AZD7442 (Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab) for Post-exposure Prophylaxis of Symptomatic COVID-19
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac899 (date from FDA disclosure of results), STORM CHASER, NCT04625972, Dec 2021
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
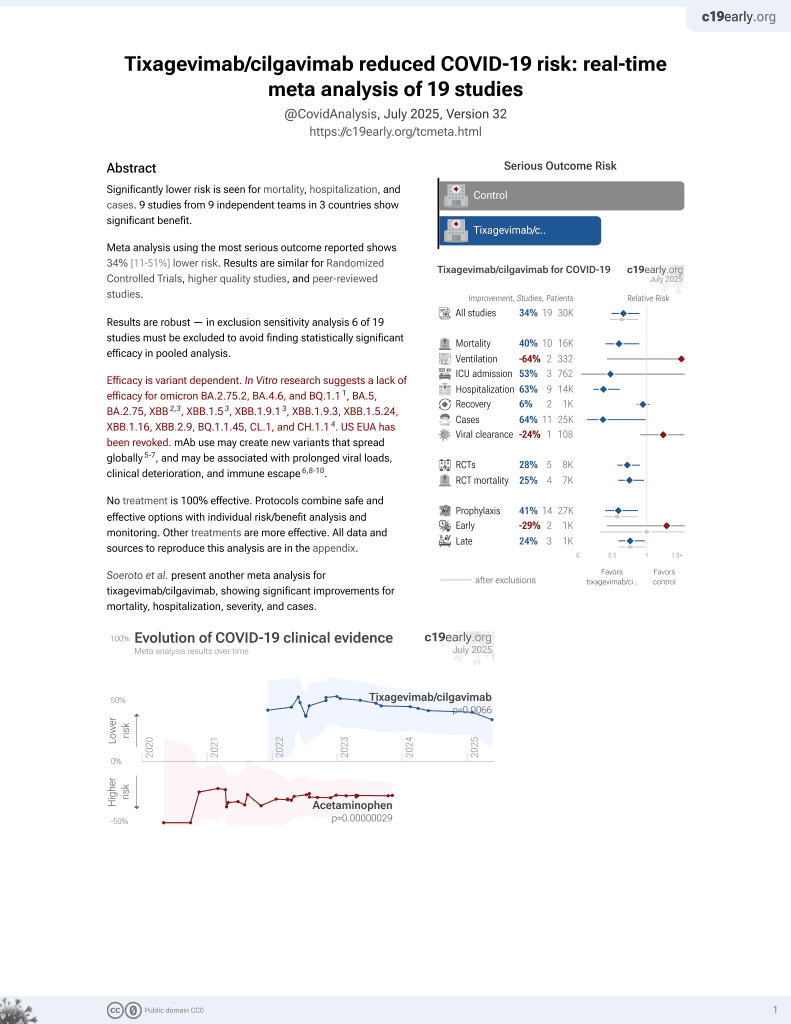
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
1,121 patient PEP RCT showing lower symptomatic cases with tixagevimab/cilgavimab, without statistical significance.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.53, ХВВ.1.9.13, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.14.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments5.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
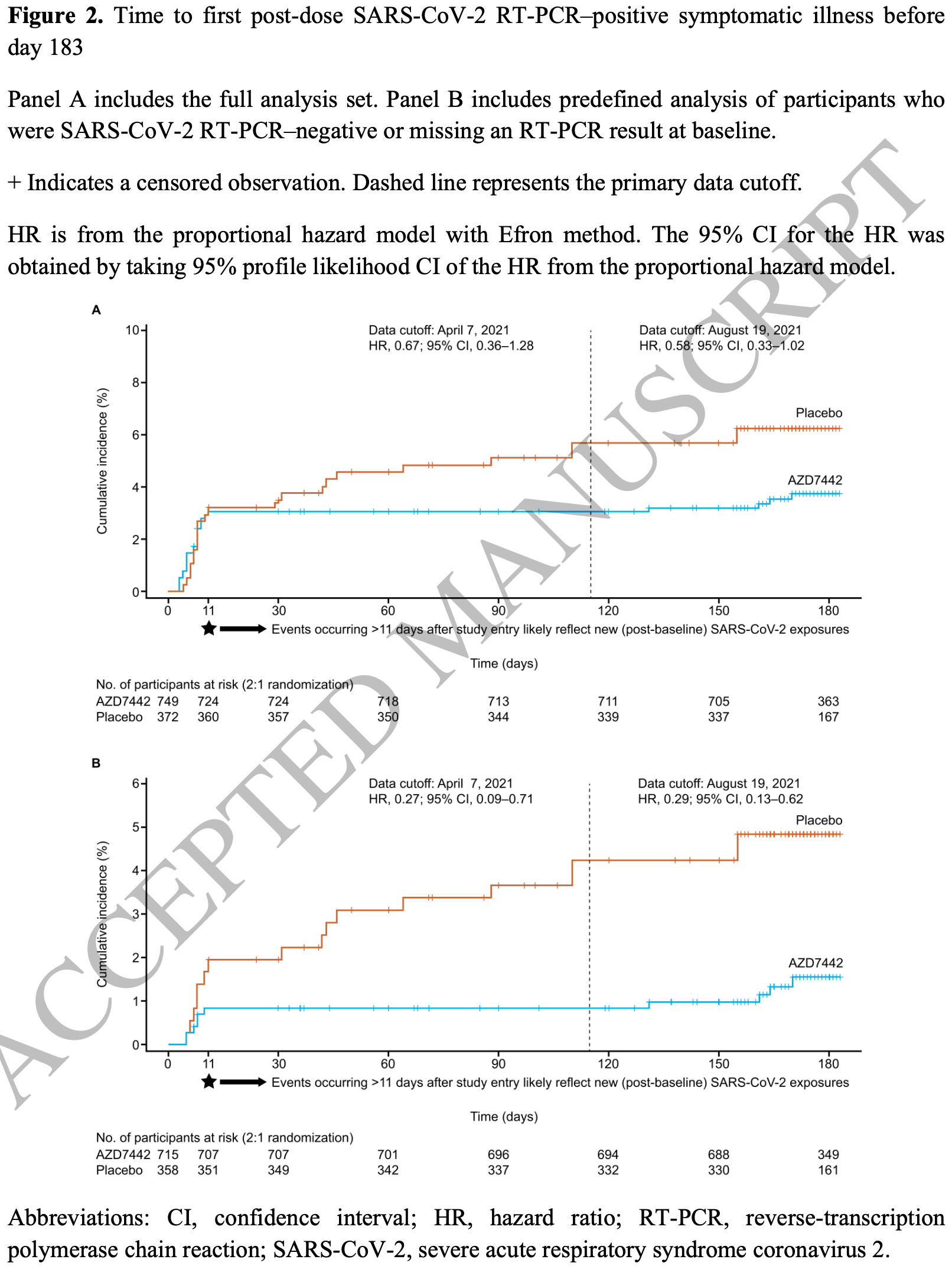
risk of symptomatic case, 41.7% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.06, treatment 27 of 749 (3.6%), control 23 of 372 (6.2%), NNT 39, extended data cutoff.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 32.8% lower, RR 0.67, p = 0.23, treatment 23 of 749 (3.1%), control 17 of 372 (4.6%), NNT 67, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
2.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
3.
Uraki et al., Antiviral efficacy against and replicative fitness of an XBB.1.9.1 clinical isolate, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108147.
Levin et al., 8 Dec 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 46.0, 21 authors, study period 2 December, 2020 - 19 March, 2021, trial NCT04625972 (history) (STORM CHASER).
Contact: mark.esser@astrazeneca.com.
AZD7442 (Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab) for Post-Exposure Prophylaxis of Symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac899
Background: We report primary results of a phase 3 trial of AZD7442 (tixagevimab/cilgavimab) for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 Methods: Adults without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccination were enrolled within 8 days of exposure to a SARS-CoV-2-infected individual and randomized 2:1 to a single 300-mg AZD7442 dose (one 1.5-mL intramuscular injection each of tixagevimab and cilgavimab consecutively) or placebo. Primary endpoints were safety and first post-dose SARS-CoV-2 reverse-transcription-polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR)-positive symptomatic COVID-19 event before day 183. Results: 1121 participants were randomized and dosed (mean age 46 years; 49% females; AZD7442, n=749; placebo, n=372). Median (range) follow-up was 49 (5-115) and 48 (20-113) days for AZD7442 and placebo, respectively. Adverse events occurred in 162/749 (21.6%) and 111/372 (29.8%) participants with AZD7442 and placebo, respectively, mostly mild/moderate. RT-PCR-positive symptomatic COVID-19 occurred in 23/749 (3.1%) and 17/372 (4.6%) AZD7442-and placebo-treated participants, respectively (relative risk reduction 33.3%; 95% confidence interval [CI] -25.9 to 64.7; P=.21). In predefined subgroup analyses of 1073 (96%) participants who were SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-negative (n=974 [87%]) or missing an RT-PCR result (n=99 [9%]) at baseline, AZD7442 reduced RT-PCR-positive symptomatic COVID-19 by 73.2% (95% CI 27.1 to 90.1) versus placebo. Conclusions: This study did not meet the primary efficacy endpoint of post-exposure prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 with AZD7442 versus placebo. However, predefined analysis of participants who were SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-negative or missing an RT-PCR result at baseline support a role for AZD7442 in preventing symptomatic COVID-19.
References
Astrazeneca, Update to Evusheld recommended dosage regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19
Bader, Mckinsey, Postexposure prophylaxis for common infectious diseases, Am Fam Physician
Bernal, Andrews, Gower, Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on COVID-19 related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: Test negative case-control study, Bmj
Brandal, Macdonald, Veneti, Outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in Norway, November to, Euro Surveill
Burugorri-Pierre, Lafuente-Lafuente, Oasi, Investigation of an outbreak of COVID-19 in a French nursing home with most residents vaccinated, JAMA Netw Open
Cao, Yisimayi, Jian, 2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection, Nature
Conte, Golzarri-Arroyo, Tixagevimab and Cilgavimab (Evusheld) boosts antibody levels to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with multiple sclerosis on b-cell depleters, Mult Scler Relat Disord
De Gier, Andeweg, Backer, Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 transmission to household contacts during dominance of Delta variant (B.1.617.2), the Netherlands, Euro Surveill
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell
Dong, Zost, Greaney, Genetic and structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 variant neutralization by a two-antibody cocktail, Nat Microbiol
Ikematsu, Hayden, Kawaguchi, Baloxavir marboxil for prophylaxis against influenza in household contacts, N Engl J Med
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature
Lachiewicz, Srinivas, Varicella-zoster virus post-exposure management and prophylaxis: A review, Preventive medicine reports
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application, Ann Int Med
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) for Prevention of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Loo, Cai, Ren, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination AZD7442 (tixagevimab/cilgavimab) does not interfere with COVID-19 vaccine-induced immunogenicity ECCMID
Loo, Mctamney, Arends, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans, Sci Transl Med
Montgomery, Hobbs, Padilla, Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab-cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent Covid-19, N Engl J Med
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Sarkar, Effect of Subcutaneous Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Combination vs Placebo on Development of Symptomatic COVID-19 in Early Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama
Petros, Turcinovic, Welch, Early introduction and rise of the Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant in highly vaccinated university populations, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac1413
Pritchard, Matthews, Stoesser, Impact of vaccination on new SARS-CoV-2 infections in the United Kingdom, Nat Med
Shitrit, Zuckerman, Mor, Gottesman, Chowers, Nosocomial outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a highly vaccinated population, Israel, July 2021, Euro Surveill
Singanayagam, Hakki, Dunning, Community transmission and viral load kinetics of the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in the UK: A prospective, longitudinal, cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Tuekprakhon, Nutalai, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum, Cell
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med
Young-Xu, Epstein, Marconi, Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab for Prevention of COVID-19 during the Omicron Surge: Retrospective Analysis of National VA Electronic Data, medRxiv
Zhou, Wang, Misasi, Structural basis for potent antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants including B.1.1.529, Science
Zost, Gilchuk, Case, Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Zost, Gilchuk, Chen, Rapid isolation and profiling of a diverse panel of human monoclonal antibodies targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Nat Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac899",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac899",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We report primary results of a phase 3 trial of AZD7442 (tixagevimab/cilgavimab) for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Adults without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccination were enrolled within 8 days of exposure to a SARS-CoV-2–infected individual and randomized 2:1 to a single 300-mg AZD7442 dose (one 1.5-mL intramuscular injection each of tixagevimab and cilgavimab consecutively) or placebo. Primary endpoints were safety and first post-dose SARS-CoV-2 reverse-transcription–polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR)–positive symptomatic COVID-19 event before day 183.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>1121 participants were randomized and dosed (mean age 46 years; 49% females; AZD7442, n=749; placebo, n=372). Median (range) follow-up was 49 (5–115) and 48 (20–113) days for AZD7442 and placebo, respectively. Adverse events occurred in 162/749 (21.6%) and 111/372 (29.8%) participants with AZD7442 and placebo, respectively, mostly mild/moderate. RT-PCR–positive symptomatic COVID-19 occurred in 23/749 (3.1%) and 17/372 (4.6%) AZD7442- and placebo-treated participants, respectively (relative risk reduction 33.3%; 95% confidence interval [CI] –25.9 to 64.7; P=.21). In predefined subgroup analyses of 1073 (96%) participants who were SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR–negative (n=974 [87%]) or missing an RT-PCR result (n=99 [9%]) at baseline, AZD7442 reduced RT-PCR–positive symptomatic COVID-19 by 73.2% (95% CI 27.1 to 90.1) versus placebo.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This study did not meet the primary efficacy endpoint of post-exposure prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 with AZD7442 versus placebo. However, predefined analysis of participants who were SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR–negative or missing an RT-PCR result at baseline support a role for AZD7442 in preventing symptomatic COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Colorado Denver School of Medicine , Aurora, Colorado , USA"
}
],
"family": "Levin",
"given": "Myron J",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "North Manchester General Hospital , Manchester , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Ustianowski",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biometrics, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biometrics, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D , AstraZeneca, Cambridge , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Templeton",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biometrics, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biometrics, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D , AstraZeneca, Cambridge , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Seegobin",
"given": "Seth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Virology, UCL Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust , London , United Kingdom"
},
{
"name": "Department of Infection and Immunity, University College London , London , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Houlihan",
"given": "Catherine F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Project 4 Research , Miami, Florida , USA"
}
],
"family": "Menendez-Perez",
"given": "Ibrahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Clinical Research Program, Department of Preventive Medicine and Biostatistics, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
},
{
"name": "Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, Inc. , Bethesda, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pollett",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Pharmacology and Quantitative Pharmacology, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Arends",
"given": "Rosalinda H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Cambridge , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Beavon",
"given": "Rohini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Dey",
"given": "Kanika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Garbes",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Translational Medicine, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "Elizabeth J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Cambridge , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Koh",
"given": "Gavin C K W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gothenburg , Sweden"
}
],
"family": "Ivanov",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Near",
"given": "Karen A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Development, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Durham, North Carolina , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sharbaugh",
"given": "Audrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Translational Medicine, Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Streicher",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Cambridge , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Pangalos",
"given": "Menelas N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vaccines and Immune Therapies, BioPharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca , Gaithersburg, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Esser",
"given": "Mark T",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T03:59:20Z",
"timestamp": 1669089560000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T03:59:21Z",
"timestamp": 1669089561000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T05:58:08Z",
"timestamp": 1669096688031
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669075200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac899/47174975/ciac899.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac899/47174975/ciac899.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac899/6835900"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "AZD7442 (Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab) for Post-exposure Prophylaxis of Symptomatic COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}