Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy with Best Available Treatment (BAT) among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Center Study
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424, Mar 2022
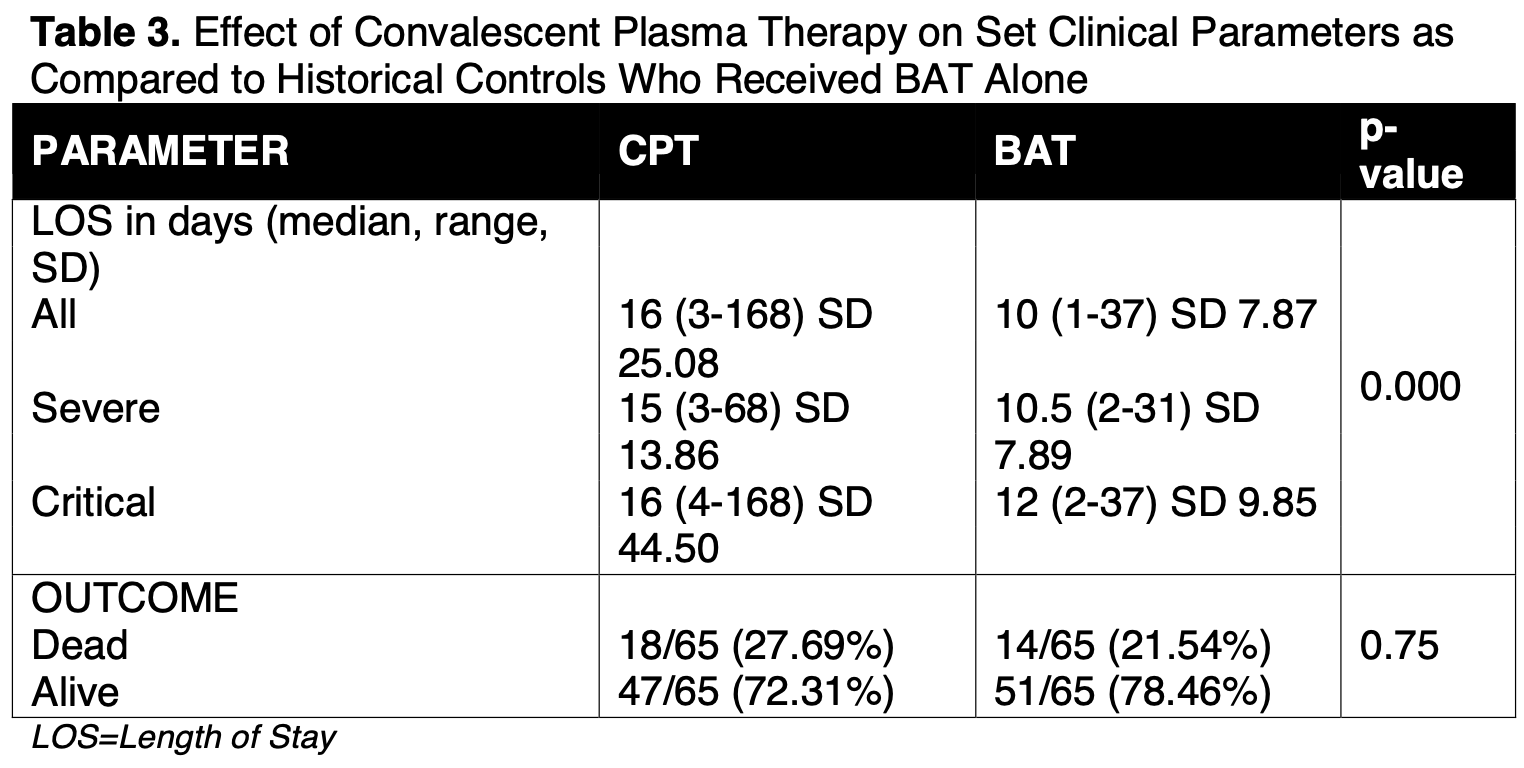
Prospective study of 65 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the Philippines treated with convalescent plasma and 65 matched controls showing no significant difference in mortality and longer hospitalization with treatment.
|
risk of death, 28.6% higher, RR 1.29, p = 0.54, treatment 18 of 65 (27.7%), control 14 of 65 (21.5%).
|
|
hospitalization time, 60.0% higher, relative time 1.60, p = 0.07, treatment mean 16.0 (±25.08) n=65, control mean 10.0 (±7.87) n=65.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mesina et al., 1 Mar 2022, prospective, Philippines, preprint, median age 60.0, 7 authors, study period April 2020 - March 2021.
Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy with Best Available Treatment (BAT) among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Center Study
doi:10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424
The COVID-19 disease caused by SARS-CoV2 virus has gripped the whole world with overwhelming strain in our health system. Currently, there are no standard guidelines in its treatment but the possible benefits of convalescent plasma in limiting complications and severity of the COVID-19 disease have emerged. OBJECTIVE: This study aims to determine the effectiveness and safety of using convalescent plasma in improving the clinical course of hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19 disease admitted at University of Santo Tomas and Makati Medical Center. METHODS: This study is a quasi-experimental (prospective analytical), and multi-center study involving 65 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 Disease who received convalescent plasma, with 65 patients who only received best available treatment serving as age-gendermatched control. RESULTS: Median age of the population who received convalescent plasma was 60 years old, mostly male (68%), and manifested severe pneumonia (47%). There was noted statistically signifcant decrease between the pre-and post-treatment values of hemoglobin (p=0.04) and LDH (p=0.086). There was also statistically significant increase in platelet counts (p=0.01). WBC and PaO2 increased while ferritin and PFR decreased after convalescent plasma transfusion, however, these were not statistically significant. Length of stay and clinical outcome of those who received convalescent plasma were then compared to age-gender matched controls who only received best available treatment. There was noted statistically significant difference between length of stay (p=0.00) among those who received convalescent plasma as compared to those who did not. This was seen across severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients. There was also more mortality seen in the best available treatment alone group, but this was non-significant. CONCLUSIONS: Convalescent plasma use showed no significant impact in the recovery rate and outcome of patients who received it as compared to those who did not, however, its use was proven to be safe among all patients regardless of the level of severity and clinical profile.
References
Abolghasemi, Eshghi, Cheraghali, Fooladi, Moghaddam et al., Clinical efficacy of convalescent plasma for treatment of COVID-19 infections: Results of a multicenter clinical CP in COVID-19 27/27 study, Transfusion and Apheresis Science, doi:10.1016/j.transci.2020.102875
Abramson, Melton, Leukocytosis: Basics of Clinical Assessment
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate COVID-19 in India: An open-label parallel-arm phase II multicentre randomized controlled trial, PLACID Trial, doi:10.1101/2020.09.03.20187252
Allahyari, Seddigh-Shamsi, Mahmoudi, Jamehdar, Amini et al., Efficacy and safety of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107239
Alsharidah, Ayed, Ameen, Alhuraish, Rouheldeen et al., COVID-19 convalescent plasma treatment of moderate and severe cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter interventional study, International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.198
Assinger, Platelets and Infection â€" An Emerging Role of Platelets in Viral Infection, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00649
Cheng, Soo, Wong, Lee, Ng, Use of convalescent plasma therapy in SARS patients in Hong Kong, European journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious diseases
Dr, Burnett, Immunoglobulins in the Lung, Thorax
Duan, Liu, Li, Zhang, Yu et al., Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2004168117
Fan, Chong, Chan, Lim, Lim et al., Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection, American Journal of Hematology, doi:10.1002/ajh.25774
Gharbharan, Jordans, Geurtsvankessel, Hollander, Karim et al., Convalescent Plasma for COVID-19, A randomized clinical trial, doi:10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857
Griffith, Sharma, Holliday, Enyia, Valliere et al., Men and COVID-19: A Biopsychosocial Approach to Understanding Sex Differences in Mortality and Recommendations for Practice and Policy Interventions, Prev Chronic Dis, doi:10.5888/pcd17.200247
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2002032
Gulhar, Physiology, Acute Phase Reactants
Hu, Hu, Yang, Chen, Zhong et al., Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severity of COVID-19 outside Wuhan: A double-center retrospective cohort study of 213 cases in Hunan, China, Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease, doi:10.1177/1753466620963035
Hung, To, Lee, Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A(H1N1) 2009 virus infection, Clin Infectious dis
Ibrahim, Dulipsingh, Zapatka, Factors Associated with Good Patient Outcomes Following Convalescent Plasma in COVID-19: A Prospective Phase II Clinical Trial, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00341-2
Im, Nahm, Baek, Kwon, Lee, Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Case Report and Suggestions to Overcome Obstacles, Journal of Korean Medical Science, doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239
Kurtz, Righy, Gadelha, Bozza, Bozza et al., Effect of Convalescent Plasma in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: An Observational Study, Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.630982
Leng, Cao, Ma, Pathological features of COVID-19-associated lung injury: a preliminary proteomics report based on clinical samples, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00355-9
Li, Zhang, Hu, Tong, Zheng et al., Effect of Convalescent Plasma Therapy on Time to Clinical Improvement in Patients With Severe and Life-threatening COVID-19, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10044
Liu, Wang, Nair, Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2571-7
Manson, Crooks, Naja, Ledlie, Goulden et al., COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: A retrospective longitudinal cohort study, The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30275-7
Marquez, Schwartz, Wu, Transfusion Therapy: Clinical Principles and Practice
Mesina, Mangahas, Gatchalian, Ramos-Ariola, Torres, Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy among Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Single-Center Experience, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.16.21251824
Mi, Zhong, Huang, Zhang, Tan et al., Gender, age and comorbidities as the main prognostic factors in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, American journal of translational research
Nemeth, Ganz, Anemia of Inflammation, Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America, doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2014.04.005
Poggiali, Zaino, Immovilli, Rovero, Losi et al., Lactate dehydrogenase and C-reactive protein as predictors of respiratory failure in CoVID-19 patients, Clinica Chimica Acta, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.012
Sahr, Ansumana, Massaquoi, Idriss, Sesay et al., Evaluation of convalescent whole blood for treating Ebola Virus Disease in freetown, Sierra leone, Journal of Infection
Salazar, Perez, Ashraf, Chen, Castillo et al., Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients with Convalescent Plasma, The American Journal of Pathology, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.05.014
Shen, Wang, Zhao, Yang, Li et al., Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 With Convalescent Plasma, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4783
Siddiqi, Hasan, COVID-19 Illness in Native and Immunosuppressed States: A Clinical-Therapeutic Staging Proposal, The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2031304
Terpos, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Elalamy, Kastritis, Sergentanis et al., Hematological findings and complications of COVID -19, American Journal of Hematology, doi:10.1002/ajh.25829
Yuan, Huang, Ye, Chen, Huang et al., Changes of hematological and immunological parameters in COVID-19 patients, International Journal of Hematology, doi:10.1007/s12185-020-02930-w
Zeng, Chen, Deng, Convalescent plasma for patients with COVID-19, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2006961117
Zeng, Huang, Guo, Yin, Chen et al., Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID-19: A metaanalysis, International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055
Zeng, Ma, Ding, Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients reveals highly potent neutralizing IgA, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00478-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:p>The COVID-19 disease caused by SARS-CoV2 virus has gripped the whole world with overwhelming strain in our health system. Currently, there are no standard guidelines in its treatment but the possible benefits of convalescent plasma in limiting complications and severity of the COVID-19 disease have emerged.</jats:p><jats:sec><jats:title>OBJECTIVE</jats:title><jats:p>This study aims to determine the effectiveness and safety of using convalescent plasma in improving the clinical course of hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19 disease admitted at University of Santo Tomas and Makati Medical Center.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>METHODS</jats:title><jats:p>This study is a quasi-experimental (prospective analytical), and multi-center study involving 65 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 Disease who received convalescent plasma, with 65 patients who only received best available treatment serving as age-gender-matched control.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>RESULTS</jats:title><jats:p>Median age of the population who received convalescent plasma was 60 years old, mostly male (68%), and manifested severe pneumonia (47%). There was noted statistically signifcant decrease between the pre-and post-treatment values of hemoglobin (p=0.04) and LDH (p=0.086). There was also statistically significant increase in platelet counts (p=0.01). WBC and PaO2 increased while ferritin and PFR decreased after convalescent plasma transfusion, however, these were not statistically significant. Length of stay and clinical outcome of those who received convalescent plasma were then compared to age-gender matched controls who only received best available treatment. There was noted statistically significant difference between length of stay (p=0.00) among those who received convalescent plasma as compared to those who did not. This was seen across severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients. There was also more mortality seen in the best available treatment alone group, but this was non-significant.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>CONCLUSIONS</jats:title><jats:p>Convalescent plasma use showed no significant impact in the recovery rate and outcome of patients who received it as compared to those who did not, however, its use was proven to be safe among all patients regardless of the level of severity and clinical profile.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5624-5435",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mesina",
"given": "Flordeluna",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Julian",
"given": "Jomell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Relos",
"given": "Jesus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres",
"given": "Rosalio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Comia",
"given": "Maureen Via M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ongkingco",
"given": "June Marie P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lafavilla",
"given": "Jimmy R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T22:35:21Z",
"timestamp": 1646174121000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-03T19:45:30Z",
"timestamp": 1646336730000
},
"group-title": "Hematology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-14T10:54:43Z",
"timestamp": 1673693683773
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.1",
"unstructured": "Marquez, M. , Schwartz, J. , & Wu, Y. (2019). Transfusion Therapy: Clinical Principles and Practice (4th ed.). Bethesda, MD: AABB Press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thx.41.5.337",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.2"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of convalescent whole blood for treating Ebola Virus Disease in freetown, Sierra leone",
"first-page": "147",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.3",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-004-1271-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4783",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciq106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.7",
"unstructured": "Siddiqi, Hasan K. et al. COVID-19 Illness in Native and Immunosuppressed States: A Clinical-Therapeutic Staging Proposal. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, Volume 0, Issue 0. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.8",
"unstructured": "WHO Interim Guidance for National Health Authorities and Blood Transfusion Services. Version 01. Sept 2014"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.9",
"unstructured": "Decision on convalescent plasma for COVID-19 raises questions. (2020, August 28). Retrieved from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/features/decision-on-convalescent-plasma-for-covid-19-raises-questions/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2031304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.10"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.11",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Tracker: Department of Health website. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.12",
"unstructured": "Convalescent Plasma as Adjunctive Therapy for Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 - Full Text View. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04567173"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.03.20187252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2006961117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.16"
},
{
"article-title": "Gender, age and comorbidities as the main prognostic factors in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"first-page": "6537",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "American journal of translational research",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.17",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5888/pcd17.200247",
"article-title": "Men and COVID-19: A Biopsychosocial Approach to Understanding Sex Differences in Mortality and Recommendations for Practice and Policy Interventions",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200247",
"journal-title": "Prev Chronic Dis",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.18",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hoc.2014.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.19"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.20",
"unstructured": "Abramson, N. , & Melton, B. (2000, November 01). Leukocytosis: Basics of Clinical Assessment. Retrieved from https://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/1101/p2053.html"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.21",
"unstructured": "Leukocytosis and Leukopenia. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.antimicrobe.org/e19.asp"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2014.00649",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25829",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25774",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12185-020-02930-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2004168117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00478-7",
"article-title": "Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients reveals highly potent neutralizing IgA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.28",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.29"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.30",
"unstructured": "Gulhar, R. (2021, April 30). Physiology, Acute Phase Reactants. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519570/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30275-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753466620963035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.198",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.05.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00355-9",
"article-title": "Pathological features of COVID-19-associated lung injury: a preliminary proteomics report based on clinical samples",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "Sig Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.36",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.630982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107239",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2571-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00341-2",
"article-title": "Factors Associated with Good Patient Outcomes Following Convalescent Plasma in COVID-19: A Prospective Phase II Clinical Trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "913",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.42",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.43",
"unstructured": "PSMID Clinical Practice Guidelines for COVID-19 Version 2.1 https://www.psmid.org/cpg-for-covid-19-ver-2-1-as-of-march.../"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.44",
"unstructured": "Interim Treatment guidelines for COVID-19 (version 1.0, dated 2 april 2020) National Center for Infectious Disease Singapore"
},
{
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.45",
"unstructured": "Protocol Summary of Convalescent Plasma to Limit Coronavirus Associated Complications: An Open label, Phase 2A Study of High-titer Anti-SARS COV 2 plasma in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins Collaborative Study."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.16.21251824",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030311450825000_2022.02.23.22271424v1.46",
"unstructured": "Mesina, F. Z. , Mangahas, C. G. , Gatchalian, E. M. , Ramos-Ariola, M. S. , Torres, R. P. (2021). Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy among Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Single-Center Experience. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.16.21251824."
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2022.02.23.22271424"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy with Best Available Treatment (BAT) among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Center Study",
"type": "posted-content"
}