The effect of Chronic treatments of Type 2-diabetes mellitus on COVID-19 Morbidity and Symptoms Severity
et al., Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2023.00831, Nov 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
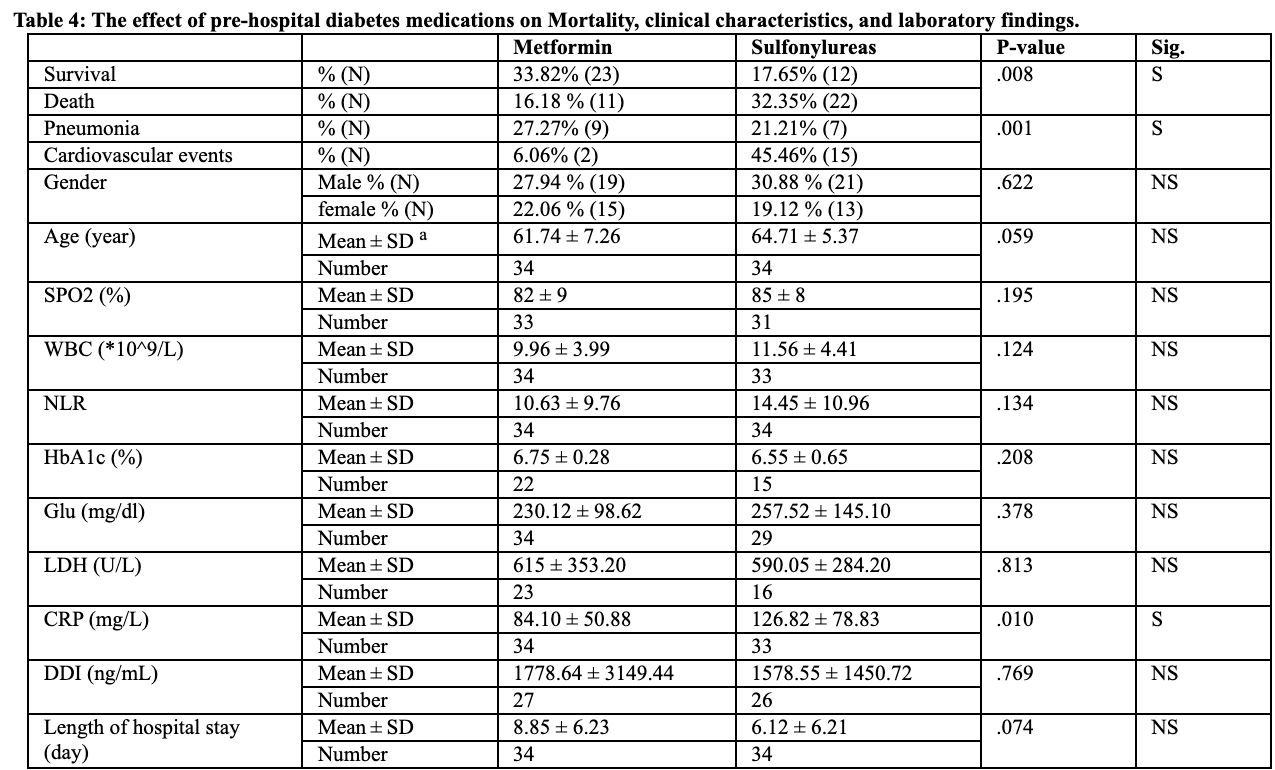
Retrospective 109 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Syria, 68 with diabetes, showing significantly lower mortality with metformin vs. sulfonylureas, and significantly higher mortality with discontinuation of metformin.
|
risk of death, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.01, treatment 11 of 34 (32.4%), control 22 of 34 (64.7%), NNT 3.1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mamari et al., 30 Nov 2023, retrospective, Syria, peer-reviewed, 2 authors, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
The effect of Chronic treatments of Type 2diabetes mellitus on COVID-19 Morbidity and Symptoms Severity
doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2023.00831(
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious viral disease that causes the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and has had a disastrous impact on demographics around the world. Studies have classified type 2-diabetes mellitus (T2DM) as a risk factor for increasing mortality and se-verity of disease symptoms. However, the effect of different T2DMchronic medications on disease progression is still unclear. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of glycemic control on COVID-19-related mortality and symptom severity, as well as the impact of commonly used T2DM therapeutic approaches on disease outcomes. This study included 109 COVID-19 patients with (68 patients) or without (41 patients) type 2-diabetes mellitus. Diabetic patients were further classified according to: 1) their glycemic control [HbA1c levels ˂6.5% (Well-controlled) and ≥ 6.5% (Less-controlled)], or 2) their pre-hospital anti-hyperglycemic med-ication [metformin (50%) or sulfonylureas (50%)]. Our results showed that diabetes is associated with a significantly higher risk of death in COVID-19 pa-tients. We also found that metformin treatment reduces plasma C-reactive protein levels and mortality Compared with sulfonylureas, and continuing with metformin during the hospital stay had a better prog-nostic for survival. We also, demonstrated that taking sulfonylurea is associated with an increase in COVID-19 mortality as compared to metformin by increasing cardiovascular events.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have no conflicts of interest regarding this investigation.
References
Amin, Lux, 'callaghan, The journey of metformin from glycaemic control to mTOR inhibition and the suppression of tumour growth, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.13780
Association, Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc21-S006
Ayoub, Fatima, Kaushik, Pulmonary Aerosolized Formulation or Nasal Drops containing Recombinant Human Angiotensin converting Enzyme 2 (rhACE2) as a Potential Therapy against COVID-19, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00597
Ayoub, Pleiotropic Repositioning of Metformin as a Potential Pluripotent Drug, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00989
Babu, Veerasamy, Sivadasan, Metformin-A Drug of Plant Origin, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.5958/0974-360X.2018.00499
Bode, Garrett, Messler, Glycemic Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in the United States, J Diabetes Sci Technol, doi:10.1177/1932296820924469
Dawood, Altobje, Alnori, Compatibility of the Ligand Binding Sites in the Spike Glycoprotein of COVID-19 with those in the Aminopeptidase and the Caveolins 1, 2 Proteins, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00828
Elnaem, Cheema, Caring for patients with diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic: Important considerations for pharmacists, Res Soc Adm Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.05.030
Gabir, Hanson, Dabelea, The 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for hyperglycemia in the diagnosis and prediction of diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/diacare.23.8.1108
Guo, Li, Dong, Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290
Herman-Edelstein, Guetta, Barnea, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 receptorACE2 in human heart is associated with uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, and activation of the renin angiotensin system, Cardiovasc Diabetol, doi:10.1186/s12933-021-01275-w
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Kondody, Varma, Patil, Cytokine Storm, Immunomodulators and Mucormycosis in COVID-19: Bench To Bed Side, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00818
Krysiak, Gdula-Dymek, Okopieñ, Monocyte-suppressing effect of high-dose metformin in fenofibrate-treated patients with impaired glucose tolerance, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71489-0
Kumar, Arora, Sharma, Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044
Menon, Bhagat, Review of the impact Covid-19 has on the Psychosocial factors affecting Well-Being, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00592
Mishra, Pathak, Mohakuda, Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.09.035
Mor, Saini, Wangnoo, Bawa, Worldwide spread of COVID-19 Pandemic and risk factors among Co-morbid conditions especially Diabetes Mellitus in India, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00450
Patel, Klek, Peragallo-Dittko, Correlation of Hemoglobin A1C and Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19, Endocr Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.07.008
Petersons, Second steps in managing type 2 diabetes, Aust Prescr, doi:10.18773/austprescr.2018.043
Saber, Khodir, Maghmomeh, Nouh, El-Baz, COVID-19 Pandemic: current Challenges and future Perspectives, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00054
Shaty, Al-Ezzi, Arif, Effect of Metformin on inflammatory markers involved in Cardiotoxicity induced by Doxorubicin, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.5958/0974-360X.2019.01007
Simpson, Lee, Choi, Mortality risk among sulfonylureas: a systematic review and network meta-analysis, lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70213-X
Toniolo, Cassani, Puggioni, The diabetes pandemic and associated infections: suggestions for clinical microbiology, Rev Med Microbiol, doi:10.1097/MRM.0000000000000155
Venter, Richter, Towards effective diagnostic assays for COVID-19: a review, J Clin Pathol, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206685
Zakarya, Alfahoum, Exploring COVID-19 Progression Patterns, Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00217
Zhu, Wei, Niu, The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, Glob Heal Res Policy, doi:10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2023.00831",
"ISSN": [
"0974-360X",
"0974-3618"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.52711/0974-360X.2023.00831",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious viral disease that causes the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and has had a disastrous impact on demographics around the world. Studies have classified type 2-diabetes mellitus (T2DM) as a risk factor for increasing mortality and se-verity of disease symptoms. However, the effect of different T2DM-chronic medications on disease progression is still unclear. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of glycemic control on COVID-19-related mortality and symptom severity, as well as the impact of commonly used T2DM therapeutic approaches on disease outcomes. This study included 109 COVID-19 patients with (68 patients) or without (41 patients) type 2-diabetes mellitus. Diabetic patients were further classified according to: 1) their glycemic control [HbA1c levels ˂6.5% (Well-controlled) and ≥ 6.5% (Less-controlled)], or 2) their pre-hospital anti-hyperglycemic med-ication [metformin (50%) or sulfonylureas (50%)]. Our results showed that diabetes is associated with a significantly higher risk of death in COVID-19 pa-tients. We also found that metformin treatment reduces plasma C-reactive protein levels and mortality Compared with sulfonylureas, and continuing with metformin during the hospital stay had a better prog-nostic for survival. We also, demonstrated that taking sulfonylurea is associated with an increase in COVID-19 mortality as compared to metformin by increasing cardiovascular events.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Latakia, Syria Latakia, Syria."
}
],
"family": "Mamari",
"given": "Rozalia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Latakia, Syria Latakia, Syria."
}
],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "Rama",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology",
"container-title-short": "RJPT",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-27T12:41:01Z",
"timestamp": 1706359261000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-27T12:41:06Z",
"timestamp": 1706359266000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-28T00:11:05Z",
"timestamp": 1706400665139
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
30
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "30507",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5130-5136",
"prefix": "10.52711",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "A and V Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2021.00592",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref0",
"unstructured": "Sheila Menon FBSCH, Bhagat V. Review of the impact Covid-19 has on the Psychosocial factors affecting Well-Being. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2021; 14: 3404–3408. doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00592"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Zhu H, Wei L, Niu P. The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Glob Heal Res Policy. 2020; 5:1–3. doi: 10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2022.00217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Zakarya, Zalak A, Alfahoum S, et al. Exploring COVID-19 Progression Patterns. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2022; 15: 1299–1306. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00217"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ww/9780199540884.013.u45730",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the COVID-19 media briefing – 8 June 2022. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-covid-19-media-briefing---8-june-2022. Accessed 9 Jun 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2021.00828",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Dawood AA, Altobje MA, Alnori HAM. Compatibility of the Ligand Binding Sites in the Spike Glycoprotein of COVID-19 with those in the Aminopeptidase and the Caveolins 1, 2 Proteins. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2021; 14:4760–4766. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00828"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2021.00597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Ayoub A, Fatima N, Kaushik V. Pulmonary Aerosolized Formulation or Nasal Drops containing Recombinant Human Angiotensin converting Enzyme 2 (rhACE2) as a Potential Therapy against COVID-19. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2021; 14:3433–3436. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00597"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020; 181:271-280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2022.00054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Saber S, Khodir AE, Maghmomeh AO, Nouh NA, El-Baz AM. COVID-19 Pandemic: current Challenges and future Perspectives. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2022; 15:329–337. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00054"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52711/0974-360x.2022.00818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Kondody RT, Varma SR, Patil A, et al. Cytokine Storm, Immunomodulators and Mucormycosis in COVID-19: Bench To Bed Side. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2022; 15:4871–4875. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00818"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/0974-360x.2020.00450.3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Mor S, Saini P, Wangnoo SK, Bawa T. Worldwide spread of COVID-19 Pandemic and risk factors among Co-morbid conditions especially Diabetes Mellitus in India. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2020; 13:2530–2532. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00450.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.05.030",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Elnaem MH, Cheema E. Caring for patients with diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic: Important considerations for pharmacists. Res Soc Adm Pharm. 2021: 1938. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.05.030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Kumar A, Arora A, Sharma P, et al. Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020: 535–545. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3319",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Guo W, Li M, Dong Y, et al. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020: e3319. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.09.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Mishra Y, Pathak BK, Mohakuda SS, et al. Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Oct 14:1927. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.09.035"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/0974-360x.2018.00499.7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Babu A, Veerasamy R, Sivadasan S. Metformin- A Drug of Plant Origin. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2018; 11: 2701–2708. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2018.00499.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.13780",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Amin S, Lux A, O’Callaghan F. The journey of metformin from glycaemic control to mTOR inhibition and the suppression of tumour growth. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019:37–46. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/0974-360x.2019.01007.2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Shaty MH, Al-Ezzi MI, Arif IS, et al. Effect of Metformin on inflammatory markers involved in Cardiotoxicity induced by Doxorubicin. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2019; 12: 5815–5821. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2019.01007.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5958/0974-360x.2019.00989.2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Ayoub BM. Pleiotropic Repositioning of Metformin as a Potential Pluripotent Drug. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2019; 12: 5716–5722. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00989.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Hariyanto TI, Kurniawan A. Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Obes Med. 2020; 100290. doi: 10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18773/austprescr.2018.043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Petersons CJ. Second steps in managing type 2 diabetes. Aust Prescr. 2018:141. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2018.043"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70213-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Simpson SH, Lee J, Choi S, et al. Mortality risk among sulfonylureas: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015:43–51. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70213-X"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1932296820924469",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Bode B, Garrett V, Messler J, et al. Glycemic Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in the United States. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020: 813–821. doi: 10.1177/1932296820924469"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206685",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Venter M, Richter K. Towards effective diagnostic assays for COVID-19: a review. J Clin Pathol. 2020: 370–377. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206685"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.23.8.1108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Gabir MM, Hanson RL, Dabelea D, et al.The 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for hyperglycemia in the diagnosis and prediction of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000:1108–1112. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.8.1108"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/mrm.0000000000000155",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Toniolo A, Cassani G, Puggioni A, et al. The diabetes pandemic and associated infections: suggestions for clinical microbiology. Rev Med Microbiol. 2019:1. doi: 10.1097/MRM.0000000000000155"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-021-01402-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Herman-Edelstein M, Guetta T, Barnea A, et al. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 receptorACE2 in human heart is associated with uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, and activation of the renin angiotensin system. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01275-w"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71489-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Krysiak R, Gdula-Dymek A, Okopieñ B. Monocyte-suppressing effect of high-dose metformin in fenofibrate-treated patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Pharmacol Rep. 2013; 65:1311–1316. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71489-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-s006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Association AD. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care. 2021: S73-S841. doi: 10.2337/dc21-S006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.07.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Patel AJ, Klek SP, Peragallo-Dittko V, et al. Correlation of Hemoglobin A1C and Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Endocr Pract. 2021: 1046–1051. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.07.008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Henry BM, De Oliveira MHS, Benoit S, et al. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020: 1021–1028. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15605/jafes.036.02.20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Ong AN, Tan CC, Cañete MT, et al, Association Between Metformin Use and Mortality among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hospitalized for COVID-19 Infection. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2021:133. doi: 10.15605/jafes.036.02.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Ursini F, Ciaffi J, Landini MP, et al. COVID-19 and diabetes: Is metformin a friend or foe? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Jun 164:108167. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108167"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201712-2570oc",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "Zhang J, Dong J, Martin M, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelium mitigates pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;8:509–520. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2570OC"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Sharma S, Ray A, Sadasivam B. Metformin in COVID-19: A possible role beyond diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 :108183. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.731974",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Shao S, Yang Q, Pan R, et al. Interaction of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 and Diabetes. Front Endocrinol. 2021. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.731974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.03659-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Kindrachuk J, Ork B, Hart BJ, et al. Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015:1088–1099. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03659-14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2006.02.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Thisted H, Johnsen SP, Rungby J. Sulfonylureas and the risk of myocardial infarction. Metabolism.. 2006 doi.:10.1016/j.metabol.2006.02.004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1056-8727(00)00081-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM. Tissue-specific effects of sulfonylureas: lessons from studies of cloned K(ATP) channels. J Diabetes Complications. 2000:192–196. doi: 10.1016/s1056-8727(00)00081-7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-013-0528-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Nordin C. The proarrhythmic effect of hypoglycemia: evidence for increased risk from ischemia and bradycardia. Acta Diabetol. 2014: 5–14. doi: 10.1007/s00592-013-0528-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Cheng X, Liu YM, Li H, et al. Metformin Is Associated with Higher Incidence of Acidosis, but Not Mortality, in Individuals with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020: 537-547.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://rjptonline.org/AbstractView.aspx?PID=2023-16-11-25"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The effect of Chronic treatments of Type 2-diabetes mellitus on COVID-19 Morbidity and Symptoms Severity",
"type": "journal-article"
}
