Viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for lung-transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2
et al., Biosafety and Health, doi:10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004, Oct 2023
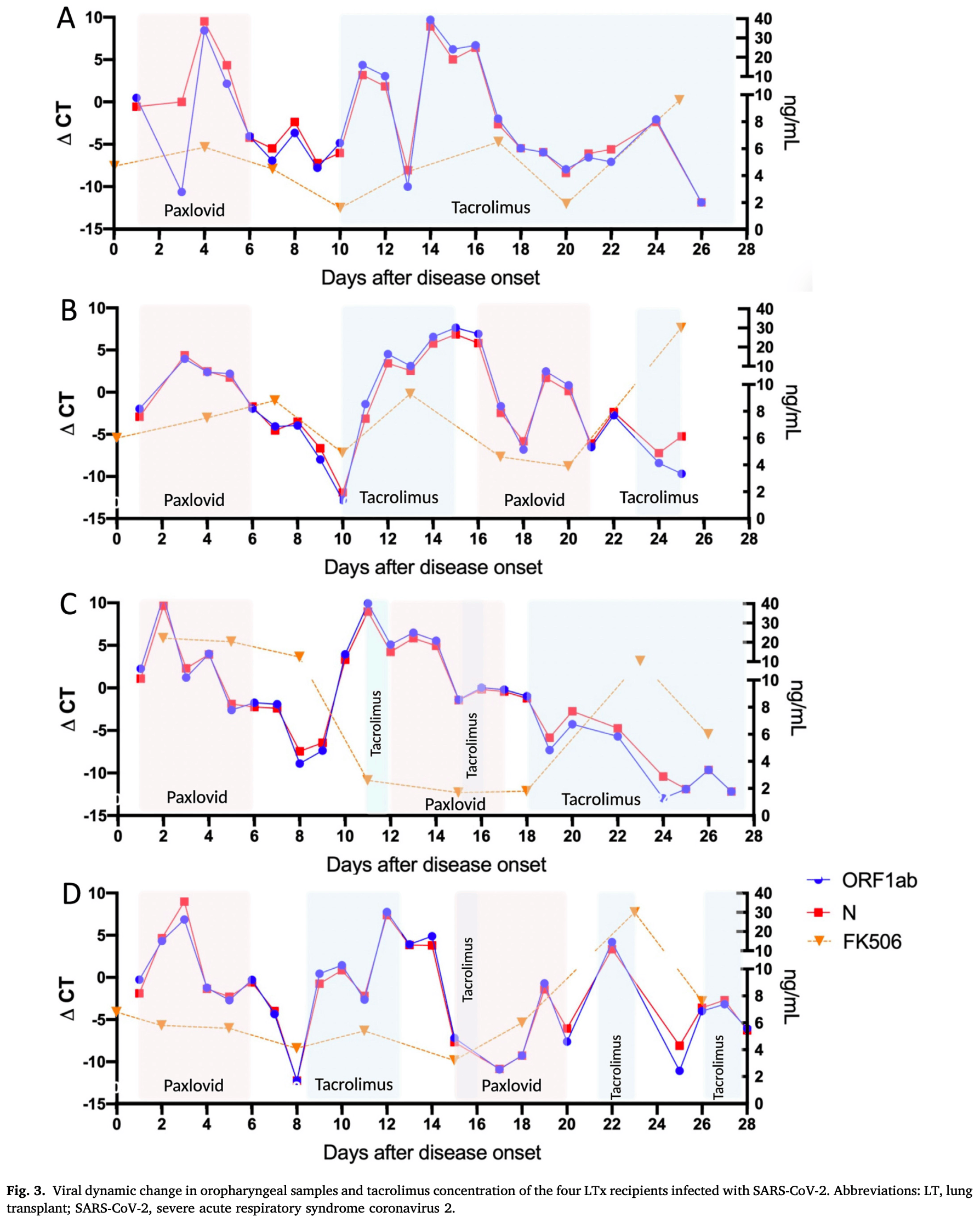
Prospective study of 4 lung transplant recipients showing viral rebound in all patients after initial paxlovid treatment. All four patients received paxlovid within 2 days of SARS-CoV-2 infection, with viral loads initially decreasing but rebounding within 4 days after completing the standard 5-day course. Duration of positive PCR testing was 25-28 days despite antiviral therapy.
Li et al., 31 Oct 2023, prospective, China, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: caobin_ben@163.com, wenhuichen1004@sina.com.
Viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for lung-transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2
Biosafety and Health, doi:10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004
Data on the viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in lung transplant (LTx) recipients are limited. The study prospectively followed four LTx recipients. Clinical characteristics, viral RNA dynamic in throat swabs, and tacrolimus blood concentration were monitored regularly. All four LTx recipients, aged 35-74 years, were not vaccinated against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). They got coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) after more than one week of admission during the era of Omicron. All cases received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NM/r) within two days of infection, and the relative viral RNA copies dropped quickly. Viral load rebound was observed in all four cases after discontinuation of the first five days of NM/r treatment. Three of them received another 5-days antiviral therapy with NM/r. The duration of positive viral PCR testing was 25-28 days. None of them progressed into severe or critical COVID-19. Tacrolimus was stopped 12 h before NM/r and held during the 5-day course of antiviral therapy. Blood concentration of tacrolimus were maintained at a baseline level during these five days. Tacrolimus was reinitiated at its baseline daily dose 3-4 days after NM/r therapy. However, during the second round of antiviral therapy with NM/r, the concentration of tacrolimus fluctuated wildly. In conclusion, the 5-day course of NM/r treatment was not sufficient for LTx recipients and the viral rebound was common. More data are needed to clarify whether LTx recipients with SARS-CoV-2 viral rebound could benefit from additional treatment with NM/r.
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author contributions Hui Li: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writingoriginal draft, Writingreview & editing. Li Zhao: Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writingoriginal draft. Ke Huang: Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writingoriginal draft. Xiaoxing Wang: Methodology, Investigation. Fei Zhou: Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writingoriginal draft. Yiming Feng: Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writingoriginal draft. Liang Ma: Methodology, Investigation. Bin Cao: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writingreview & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources. Wenhui Chen: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writingreview & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources.
References
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
An, Wang, Kim, Kang, Clinical characteristics and outcome of coronavirus disease 2019 infection in patients with solid organ transplants: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.02.002
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Battat, Lavie et al., Nirmatrelvir use and severe Covid-19 outcomes during the Omicron surge, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919
Bonhoeffer, May, Shaw, Nowak, Virus dynamics and drug therapy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A, doi:10.1073/pnas.94.13.6971
Charness, Gupta, Stack, Strymish, Adams et al., Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 infection after Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir treatment, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2206449
Dai, Lee, Nathanson, Leonelli, Petros et al., Viral kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron infection in mRNA-vaccinated individuals treated and not treated with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.08.04.22278378
Devresse, Briol, De Greef, Lemaitre, Boland et al., Efficacy, and relapse of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in kidney transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2, Kidney Int. Rep, doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2022.08.026
Esper, Adhikari, Tu, Cheng, El-Haddad et al., Alpha to Omicron: Disease severity and clinical outcomes of major SARS-CoV-2 variants, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac411
Hansen, Friis, Bager, Stegger, Fonager et al., Risk of reinfection, vaccine protection, and severity of infection with the BA.5 omicron subvariant: a nation-wide population-based study in Denmark, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac411
Hsu, Granneman, Rj, Ritonavir, Clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents, Clin. Pharmacokinet, doi:10.2165/00003088-199835040-00002
Hyams, Challen, Marlow, Nguyen, Begier et al., Severity of Omicron (B.1.1.529) and Delta (B.1.617.2) SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospitalised adults: A prospective cohort study in Bristol, United Kingdom, Lancet Reg Health Eur, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.8823
Kotecha, Ivulich, Snell, Review: immunosuppression for the lung transplant patient, J. Thoracic Dis, doi:10.21037/jtd-2021-11
Kozlov, COVID drug Paxlovid was hailed as a game-changer. What happened?, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-022-04576-6
Kremer, Pieters, Verhaar, Berger, Bakker et al., A systematic review and metaanalysis of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: Lessons to be learned, Am. J. Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.16742
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Khoury, Amar et al., Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac443
Pan, Wang, Feng, Xu, Li et al., Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Beijing during 2022: an epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00129-0
Raja, Mendoza, Villavicencio, Anjan, Reynolds et al., COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature, Transplantat. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.trre.2020.100588
Salerno, Jennings, Lange, Kovac, Shertel et al., Early clinical experience with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients, Am. J. Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.17027
Vo, La, Wu, Strymish, Ronan et al., Factors associated with severe COVID-19 among vaccinated adults treated in US veterans affairs hospitals, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.40037
Wang, Berger, Davis, Kaelber, Volkow et al., COVID-19 rebound after Paxlovid and Molnupiravir during, doi:10.1101/2022.06.21.22276724
Wang, Liu, Wang, Li, Tian et al., Clinical characteristics of 1,139 mild cases of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infected patients in Shanghai, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28224
Wolter, Jassat, Walaza, Welch, Moultrie et al., Clinical severity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 lineages compared to BA.1 and Delta in South Africa, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33614-0
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Realworld effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004",
"ISSN": [
"2590-0536"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004",
"alternative-id": [
"S2590053623001064"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for lung-transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Biosafety and Health"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Chinese Medical Association Publishing House. Published by Elsevier BV."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xiaoxing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Fei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feng",
"given": "Yiming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Wenhui",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biosafety and Health",
"container-title-short": "Biosafety and Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-02T23:24:19Z",
"timestamp": 1693697059000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-20T22:17:00Z",
"timestamp": 1703110620000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003345",
"award": [
"2021-I2M-1-049"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100003345",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-29T17:05:36Z",
"timestamp": 1743267936135,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1693353600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2590053623001064?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2590053623001064?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "266-271",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00129-0",
"article-title": "Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Beijing during 2022: an epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "664",
"issue": "10377",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0005",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100556",
"article-title": "Severity of Omicron (B.1.1.529) and Delta (B.1.617.2) SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospitalised adults: A prospective cohort study in Bristol, United Kingdom",
"author": "Hyams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100556",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health Eur",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0010",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33614-0",
"article-title": "Clinical severity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 lineages compared to BA.1 and Delta in South Africa",
"author": "Wolter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5860",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0015",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac411",
"article-title": "Alpha to Omicron: Disease severity and clinical outcomes of major SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Esper",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0020",
"volume": "227",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00595-3",
"article-title": "Risk of reinfection, vaccine protection, and severity of infection with the BA.5 omicron subvariant: a nation-wide population-based study in Denmark",
"author": "Hansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0025",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28224",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 1,139 mild cases of the SARS‐CoV‐2 Omicron variant infected patients in Shanghai",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0030",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.40037",
"article-title": "Factors associated with severe COVID-19 among vaccinated adults treated in US veterans affairs hospitals",
"author": "Vo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0035",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trre.2020.100588",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature",
"author": "Raja",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100588",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transplantat. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0040",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0045",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir use and severe Covid-19 outcomes during the Omicron surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0050",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1213",
"issue": "10359",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0055",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 rebound after Paxlovid and Molnupiravir during January-June 2022 [Preprint]",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0060",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.16742",
"article-title": "A systematic review and meta-analysis of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: Lessons to be learned",
"author": "Kremer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3936",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Transplant.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0065",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2022.02.002",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcome of coronavirus disease 2019 infection in patients with solid organ transplants: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "An",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0070",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0075",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-022-04576-6",
"article-title": "COVID drug Paxlovid was hailed as a game-changer. What happened?",
"author": "Kozlov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"issue": "7943",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0080",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2206449",
"article-title": "Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 infection after Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir treatment",
"author": "Charness",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1045",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0085",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Viral kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron infection in mRNA-vaccinated individuals treated and not treated with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir [Preprint]",
"author": "Dai",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0090",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ekir.2022.08.026",
"article-title": "Efficacy, and relapse of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in kidney transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Devresse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2356",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0095",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/jtd-2021-11",
"article-title": "Review: immunosuppression for the lung transplant patient",
"author": "Kotecha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6628",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Thoracic Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0100",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.94.13.6971",
"article-title": "Virus dynamics and drug therapy",
"author": "Bonhoeffer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6971",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0105",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-199835040-00002",
"article-title": "Clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents",
"author": "Hsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "275",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacokinet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0110",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.17027",
"article-title": "Early clinical experience with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients",
"author": "Salerno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2083",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Transplant.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.08.004_b0115",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2590053623001064"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Viral rebound and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for lung-transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "5"
}