Protective Effects of Astodrimer Sodium 1% Nasal Spray Formulation against SARS-CoV-2 Nasal Challenge in K18-hACE2 Mice
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13081656, Aug 2021
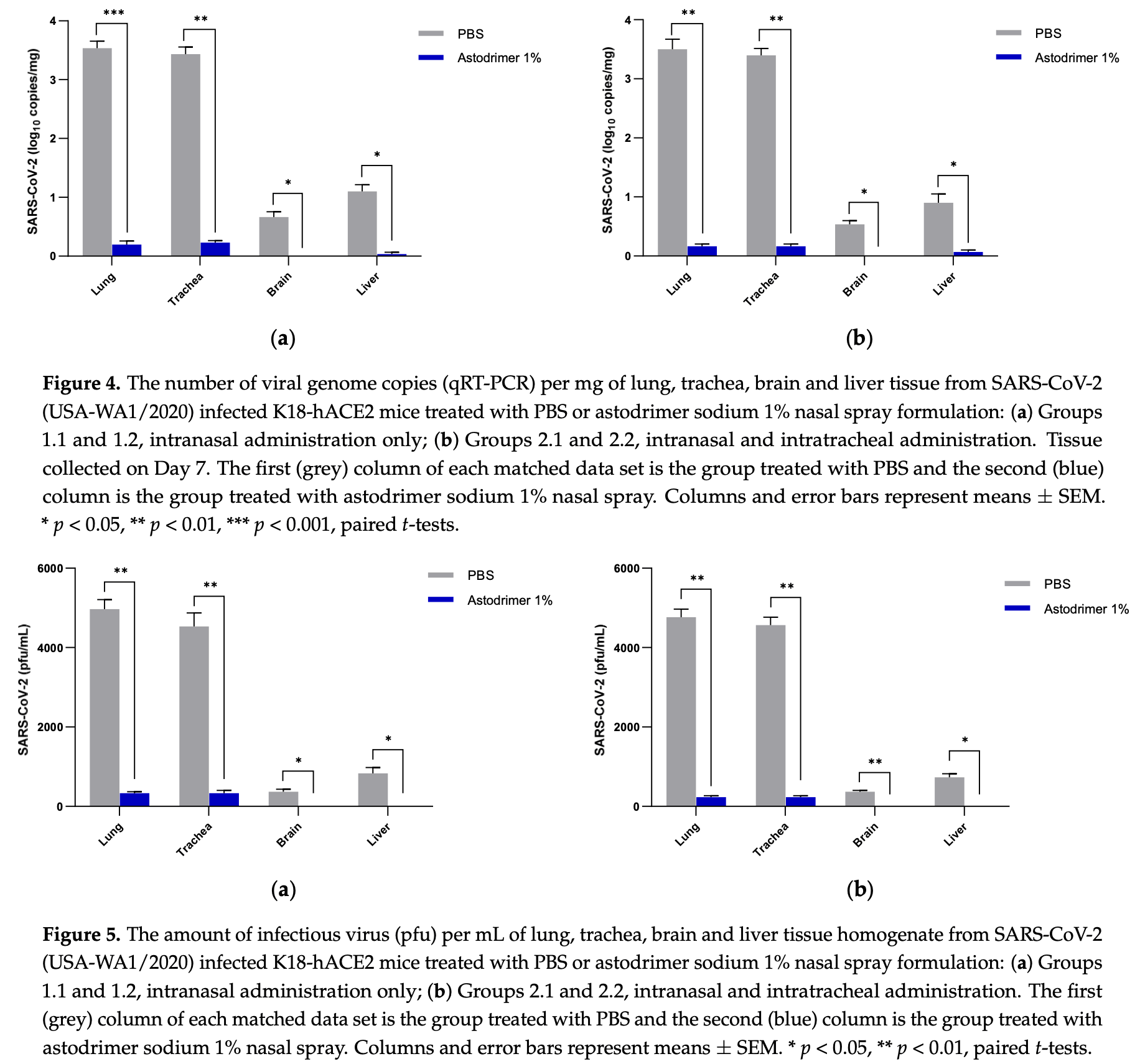
Mouse study showing astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication, tissue viral loads, and proinflammatory cytokine production in K18-hACE2 mice. Astodrimer sodium reduced viral genome copies and infectious virus in the lung and trachea by >99%, prevented detectable virus in the brain and liver, and significantly reduced IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNFα, TGFβ, and MCP-1 in serum and tissues compared to placebo.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of astodrimer sodium for COVID-19:
1 in vivo animal study3
1.
Paull et al., Astodrimer sodium nasal spray forms a barrier to SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and preserves normal mucociliary function in human nasal epithelium, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-72262-w.
Paull et al., 20 Aug 2021, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: jeremy.paull@starpharma.com (corresponding author), carolyn.luscombe@starpharma.com, alex.castellarnau@starpharma.com, graham.heery@starpharma.com, mbobardt@scripps.edu, gallay@scripps.edu.
Protective Effects of Astodrimer Sodium 1% Nasal Spray Formulation against SARS-CoV-2 Nasal Challenge in K18-hACE2 Mice
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13081656
Strategies to combat COVID-19 require multiple ways to protect vulnerable people from infection. SARS-CoV-2 is an airborne pathogen and the nasal cavity is a primary target of infection. The K18-hACE2 mouse model was used to investigate the anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of astodrimer sodium formulated in a mucoadhesive nasal spray. Animals received astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray or PBS intranasally, or intranasally and intratracheally, for 7 days, and they were infected intranasally with SARS-CoV-2 after the first product administration on Day 0. Another group was infected intranasally with SARS-CoV-2 that had been pre-incubated with astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray or PBS for 60 min before the neutralisation of test product activity. Astodrimer sodium 1% significantly reduced the viral genome copies (>99.9%) and the infectious virus (~95%) in the lung and trachea vs. PBS. The pre-incubation of SARS-CoV-2 with astodrimer sodium 1% resulted in a significant reduction in the viral genome copies (>99.9%) and the infectious virus (>99%) in the lung and trachea, and the infectious virus was not detected in the brain or liver. Astodrimer sodium 1% resulted in a significant reduction of viral genome copies in nasal secretions vs. PBS on Day 7 post-infection. A reduction in the viral shedding from the nasal cavity may result in lower virus transmission rates. Viraemia was low or undetectable in animals treated with astodrimer sodium 1% or infected with treated virus, correlating with the lack of detectable viral replication in the liver. Similarly, low virus replication in the nasal cavity after treatment with astodrimer sodium 1% potentially protected the brain from infection. Astodrimer sodium 1% significantly reduced the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNFα and TGFβ and the chemokine MCP-1 in the serum, lung and trachea vs. PBS. Astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray blocked or reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication and its sequelae in K18-hACE2 mice. These data indicate a potential role for the product in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection or for reducing the severity of COVID-19.
References
Bao, Deng, Huang, Gao, Liu et al., The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2312-y
Bernstein, Stanberry, Sacks, Ayisi, Gong et al., Evaluations of Unformulated and FormulatedDendrimer-Based Microbicide Candidates in Mouse and Guinea Pig Models of Genital Herpes, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.47.12.3784-3788.2003
Bhaskar, Sinha, Banach, Mittoo, Weissert et al., Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648
Buonanno, Stabile, Morawaska, Estimation of airborne viral emission: Quanta emission rate of SARS-CoV-2 for infection risk assessment, Environ. Int, doi:10.1016/j.envint.2020.105794
Burks, Rosas-Hernandez, Ramirez-Lee, Cuevas, Talpos, Can SARS-CoV-2 infect the central nervous system via the olfactory bulb or the blood-brain barrier?, Brain Behav. Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.031
Chow, O'brodovich, Plumb, Wen, Sohn et al., Development of an epithelium-specific expression cassette with human DNA regulatory elements for transgene expression in lung airways, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14695
Chow, Plumb, Wen, Steer, Lu et al., Targeting Transgene Expression to Airway Epithelia and Submucosal Glands, Prominent Sites of Human CFTR Expression, Mol. Ther, doi:10.1006/mthe.2000.0135
Huang, Huang, Wang, Li, Ren et al., 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: A cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8
Jiang, Emau, Cairns, Flanary, Morton et al., SPL7013 Gel as a Topical Microbicide for Prevention of Vaginal Transmission of SHIV89.6Pin Macaques, AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, doi:10.1089/aid.2005.21.207
Jiang, Liu, Chen, Shan, Zhou et al., Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in Transgenic Mice Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.027
Jørgensen, Holter, Christensen, Schjalm, Tonby et al., Increased interleukin-6 and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 are associated with respiratory failure in COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78710-7
Liu, Ning, Chen, Guo, Liu et al., Aerodynamic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in two Wuhan hospitals, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2271-3
Matschke, Lütgehetmann, Hagel, Sperhake, Schröder et al., Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: A post-mortem case series, Lancet Neurol, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30308-2
Mccray, Jr, Pewe, Wohlford-Lenane, Hickey et al., Lethal Infection of K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02012-06
Mcgowan, Gomez, Bruder, Febo, Chen et al., Phase 1 randomized trial of the vaginal safety and acceptability of SPL7013 gel (VivaGel) in sexually active young women (MTN-004), AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328346bd3e
O'loughlin, Millwood, Mcdonald, Price, Kaldor et al., Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of SPL7013 Gel (VivaGel ® ): A Dose Ranging, Phase I Study, Sex. Transm. Dis, doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181bc0aac
Olbei, Hautefort, Modos, Treveil, Poletti et al., SARS-CoV-2 Causes a Different Cytokine Response Compared to Other Cytokine Storm-Causing Respiratory Viruses in Severely Ill Patients, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.629193
Paull, Heery, Bobardt, Castellarnau, Luscombe et al., Virucidal and antiviral activity of astodrimer sodium against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105089
Smith, Somsen, Van Rijn, Kooij, Van Der Hoek et al., Aerosol persistence in relation to possible transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Phys. Fluids, doi:10.1063/5.0027844
Song, Zhang, Israelow, Lu-Culligan, Prado et al., Neuroinvasion of SARS-CoV-2 in human and mouse brain, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20202135
Sungnak, Huang, Becavin, Berg, Queen et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6
Tang, Mao, Jones, Tan, Ji et al., Aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2? Evidence, prevention and control, Environ. Int, doi:10.1016/j.envint.2020.106039
Telwatte, Moore, Johnson, Tyssen, Sterjovski et al., Virucidal activity of the dendrimer microbicide SPL7013 against HIV-1, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.03.186
Tyssen, Henderson, Johnson, Sterjovski, Moore et al., Structure Activity Relationship of Dendrimer Microbicides with Dual Action Antiviral Activity, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012309
Wang, Liu, Liu, Li, Lin et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002
Winkler, Bailey, Kafai, Nair, Mccune et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2
Wölfel, Corman, Guggemos, Seilmaier, Zange et al., Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x
Zhang, Chen, Swaroop, Xu, Wang et al., Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-00222-5
Zhang, Shi, Wang, Liver injury in COVID-19: Management and challenges, Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol
Zheng, Wong, Li, Verma, Ortiz et al., COVID-19 treatments and pathogenesis including anosmia in K18-hACE2 mice, Nat. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2943-z
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13081656",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v13081656",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Strategies to combat COVID-19 require multiple ways to protect vulnerable people from infection. SARS-CoV-2 is an airborne pathogen and the nasal cavity is a primary target of infection. The K18-hACE2 mouse model was used to investigate the anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of astodrimer sodium formulated in a mucoadhesive nasal spray. Animals received astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray or PBS intranasally, or intranasally and intratracheally, for 7 days, and they were infected intranasally with SARS-CoV-2 after the first product administration on Day 0. Another group was infected intranasally with SARS-CoV-2 that had been pre-incubated with astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray or PBS for 60 min before the neutralisation of test product activity. Astodrimer sodium 1% significantly reduced the viral genome copies (>99.9%) and the infectious virus (~95%) in the lung and trachea vs. PBS. The pre-incubation of SARS-CoV-2 with astodrimer sodium 1% resulted in a significant reduction in the viral genome copies (>99.9%) and the infectious virus (>99%) in the lung and trachea, and the infectious virus was not detected in the brain or liver. Astodrimer sodium 1% resulted in a significant reduction of viral genome copies in nasal secretions vs. PBS on Day 7 post-infection. A reduction in the viral shedding from the nasal cavity may result in lower virus transmission rates. Viraemia was low or undetectable in animals treated with astodrimer sodium 1% or infected with treated virus, correlating with the lack of detectable viral replication in the liver. Similarly, low virus replication in the nasal cavity after treatment with astodrimer sodium 1% potentially protected the brain from infection. Astodrimer sodium 1% significantly reduced the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNFα and TGFβ and the chemokine MCP-1 in the serum, lung and trachea vs. PBS. Astodrimer sodium 1% nasal spray blocked or reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication and its sequelae in K18-hACE2 mice. These data indicate a potential role for the product in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection or for reducing the severity of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v13081656"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9981-421X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Starpharma Pty Ltd., Abbotsford, VIC 3067, Australia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Paull",
"given": "Jeremy R. A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Starpharma Pty Ltd., Abbotsford, VIC 3067, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Luscombe",
"given": "Carolyn A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Starpharma Pty Ltd., Abbotsford, VIC 3067, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Castellarnau",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Starpharma Pty Ltd., Abbotsford, VIC 3067, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Heery",
"given": "Graham P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Microbiology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92307, USA"
}
],
"family": "Bobardt",
"given": "Michael D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Microbiology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92307, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gallay",
"given": "Philippe A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-23T03:00:09Z",
"timestamp": 1629687609000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-17T16:42:17Z",
"timestamp": 1721234537000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"BTBR300093"
],
"name": "Australian Medical Research Future Fund (MRFF) Biomedical Translation Bridge (BTB) Program"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-06T10:14:46Z",
"timestamp": 1725617686809
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 16,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629417600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/8/1656/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1656",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8",
"article-title": "6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: A cohort study",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "220",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105089",
"article-title": "Virucidal and antiviral activity of astodrimer sodium against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Paull",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105089",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-00222-5",
"article-title": "Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0012309",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Tyssen, D., Henderson, S.A., Johnson, A., Sterjovski, J., Moore, K., La, J., Zanin, M., Sonza, S., Karellas, P., and Giannis, M.P. (2010). Structure Activity Relationship of Dendrimer Microbicides with Dual Action Antiviral Activity. PLoS ONE, 5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.03.186",
"article-title": "Virucidal activity of the dendrimer microbicide SPL7013 against HIV-1",
"author": "Telwatte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.47.12.3784-3788.2003",
"article-title": "Evaluations of Unformulated and FormulatedDendrimer-Based Microbicide Candidates in Mouse and Guinea Pig Models of Genital Herpes",
"author": "Bernstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3784",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/aid.2005.21.207",
"article-title": "SPL7013 Gel as a Topical Microbicide for Prevention of Vaginal Transmission of SHIV89.6Pin Macaques",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "207",
"journal-title": "AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181bc0aac",
"article-title": "Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of SPL7013 Gel (VivaGel®): A Dose Ranging, Phase I Study",
"author": "Millwood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Sex. Transm. Dis.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0b013e328346bd3e",
"article-title": "Phase 1 randomized trial of the vaginal safety and acceptability of SPL7013 gel (VivaGel) in sexually active young women (MTN-004)",
"author": "McGowan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1057",
"journal-title": "AIDS",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes",
"author": "Sungnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02012-06",
"article-title": "Lethal Infection of K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus",
"author": "McCray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 treatments and pathogenesis including anosmia in K18-hACE2 mice",
"author": "Zheng",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Nat. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "589",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "807",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.94.26.14695",
"article-title": "Development of an epithelium-specific expression cassette with human DNA regulatory elements for transgene expression in lung airways",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14695",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/mthe.2000.0135",
"article-title": "Targeting Transgene Expression to Airway Epithelia and Submucosal Glands, Prominent Sites of Human CFTR Expression",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Mol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2312-y",
"article-title": "The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice",
"author": "Bao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "830",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.027",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in Transgenic Mice Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function",
"author": "Winkler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envint.2020.106039",
"article-title": "Aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2? Evidence, prevention and control",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106039",
"journal-title": "Environ. Int.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x",
"article-title": "Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envint.2020.105794",
"article-title": "Estimation of airborne viral emission: Quanta emission rate of SARS-CoV-2 for infection risk assessment",
"author": "Buonanno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105794",
"journal-title": "Environ. Int.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2271-3",
"article-title": "Aerodynamic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in two Wuhan hospitals",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "557",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "582",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/5.0027844",
"article-title": "Aerosol persistence in relation to possible transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107108",
"journal-title": "Phys. Fluids",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648",
"article-title": "Cytokine Storm in COVID-19—Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper",
"author": "Bhaskar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1648",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Increased interleukin-6 and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 are associated with respiratory failure in COVID-19",
"author": "Holter",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.629193",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Causes a Different Cytokine Response Compared to Other Cytokine Storm-Causing Respiratory Viruses in Severely Ill Patients",
"author": "Olbei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "629193",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30308-2",
"article-title": "Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: A post-mortem case series",
"author": "Matschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "919",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.031",
"article-title": "Can SARS-CoV-2 infect the central nervous system via the olfactory bulb or the blood-brain barrier?",
"author": "Burks",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20202135",
"article-title": "Neuroinvasion of SARS-CoV-2 in human and mouse brain",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20202135",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30057-1",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19: Management and challenges",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/8/1656"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Protective Effects of Astodrimer Sodium 1% Nasal Spray Formulation against SARS-CoV-2 Nasal Challenge in K18-hACE2 Mice",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}