Selective Degradation and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro by MMP14 Reveals a Novel Strategy for COVID-19 Therapeutics
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26199401, Sep 2025
In vitro study showing that matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP14) selectively degrades SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro protease and inhibits viral replication.
Lee et al., 26 Sep 2025, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: dazar@uic.edu (corresponding author), danielhl@uic.edu, ejmulder@uic.edu, ysong211@uic.edu, cchoi46@uic.edu, yjhwang1@uic.edu, lijun@uic.edu, biohan72@uic.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Selective Degradation and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro by MMP14 Reveals a Novel Strategy for COVID-19 Therapeutics
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26199401
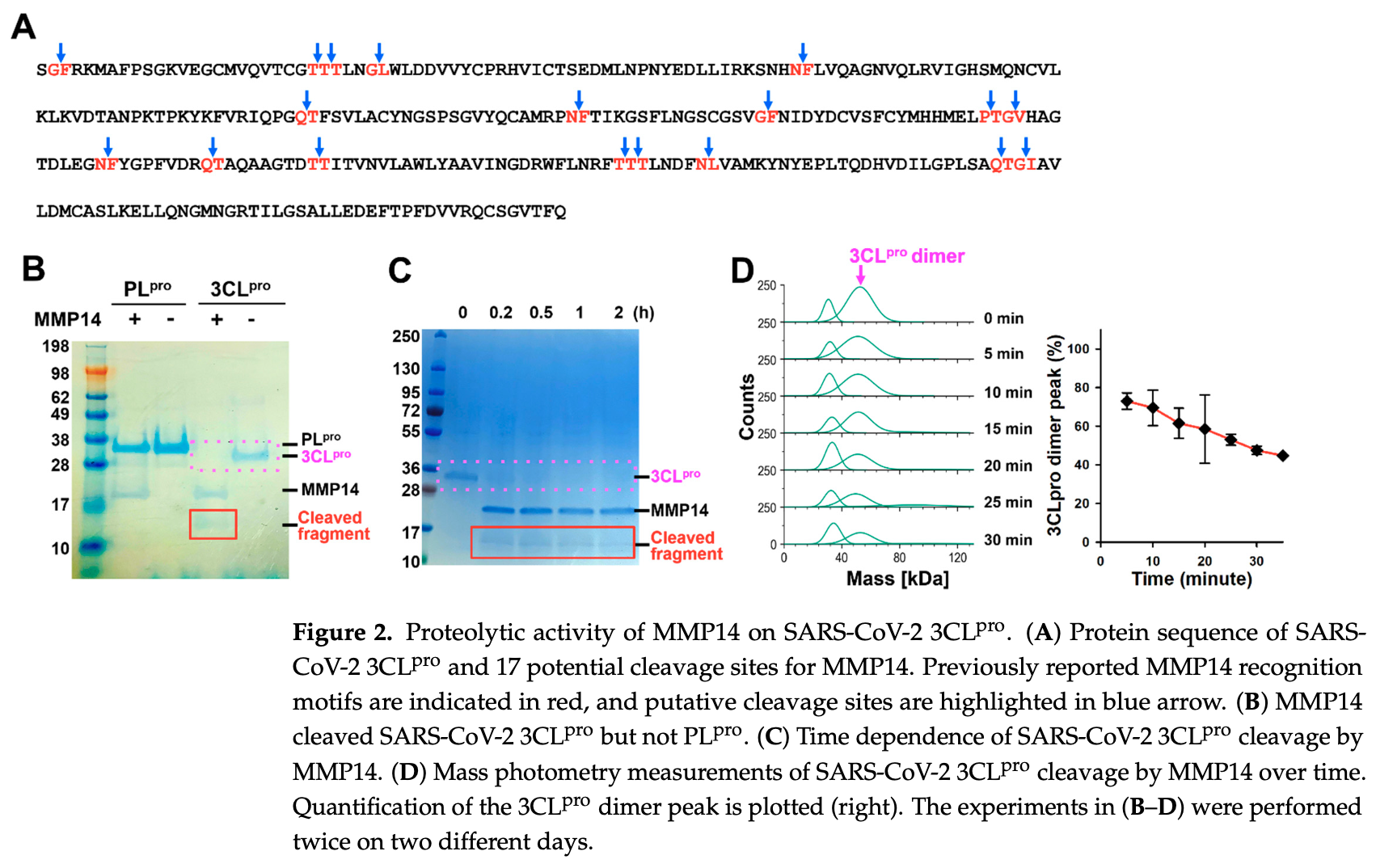
Novel therapies to treat infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of respiratory coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), would be of great clinical value to combat the current and future pandemics. Two viral proteases, papain-like protease (PL pro ) and the main protease 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CL pro ), are vital in processing the SARS-CoV-2 polyproteins (pp1a and pp1ab) and in releasing 16 nonstructural proteins, making them attractive antiviral drug targets. In this study, we investigated the degradation of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease 3CL pro by matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP14). MMP14 is known to recognize over 10 distinct substrate cleavage sequences. Through sequence analysis, we identified 17 and 10 putative MMP14 cleavage motifs within the SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro and PL pro proteases, respectively. Despite the presence of potential sites in both proteins, our in vitro proteolysis assays demonstrated that MMP14 selectively binds to and degrades 3CL pro , but not PL pro . This selective proteolysis by MMP14 results in the complete loss of 3CL pro enzymatic activity. In addition, SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus replication was inhibited in 293 T cells when either full-length MMP14 or its catalytic domain (cat-MMP14) were overexpressed, presumably due to 3CL pro degradation by MMP14. Finally, to prevent MMP14 from degrading off-target proteins, we propose a new recombinant pro-PL-MMP14 construct that can be activated only by another SARS-CoV-2 protease, PL pro . These findings could open the potential of an alternative therapeutic strategy against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
References
Al-Tawfiq, Memish, Update on therapeutic options for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2017.1271712
Alburikan, Abuelizz, Identifying factors and target preventive therapies for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome sucsibtable patients, Saudi Pharm. J, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.016
Apte, Fukai, Beier, Olsen, The matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) gene is structurally distinct from other MMP genes and is co-expressed with the TIMP-2 gene during mouse embryogenesis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.272.41.25511
Arons, Hatfield, Reddy, Kimball, James et al., Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Transmission in a Skilled Nursing Facility, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008457
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19-Preliminary Report, Reply. N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bonnans, Chou, Werb, Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/nrm3904
Cavanagh, Nidovirales: A new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae, Arch. Virol
Ceccarelli, Berretta, Venanzi Rullo, Nunnari, Cacopardo, Differences and similarities between Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)-CoronaVirus (CoV) and SARS-CoV-2. Would a rose by another name smell as sweet?, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Chan, Wong, Jin, Liu, Cao et al., MT1-MMP inactivates ADAM9 to regulate FGFR2 signaling and calvarial osteogenesis, Dev. Cell, doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2012.04.014
Chang, Huang, Cunningham, Han, Chang et al., Matrix metalloproteinase 14 modulates signal transduction and angiogenesis in the cornea, Surv. Ophthalmol, doi:10.1016/j.survophthal.2015.11.006
D'alessio, Ferrari, Cinnante, Scheerer, Galloway et al., Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 binding to membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces MAPK activation and cell growth by a non-proteolytic mechanism, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M705492200
Golubkov, Chekanov, Doxsey, Strongin, Centrosomal pericentrin is a direct cleavage target of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in humans but not in mice: Potential implications for tumorigenesis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M510139200
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Han, Chang, Azar, MMP14 Regulates VEGFR3 Expression on Corneal Epithelial Cells, Protein Pept. Lett, doi:10.2174/0929866523666161024142824
Han, Chang, Lee, Azar, Proangiogenic Interactions of Vascular Endothelial MMP14 With VEGF Receptor 1 in VEGFA-Mediated Corneal Angiogenesis, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci, doi:10.1167/iovs.16-19420
Han, Dugas-Ford, Lee, Chang, Azar, MMP14 Cleavage of VEGFR1 in the Cornea Leads to a VEGF-Trap Antiangiogenic Effect, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci, doi:10.1167/iovs.14-16248
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Kannan, Shaik Syed Ali, Sheeza, Hemalatha, COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus 2019)-Recent trends, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Ksiazek, Erdman, Goldsmith, Zaki, Peret et al., A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030781
Lee, Mittal, Patel, Gatuz, Truong et al., Identification of novel drug scaffolds for inhibition of SARS-CoV 3-Chymotrypsin-like protease using virtual and high-throughput screenings, Bioorg. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.11.041
Liu, Gayle, Wilder-Smith, Rocklöv, The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus, J. Travel Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taaa021
Lombardi, Afsahi, Gupta, Gholamrezanezhad, Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), influenza, and COVID-19, beyond the lungs: A review article, Radiol. Med, doi:10.1007/s11547-020-01311-x
Macpherson, Rainero, Mitchell, Van Den Berghe, Speirs et al., CLIC3 controls recycling of late endosomal MT1-MMP and dictates invasion and metastasis in breast cancer, J. Cell Sci, doi:10.1242/jcs.135947
Massova, Kotra, Fridman, Mobashery, Matrix metalloproteinases: Structures, evolution, and diversification, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fasebj.12.12.1075
Mattei, Roeckel, Olsen, Apte, Genes of the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) gene family, MMP14, MMP15, and MMP16, localize to human chromosomes 14, 16, and 8, respectively, Genomics, doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4559
Morrison, Butler, Rodriguez, Overall, Matrix metalloproteinase proteomics: Substrates, targets, and therapy, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.06.006
Nam, Lee, Ge, Functional Production of Catalytic Domains of Human MMPs in Escherichia coli Periplasm, Methods Mol. Biol
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Paiva, Crews, Targeted protein degradation: Elements of PROTAC design, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.02.022
Pei, Weiss, Furin-dependent intracellular activation of the human stromelysin-3 zymogen, Nature, doi:10.1038/375244a0
Sakamoto, Seiki, A membrane protease regulates energy production in macrophages by activating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 via a non-proteolytic mechanism, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.132704
Sato, Takino, Okada, Cao, Shinagawa et al., A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells, Nature, doi:10.1038/370061a0
Schoeman, Fielding, Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-019-1182-0
Shen, Ratia, Cooper, Kong, Lee et al., Design of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro Inhibitors for COVID-19 Antiviral Therapy Leveraging Binding Cooperativity, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01307
Shin, Mukherjee, Grewe, Bojkova, Baek et al., Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2601-5
Steuten, Kim, Widen, Babin, Onguka et al., Challenges for Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteases as a Therapeutic Strategy for COVID-19, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00815
Tang, Bragazzi, Li, Tang, Xiao et al., An updated estimation of the risk of transmission of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCov), Infect. Dis. Model, doi:10.1016/j.idm.2020.02.001
Van Doremalen, Bushmaker, Morris, Holbrook, Gamble et al., Aerosol and Surface Stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2004973
Virág, Seffer, Varajti, Heged Űs, Jankovics et al., Repurposed Nystatin to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and Mutants in the GI Tract, Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res, doi:10.26717/BJSTR.2021.40.006392
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
Yana, Weiss, Regulation of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activation by proprotein convertases, Mol. Biol. Cell, doi:10.1091/mbc.11.7.2387
Zhang, Lin, Sun, Curth, Drosten et al., Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb3405
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms26199401",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199401",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Novel therapies to treat infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of respiratory coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), would be of great clinical value to combat the current and future pandemics. Two viral proteases, papain-like protease (PLpro) and the main protease 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro), are vital in processing the SARS-CoV-2 polyproteins (pp1a and pp1ab) and in releasing 16 nonstructural proteins, making them attractive antiviral drug targets. In this study, we investigated the degradation of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease 3CLpro by matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP14). MMP14 is known to recognize over 10 distinct substrate cleavage sequences. Through sequence analysis, we identified 17 and 10 putative MMP14 cleavage motifs within the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and PLpro proteases, respectively. Despite the presence of potential sites in both proteins, our in vitro proteolysis assays demonstrated that MMP14 selectively binds to and degrades 3CLpro, but not PLpro. This selective proteolysis by MMP14 results in the complete loss of 3CLpro enzymatic activity. In addition, SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus replication was inhibited in 293 T cells when either full-length MMP14 or its catalytic domain (cat-MMP14) were overexpressed, presumably due to 3CLpro degradation by MMP14. Finally, to prevent MMP14 from degrading off-target proteins, we propose a new recombinant pro-PL-MMP14 construct that can be activated only by another SARS-CoV-2 protease, PLpro. These findings could open the potential of an alternative therapeutic strategy against SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms26199401"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2570-8120",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmaceutical Science, College of Pharmacy & Biophysics Core, the Research Resource Center, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA"
},
{
"name": "Biophysics Core, the Research Resource Center, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Hyun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary, College of Medicine, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60612, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hwang",
"given": "Yunjeong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8613-2340",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biophysics Core, the Research Resource Center, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mulder",
"given": "Elizabeth J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biophysics Core, the Research Resource Center, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Yuri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biophysics Core, the Research Resource Center, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA"
}
],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Calista",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology and Immunology, College of Medicine, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60612, USA"
}
],
"family": "Rong",
"given": "Lijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary, College of Medicine, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60612, USA"
}
],
"family": "Azar",
"given": "Dimitri T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary, College of Medicine, University of Illinois Chicago, Chicago, IL 60612, USA"
}
],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Kyu-Yeon",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.mdpi.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T08:31:28Z",
"timestamp": 1758875488000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T08:37:28Z",
"timestamp": 1758875848000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"R01 R01EY033758 (NEI)",
"R21AI168744 (NIAID)",
"P30 EY001792 (NEI)"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/100000002",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"award": [
"G1781"
],
"name": "Eversight"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T09:10:08Z",
"timestamp": 1758877808115,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "19",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "19",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1758844800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/19/9401/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "9401",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa030781",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Ksiazek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1953",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "An updated estimation of the risk of transmission of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCov)",
"author": "Tang",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Model.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taaa021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "Liu, Y., Gayle, A.A., Wilder-Smith, A., and Rocklöv, J. (2020). The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus. J. Travel Med., 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2008457",
"article-title": "Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Transmission in a Skilled Nursing Facility",
"author": "Arons",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2081",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Nidovirales: A new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae",
"author": "Cavanagh",
"first-page": "629",
"journal-title": "Arch. Virol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "142",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-019-1182-0",
"article-title": "Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge",
"author": "Schoeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2004973",
"article-title": "Aerosol and Surface Stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1",
"author": "Bushmaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1564",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Differences and similarities between Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)-CoronaVirus (CoV) and SARS-CoV-2. Would a rose by another name smell as sweet?",
"author": "Ceccarelli",
"first-page": "2781",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2017.1271712",
"article-title": "Update on therapeutic options for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)",
"author": "Memish",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.016",
"article-title": "Identifying factors and target preventive therapies for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome sucsibtable patients",
"author": "Alburikan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharm. J.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11547-020-01311-x",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), influenza, and COVID-19, beyond the lungs: A review article",
"author": "Lombardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Radiol. Med.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus 2019)—Recent trends",
"author": "Kannan",
"first-page": "2006",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb3405",
"article-title": "Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Preliminary Report. Reply",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "994",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients",
"author": "Musungaie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Repurposed Nystatin to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and Mutants in the GI Tract",
"author": "Seffer",
"first-page": "31854",
"journal-title": "Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01307",
"article-title": "Design of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro Inhibitors for COVID-19 Antiviral Therapy Leveraging Binding Cooperativity",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2940",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.02.022",
"article-title": "Targeted protein degradation: Elements of PROTAC design",
"author": "Paiva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/geno.1996.4559",
"article-title": "Genes of the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) gene family, MMP14, MMP15, and MMP16, localize to human chromosomes 14, 16, and 8, respectively",
"author": "Mattei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Genomics",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.272.41.25511",
"article-title": "The matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) gene is structurally distinct from other MMP genes and is co-expressed with the TIMP-2 gene during mouse embryogenesis",
"author": "Apte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25511",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "272",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm3904",
"article-title": "Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease",
"author": "Bonnans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "786",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929866523666161024142824",
"article-title": "MMP14 Regulates VEGFR3 Expression on Corneal Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1095",
"journal-title": "Protein Pept. Lett.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ceb.2009.06.006",
"article-title": "Matrix metalloproteinase proteomics: Substrates, targets, and therapy",
"author": "Morrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "645",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-7595-2_7",
"article-title": "Functional Production of Catalytic Domains of Human MMPs in Escherichia coli Periplasm",
"author": "Nam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "1731",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/370061a0",
"article-title": "A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells",
"author": "Sato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "370",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1167/iovs.14-16248",
"article-title": "MMP14 Cleavage of VEGFR1 in the Cornea Leads to a VEGF-Trap Antiangiogenic Effect",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5450",
"journal-title": "Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1167/iovs.16-19420",
"article-title": "Proangiogenic Interactions of Vascular Endothelial MMP14 With VEGF Receptor 1 in VEGFA-Mediated Corneal Angiogenesis",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3313",
"journal-title": "Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fasebj.12.12.1075",
"article-title": "Matrix metalloproteinases: Structures, evolution, and diversification",
"author": "Massova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1075",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.survophthal.2015.11.006",
"article-title": "Matrix metalloproteinase 14 modulates signal transduction and angiogenesis in the cornea",
"author": "Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "478",
"journal-title": "Surv. Ophthalmol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2012.04.014",
"article-title": "MT1-MMP inactivates ADAM9 to regulate FGFR2 signaling and calvarial osteogenesis",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1176",
"journal-title": "Dev. Cell",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M705492200",
"article-title": "Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 binding to membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces MAPK activation and cell growth by a non-proteolytic mechanism",
"author": "Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M110.132704",
"article-title": "A membrane protease regulates energy production in macrophages by activating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 via a non-proteolytic mechanism",
"author": "Sakamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29951",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/375244a0",
"article-title": "Furin-dependent intracellular activation of the human stromelysin-3 zymogen",
"author": "Pei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "244",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "375",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.11.7.2387",
"article-title": "Regulation of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activation by proprotein convertases",
"author": "Yana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2387",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "CLIC3 controls recycling of late endosomal MT1-MMP and dictates invasion and metastasis in breast cancer",
"author": "Macpherson",
"first-page": "3893",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Sci.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "127 Pt 18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M510139200",
"article-title": "Centrosomal pericentrin is a direct cleavage target of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in humans but not in mice: Potential implications for tumorigenesis",
"author": "Golubkov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42237",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "280",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2601-5",
"article-title": "Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity",
"author": "Shin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "587",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00815",
"article-title": "Challenges for Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteases as a Therapeutic Strategy for COVID-19",
"author": "Steuten",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1457",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2013.11.041",
"article-title": "Identification of novel drug scaffolds for inhibition of SARS-CoV 3-Chymotrypsin-like protease using virtual and high-throughput screenings",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/19/9401"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Selective Degradation and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro by MMP14 Reveals a Novel Strategy for COVID-19 Therapeutics",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3390/mdpi_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "26"
}