Ion channel inhibition with amiodarone or verapamil in symptomatic hospitalized nonintensive-care COVID-19 patients: The ReCOVery-SIRIO randomized trial
et al., Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2022.0072, RECOVERY-SIRIO, NCT04351763, Sep 2022
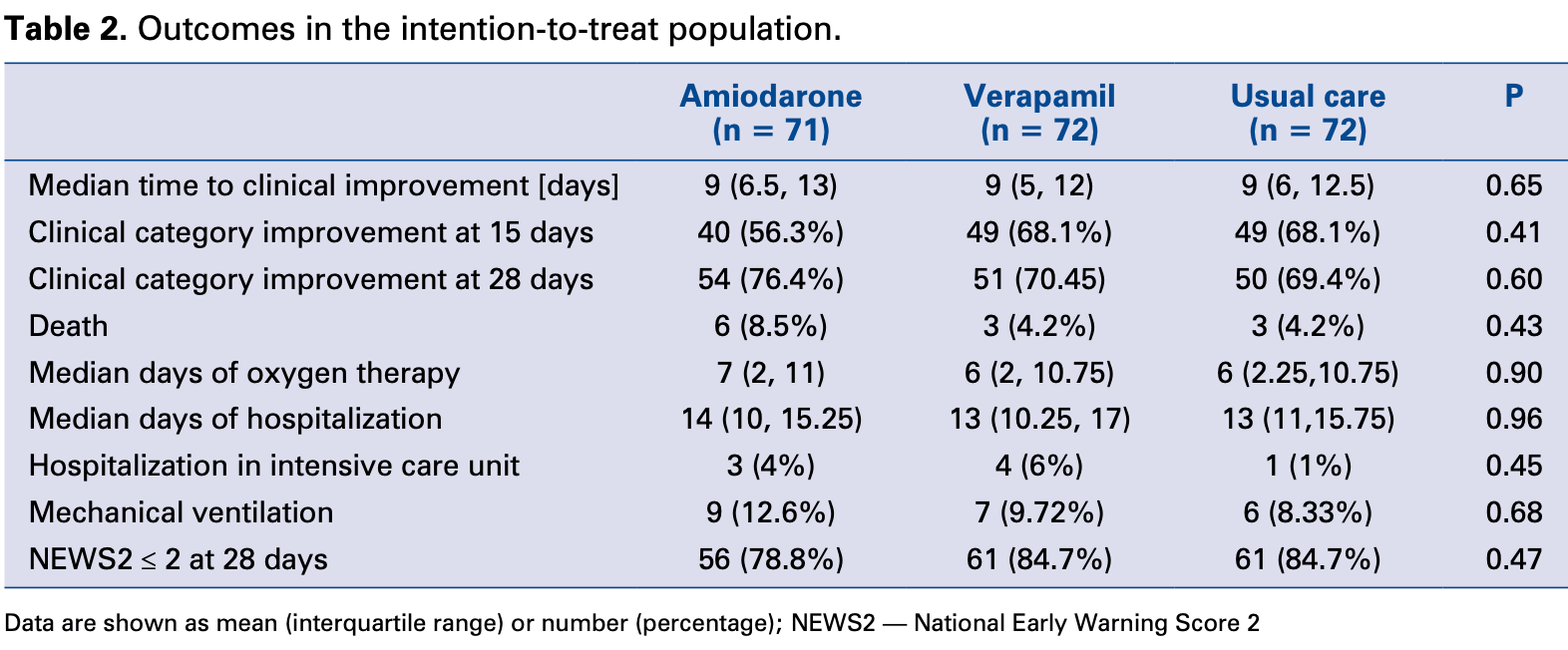
RCT 215 hospitalized non-intensive care COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in clinical improvement with amiodarone or verapamil. The trial, which aimed to assess the effects of ion channel inhibitors on COVID-19 progression, was prematurely terminated due to slow enrollment.
Study covers amiodarone and verapamil.
|
risk of death, 102.8% higher, RR 2.03, p = 0.33, treatment 6 of 71 (8.5%), control 3 of 72 (4.2%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 52.1% higher, RR 1.52, p = 0.43, treatment 9 of 71 (12.7%), control 6 of 72 (8.3%).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 29.9% higher, HR 1.30, p = 0.19, treatment 71, control 72, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, clinical category improvement, Kaplan-Meier, day 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Navarese et al., 30 Sep 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Poland, peer-reviewed, median age 62.0, 23 authors, study period 20 May, 2020 - 13 May, 2021, trial NCT04351763 (history) (RECOVERY-SIRIO).
Contact: elianonavarese@gmail.com, eliano.navarese@cm.umk.pl.
Ion channel inhibition with amiodarone or verapamil in symptomatic hospitalized nonintensive-care COVID-19 patients: The ReCOVery-SIRIO randomized trial
Cardiology Journal, doi:10.5603/cj.a2022.0072
Background: Ion channel inhibition may offer protection against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Inflammation and reduced platelet count occur during COVID-19 but precise quantification of risk thresholds is unclear. The ReCOVeRy-SIRIO study aimed to assess clinical effects of amiodarone and verapamil and to relate patient phenotypes to outcomes. Methods: ReCOVeRy-SIRIO is a multicenter open-label 1:1:1 investigator-initiated randomized trial with blinded event adjudication. A sample of 804 symptomatic hospitalized nonintensive-care COVID-19 patients, follow-up for 28 days was initially planned. Results: The trial was stopped when a total of 215 patients had been randomized to amiodarone (n = 71), verapamil (n = 72) or standard care alone (n = 72). At 15 days, the hazard ratio (hazard ratio [HR], 95% confidence interval [CI]) for clinical improvement was 0.77 (0.52-1.14) with amiodarone and 0.97 (0.81-1.17) with verapamil as compared to usual care. Clinically relevant associations were found 739 www.cardiologyjournal.org between mortality or lack of clinical improvement and higher peak C-reactive protein (CRP) levels or nadir platelet count at 7, 10 and 15 days. Mortality rate increased by 73% every 5 mg/dL increment in peak CRP (HR 1.73,) and was two-fold higher for every decrement of 100 units in nadir platelet count (HR 2.19,. By cluster analysis, thresholds of 5 mg/dL for peak CRP and 187 × 10 3 /mcL for nadir platelet count identified the phenogroup at greatest risk of dying. Conclusions: In this randomized trial, neither amiodarone nor verapamil were found to significantly accelerate short-term clinical improvement. Peak CRP and nadir platelet counts were associated with increased mortality both in isolation and by cluster analysis. (
Conflict of interest: None declared
References
Azar, Shin, Kang, Diagnosis of SARS--CoV-2 infection in the setting of the cytokine release syndrome, Expert Rev Mol Diagn, doi:10.1080/14737159.2020.1830760
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Castaldo, Aimo, Castiglione, Safety and efficacy of amiodarone in a patient with COVID-19, JACC Case reports
Chan, Yuan, Kok, A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to--person transmission: a study of a family cluster, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9
Charlton, Pearson, Hover, Ion channels as therapeutic targets for viral infections: further discoveries and future perspectives, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12080844
Chen, Sang, Jiang, Longitudinal hematologic and immunologic variations associated with the progression of COVID-19 patients in China, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.003
Dodd, Follmann, Wang, Endpoints for randomized controlled clinical trials for COVID-19 treatments, Clin Trials, doi:10.1177/1740774520939938
Gustine, Jones, Immunopathology of hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Am J Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hojyo, Uchida, Tanaka, How COVID-19 induces cytokine storm with high mortality, Inflamm Regen, doi:10.1186/s41232-020-00146-3
Hover, Foster, Barr, Viral dependence on cellular ion channels: an emerging anti-viral target?, J Gen Virol, doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000712
Jiang, Huang, Xie, The association between severe COVID-19 and low platelet count: evidence from 31 observational studies involving 7613 participants, Br J Haematol, doi:10.1111/bjh.16817
Lai, Millet, Daniel, The SARS-CoV Fusion Peptide Forms an Extended Bipartite Fusion Platform that Perturbs Membrane Order in a Calcium-Dependent Manner, J Mol Biol
Levi, Thachil, Iba, Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Haematol, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9
Maggioni, Andreotti, Gervasoni, COVID-19 trials in Italy: a call for simplicity, top standards and global pooling, Int J Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.06.043
Navarese, Musci, Frediani, Ion channel inhibition against COVID-19: A novel target for clinical investigation, Cardiol J, doi:10.5603/CJ.a2020.0090
Popat, Review and comparative study of clustering techniques, Int J Comp Sci Info Tech
Sanchis-Gomar, Lavie, Morin, Amiodarone in the COVID-19 era: treatment for symptomatic patients only, or drug to prevent infection?, Am J Cardiovasc Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40256-020-00429-7
Socio, Gidari, Sicari, National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2) better predicts critical Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) illness than COVID-GRAM, a multi-centre study, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-021-01620-x
Stadler, Ha, Ciminale, Amiodarone alters late endosomes and inhibits SARS coronavirus infection at a postendosomal level, Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol
Tang, Bidon, Jaimes, Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104792
Wood, Neuberg, Thompson, Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: a report from the ASH Research Collaborative Data Hub, Blood Advances
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5603/cj.a2022.0072",
"ISSN": [
"1898-018X",
"1897-5593"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5603/CJ.a2022.0072",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navarese",
"given": "Eliano P.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Podhajski",
"given": "Przemysław",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andreotti",
"given": "Felicita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "La Torre",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gajda",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radziwanowski",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nowicka",
"given": "Małgorzata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bukowski",
"given": "Paweł",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gajda",
"given": "Jacek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omyła",
"given": "Maciej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lackowski",
"given": "Piotr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piasecki",
"given": "Maciej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jasiewicz",
"given": "Małgorzata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szymański",
"given": "Paweł",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pietrzykowski",
"given": "Łukasz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michalski",
"given": "Piotr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kubica",
"given": "Aldona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Urbanowicz",
"given": "Iwona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orsini",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conte",
"given": "Max",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinkas",
"given": "Jarosław",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brouwer",
"given": "Marc A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kubica",
"given": "Jacek",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cardiology Journal",
"container-title-short": "Cardiol J.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-01T09:14:35Z",
"timestamp": 1659345275000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-05T08:31:13Z",
"timestamp": 1664958673000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T15:43:12Z",
"timestamp": 1724427792243
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.viamedica.pl/cardiology_journal/article/viewFile/88627/68179",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "3595",
"original-title": [],
"page": "739-750",
"prefix": "10.5603",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "VM Media SP. zo.o VM Group SK",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.viamedica.pl/cardiology_journal/article/view/88627"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ion channel inhibition with amiodarone or verapamil in symptomatic hospitalized nonintensive-care COVID-19 patients: The ReCOVery-SIRIO randomized trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "29"
}