Role of Zinc and Clinicopathological Factors for COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis (CAM) in a Rural Hospital of Central India: A Case-Control Study
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.22528, Feb 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
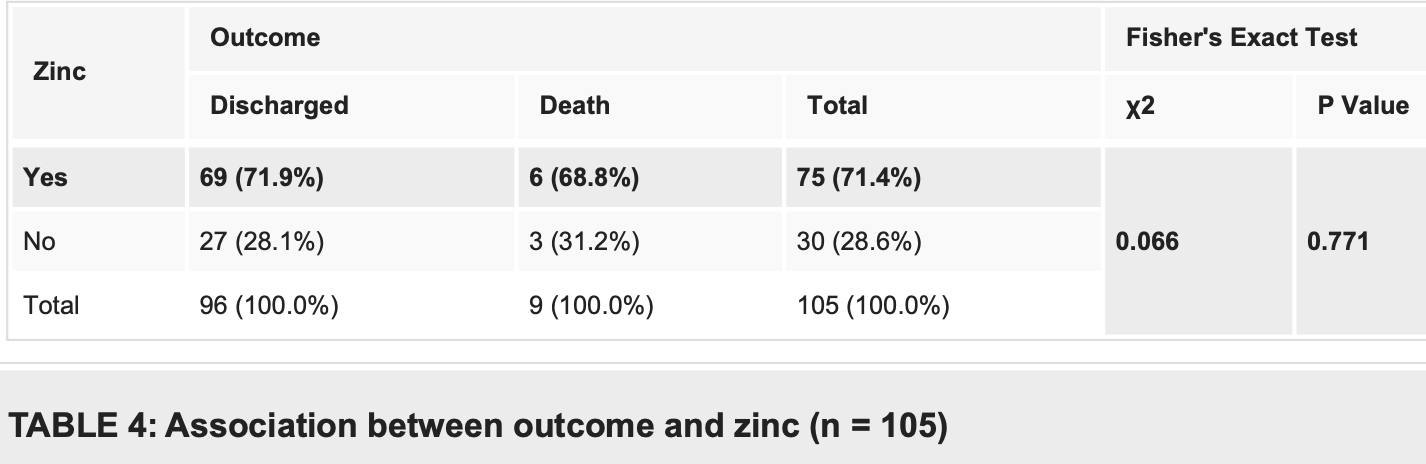
Case control study of 105 COVID-19 patients in India, 55 with mucormycosis and 50 without, showing zinc prophylaxis and diabetes both associated with mucormycosis in unadjusted results. This is likely confounded because zinc supplementation is commonly used with diabetes1, and Arora et al. show lower risk of mucormycosis with zinc prophylaxis, aOR 0.05 [0.01-0.19]2. There was no significant difference in mortality based on zinc prophylaxis in unadjusted results.
Table 3 reports 93 total discharged patients and 12 total deaths. However, Table 4 reports 96 total discharged patients and 9 total deaths.
The reported chi-square statistic in Table 3 is 12.158 with a p-value less than 0.001. However, manual calculation of the 2x2 table (46/9 vs 47/3) yields a chi-square of approximately 2.76 and a non-significant p-value of 0.096.
Table 1 and the abstract report steroid use as 54 out of 55 (98.2%) in cases and 27 out of 50 (54.0%) in controls, yet list the p-value as 1.000. A Fisher's exact test for this distribution yields a p-value of less than 0.0001.
Authors do not perform any multivariate analysis to adjust for large baseline differences. Steroid use (98.2% vs 54%) and diabetes (83.6% vs 16.0%) are highly imbalanced between groups and are established primary drivers of mucormycosis, making the univariate association with zinc of very limited value.
Several variables (AST, ALT, CRP, D-dimer) exhibit standard deviations that are much larger than their respective means (e.g., AST mean 184.04 with SD 1094.36). For non-negative values, this indicates extreme skewness, extreme outliers, or potential data entry errors.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
data issues pending author responsedata issues pending author response; unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of death, 20.0% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.71, treatment 6 of 75 (8.0%), control 3 of 30 (10.0%), NNT 50, unadjusted.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kumar et al., 23 Feb 2022, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period June 2021 - August 2021.
Role of Zinc and Clinicopathological Factors for COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis (CAM) in a Rural Hospital of Central India: A Case-Control Study
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.22528
Introduction Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)has been a difficult enemy to beat for healthcare professionals around the world. However, even before the end of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an emergence of a new combatant in the form of opportunistic fungal infections with a high rate of morbidity and mortality, creating havoc throughout the globe.
Methods A case-control single-center study was conducted in Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, Maharashtra. All the subjects who were included in the study were tested positive for COVID-19 through the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method and the cases were defined as patients with biopsy-proven mucormycosis, whereas control were subjects who did not develop mucormycosis. The duration of the study was three months, from June 2021 to August 2021.
Result A total of 55 cases and 50 controls were enrolled in the study. The use of zinc was found to be significantly associated with COVID-19-associated mucormycosis, with 89.1% of the cases having a history of zinc intake and only 52% of controls having a history of zinc intake( p-value <0.001). Diabetes mellitus was found to be significantly associated with COVID-19-associated mucormycosis with 83.6% of the cases and 16% of the controls having diabetes mellitus (p-value <0.001). Although the use of steroids in cases was more with 98.2% of the cases and 54% of the control receiving steroids; this difference was not significant statistically (p-value of 1.00).
Conclusion We conclude that apart from diabetes mellitus and other immunosuppressive states, zinc might be the hidden culprit behind the sudden surge of COVID-19-associated mucormycosis worldwide owing to the selfadministration of zinc by the patients to acquire innate immunity and over-prescription of multivitamins by the treating clinicians. However, this association required further studies in order to be proved.
Additional Information Disclosures
References
Ahmadikia, Hashemi, Khodavaisy, The double-edged sword of systemic corticosteroid therapy in viral pneumonia: A case report and comparative review of influenza-associated mucormycosis versus COVID-19 associated mucormycosis, Mycoses, doi:10.1111/myc.13256
Alanio, Dellière, Fodil, Bretagne, Mégarbane, Prevalence of putative invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30237-X
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin d for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Bawiskar, Talwar, Acharya, Kumar, Hematological manifestations of COVID-19 and their prognostic significance in an intensive care unit: a cross-sectional study, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.19887
Gupta, Kesavadev, Krishnan, COVID-19 associated mucormycosis: a descriptive multisite study from India, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102322
John, Jacob, Kontoyiannis, When uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and severe COVID-19 converge: the perfect storm for mucormycosis, J Fungi, doi:10.3390/jof7040298
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Kehl-Fie, Skaar, Nutritional immunity beyond iron: a role for manganese and zinc, Curr Opin Chem Biol, doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.11.008
Kumar, Dronamraju, Acharya, COVID-PIRO (predisposition, insult, response, organ dysfunction) score: a reliable predictor of outcomes in COVID-19 patients admitted in intensive care unit, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.18960
Leonardelli, Macedo, Dudiuk, Theill, Cabeza et al., In vitro activity of combinations of zinc chelators with amphotericin b and posaconazole against six Mucorales species, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00266-19
Mishra, Prashar, Sharma, Akash, Kumar et al., Diabetes, COVID 19 and mucormycosis: clinical spectrum and outcome in a tertiary care medical center in Western India, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102196
Muthu, Kumar, Paul, Is there an association between zinc and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis? Results of an experimental and clinical study, Mycoses, doi:10.1111/myc.13365
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9
Salehi, Ahmadikia, Badali, Khodavaisy, Opportunistic fungal infections in the epidemic area of COVID-19: a clinical and diagnostic perspective from Iran, Mycopathologia, doi:10.1007/s11046-020-00472-7
Selarka, Sharma, Saini, Mucormycosis and COVID-19: an epidemic within a pandemic in India, Mycoses, doi:10.1111/myc.13353
Sen, Honavar, Bansal, Epidemiology, clinical profile, management, and outcome of COVID-19-associated rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis in 2826 patients in India -collaborative OPAI-IJO study on mucormycosis in COVID-19 (COSMIC), report 1, Indian J Ophthalmol, doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1565_21
Singh, Singh, Joshi, Misra, Mucormycosis in COVID-19: a systematic review of cases reported worldwide and in India, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.019
Talwar, Kumar, Acharya, Interleukin 6 and its correlation with COVID-19 in terms of outcomes in an intensive care unit of a rural hospital: a cross-sectional study, Indian J Crit Care Med, doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24075
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.22528",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.22528",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Sunil",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acharya",
"given": "Sourya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "Shraddha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shukla",
"given": "Samarth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talwar",
"given": "Dhruv",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Divit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulkoti",
"given": "Vidyashree",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parveen",
"given": "Sana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Mansi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Sujal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Cureus"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T16:25:24Z",
"timestamp": 1645633524000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T16:25:26Z",
"timestamp": 1645633526000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-30T09:54:45Z",
"timestamp": 1648634085206
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2168-8184"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/87998-role-of-zinc-and-clinicopathological-factors-for-covid-19-associated-mucormycosis-cam-in-a-rural-hospital-of-central-india-a-case-control-study",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4492",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cureus, Inc.",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11046-020-00472-7",
"article-title": "Opportunistic fungal infections in the epidemic area of COVID- 19: a clinical and diagnostic perspective from Iran",
"author": "Salehi M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mycopathologia",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Salehi M, Ahmadikia K, Badali H, Khodavaisy S. Opportunistic fungal infections in the epidemic area of COVID- 19: a clinical and diagnostic perspective from Iran. Mycopathologia. 2020, 185:607-11. 10.1007/s11046-020-00472-7",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30237-X",
"article-title": "Prevalence of putative invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Alanio A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Alanio A, Dellière S, Fodil S, Bretagne S, Mégarbane B. Prevalence of putative invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8:e48-9. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30237-X",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/myc.13256",
"article-title": "The double-edged sword of systemic corticosteroid therapy in viral pneumonia: A case report and comparative review of influenza-associated mucormycosis versus COVID-19 associated mucormycosis",
"author": "Ahmadikia K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mycoses",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Ahmadikia K, Hashemi SJ, Khodavaisy S, et al.. The double-edged sword of systemic corticosteroid therapy in viral pneumonia: A case report and comparative review of influenza-associated mucormycosis versus COVID-19 associated mucormycosis. Mycoses. 2021, 64:798-808. 10.1111/myc.13256",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102196",
"article-title": "Diabetes, COVID 19 and mucormycosis: clinical spectrum and outcome in a tertiary care medical center in Western India",
"author": "Mishra Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Mishra Y, Prashar M, Sharma D, Akash, Kumar VP, Tilak TV. Diabetes, COVID 19 and mucormycosis: clinical spectrum and outcome in a tertiary care medical center in Western India. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021, 15:102196. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102196",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/myc.13353",
"article-title": "Mucormycosis and COVID-19: an epidemic within a pandemic in India",
"author": "Selarka L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mycoses",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Selarka L, Sharma S, Saini D, et al.. Mucormycosis and COVID-19: an epidemic within a pandemic in India. Mycoses. 2021, 64:1253-60. 10.1111/myc.13353",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102322",
"article-title": "COVID-19 associated mucormycosis: a descriptive multisite study from India",
"author": "Gupta R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Gupta R, Kesavadev J, Krishnan G, et al.. COVID-19 associated mucormycosis: a descriptive multisite study from India. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021, 15:102322. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102322",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.019",
"article-title": "Mucormycosis in COVID-19: a systematic review of cases reported worldwide and in India",
"author": "Singh AK",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Singh R, Joshi SR, Misra A. Mucormycosis in COVID-19: a systematic review of cases reported worldwide and in India. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021, 15:102146. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.019",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijo.IJO_1565_21",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, clinical profile, management, and outcome of COVID-19-associated rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis in 2826 patients in India - collaborative OPAI-IJO study on mucormycosis in COVID-19 (COSMIC), report 1",
"author": "Sen M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Indian J Ophthalmol",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Sen M, Honavar SG, Bansal R, et al.. Epidemiology, clinical profile, management, and outcome of COVID-19-associated rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis in 2826 patients in India - collaborative OPAI-IJO study on mucormycosis in COVID-19 (COSMIC), report 1. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021, 69:1670-92. 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1565_21",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.11.008",
"article-title": "Nutritional immunity beyond iron: a role for manganese and zinc",
"author": "Kehl-Fie TE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Chem Biol",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Kehl-Fie TE, Skaar EP. Nutritional immunity beyond iron: a role for manganese and zinc. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010, 14:218-24. 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.11.008",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/myc.13365",
"article-title": "Is there an association between zinc and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis? Results of an experimental and clinical study",
"author": "Muthu V",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mycoses",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Muthu V, Kumar M, Paul RA, et al.. Is there an association between zinc and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis? Results of an experimental and clinical study. Mycoses. 2021, 64:1291-7. 10.1111/myc.13365",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9",
"article-title": "Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials",
"author": "Pal A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Pal A, Squitti R, Picozza M, et al.. Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021, 199:2882-92. 10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"article-title": "Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin d for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19",
"author": "Alexander J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Alexander J, Tinkov A, Strand TA, Alehagen U, Skalny A, Aaseth J. Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin d for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19. Nutrients. 2020, 12:2358. 10.3390/nu12082358",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Jothimani D, Kailasam E, Danielraj S, et al.. COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int J Infect Dis. 2020, 100:343-9. 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Thomas S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, et al.. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4:e210369. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00266-19",
"article-title": "In vitro activity of combinations of zinc chelators with amphotericin b and posaconazole against six Mucorales species",
"author": "Leonardelli F",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Leonardelli F, Macedo D, Dudiuk C, Theill L, Cabeza MS, Gamarra S, Garcia-Effron G. In vitro activity of combinations of zinc chelators with amphotericin b and posaconazole against six Mucorales species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019, 63:10.1128/AAC.00266-19",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24075",
"article-title": "Interleukin 6 and its correlation with COVID-19 in terms of outcomes in an intensive care unit of a rural hospital: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Talwar D",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Indian J Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Talwar D, Kumar S, Acharya S, et al.. Interleukin 6 and its correlation with COVID-19 in terms of outcomes in an intensive care unit of a rural hospital: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2022, 26:39-42. 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24075",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.19887",
"article-title": "Hematological manifestations of COVID-19 and their prognostic significance in an intensive care unit: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Bawiskar N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Bawiskar N, Talwar D, Acharya S, Kumar S. Hematological manifestations of COVID-19 and their prognostic significance in an intensive care unit: a cross-sectional study. Cureus. 2021, 13:e19887. 10.7759/cureus.19887",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.18960",
"article-title": "COVID-PIRO (predisposition, insult, response, organ dysfunction) score: a reliable predictor of outcomes in COVID-19 patients admitted in intensive care unit",
"author": "Kumar S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Kumar S, Dronamraju S, Acharya S, et al.. COVID-PIRO (predisposition, insult, response, organ dysfunction) score: a reliable predictor of outcomes in COVID-19 patients admitted in intensive care unit. Cureus. 2021, 13:e18960. 10.7759/cureus.18960",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jof7040298",
"article-title": "When uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and severe COVID-19 converge: the perfect storm for mucormycosis",
"author": "John TM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Fungi (Basel)",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "John TM, Jacob CN, Kontoyiannis DP. When uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and severe COVID-19 converge: the perfect storm for mucormycosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2021, 7:298. 10.3390/jof7040298",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/87998-role-of-zinc-and-clinicopathological-factors-for-covid-19-associated-mucormycosis-cam-in-a-rural-hospital-of-central-india-a-case-control-study"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Aerospace Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Role of Zinc and Clinicopathological Factors for COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis (CAM) in a Rural Hospital of Central India: A Case-Control Study"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
