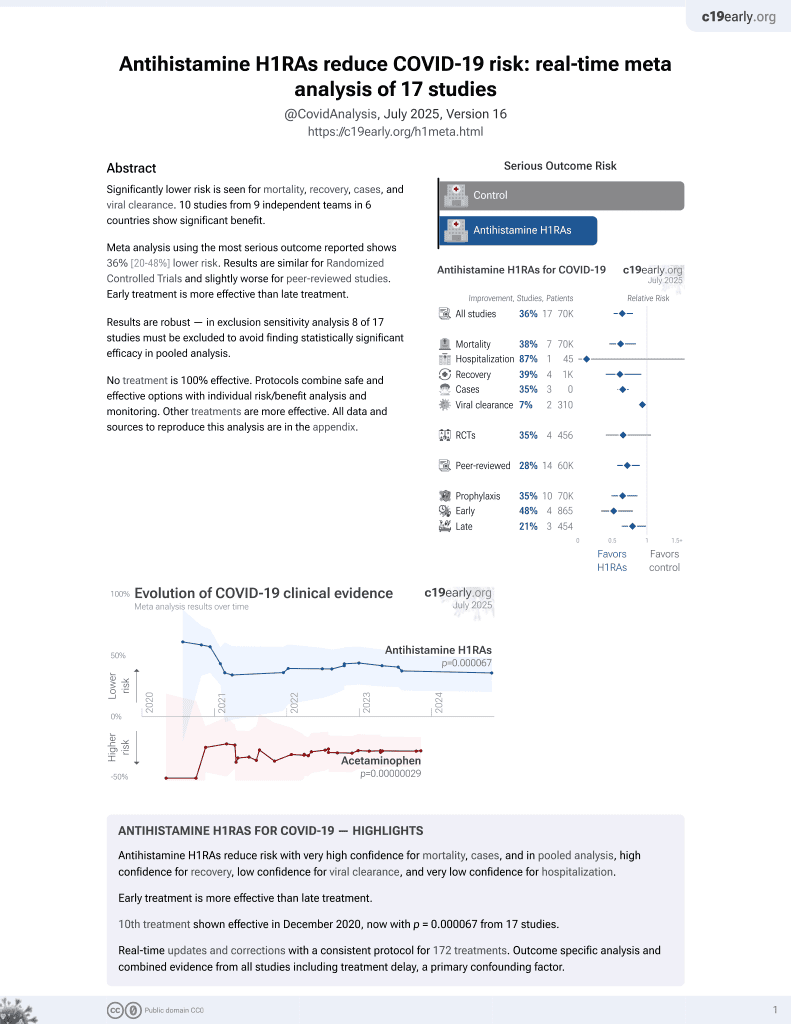
Real-world evidence for improved outcomes with histamine antagonists and aspirin in 22,560 COVID-19 patients
et al., Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00689-y, Mar 2021 (preprint)
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000052 from 17 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
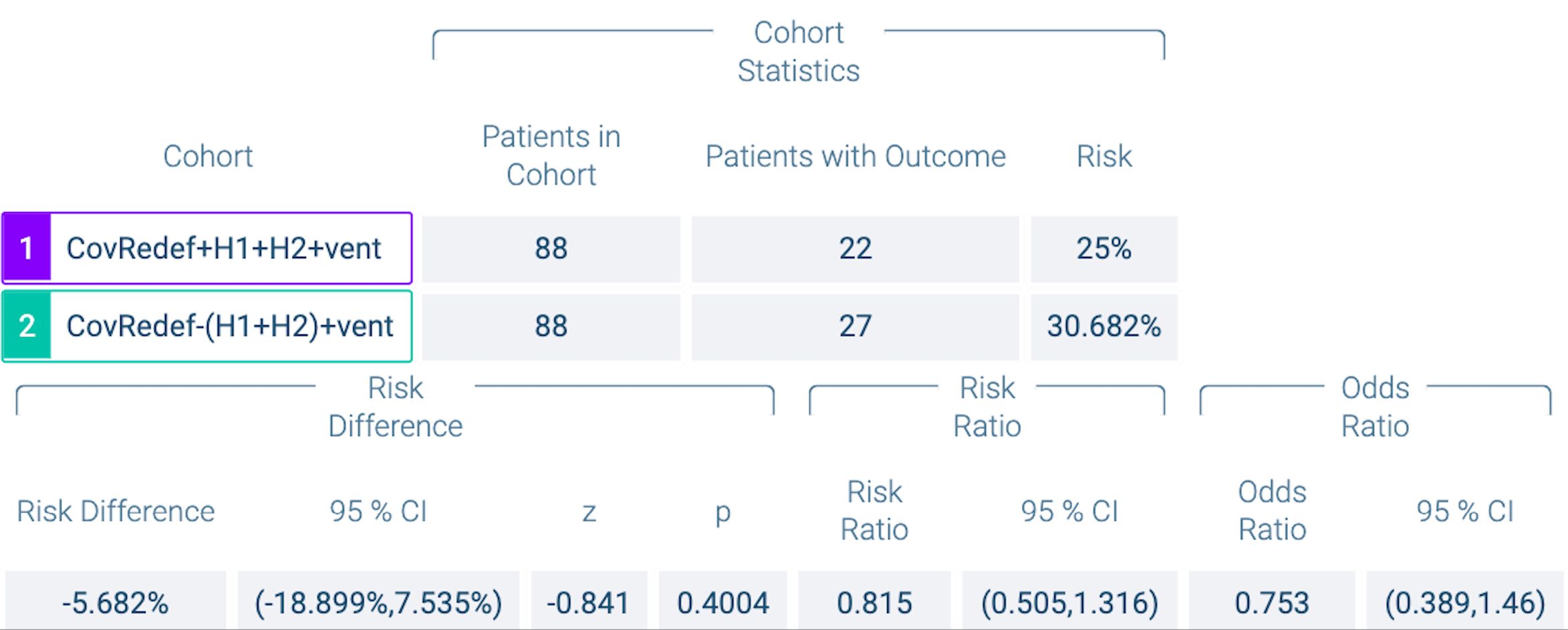
PSM retrospective TriNetX database analysis of 1,379 severe COVID-19 patients requiring respiratory support, showing lower mortality with H1RAs+H2RAs versus famotidine alone, without statistical significance.
Study covers antihistamine H1RAs, famotidine, and aspirin.
|
risk of death, 25.0% lower, OR 0.75, p = 0.40, treatment 88, control 88, H1+H2 vs. famotidine, propensity score matching, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mura et al., 31 Mar 2021, retrospective, database analysis, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Abstract: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
LETTER
www.nature.com/sigtrans
OPEN
1234567890();,:
Real-world evidence for improved outcomes with histamine
antagonists and aspirin in 22,560 COVID-19 patients
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)6:267
; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00689-y
Dear Editor,
The COVID-19 pandemic has driven great interest in the
therapeutic potential of repurposed drugs with well-established
benefits and safety profiles (toxicity, bioavailability, etc.), many of
which act via signal transduction pathways. One category of such
drugs is those that reduce acid production in gastroenterological
contexts. Acid-suppressing drugs belong to two main classes,
based on their mechanisms of action: (i) proton-pump inhibitors
(PPIs) sterically block H+/K+-ATPase pumps, impeding the final
step of acid release in the gastric mucosa. (ii) Histamine H2
receptor antagonists (H2RA) competitively bind the H2R, a type of
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR),1 and block the natural
stimulation of its downstream signal transduction cascade by
histamine; famotidine (e.g., Pepcid®) and ranitidine (e.g., Zantac®)
are exemplary H2RAs.
A dense web of functional linkages exists between histamine
and H2RAs, on the one hand, and disparate physiological
pathways on the other hand. These downstream signaling
pathways include gastrointestinal systems (acid reduction) as well
as the dysregulated inflammatory cascades (cytokine storm) that
likely underlie much of the pathophysiology of COVID-19.1 The
mechanistic basis of a putative role of famotidine in COVID-19
likely involves its roles as an H2RA versus, for instance, direct
binding to the viral protease 3CLpro (and resultant inhibition), as
had been originally suspected from molecular docking studies.
Given its many possible mechanistic and regulatory linkages to
signal transduction pathways, is famotidine beneficial in treating
COVID-19, as gauged by outcomes involving either (i) infection
transmissibility, (ii) disease severity indicators (e.g., likelihood of
cases reaching the point of ventilation, WHO severity index), or (iii)
mortality rates? This question remains unresolved, though not for
lack of effort: since a pioneering report2 of positive clinical
outcomes with famotidine use in COVID-19, over 10 studies have
considered the potential therapeutic benefits of famotidine. As we
recently reviewed,3 many of these reports concluded in favor of
famotidine use, others found little to no association between
famotidine (or PPIs) and 30-day mortality, and a recent study
found a negative association for both PPIs and famotidine. These
independent studies have been retrospective and observational;
most were cohort-based, with some as case-series (e.g., symptom
tracking across longitudinal data); most evaluated inpatient cases;
and most attempted to account for confounders and other biases
(e.g., via propensity-score matching). Given the conflicting reports
thus far, particularly the evidence suggesting a beneficial impact
of famotidine on mortality and overall disease progression (e.g.,
mechanical ventilation), we have undertaken the new analysis
reported herein.
Note that all three parallel tracks of findings—those indicating
for and against famotidine, as well as neutral (i.e., no association)—
rest upon substantially smaller datasets than were drawn upon in
the present work. Are any beneficial effects of famotidine
detectable on population-wide, international scales? Is it synergistic..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00689-y",
"ISSN": [
"2059-3635"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00689-y",
"alternative-id": [
"689"
],
"article-number": "267",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "27 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "21 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "14 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Patient consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "Not required; see Supplementary Methods section for IRB review."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7985-2561",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mura",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Preissner",
"given": "Saskia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nahles",
"given": "Susanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heiland",
"given": "Max",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourne",
"given": "Philip E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Preissner",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-14T13:05:59Z",
"timestamp": 1626267959000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T11:58:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638446280000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000001",
"award": [
"MCB-1350957"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Science Foundation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-03T13:42:49Z",
"timestamp": 1638538969956
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2059-3635"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1626220800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1626220800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00689-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00689-y",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00689-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-020-01422-1",
"author": "M Ennis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "689_CR1",
"unstructured": "Ennis, M. & Tiligada, K. Histamine receptors and COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 70, 67–75 (2021).",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"author": "DE Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "689_CR2",
"unstructured": "Freedberg, D. E. et al. Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study. Gastroenterology 159, 1129–1131 e1123 (2020).",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "689_CR3",
"unstructured": "Mura, C., Preissner, S., Preissner, R. & Bourne, P. E. A birds-eye (Re)view of acid-suppression drugs, COVID-19, and the highly variable literature. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.12003 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2020.101942",
"author": "RB Hogan II",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101942",
"journal-title": "Pulm. Pharm. Ther.",
"key": "689_CR4",
"unstructured": "Hogan II, R. B. et al. Dual-histamine receptor blockade with cetirizine-famotidine reduces pulmonary symptoms in COVID-19 patients. Pulm. Pharm. Ther. 63, 101942 (2020).",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00417-y",
"author": "C Loucera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "689_CR5",
"unstructured": "Loucera, C. et al. Drug repurposing for COVID-19 using machine learning and mechanistic models of signal transduction circuits related to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 5, 290 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 5,
"references-count": 5,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Sig Transduct Target Ther"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cancer Research",
"Genetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Real-world evidence for improved outcomes with histamine antagonists and aspirin in 22,560 COVID-19 patients"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "6"
}
mura