A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia
et al., NEJM, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304, PlasmAr, NCT04383535, Nov 2020
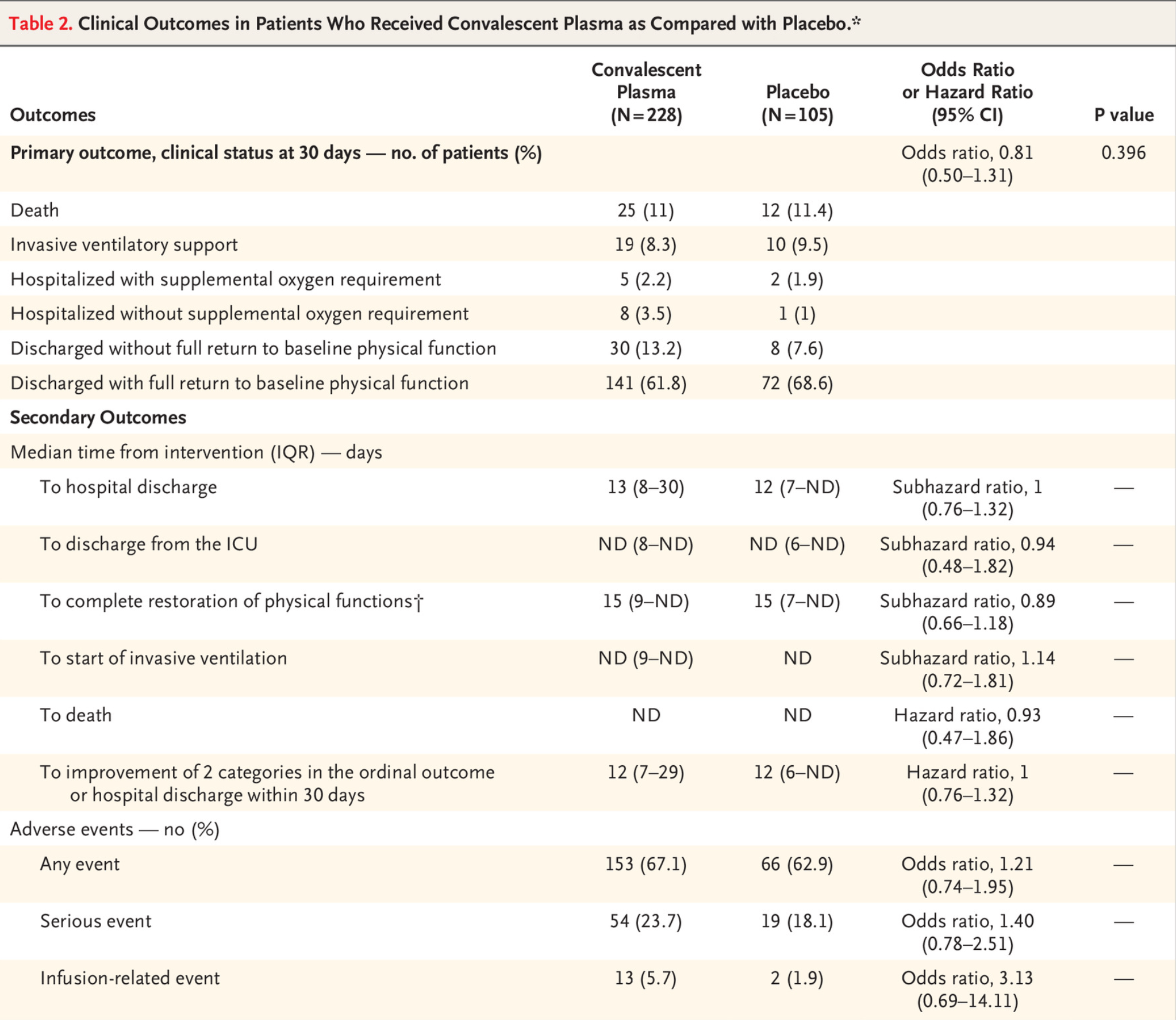
RCT 333 hospitalized patients in Argentina, 228 treated with convalescent plasma, showing no significant differences in clinical status or mortality.
|
risk of death, 4.1% lower, RR 0.96, p = 1.00, treatment 25 of 228 (11.0%), control 12 of 105 (11.4%), NNT 216.
|
|
risk of 7-point scale, 19.0% lower, OR 0.81, p = 0.40, treatment 228, control 105, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Simonovich et al., 24 Nov 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Argentina, peer-reviewed, 39 authors, study period 28 May, 2020 - 27 August, 2020, average treatment delay 8.0 days, trial NCT04383535 (history) (PlasmAr).
A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia
New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2031304
BACKGROUND Convalescent plasma is frequently administered to patients with Covid-19 and has been reported, largely on the basis of observational data, to improve clinical outcomes. Minimal data are available from adequately powered randomized, controlled trials.
METHODS We randomly assigned hospitalized adult patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia in a 2:1 ratio to receive convalescent plasma or placebo. The primary outcome was the patient's clinical status 30 days after the intervention, as measured on a six-point ordinal scale ranging from total recovery to death.
RESULTS A total of 228 patients were assigned to receive convalescent plasma and 105 to receive placebo. The median time from the onset of symptoms to enrollment in the trial was 8 days (interquartile range, 5 to 10), and hypoxemia was the most frequent severity criterion for enrollment. The infused convalescent plasma had a median titer of 1:3200 of total SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (interquartile range, 1:800 to 1:3200). No patients were lost to follow-up. At day 30 day, no significant difference was noted between the convalescent plasma group and the placebo group in the distribution of clinical outcomes according to the ordinal scale (odds ratio, 0.83 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.52 to 1.35; P = 0.46). Overall mortality was 10.96% in the convalescent plasma group and 11.43% in the placebo group, for a risk difference of −0.46 percentage points (95% CI, −7.8 to 6.8). Total SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers tended to be higher in the convalescent plasma group at day 2 after the intervention. Adverse events and serious adverse events were similar in the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS No significant differences were observed in clinical status or overall mortality between patients treated with convalescent plasma and those who received placebo. (PlasmAr ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04383535.
The New England Journal of Medicine
TRACK THIS ARTICLE'S IMPACT AND REACH Visit the article page at NEJM.org and click on Metrics for a dashboard that logs views, citations, media references, and commentary. NEJM.org/about-nejm/article-metrics.
References
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open-label phase II multicentre ran
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -preliminary report: reply, N Engl J Med
Cheng, Wong, Soo, Use of convalescent plasma therapy in SARS patients in Hong Kong, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Harris, Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) -planning, collecting and managing data for clinical and translational research, BMC Bioinformatics
Hung, To, Lee, Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection, Clin Infect Dis
Joyner, Bruno, Klassen, Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients, Mayo Clin Proc
Joyner, Senefeld, Klassen, Effect of convalescent plasma on mortality among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: initial three-month experience, doi:10.1101/2020.08.12.20169359v1
Luke, Kilbane, Jackson, Hoffman, Meta-analysis: convalescent blood products for Spanish influenza pneumonia: a future H5N1 treatment?, Ann Intern Med
Maiztegui, Fernandez, De Damilano, Efficacy of immune plasma in treatment of Argentine haemorrhagic fever and association between treatment and a late neurological syndrome, Lancet
Oguntuyo, Stevens, Hung, Quantifying absolute neutralization titers against SARS-CoV-2 by a standardized virus neutralization assay allows for cross-cohort comparisons of COVID-19 sera, doi:10.1101/2020.08.13.20157222v2
Shen, Wang, Zhao, Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma, JAMA
The, Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Van Griensven, Edwards, De Lamballerie, Evaluation of convalescent plasma for Ebola virus disease in Guinea, N Engl J Med
Whitehead, Sample size calculations for ordered categorical data, Stat Med
Zhou, Zhong, Guan, Treatment with convalescent plasma for influenza A (H5N1) infection, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2031304",
"ISSN": [
"0028-4793",
"1533-4406"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1056/NEJMoa2031304"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Simonovich",
"given": "Ventura A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Burgos Pratx",
"given": "Leandro D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Scibona",
"given": "Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Beruto",
"given": "María V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Vallone",
"given": "Marcelo G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Vázquez",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Savoy",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8427-6033",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Giunta",
"given": "Diego H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Pérez",
"given": "Lucía G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Sánchez",
"given": "Marisa del L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Gamarnik",
"given": "Andrea Vanesa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Ojeda",
"given": "Diego S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Santoro",
"given": "Diego M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Camino",
"given": "Pablo J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Antelo",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Rainero",
"given": "Karina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Vidiella",
"given": "Gabriela P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Miyazaki",
"given": "Erica A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Cornistein",
"given": "Wanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Trabadelo",
"given": "Omar A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "Fernando M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Spotti",
"given": "Mariano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Funtowicz",
"given": "Gabriel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Scordo",
"given": "Walter E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Losso",
"given": "Marcelo H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Ferniot",
"given": "Inés",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Pardo",
"given": "Pablo E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Rodriguez",
"given": "Eulalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Rucci",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Pasquali",
"given": "Julieta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4893-3374",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fuentes",
"given": "Nora A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Esperatti",
"given": "Mariano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Speroni",
"given": "Gerardo A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Nannini",
"given": "Esteban C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Matteaccio",
"given": "Alejandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Michelangelo",
"given": "Hernán G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Follmann",
"given": "Dean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "H. Clifford",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the Clinical Pharmacology Section (V.A.S., P.S., M.V.B., N.S.), Intermediate Care Unit (M.G.V., C.V., H.G.M.), and Infectious Diseases Section (M.L.S.), Department of Internal Medicine, and the Departments of Research (V.A.S., D.H.G., L.G.P., W.H.B.) and Transfusional Medicine (L.D.B.P., D.M.S., P.J.C., S.A.), Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires; Department of Virology, Leloir Institute Foundation, Buenos Aires (A.V.G., D.S.O.), the Departments of Transfusional Medicine (K.R.),..."
}
],
"family": "Belloso",
"given": "Waldo H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "N Engl J Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-24T22:07:37Z",
"timestamp": 1606255657000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-05T14:33:55Z",
"timestamp": 1683297235000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Hospital Privado de la Comunidad"
},
{
"name": "Hospital Zonal Ramón Carrillo de Bariloche"
},
{
"name": "Hospital Privado de Córdoba"
},
{
"name": "Sanatorio Británico de Rosario"
},
{
"name": "Sanatorio Trinidad de Palermo"
},
{
"name": "Clínica Santa Isabel"
},
{
"name": "Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002923",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas"
},
{
"name": "Gobierno de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires"
},
{
"name": "Swiss Medical Group"
},
{
"name": "Hospital Universitario Austral"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-18T08:20:20Z",
"timestamp": 1716020420082
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 667,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
18
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nejmgroup.org/legal/terms-of-use.htm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1613606400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "150",
"original-title": [],
"page": "619-629",
"prefix": "10.1056",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Massachusetts Medical Society",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-145-8-200610170-00139",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(79)92335-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-004-1271-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciq106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc070359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1511812",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-13-S12-A15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.4780122404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4783",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1038-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd4585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r26"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2031304"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "384"
}