Unveiling risk factors for post-COVID-19 syndrome development in people with type 2 diabetes
et al., Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171, Dec 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
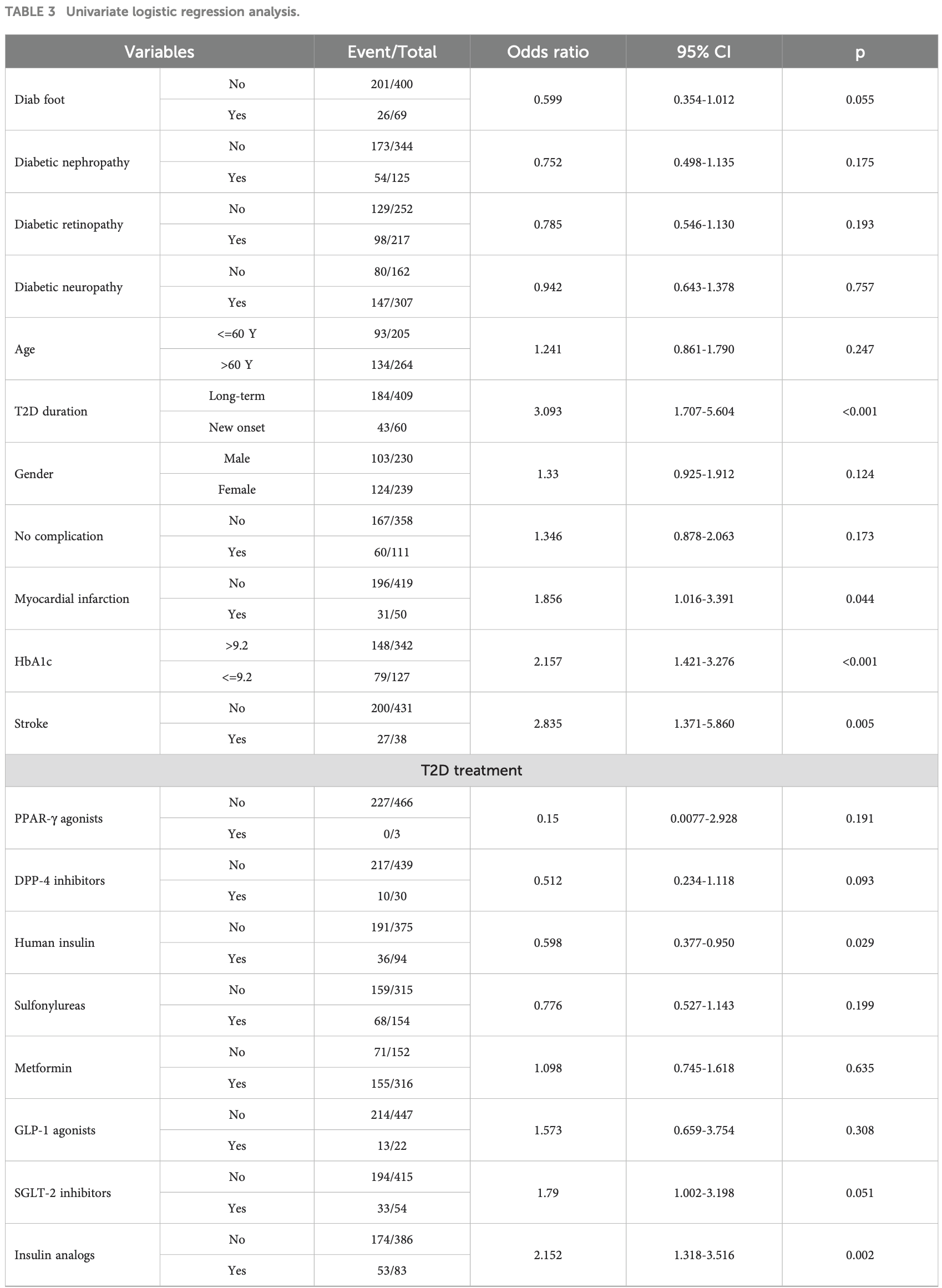
Retrospective 469 patients with type 2 diabetes in Ukraine showing no significant difference in post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) with metformin. There was higher risk with insulin analogs, but lower risk with human insulin.
|
risk of long COVID, 5.0% higher, RR 1.05, p = 0.64, treatment 155 of 316 (49.1%), control 71 of 152 (46.7%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Matviichuk et al., 11 Dec 2024, retrospective, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: nazariikobyliak@gmail.com.
Unveiling risk factors for post-COVID-19 syndrome development in people with type 2 diabetes
Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171
Introduction: Post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) is a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection-associated chronic condition characterized by long-term violations of physical and mental health. People with type 2 diabetes (T2D) are at high risk for severe COVID-19 and PCS.
Aim: The current study aimed to define the predictors of PCS development in people with T2D for further planning of preventive measures and improving patient outcomes.
Materials and methods: The data were collected through the national survey targeting persons with T2D concerning the history of COVID-19 course and signs and symptoms that developed during or after COVID-19 and continued for more than 12 weeks and were not explained by an alternative diagnosis. In total, 469 patients from different regions of Ukraine were enrolled in the study. Among them, 227 patients reported PCS development (main group), while 242 patients did not claim PCS symptoms (comparison group). Stepwise multivariate logistic regression and probabilistic neural network (PNN) models were used to select independent risk factors. Results: Based on the survey data, 8 independent factors associated with the risk of PCS development in T2D patients were selected: newly diagnosed T2D (OR 4.86; 95% CI 2.55-9.28; p<0.001), female sex (OR 1.29; 95% CI 0.86-1.94; p=0.220), COVID-19 severity (OR 1.35 95% CI 1.05-1.70; p=0.018), myocardial infarction (OR 2.42 95% CI 1.26-4.64; p=0.002) and stroke (OR 3.68 95% CI 1.70-7.96; p=0.001) in anamnesis, HbA1c above 9.2% (OR 2.17 95% CI 1.37-3.43; p=0.001), and the use of insulin analogs p=0.003) vs human insulin p=0.146). Although obesity aggravated COVID-19 severity, it did not impact PCS development. In ROC analysis, the 8factor multilayer perceptron (MLP) model exhibited better performance (AUC 0.808; 95% CІ 0.770-0.843), allowing the prediction of the risk of PCS development with a sensitivity of 71.4%, specificity of 76%, PPV of 73.6% and NPV of 73.9%.
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by Bogomolets National Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abumayyaleh, Gil, Mc, Roubin, Romero et al., Post-COVID-19 syndrome and diabetes mellitus: a propensity-matched analysis of the International HOPE-II COVID-19 Registry, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/FENDO.2023.1167087
Bramante, Buse, Liebovitz, Nicklas, Puskarich et al., Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallelgroup, phase 3 trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2
Buchynskyi, Kamyshna, Lyubomirskaya, Moshynets, Kobyliak et al., Efficacy of interferon alpha for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2023.1069894
Cao, Baranova, Wei, Wang, Zhang, Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/JMV.28100
De-Madaria, Capurso, COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: examining the causality, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/S41575-020-00389-Y
Dimnjakovićj, Buble, Ivanko, Pristaši, Brborovićo, Association of anti-diabetic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 and cardiomyopathy, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/S41598-024-57871-9
Fedotkina, Sulaieva, Ozgumus, Cherviakova, Khalimon et al., Novel reclassification of adult diabetes is useful to distinguish stages of b-cell function linked to the risk of vascular complications: the DOLCE study from northern Ukraine, Front Genet, doi:10.3389/FGENE.2021.637945
Feldman, Savelieff, Hayek, Pennathur, Kretzler et al., COVID-19 and diabetes: A collision and collusion of two diseases, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/DBI20-0032
Fernoández-De-Las-Penas, Guijarro, Torres-Macho, Velasco-Arribas, Plaza-Canteli et al., Diabetes and the risk of long-term post-COVID symptoms, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/DB21-0329
Fignani, Licata, Brusco, Nigi, Grieco et al., SARS-coV-2 receptor angiotensin I-converting enzyme type 2 (ACE2) is expressed in human pancreatic b-cells and in the human pancreas microvasculature, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/FENDO.2020.596898
Fleming, Sacks, Pham, Neoh, Ekinci, An overview of COVID-19 in people with diabetes: Pathophysiology and considerations in the inpatient setting, J Br Diabetic Assoc, doi:10.1111/DME.14509
Geerlings, Hoepelman, Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, doi:10.1111/J.1574-695X.1999.TB01397.X
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol, doi:10.1002/PATH.1570
Harding, Oviedo, Ali, Ofotokun, Gander et al., The bidirectional association between diabetes and long-COVID-19 -A systematic review, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/J.DIABRES.2022.110202
Heald, Williams, Jenkins, Stewart, Bakerly et al., The prevalence of long COVID in people with diabetes mellitus-evidence from a UK cohort, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/J.ECLINM.2024.102607
Hegazy, Lithy, Hamid, Wahba, Ashoush et al., COVID-19 disease outcomes: does gastrointestinal burden play a role?, Clin Exp Gastroenterol, doi:10.2147/CEG.S297428
Khunti, Prato, Mathieu, Kahn, Gabbay et al., COVID-19, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/DC21-1318
Kim, Arora, Hsia, Knowler, Leblanc et al., Newonset diabetes after COVID-19, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/CLINEM/DGAD284
Kirbišs, Sobotkiewicz, Schaubach, Zavrsňik, Kokol et al., The effects of diabetes and being overweight on patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome, Infect Dis Rep, doi:10.3390/IDR15060067
Kumar, Sridhar, Nair, Banurekha, Nutman et al., Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with altered CD8(+) T and natural killer cell function in pulmonary tuberculosis, Immunology, doi:10.1111/IMM.12421
Lai, Yang, Sun, Pan, Wang et al., Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism: Clin Exp, doi:10.1016/J.METABOL.2022.155330
Lemhöfer, Bahmer, Baumbach, Besteher, Boekel et al., Variations and predictors of post-COVID syndrome severity in patients attending a post-COVID outpatient clinic, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/JCM12124013
Li, Zhou, Ma, Zhang, Shao et al., The long-term health outcomes, pathophysiological mechanisms and multidisciplinary management of long COVID, Signal transduction targeted Ther, doi:10.1038/S41392-023-01640-Z
Lima-Martıńez, Boada, Madera-Silva, Marıń, Contreras, COVID-19 and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship, Clinica e investigacion en arteriosclerosis: publicacion oficial la Sociedad Espanola Arterioscler, doi:10.1016/J.ARTERI.2020.10.001
Maglietta, Diodati, Puntoni, Lazzarelli, Marcomini et al., Prognostic factors for post-COVID-19 syndrome: A systematic review and metaanalysis, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/JCM11061541
Marushchak, Kozak, Krynytska, Comorbid overweight/obesity and chronic pancreatitis exacerbate the dyslipidemia progression in type 2 diabetic patients, Endocrine Regulations, doi:10.2478/enr-2022-0018
Matviichuk, Yerokhovych, Ilkiv, Krasnienkov, Korcheva et al., HbA1c and leukocyte mtDNA levels as major factors associated with post-COVID-19 syndrome in type 2 diabetes patients, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/S41598-024-77496-2
Mccarthy, Metformin as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Expert Opin pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2215385
Mehandru, Merad, Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/S41590-021-01104-Y
Mittal, Ghosh, Bhatt, Anoop, Ansari et al., High prevalence of post COVID-19 fatigue in patients with type 2 diabetes: A case-control study, Diabetes Metab syndrome, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102302
Moustafa, Jackson, Brotman, Guan, Villicaña et al., ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition-implications for COVID-19, Int J Obes, doi:10.1038/S41366-022-01136-W
Mykhalchyshyn, Kobyliak, Bodnar, Diagnostic accuracy of acyl-ghrelin and it association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients, J Diabetes Metab Disord, doi:10.1186/s40200-015-0170-1
Müller, Groß, Conzelmann, Krüger, Merle et al., SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas, Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/S42255-021-00347-1
Nance, Muir, Lumeng, Adipose tissue macrophages: Regulators of adipose tissue immunometabolism during obesity, Mol Metab, doi:10.1016/J.MOLMET.2022.101642
Nassar, Abosheaishaa, Singh, Misra, Bloomgarden, Noninsulinbased antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13359
Nazari, Pozzilli, Type 2 diabetes and Covid-19: Lessons learnt, unanswered questions and hints for the future, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/J.DIABRES.2023.110896
Nguyen, Ho, Nguyen, Ho, Li et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis, Metabolism: Clin Exp, doi:10.1016/J.METABOL.2022.155196
Ong, Stafford, Mclaughlin, Boyko, Vollset et al., Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6
Petakh, Kobyliak, Kamyshnyi, Gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A culture-based method, Front Cell infection Microbiol, doi:10.3389/FCIMB.2023.1142578
Peŕez-Belmonte, Torres-Peña, Loṕez-Carmona, Ayala-Gutieŕrez, Fuentes-Jimeńez et al., Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/S12916-020-01832-2
Pons, Fodil, Azoulay, Zafrani, The vascular endothelium: the cornerstone of organ dysfunction in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/S13054-020-03062-7
Pranata, Henrina, Raffaello, Lawrensia, Huang, Diabetes and COVID-19: The past, the present, and the future, Metabolism: Clin Exp, doi:10.1016/J.METABOL.2021.154814
Primorac, Vrdoljak, Brlek, Paveliće, Molnar et al., Adaptive immune responses and immunity to SARS-coV-2, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2022.848582
Rajpal, Rahimi, Ismail-Beigi, Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13085
Raveendran, Misra, Post COVID-19 syndrome ("Long COVID") and diabetes: challenges in diagnosis and management, Diabetes Metab syndrome, doi:10.1016/J.DSX.2021.102235
S ̌estan, Marinovićs, Kavazovići, Cekinovićđ, Wueest et al., Virus-induced interferon-g Causes insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and derails glycemic control in obesity, Immunity, doi:10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2018.05.005
Sharma, Tiwari, Deb, Marty, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): a global pandemic and treatment strategies, Int J antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.106054
Sherif, Gomez, Connors, Henrich, Reeves, Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), eLife, doi:10.7554/ELIFE.86002
Souza, Buzzetti, Pozzilli, Diabetes, COVID-19, and questions unsolved, Diabetes/metabolism Res Rev, doi:10.1002/DMRR.3666
Steenblock, Hassanein, Khan, Yaman, Kamel et al., Diabetes and COVID-19: short-and long-term consequences, Hormone Metab Res = Hormon-und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones metabolisme, doi:10.1055/A-1878-9566
Sulaieva, Dudin, Botsun, Pischanska, Karpachova et al., The detrimental consequences of two consecutive disasters impacting cytopathology in Ukraine: COVID followed by the war, Cytopathology: Off J Br Soc Clin Cytology, doi:10.1111/CYT.13236
Tsai, Clemente-Casares, Zhou, Lei, Ahn et al., Insulin receptor-mediated stimulation boosts T cell immunity during inflammation and infection, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/J.CMET.2018.08.003
Turk Wensveen, Gasparini, Rahelićd, Wensveen, Type 2 diabetes and viral infection; cause and effect of disease, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/J.DIABRES.2020.108637
Vigili De Kreutzenberg, Long COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: a short review, Metab Target Organ Damage, doi:10.20517/MTOD.2022.30
Wise, Metformin reduces the risk of developing long term symptoms by 40%, study finds, BMJ (Clinical Res ed), doi:10.1136/BMJ.P1306
Wu, He, Bennett, Li, Chan, Shared genetic mechanism between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19 using pathway-based association analysis, Front Genet, doi:10.3389/FGENE.2022.1063519
Wu, Lidsky, Lee, Cheng, Nakayama, SARS-CoV-2 infects human pancreatic b cells and elicits b cell impairment, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/J.CMET.2021.05.013
Wu, Zhang, Sun, Wang, Xu et al., Influence of diabetes mellitus on the severity and fatality of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/DOM.14105
Xie, Al-Aly, Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00044-4
Yang, Han, Nilsson-Payant, Gupta, Wang et al., A human pluripotent stem cell-based platform to study SARS-coV-2 tropism and model virus infection in human cells and organoids, Cell Stem Cell, doi:10.1016/J.STEM.2020.06.015
Yin, Rohli, Shen, Lu, Liu et al., The epidemiology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and management toward COVID-19 patients with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review, Primary Care Diabetes, doi:10.1016/J.PCD.2021.08.014
Yousri, Suhre, Yassin, Al-Shakaki, Robay et al., Metabolic and metabo-clinical signatures of type 2 diabetes, obesity, retinopathy, and dyslipidemia, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db21-0490
Zemni, Gara, Bennasrallah, Ezzar, Kacem et al., Incidence and risk factors of post COVID-19 syndrome: a Tunisian cohort study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/S12879-023-08949-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171",
"ISSN": [
"1664-2392"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) is a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection-associated chronic condition characterized by long-term violations of physical and mental health. People with type 2 diabetes (T2D) are at high risk for severe COVID-19 and PCS.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Aim</jats:title><jats:p>The current study aimed to define the predictors of PCS development in people with T2D for further planning of preventive measures and improving patient outcomes.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title><jats:p>The data were collected through the national survey targeting persons with T2D concerning the history of COVID-19 course and signs and symptoms that developed during or after COVID-19 and continued for more than 12 weeks and were not explained by an alternative diagnosis. In total, 469 patients from different regions of Ukraine were enrolled in the study. Among them, 227 patients reported PCS development (main group), while 242 patients did not claim PCS symptoms (comparison group). Stepwise multivariate logistic regression and probabilistic neural network (PNN) models were used to select independent risk factors.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Based on the survey data, 8 independent factors associated with the risk of PCS development in T2D patients were selected: newly diagnosed T2D (OR 4.86; 95% CI 2.55–9.28; p&lt;0.001), female sex (OR 1.29; 95% CI 0.86–1.94; p=0.220), COVID-19 severity (OR 1.35 95% CI 1.05–1.70; p=0.018), myocardial infarction (OR 2.42 95% CI 1.26–4.64; p=0.002) and stroke (OR 3.68 95% CI 1.70–7.96; p=0.001) in anamnesis, HbA1c above 9.2% (OR 2.17 95% CI 1.37–3.43; p=0.001), and the use of insulin analogs (OR 2.28 95% CI 1.31–3.94; p=0.003) vs human insulin (OR 0.67 95% CI 0.39–1.15; p=0.146). Although obesity aggravated COVID-19 severity, it did not impact PCS development. In ROC analysis, the 8-factor multilayer perceptron (MLP) model exhibited better performance (AUC 0.808; 95% CІ 0.770–0.843), allowing the prediction of the risk of PCS development with a sensitivity of 71.4%, specificity of 76%, PPV of 73.6% and NPV of 73.9%.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Patients who were newly diagnosed with T2D, had HbA1c above 9.2%, had previous cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events, and had severe COVID-19 associated with mechanical lung ventilation were at high risk for PCS.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matviichuk",
"given": "Anton",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yerokhovych",
"given": "Viktoriia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zemskov",
"given": "Sergii",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilkiv",
"given": "Yeva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurianov",
"given": "Vitalii",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaienko",
"given": "Zlatoslava",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Falalyeyeva",
"given": "Tetyana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sulaieva",
"given": "Oksana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kobyliak",
"given": "Nazarii",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Endocrinology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-11T05:18:00Z",
"timestamp": 1733894280000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-11T05:18:08Z",
"timestamp": 1733894288000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100018227",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100018227",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Research Foundation of Ukraine"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-12T05:18:20Z",
"timestamp": 1733980700574,
"version": "3.30.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1733875200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021",
"author": "Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London England)",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "402",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db21-0490",
"article-title": "Metabolic and metabo-clinical signatures of type 2 diabetes, obesity, retinopathy, and dyslipidemia",
"author": "Yousri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/enr-2022-0018",
"article-title": "Comorbid overweight/obesity and chronic pancreatitis exacerbate the dyslipidemia progression in type 2 diabetic patients",
"author": "Marushchak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Regulations",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.106054",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): a global pandemic and treatment strategies",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J antimicrobial Agents",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/CYT.13236",
"article-title": "The detrimental consequences of two consecutive disasters impacting cytopathology in Ukraine: COVID followed by the war",
"author": "Sulaieva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cytopathology: Off J Br Soc Clin Cytology",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FIMMU.2023.1069894",
"article-title": "Efficacy of interferon alpha for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Buchynskyi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FENDO.2023.1167087",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 syndrome and diabetes mellitus: a propensity-matched analysis of the International HOPE-II COVID-19 Registry",
"author": "Abumayyaleh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FCIMB.2023.1142578",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A culture-based method",
"author": "Petakh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell infection Microbiol",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JMV.28100",
"article-title": "Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.METABOL.2021.154814",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: The past, the present, and the future",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism: Clin Exp",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.DIABRES.2023.110896",
"article-title": "Type 2 diabetes and Covid-19: Lessons learnt, unanswered questions and hints for the future",
"author": "Nazari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13085",
"article-title": "Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Rajpal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "895",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.PCD.2021.08.014",
"article-title": "The epidemiology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and management toward COVID-19 patients with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "Primary Care Diabetes",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FGENE.2022.1063519",
"article-title": "Shared genetic mechanism between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19 using pathway-based association analysis",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Genet",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/DC21-1318",
"article-title": "COVID-19, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/CLINEM/DGAD284",
"article-title": "New-onset diabetes after COVID-19",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102302",
"article-title": "High prevalence of post COVID-19 fatigue in patients with type 2 diabetes: A case-control study",
"author": "Mittal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab syndrome",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.DSX.2021.102235",
"article-title": "Post COVID-19 syndrome (“Long COVID”) and diabetes: challenges in diagnosis and management",
"author": "Raveendran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab syndrome",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41598-024-77496-2",
"article-title": "HbA1c and leukocyte mtDNA levels as major factors associated with post-COVID-19 syndrome in type 2 diabetes patients",
"author": "Matviichuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25533",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "B20",
"unstructured": "Post COVID-19 condition"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00044-4",
"article-title": "Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.DIABRES.2022.110202",
"article-title": "The bidirectional association between diabetes and long-COVID-19 - A systematic review",
"author": "Harding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/IDR15060067",
"article-title": "The effects of diabetes and being overweight on patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Kirbiš",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Rep",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.METABOL.2022.155330",
"article-title": "Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism: Clin Exp",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B25",
"unstructured": "Clinical management of COVID-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CEG.S297428",
"article-title": "COVID-19 disease outcomes: does gastrointestinal burden play a role",
"author": "Hegazy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Gastroenterol",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.MOLMET.2022.101642",
"article-title": "Adipose tissue macrophages: Regulators of adipose tissue immunometabolism during obesity",
"author": "Nance",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol Metab",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41366-022-01136-W",
"article-title": "ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition-implications for COVID-19",
"author": "El-Sayed Moustafa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Obes (2005)",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40200-015-0170-1",
"article-title": "Diagnostic accuracy of acyl-ghrelin and it association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients",
"author": "Mykhalchyshyn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Metab Disord",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/DMRR.3666",
"article-title": "Diabetes, COVID-19, and questions unsolved",
"author": "D’Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes/metabolism Res Rev",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/JCM11061541",
"article-title": "Prognostic factors for post-COVID-19 syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Maglietta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/JCM12124013",
"article-title": "Variations and predictors of post-COVID syndrome severity in patients attending a post-COVID outpatient clinic",
"author": "Lemhöfer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12879-023-08949-8",
"article-title": "Incidence and risk factors of post COVID-19 syndrome: a Tunisian cohort study",
"author": "Zemni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "461",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/DB21-0329",
"article-title": "Diabetes and the risk of long-term post-COVID symptoms",
"author": "Fernóandez-De-las-Penas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13359",
"article-title": "Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nassar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.METABOL.2022.155196",
"article-title": "Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism: Clin Exp",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41598-024-57871-9",
"article-title": "Association of anti-diabetic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 and cardiomyopathy",
"author": "Dimnjaković",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7227",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12916-020-01832-2",
"article-title": "Mortality and other adverse outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus admitted for COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering drugs: a nationwide cohort study",
"author": "Pérez-Belmonte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14656566.2023.2215385",
"article-title": "Metformin as a potential treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "MCCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin pharmacotherapy",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/BMJ.P1306",
"article-title": "Covid-19: Metformin reduces the risk of developing long term symptoms by 40%, study finds",
"author": "Wise",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "p1306",
"journal-title": "BMJ (Clinical Res ed)",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.58347/TML.2023.1677E",
"article-title": "COVID-19 update: Metformin to prevent long COVID",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med letter Drugs Ther",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2",
"article-title": "Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): a multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.ARTERI.2020.10.001",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship",
"author": "Lima-Martínez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clinica e investigacion en arteriosclerosis: publicacion oficial la Sociedad Espanola Arterioscler",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.ECLINM.2024.102607",
"article-title": "The prevalence of long COVID in people with diabetes mellitus-evidence from a UK cohort",
"author": "Heald",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/DOM.14105",
"article-title": "Influence of diabetes mellitus on the severity and fatality of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/A-1878-9566",
"article-title": "Diabetes and COVID-19: short- and long-term consequences",
"author": "Steenblock",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Hormone Metab Res = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones metabolisme",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FIMMU.2022.848582",
"article-title": "Adaptive immune responses and immunity to SARS-coV-2",
"author": "Primorac",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/DME.14509",
"article-title": "An overview of COVID-19 in people with diabetes: Pathophysiology and considerations in the inpatient setting",
"author": "Fleming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetic medicine: J Br Diabetic Assoc",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FGENE.2021.637945",
"article-title": "Novel reclassification of adult diabetes is useful to distinguish stages of β-cell function linked to the risk of vascular complications: the DOLCE study from northern Ukraine",
"author": "Fedotkina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Genet",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/DBI20-0032",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and diabetes: A collision and collusion of two diseases",
"author": "Feldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.DIABRES.2020.108637",
"article-title": "Type 2 diabetes and viral infection; cause and effect of disease",
"author": "Turk Wensveen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CMET.2018.08.003",
"article-title": "Insulin receptor-mediated stimulation boosts T cell immunity during inflammation and infection",
"author": "Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "922",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2018.05.005",
"article-title": "Virus-induced interferon-γ Causes insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and derails glycemic control in obesity",
"author": "Šestan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/J.1574-695X.1999.TB01397.X",
"article-title": "Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM)",
"author": "Geerlings",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/IMM.12421",
"article-title": "Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with altered CD8(+) T and natural killer cell function in pulmonary tuberculosis",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20517/MTOD.2022.30",
"article-title": "Long COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: a short review",
"author": "Vigili de Kreutzenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Metab Target Organ Damage",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41392-023-01640-Z",
"article-title": "The long-term health outcomes, pathophysiological mechanisms and multidisciplinary management of long COVID",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "416",
"journal-title": "Signal transduction targeted Ther",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41590-021-01104-Y",
"article-title": "Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID",
"author": "Mehandru",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/ELIFE.86002",
"article-title": "Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)",
"author": "Sherif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CMET.2021.05.013",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infects human pancreatic β cells and elicits β cell impairment",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1565",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41575-020-00389-Y",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: examining the causality",
"author": "de-Madaria",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/PATH.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S13054-020-03062-7",
"article-title": "The vascular endothelium: the cornerstone of organ dysfunction in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Pons",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "353",
"journal-title": "Crit Care (London England)",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FENDO.2020.596898",
"article-title": "SARS-coV-2 receptor angiotensin I-converting enzyme type 2 (ACE2) is expressed in human pancreatic β-cells and in the human pancreas microvasculature",
"author": "Fignani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S42255-021-00347-1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas",
"author": "Müller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.STEM.2020.06.015",
"article-title": "A human pluripotent stem cell-based platform to study SARS-coV-2 tropism and model virus infection in human cells and organoids",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 66,
"references-count": 66,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1459171/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Unveiling risk factors for post-COVID-19 syndrome development in people with type 2 diabetes",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "15"
}
