25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
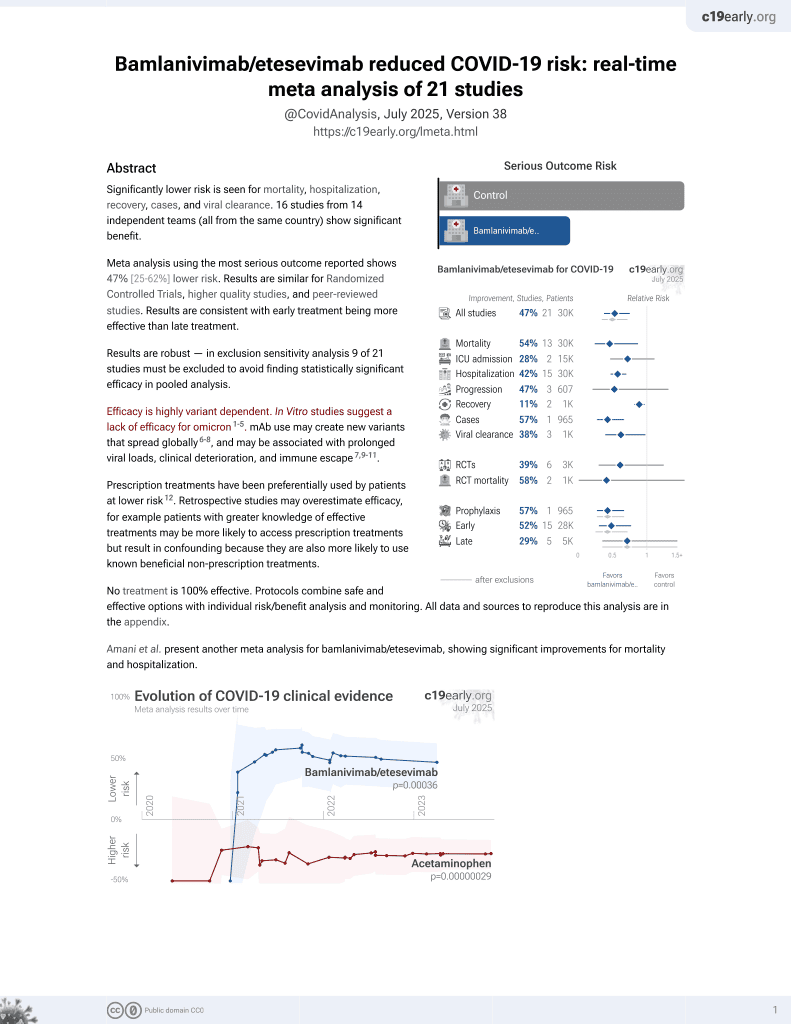
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Interim results from the BLAZE-1 outpatient RCT showing improvements in viral load, symptoms and hospitalization.
Combination therapy significantly reduced viral load at day 11 (p=0.011). A greater effect is seen at day 7 (p<0.001). The proportion of patients with persistent high viral load at day 7 for combination therapy was lower (3.0 percent) versus placebo (20.8 percent), corresponding to a nominal p value of p<0.0001 without multiplicity adjustment. No emergent putative resistance variants have been observed thus far in patients treated with combination therapy.
The rate of COVID-related hospitalization and ER visits was lower for patients treated with combination therapy (0.9 percent) versus placebo (5.8 percent), a relative risk reduction of 84.5 percent (p=0.049). This was also similar to observations for LY-CoV555 monotherapy.
Combination therapy has been generally well tolerated with no drug-related serious adverse events. In LY-CoV555 monotherapy studies there have been isolated drug-related infusion reactions or hypersensitivity that were generally mild (two reported as serious infusion reactions, all patients recovered).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization or ER visit, 84.5% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.049, treatment 112, control 156.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Lilly et al., 7 Oct 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, preprint, 1 author, trial NCT04427501 (history).