Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab–cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
et al., The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1, TACKLE, NCT04723394, Jun 2022
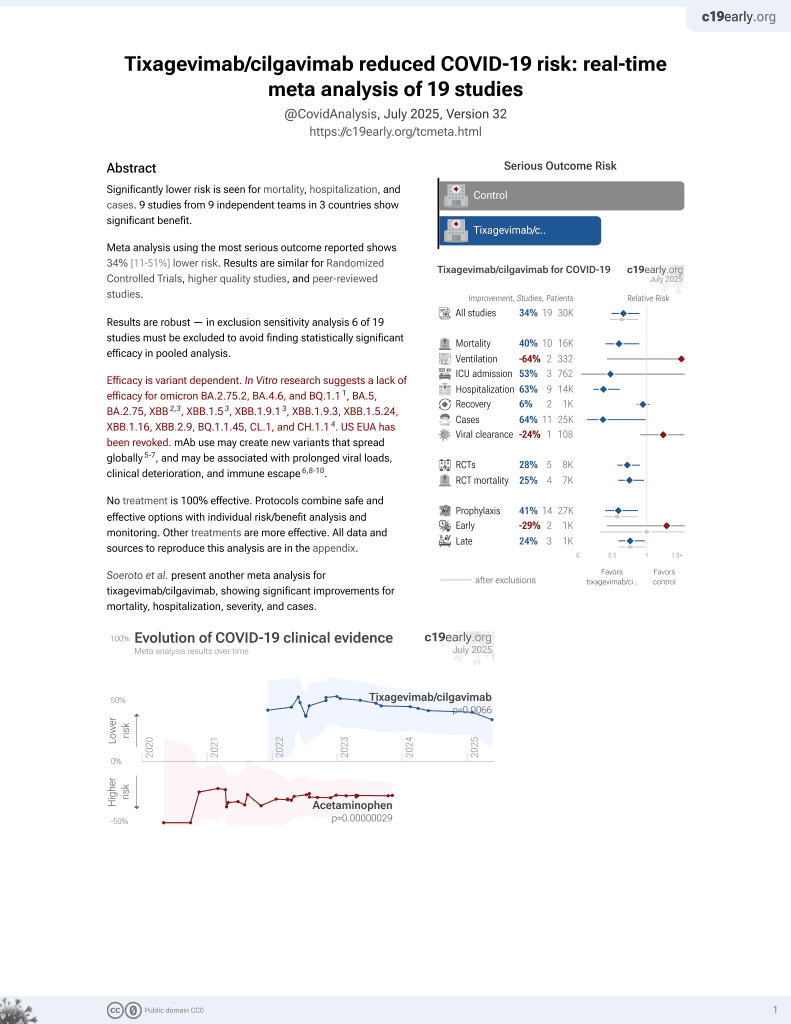
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 910 outpatients in the USA, 456 treated with tixagevimab/cilgavimab, showing significantly lower severe cases and hospitalization with treatment, but no difference in mortality.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.53, ХВВ.1.9.13, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.14.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments5.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 0.2% lower, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 6 of 452 (1.3%), control 6 of 451 (1.3%), NNT 33975, all cause mortality.
|
|
risk of death, 50.1% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.34, treatment 3 of 452 (0.7%), control 6 of 451 (1.3%), NNT 150, COVID-19 mortality.
|
|
risk of severe case, 50.4% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.010, treatment 18 of 407 (4.4%), control 37 of 415 (8.9%), NNT 22, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 56.7% lower, RR 0.43, p = 0.002, treatment 17 of 413 (4.1%), control 40 of 421 (9.5%), NNT 19.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
2.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
3.
Uraki et al., Antiviral efficacy against and replicative fitness of an XBB.1.9.1 clinical isolate, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108147.
Montgomery et al., 7 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 46.0, 20 authors, study period 28 January, 2021 - 22 July, 2021, trial NCT04723394 (history) (TACKLE).
Contact: mark.esser@astrazeneca.com.
Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab–cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(22)00180-1
Background Early intramuscular administration of SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibody combination, tixagevimab-cilgavimab, to non-hospitalised adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 has potential to prevent disease progression. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of tixagevimab-cilgavimab in preventing progression to severe COVID-19 or death. Methods TACKLE is an ongoing, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted at 95 sites in the USA, Latin America, Europe, and Japan. Eligible participants were non-hospitalised adults aged 18 years or older with a laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (determined by RT-PCR or an antigen test) from any respiratory tract specimen collected 3 days or less before enrolment and who had not received a COVID-19 vaccination. A WHO Clinical Progression Scale score from more than 1 to less than 4 was required for inclusion and participants had to receive the study drug 7 days or less from self-reported onset of mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms or measured fever. Participants were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either a single tixagevimab-cilgavimab 600 mg dose (two consecutive 3 mL intramuscular injections, one each of 300 mg tixagevimab and 300 mg cilgavimab) or placebo. Randomisation was stratified (using central blocked randomisation with randomly varying block sizes) by time from symptom onset, and high-risk versus low-risk of progression to severe COVID-19. Participants, investigators, and sponsor staff involved in the treatment or clinical evaluation and monitoring of the participants were masked to treatment-group assignments. The primary endpoints were severe COVID-19 or death from any cause through to day 29, and safety. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04723394.
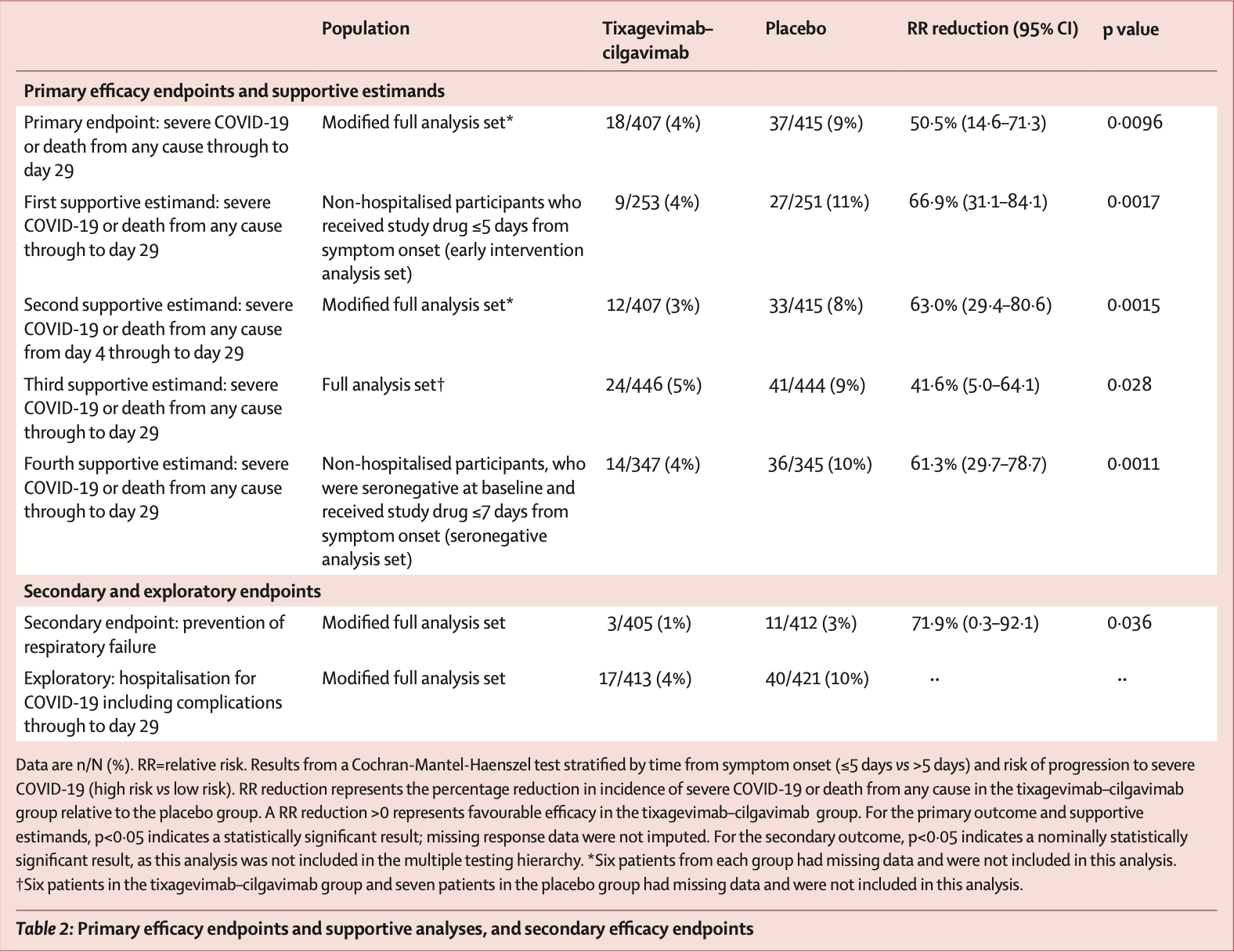
placebo in the 7 days after symptom onset. The greatest reductions in development of severe COVID-19 or death were observed when tixagevimab-cilgavimab was administered as early as possible after symptom onset, as shown by the RR reductions at 3 days or less (prespecified subgroup), 5 days or less and, at 7 days or less (prespecified subgroup) from symptom onset (figure 2B ). For most participant subgroups, reductions in the risk of developing severe COVID-19 or death with tixagevimab-cilgavimab were consistent with the primary analysis (figure 2C ). Most events were observed in participants at high risk of progression to severe COVID-19 (figure 2C ). Although the number of events was low in participants at low risk of progression to severe COVID-19, a large but not statistically significant RR reduction with tixagevimab-cilgavimab was observed in this group. There was a low proportion of seropositive participants, those aged 75 years or older, and those on corticosteroids at baseline (table 1, figure 2C ) and concomitantly a small number of events in these subgroups, resulting in low RR reductions with wide 95% CIs. There was a significant reduction in respiratory failure in participants in the tixagevimab-cilgavimab group compared with the placebo group (table 2 ). Antidrug antibody data were available in a subset of participants up to 84 days after receiving the study drug. Treatment-emergent antidrug antibodies to tixagevimabcilgavimab occurred in six (5%) of 134..
References
Agrawal, Katikireddi, Mccowan, COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths after BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccinations in 2•57 million people in Scotland (EAVE II): a prospective cohort study, Lancet Respir Med
Antonelli, Penfold, Merino, Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: a prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study, Lancet Infect Dis
Danza, Koo, Haddix, SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization among adults aged ≥18 years, by vaccination status, before and during SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (omicron) variant predominance, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell
Dessie, Zewotir, Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Egan, Turtle, Thorpe, Harrison, Semple et al., Hospital admission for symptomatic COVID-19 and impact of vaccination: analysis of linked data from the Coronavirus Clinical Information Network and the National Immunisation Management Service, Anaesthesia
Emergencies, NERVTAG: antiviral drug resistance and the use of directly acting antiviral drugs (DAAs) for COVID-19
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Hippisley-Cox, Coupland, Mehta, Risk prediction of covid-19 related death and hospital admission in adults after COVID-19 vaccination: national prospective cohort study, BMJ
Iacobucci, Covid-19: How is vaccination affecting hospital admissions and deaths?, BMJ
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 omicron sublineages, Nature
Juthani, Gupta, Borges, Hospitalisation among vaccine breakthrough COVID-19 infections, Lancet Infect Dis
Kemp, Collier, Datir, SARS-CoV-2 evolution during treatment of chronic infection, Nature
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116620
Limb, Covid-19: Scientists and medics warn that it is too soon to lift all restrictions in England, BMJ
Loo, Mctamney, Arends, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans, Sci Transl Med
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent COVID-19
Phiri, Delanerolle, Al-Sudani, Rathod, COVID-19 and Black, Asian, and minority ethnic communities: a complex relationship without just cause, JMIR Public Health Surveill
Piechotta, Harder, Waning of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness: individual and public health risk, Lancet
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(22)00180-1",
"ISSN": [
"2213-2600"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1",
"alternative-id": [
"S2213260022001801"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montgomery",
"given": "Hugh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobbs",
"given": "F D Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padilla",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arbetter",
"given": "Douglas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Templeton",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seegobin",
"given": "Seth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Kenneth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campos",
"given": "Jesus Abraham Simón",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arends",
"given": "Rosalinda H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brodek",
"given": "Bryan H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "Dennis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garbes",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez",
"given": "Julieta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koh",
"given": "Gavin C K W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padilla",
"given": "Kelly W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Streicher",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Viani",
"given": "Rolando M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alagappan",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pangalos",
"given": "Menelas N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esser",
"given": "Mark T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abe",
"given": "Wakana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adan De Varona",
"given": "Tania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adiatullina",
"given": "Daria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aguilar Zapata",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahlers",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aimo",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akere",
"given": "Ayoade",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akimova",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alatorre Alexander",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldrich",
"given": "Logan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali Garcia",
"given": "Ismael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali García",
"given": "Karim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allison",
"given": "Lee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alonso Zuñiga",
"given": "Rosa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aloysius",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Altclas",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarisqueta",
"given": "Andres",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antila",
"given": "Martti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anton",
"given": "Camila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Árboix Alamo",
"given": "Elisabet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "Samir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avilés Felix",
"given": "Ramón Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakhtina",
"given": "Natalya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barbero-Becerra",
"given": "Varenka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barragan-Reyes",
"given": "Armando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barreira",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "Mitchell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beran",
"given": "Jiri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berki",
"given": "Nikolett",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berki",
"given": "Viktoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Betten",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Binelli",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brunzová",
"given": "Lenka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bussolari",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Byargeon",
"given": "Karianna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bytnar",
"given": "Justyna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camberos",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campos Corzo",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannon",
"given": "Grazia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Canovi",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carla da Rosa",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moser",
"given": "Ana Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrera Rivas",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Casas",
"given": "Marcelo Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castañeda-Méndez",
"given": "Paulo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cavalcante",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherepova",
"given": "Eugenia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chermenskii",
"given": "Alexei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Codeluppi",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coelho",
"given": "Flavia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Contreras",
"given": "Belinda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cran",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dao",
"given": "Taylor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dharma",
"given": "Chrisette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Di Castri",
"given": "Cosimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diaz Balocchi",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durán",
"given": "Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earl",
"given": "Kara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellery",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Endo",
"given": "Tomoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Everding",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fischer",
"given": "Rainald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fonseca",
"given": "Benedito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franklin",
"given": "Chelsea C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franz",
"given": "Susan-Beatrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fumagalli",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galindo-Amaya",
"given": "Mauricio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galli",
"given": "Mariagiulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gerna",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gil Ureña",
"given": "Karolly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomes Antila",
"given": "Henrikki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomes Maricato",
"given": "Laura Ines",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goncalvez",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonzalez",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González-Lama",
"given": "Jesús",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Granier",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Granier",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grunwald",
"given": "Stephan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guardeño-Ropero",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guberti",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guduri",
"given": "Sridhar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guerrero García",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haggiagi",
"given": "Jehad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hale",
"given": "Kacie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayashi",
"given": "Toshimasa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hermes",
"given": "Maiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernandez Colin",
"given": "Dante",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hirai",
"given": "Yuji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hojo",
"given": "Masayuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Homma",
"given": "Tetsuya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hour",
"given": "Billy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huber",
"given": "Andreas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iacovelli",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ishibashi",
"given": "Noriomi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iwabe",
"given": "Yutaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Izumi",
"given": "Shinyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jessen",
"given": "Arne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jessen",
"given": "Heiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeudy",
"given": "Wilner",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiménez Marcos",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juárez-Hernández",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kabasawa",
"given": "Kiyomi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamińska",
"given": "Katarzyna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kawabe",
"given": "Megumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kemp",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khmelnitskiy",
"given": "Oleg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klassen",
"given": "Carina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kobrynska",
"given": "Olena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koleckar",
"given": "Pavel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Korn",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kornmann",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kostenko",
"given": "Viktor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kovalchuk",
"given": "Evgenii",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kovalchuk",
"given": "Yana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kümmerle",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lachmund",
"given": "Ulrike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lammersmann",
"given": "Kerstin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lastebasse",
"given": "Flávio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lattuada",
"given": "Ivana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lauer",
"given": "Felicitas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lebed",
"given": "Kyrylo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lebed",
"given": "Olga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lecona-Garcia",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leoni",
"given": "Maria Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Little",
"given": "Raymond",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Little",
"given": "Holly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lizardi-Díaz",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lobo-Becker",
"given": "Michele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luppi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macias",
"given": "Veronica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maesaki",
"given": "Shigefumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magnaghi",
"given": "Cristiano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mancini",
"given": "Annalisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazur",
"given": "Stanisław",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melnikova",
"given": "Tatiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menchaca",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menendez-Perez",
"given": "Ibrahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Międlar",
"given": "Ewa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mizunuma",
"given": "Shuuichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mochalova",
"given": "Anastasiya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohamed",
"given": "Mihad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moll",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montalvo",
"given": "Camila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mottola",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mück",
"given": "Birgit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mussi Brugnolli",
"given": "Rebeca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nanda",
"given": "Akanksha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neuner",
"given": "Dörthe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngwueke",
"given": "Agatha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noe",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novacek",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nuzzolo-Shihadeh",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Obiekwe",
"given": "Emeka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ocampo Gaytán",
"given": "Isaias G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ohmagari",
"given": "Norio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ohta",
"given": "Shin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Onyewuchi",
"given": "Ptuonye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pankov",
"given": "Iurii",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pedrosa",
"given": "Maurício",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peré",
"given": "Yael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereyra",
"given": "Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perez",
"given": "Eliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perez-Alba",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perpiña Lozano",
"given": "Paloma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perrei",
"given": "Tanya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peterson",
"given": "Dena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pierroti",
"given": "Ligia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pineda-Cárdenas",
"given": "Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plascencia Sanchez",
"given": "Teresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poletti",
"given": "Camila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pomaranzi",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Portes",
"given": "Lisette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Postel",
"given": "Nils",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Monica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramírez",
"given": "Isabel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramirez-Baena",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramjee",
"given": "Mahadev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratti",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reeve",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reichert",
"given": "Petr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reichertová",
"given": "Petra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reyes Garcia",
"given": "Edgar Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ricardo",
"given": "Celso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodríguez Rodríguez",
"given": "Nicomedes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roldán Sánchez",
"given": "Jaun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Romero-Lopez",
"given": "Matilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosales",
"given": "Tyrone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosales",
"given": "Harvey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roshan",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roshan",
"given": "Simran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rovere Querini",
"given": "Patrizia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rutter",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sachwani",
"given": "Sadaf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sagara",
"given": "Hironori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakai",
"given": "Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samson",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sánchez Mijangos",
"given": "José Héctor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sánchez",
"given": "Liliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sánchez-González",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandford",
"given": "Micko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santana",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos de Carvalho",
"given": "Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sasao",
"given": "Reiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sato",
"given": "Lubna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scheuermann",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmidt",
"given": "Olaf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seki",
"given": "Masafumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "Safia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shimada",
"given": "Daishi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shinkai",
"given": "Masaharu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shinoda",
"given": "Masahiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solorzano",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soncini",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soregine",
"given": "Katalin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sosa",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sowade",
"given": "Olalekan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Špinková",
"given": "Veronika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staniford",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steigemann",
"given": "Iska",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steiner",
"given": "Vivien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strelkov",
"given": "Vladimir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suárez Pineda",
"given": "Cintya R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suenaga",
"given": "Hiroki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suzaki",
"given": "Shintaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swayze",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tada",
"given": "Yuji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takeshita",
"given": "Yuichiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takiguchi",
"given": "Yasuo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanaka",
"given": "Akihiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarumoto",
"given": "Norihito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tatarintseva",
"given": "Albina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taubert",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Terenya",
"given": "Elizaveta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinoco",
"given": "César",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomiyasu",
"given": "Tomohiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres-Vidal",
"given": "Gladys",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trejo-Aguiar",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsushima",
"given": "Kenji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tunstall",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turrà",
"given": "Caterina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valdes",
"given": "Yoandy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valencia Castro",
"given": "Nelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Visconti",
"given": "Guilherme",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vitali",
"given": "Giordano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vutikullird",
"given": "Apinya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watti",
"given": "Jezdancher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Werth",
"given": "Doreen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Cheyanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Workman",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wörle",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wyen",
"given": "Christoph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yamaguchi",
"given": "Yoshiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yamamoto",
"given": "Kei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-07T22:35:13Z",
"timestamp": 1654641313000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-07T22:35:24Z",
"timestamp": 1654641324000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-07T23:12:31Z",
"timestamp": 1654643551731
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654041600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2213260022001801?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2213260022001801?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00282-3",
"article-title": "Waning of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness: individual and public health risk",
"author": "Piechotta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "887",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib1",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o469",
"article-title": "Covid-19: Scientists and medics warn that it is too soon to lift all restrictions in England",
"author": "Limb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o469",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib2",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00558-2",
"article-title": "Hospitalisation among vaccine breakthrough COVID-19 infections",
"author": "Juthani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1485",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib3",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06536-3",
"article-title": "Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients",
"author": "Dessie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "855",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib4",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib5",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"article-title": "Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib6",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"article-title": "REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib7",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib9",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"article-title": "An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "VanBlargan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib10",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses",
"author": "Dejnirattisai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib11",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans",
"author": "Loo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib12",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib14",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6",
"article-title": "Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: a prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study",
"author": "Antonelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib15",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00380-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths after BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccinations in 2·57 million people in Scotland (EAVE II): a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1439",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk prediction of covid-19 related death and hospital admission in adults after COVID-19 vaccination: national prospective cohort study",
"author": "Hippisley-Cox",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib17",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/anae.15677",
"article-title": "Hospital admission for symptomatic COVID-19 and impact of vaccination: analysis of linked data from the Coronavirus Clinical Information Network and the National Immunisation Management Service",
"author": "Egan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "605",
"journal-title": "Anaesthesia",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib18",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03291-y",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 evolution during treatment of chronic infection",
"author": "Kemp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib19",
"volume": "592",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7105e1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization among adults aged ≥18 years, by vaccination status, before and during SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (omicron) variant predominance—Los Angeles County, California, November 7, 2021–January 8, 2022",
"author": "Danza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib21",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19: How is vaccination affecting hospital admissions and deaths?",
"author": "Iacobucci",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib22",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"article-title": "Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab–cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2109682",
"article-title": "Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent COVID-19",
"author": "O'Brien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1184",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib24",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/22581",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Black, Asian, and minority ethnic communities: a complex relationship without just cause",
"author": "Phiri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JMIR Public Health Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib27",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"article-title": "Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 omicron sublineages",
"author": "Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1_bib28",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213260022001801"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab–cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}