",
"article-title": "Effect of Colchicine vs Usual Care Alone on Intubation and 28-Day Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Diaz R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07203-8",
"article-title": "Colchicine Is Safe Though Ineffective in the Treatment of Severe COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial (COLCHIVID)",
"author": "Absalon-Aguilar A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Gen Intern Med",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2021.2.n1560",
"article-title": "Proactive anti-inflammatory therapy with colchicine in the treatment of advanced stages of new coronavirus infection. The first results of the COLORIT study",
"author": "Mareev VY",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Kardiologiia",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref34",
"series-title": "R&D Blueprint novel Coronavirus COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref35",
"series-title": "R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S329810",
"article-title": "Colchicine in Recently Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial (COL-COVID)",
"author": "Pascual-Figal DA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5517",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7319",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of colchicine treatment in patients with COVID-19: A prospective, multicenter, randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Pourdowlat G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "891",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res: PTR",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-13424-6",
"article-title": "Efficacy of short-course colchicine treatment in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Cecconi A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9208",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/ecn.2021.0463",
"article-title": "Interleukin 17 antagonist netakimab is effective and safe in the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19)",
"author": "Maslennikov R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Cytokine Netw",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155627",
"article-title": "Anti-IL-17 monoclonal antibodies in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: A pilot study",
"author": "Avdeev SN",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155627",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2022.2066171",
"article-title": "Blockade of interleukin seventeen (IL-17A) with secukinumab in hospitalized COVID-19 patients - the BISHOP study",
"author": "Resende GG",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "591",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-019-0243-5",
"article-title": "Systemic effects of IL-17 in inflammatory arthritis",
"author": "Beringer A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0273340",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab, netakimab, and baricitinib in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: An observational study",
"author": "Bryushkova EA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2021.9658",
"article-title": "Recombinant interleukin-2 stimulates lymphocyte recovery in patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Zhu ME",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00519-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"issue": "10339",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0037-86822023000100317&tlng=en"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Parasitology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of Ixekizumab vs. low-dose IL-2 vs. Colchicine vs. standard of care in the treatment of patients hospitalized with moderate-to-critical COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical trial (STRUCK: Survival Trial Using Cytokine Inhibitors)",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "56"
}
