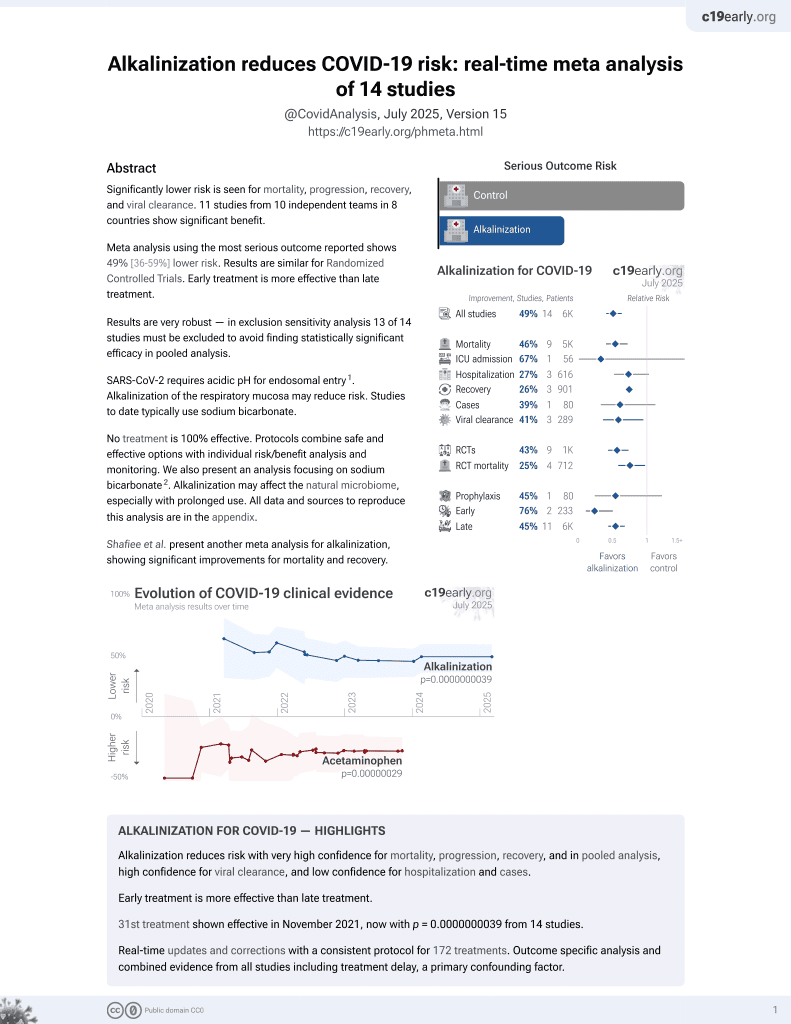
SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells
et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2209514119, Sep 2022
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0000000039 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
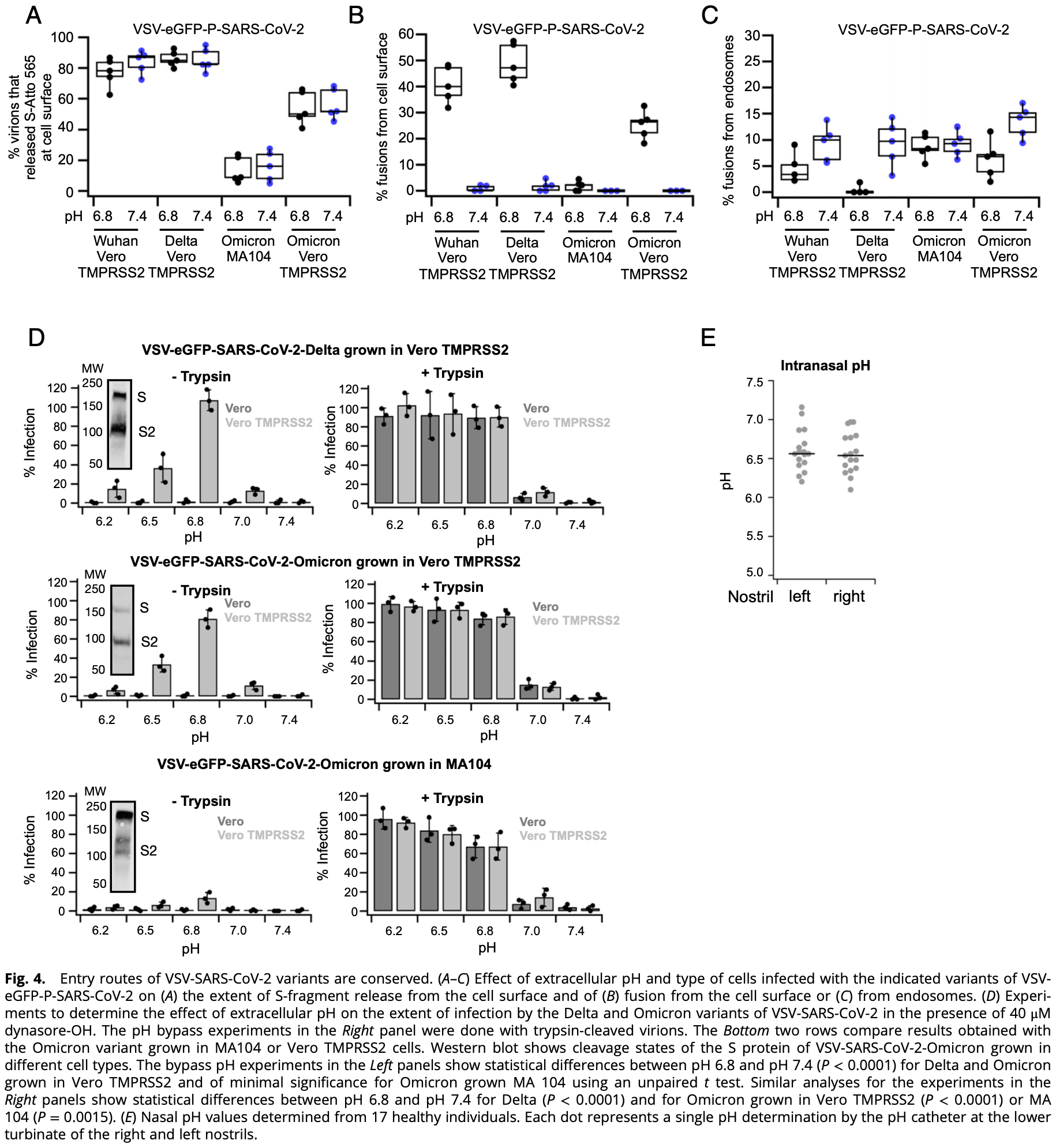
Real-time 3D single-virion tracking study showing that SARS-CoV-2 infection requires an acidic pH. Authors find the mean pH of the airway-facing surface of the nasal cavity to be 6.6, compatible with fusion.
These results suggest a beneficial effect of nasal sprays formulated to increase the pH of respiratory mucosa.
Authors note that the pH is neutral in other parts of the nasopharyngeal cavity and in the lung, suggesting no viral fusion in those locations prior to endocytic uptake.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of alkalinization for COVID-19:
Study covers alkalinization, iota-carrageenan, and povidone-iodine.
Kreutzberger et al., 30 Sep 2022, peer-reviewed, 21 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Abstract: RESEARCH ARTICLE
| MICROBIOLOGY
OPEN ACCESS
SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells
Alex J. B. Kreutzbergera,b, Anwesha Sanyala,b, Anand Saminathana,b, Louis-Marie Bloyetc , Spencer Stumpfc, Zhuoming Liuc , Ravi Ojhad,
Markku T. Patjase , Ahmed Geneide, Gustavo Scanavachia,b, Catherine A. Doylef, Elliott Somervilleb, Ricardo Bango Da Cunha Correiaa,b,
€kitiee, Volker Kiesslingi,j , Olli Vapalahtid,k,l , Sean P. J. Whelanc,1 , Giuseppe Balistrerid,k,m,1
Giuseppe Di Capriob,g, Sanna Toppila-Salmih, Antti Ma
a,b,g,1
and Tom Kirchhausen
,
Edited by Peter Palese, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; received June 07, 2022; accepted August 03, 2022
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cell entry starts with
membrane attachment and ends with spike (S) protein–catalyzed membrane fusion
depending on two cleavage steps, namely, one usually by furin in producing cells and
the second by TMPRSS2 on target cells. Endosomal cathepsins can carry out both.
Using real-time three-dimensional single-virion tracking, we show that fusion and
genome penetration require virion exposure to an acidic milieu of pH 6.2 to 6.8, even
when furin and TMPRSS2 cleavages have occurred. We detect the sequential steps
of S1-fragment dissociation, fusion, and content release from the cell surface in
TMPRRS2-overexpressing cells only when exposed to acidic pH. We define a key
role of an acidic environment for successful infection, found in endosomal compartments and at the surface of TMPRSS2-expressing cells in the acidic milieu of the nasal
cavity.
SARS-CoV-2 j live-cell imaging j virus entry j 3D imaging j infection route
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cell entry begins with
engagement at the cell surface and ends with deposition of the viral contents into the
cytosol by membrane fusion. The first step is binding of the viral spike (S) protein
with its cellular receptor angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE2) (1–4). The last step
delivers the viral genomic RNA in association with the nucleocapsid protein (N),
which is removed for translation of the input genome (5, 6). Proteolytic activation of S
by additional host-cell factors is necessary for it to function as a fusogen. Cleavage of S
by furin in producer cells (7) generates the S1 receptor binding subunit noncovalently
associated with the S2 fusion subunit. The S protein is cleaved by cell surface or endosomal proteases during virion entry into host cells, which activate the viral fusion
machinery (1, 8–10). This entry-associated proteolysis of S has led to the current
model of two routes of infectious cell entry, as follows: fusion of viral and cellular
membranes at the host-cell surface or fusion following endosomal uptake (6).
The cellular proteases that are involved in processing S during entry include the
transmembrane serine proteases TMPRSS2 or TMPRSS4 found at the cell surface
(1, 8) and the endosomal cathepsins that require the acidic milieu of the compartments
in which they are enriched (1, 10). Processing of S by TMPRSS proteases or by cathepsins, at a site designated S2’, depends on prior cleavage at the furin site in the producer cells (7, 11, 12). TMPRSS cleavage has been thought to result in infection from
the plasma membrane and cathepsin cleavage, in cells lacking TMPRSS activity, with
infection from endosomes (5,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2209514119",
"ISSN": [
"0027-8424",
"1091-6490"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2209514119",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cell entry starts with membrane attachment and ends with spike (S) protein–catalyzed membrane fusion depending on two cleavage steps, namely, one usually by furin in producing cells and the second by TMPRSS2 on target cells. Endosomal cathepsins can carry out both. Using real-time three-dimensional single-virion tracking, we show that fusion and genome penetration require virion exposure to an acidic milieu of pH 6.2 to 6.8, even when furin and TMPRSS2 cleavages have occurred. We detect the sequential steps of S1-fragment dissociation, fusion, and content release from the cell surface in TMPRRS2-overexpressing cells only when exposed to acidic pH. We define a key role of an acidic environment for successful infection, found in endosomal compartments and at the surface of TMPRSS2-expressing cells in the acidic milieu of the nasal cavity.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1073/pnas.2209514119"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-06-07"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-08-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-09-01"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Kreutzberger",
"given": "Alex J. B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Sanyal",
"given": "Anwesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Saminathan",
"given": "Anand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5648-3190",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University in Saint Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bloyet",
"given": "Louis-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University in Saint Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110"
}
],
"family": "Stumpf",
"given": "Spencer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8198-0976",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University in Saint Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Zhuoming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"family": "Ojha",
"given": "Ravi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7346-2554",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Phoniatrics - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Patjas",
"given": "Markku T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Phoniatrics - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"family": "Geneid",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Scanavachi",
"given": "Gustavo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22903"
}
],
"family": "Doyle",
"given": "Catherine A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Somerville",
"given": "Elliott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Correia",
"given": "Ricardo Bango Da Cunha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Di Caprio",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Allergy, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"family": "Toppila-Salmi",
"given": "Sanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Phoniatrics - Head and Neck Surgery, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"family": "Mäkitie",
"given": "Antti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9388-5703",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Membrane and Cell Physiology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22903"
},
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22903"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kiessling",
"given": "Volker",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2270-6824",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
},
{
"name": "Virology and Immunology, Helsinki University Hospital Diagnostic Center, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vapalahti",
"given": "Olli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1564-8590",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University in Saint Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Whelan",
"given": "Sean P. J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3585-559X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, 00290 Finland"
},
{
"name": "The Queensland Brain Institute, University of Queensland, Brisbane, 4072 Australia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Balistreri",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA 02115"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115"
}
],
"family": "Kirchhausen",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.pnas.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T17:58:42Z",
"timestamp": 1662055122000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T17:58:57Z",
"timestamp": 1662055137000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000057",
"award": [
"GM130386"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100015691",
"award": [
"AI07245"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "HHS | NIH | NIAID | Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"AI163019"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-21T18:12:03Z",
"timestamp": 1666375923924
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "38",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "38",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661990400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://pnas.org/doi/pdf/10.1073/pnas.2209514119",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "341",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1073",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_1_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18319-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03237-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00975-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-00908-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202000786",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.06.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1257998",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_14_2"
},
{
"article-title": "The morphology of vesicular stomatitis virus, (Indiana C) derived from chick embryos or cultures of BHK21/13 cells",
"author": "Bradish C. J.",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Microbiology",
"key": "e_1_3_4_15_2",
"unstructured": "C. J. Bradish, J. B. Kirkham, The morphology of vesicular stomatitis virus, (Indiana C) derived from chick embryos or cultures of BHK21/13 cells. Microbiology 44, 359–371 (1966).",
"volume": "44",
"year": "1966"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a016857",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm3266",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.127.4.915",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2007837117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012197117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0809524106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12101174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18781-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2273.1999.00223.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2013.04.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02232-10",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2011.02.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1407087111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0807771105",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.00333",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.04389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1618883114",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.2023329",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00619-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI106164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abf4896",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e16-03-0164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1004355",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2021.05.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e14-06-1146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_44_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_45_2",
"unstructured": "V. Kirchheim TrackBrowser_LabView. GitHub. https://github.com/VolkerKirchheim/TrackBrowser_LabView.git. Deposited 23 May 2022."
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2209514119"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.cm10313",
"volume": "119"
}
kreutzberger