Crying wolf in time of Corona: the strange case of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine. Is the fear of failure withholding potential life-saving treatment from clinical use?
et al., Signa Vitae, doi:10.22514/sv.2021.043, Mar 2021
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
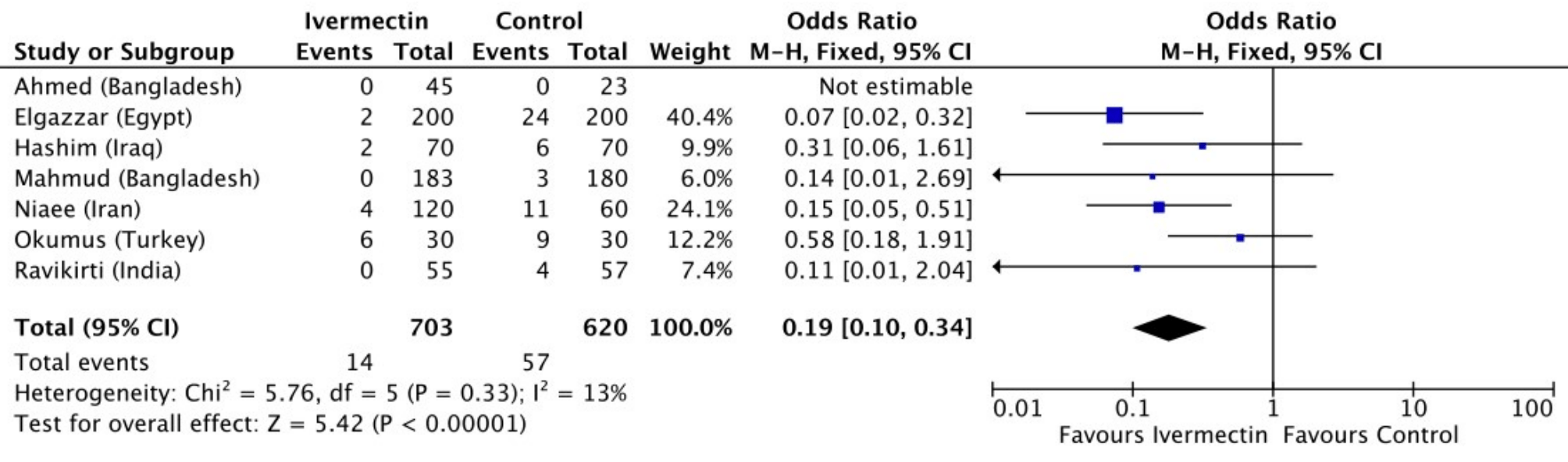
Meta analysis of RCT mortality results showing RR 0.19, p < 0.00001.
7 meta-analyses show significant improvements with ivermectin for mortality1-6,
hospitalization7,
recovery3, and
cases3.
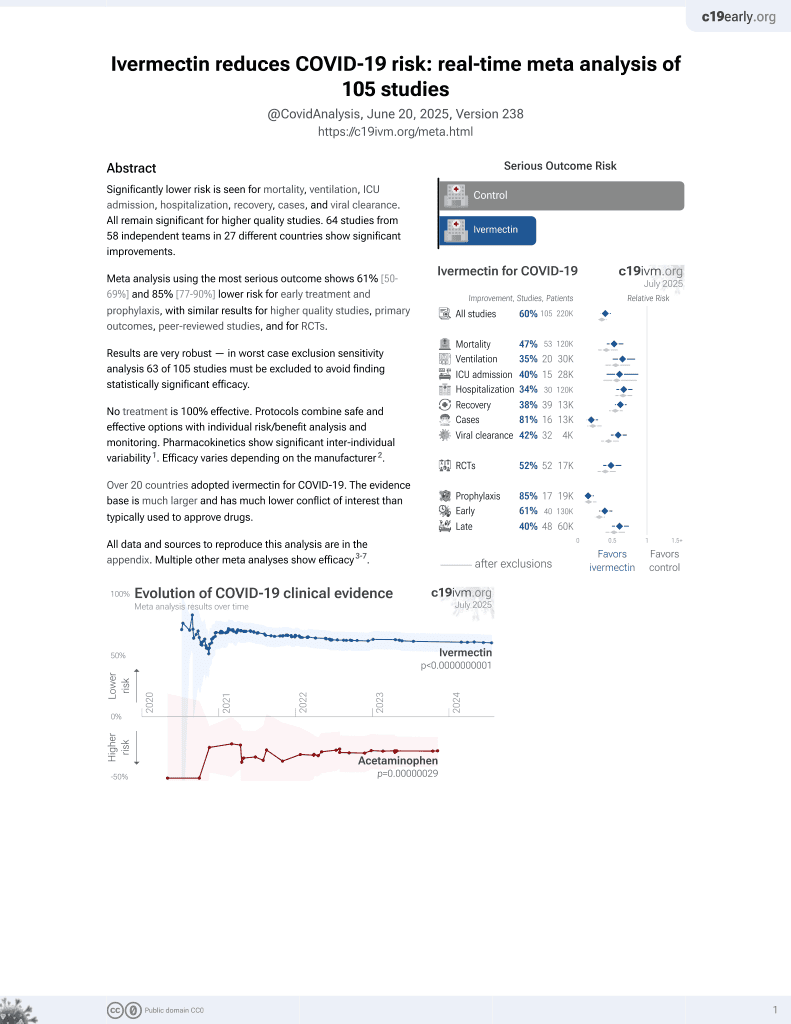
Currently there are 106 ivermectin for COVID-19 studies, showing 47% lower mortality [34‑58%], 35% lower ventilation [17‑50%], 40% lower ICU admission [12‑58%], 34% lower hospitalization [21‑44%], and 79% fewer cases [69‑86%].
|
risk of death, 79.5% lower, RR 0.21, p < 0.001, treatment 14 of 703 (2.0%), control 57 of 620 (9.2%), NNT 14, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Bryant et al., Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402.
2.
Hariyanto et al., Ivermectin and outcomes from Covid-19 pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trial studies, Reviews In Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2265.
3.
Kory et al., Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001377.
4.
Lawrie et al., Ivermectin reduces the risk of death from COVID-19 – a rapid review and meta-analysis in support of the recommendation of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, Preprint, b3d2650e-e929-4448-a527-4eeb59304c7f.filesusr.com/ugd/593c4f_8cb655bd21b1448ba6cf1f4c59f0d73d.pdf.
5.
Nardelli et al., Crying wolf in time of Corona: the strange case of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine. Is the fear of failure withholding potential life-saving treatment from clinical use?, Signa Vitae, doi:10.22514/sv.2021.043.
Nardelli et al., 11 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22514/sv.2021.043",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.22514/sv.2021.043",
"container-title": "Signa Vitae",
"container-title-short": "SV",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-12T05:41:24Z",
"timestamp": 1615527684000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-24T19:35:58Z",
"timestamp": 1645731358000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-05T20:15:11Z",
"timestamp": 1649189711123
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://oss.signavitae.com/mre-signavitae/article/20210508-344/pdf/3-4%20SV2021022602.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "26027",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.22514",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "MRE Press",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.signavitae.com/articles/10.22514/sv.2021.043"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Crying wolf in time of Corona: the strange case of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine. Is the fear of failure withholding potential life-saving treatment from clinical use?",
"type": "journal-article"
}