Association of Vitamin D, Zinc and Selenium Related Genetic Variants With COVID-19 Disease Severity
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.689419, Jun 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
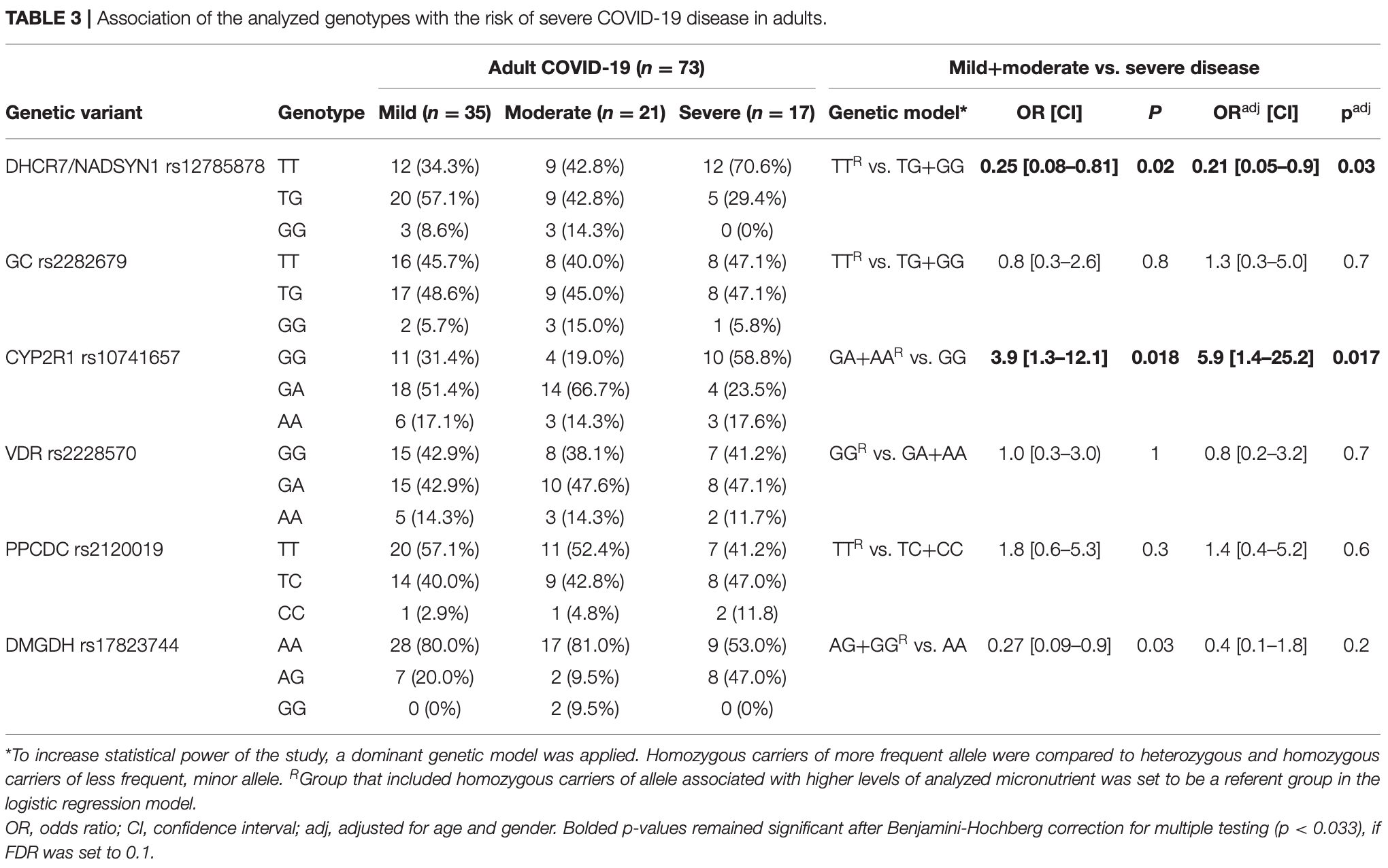
Analysis of variants in genes significant for the status of vitamin D in 120 Serbian COVID-19 patients, showing that vitamin D related genetic variants DHCR7/NADSYN rs12785878 and CYP2R1 rs10741657 were associated with severe COVID-19 in adults.
Kotur et al., 4 Jun 2021, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Association of Vitamin D, Zinc and Selenium Related Genetic Variants With COVID-19 Disease Severity
Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.689419
Background: COVID-19 pandemic has proved to be an unrelenting health threat for more than a year now. The emerging amount of data indicates that vitamin D, zinc and selenium could be important for clinical presentation of COVID-19. Here, we investigated association of genetic variants related to the altered level and bioavailability of vitamin D, zinc and selenium with clinical severity of COVID-19. Methods: We analyzed variants in genes significant for the status of vitamin D (DHCR7/NADSYN1 rs12785878, GC rs2282679, CYP2R1 rs10741657, and VDR rs2228570), zinc (PPCDC rs2120019) and selenium (DMGDH rs17823744) in 120 Serbian adult and pediatric COVID-19 patients using allelic discrimination. Furthermore, we carried out comparative population genetic analysis among European and other worldwide populations to investigate variation in allelic frequencies of selected variants. Results: Study showed that DHCR7/NADSYN rs12785878 and CYP2R1 rs10741657 variants were associated with severe COVID-19 in adults (p = 0.03, p = 0.017, respectively); carriers of DHCR7/NADSYN TG+GG and CYP2R1 GG genotypes had 0.21 and 5.9 the odds for developing severe disease, OR 0.21 (0.05-0.9) and OR 5.9 (1.4-25.2), respectively. There were no associations between selected genetic variants and disease severity in pediatric patients. Comparative population genetic analysis revealed that Serbian population had the lowest frequency of CYP2R1 rs10741657 G allele compared to other non-Finish Europeans (0.58 compared to 0.69 and 0.66 in Spanish and Italian population, respectively), suggesting that other populations should also investigate the relationship of CYP2R1 variant and the COVID-19 disease course.
Conclusion: The results of the study indicated that vitamin D related genetic variants were implicated in severe COVID-19 in adults. This could direct prevention strategies based on population specific nutrigenetic profiles.
ETHICS STATEMENT This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Molecular Genetics and Genetic Engineering University of Belgrade (approval for sample collection and biobank formation O-EO-016/2020, 06.05.2020.; approval for the genetic study O-EO-016/2020/1, 03.09.2020).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS NK: conceptualization, investigation, statistical analysis, writing -draft preparation, and editing. AS: methodology, investigation, and writing -draft preparation. KK: investigation, methodology, and writing -draft preparation. VG: data analysis and interpretation, investigation, and writing -draft preparation. BZ: methodology, investigation, writing -review, and editing, VS-T, MS, ZZ, OO, GS, and LL: methodology, sample collection, and clinical data analysis. SP: concept and design of the study, writing -review, and editing, BS: concept and design of the study, statistical analysis, results interpretation, drafting, and review of final manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021. 689419/full#supplementary-material
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Ahn, Yu, Stolzenberg-Solomon, Simon, Mccullough et al., Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq155
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Amin, Drenos, No evidence that vitamin D is able to prevent or affect the severity of COVID-19 in individuals with European ancestry: a mendelian randomisation study of open data, BMJ Nutr Prev Heal, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000151
Auton, Abecasis, Altshuler, Durbin, Bentley et al., A global reference for human genetic variation, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature15393
Batai, Trejo, Chen, Kohler, Lance et al., Genome-wide association study of response to selenium supplementation and circulating selenium concentrations in adults of European descent, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxaa355
Batur, Hekim, The role of DBP gene polymorphisms in the prevalence of new coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality rate, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26409
Bojović, Stanković, Kotur, Krstić-Milošević, Gašić et al., Genetic predictors of celiac disease, lactose intolerance, and vitamin D function and presence of peptide morphins in urine of children with neurodevelopmental disorders, Nutr Neurosci, doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1352121
Butler-Laporte, Nakanishi, Mooser, Morrison, Abdullah et al., Vitamin D and Covid-19 susceptibility and severity: a mendelian randomization study, Medrxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.09.08.20190975
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001250
Cashman, Dowling, Škrabáková, Gonzalez-Gross, Valtueña et al., Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.120873
Christakos, Dhawan, Verstuyf, Verlinden, Carmeliet, Vitamin D: metabolism, molecular mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects, Physiol Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00014.2015
Combs, Jackson, Watts, Johnson, Zeng et al., Differential responses to selenomethionine supplementation by sex and genotype in healthy adults, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511004715
Cornelis, Fornage, Foy, Xun, Gladyshev et al., Genome-wide association study of selenium concentrations, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu546
Cui, Xu, Li, Qiao, Han et al., Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: role of renin-angiotensin system, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101295
Donadio, Rogero, Guerra-Shinohara, Barbosa, Desmarchelier et al., Genetic variants in selenoprotein genes modulate biomarkers of selenium status in response to Brazil nut supplementation (the SU.BRA.NUT study), Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2018.03.011
Ellinghaus, Degenhardt, Bujanda, Buti, Albillos et al., Genomewide association study of severe Covid-19 with respiratory failure, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2020283
Evans, Zhu, Dy, Heath, Madden et al., Genomewide association study identifies loci affecting blood copper, selenium and zinc, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt239
Freitas, Calhau, Antunes, Araújo, Bandeira et al., Vitamin D-related polymorphisms and vitamin D levels as risk biomarkers of COVID-19 infection severity, Medrxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.22.21254032
Gallone, Haerty, Disanto, Ramagopalan, Ponting et al., Identification of genetic variants affecting vitamin D receptor binding and associations with autoimmune disease, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddx092
Galmés, Serra, Palou, Current state of evidence: influence of nutritional and nutrigenetic factors on immunity in the COVID-19 pandemic framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738
Gröber, Holick, The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) -a supportive approach with selected micronutrients, Int J Vitam Nutr Res, doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a000693
Helming, Böse, Ehrchen, Schiebe, Frahm et al., 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a potent suppressor of interferon γ-mediated macrophage activation, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2005-03-1029
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the covid-19 crisis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061562
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Im, Je, Baek, Chung, Kwon et al., Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018
Jiang, Reilly, Aschard, Hsu, Richards et al., Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02662-2
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Karczewski, Francioli, Tiao, Cummings, Alföldi et al., The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2308-7
Kuan, Martineau, Griffiths, Hyppönen, Walton, DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to Northern latitudes, BMC Evol Biol, doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current Vitamin D status in European and middle east countries and strategies to prevent Vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European calcified tissue society, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-18-0736
Liu, Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zhao et al., Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Moy, Mondul, Zhang, Weinstein, Wheeler et al., Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D-binding protein, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.080309
Méplan, Crosley, Nicol, Horgan, Mathers et al., Functional effects of a common single-nucleotide polymorphism (GPX4c718t) in the glutathione peroxidase 4 gene: interaction with sex, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1019
Pairo-Castineira, Clohisey, Klaric, Bretherick, Rawlik et al., Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19, Nature, doi:10.1101/2020.09.24.20200048
Pavlovic, Miletic, Zekovic, Nikolic, Glibetic, Impact of selenium addition to animal feeds on human selenium status in Serbia, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10020225
Prabhu, Luu, Li, Sharpe, Brown, DHCR7: a vital enzyme switch between cholesterol and vitamin D production, Prog Lipid Res, doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2016.09.003
Ramagopalan, Heger, Berlanga, Maugeri, Lincoln et al., A ChIP-seq defined genome-wide map of vitamin D receptor binding: associations with disease and evolution, Genome Res, doi:10.1101/gr.107920.110
Reddy, Charles, Sklavounos, Dutt, Seed et al., The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26389
Roth, Jones, Prosser, Robinson, Vohra, Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and the risk of acute lower respiratory tract infection in early childhood, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1086/527488
Shah, Saxena, Mavalankar, Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: a meta-analysis, QJM An Int J Med, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab009
Teymoori-Rad, Marashi, Vitamin D and Covid-19: from potential therapeutic effects to unanswered questions, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2159
Tizaoui, Kaabachi, Hamzaoui, Hamzaoui, Association between Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and multiple sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/cmi.2014.47
Wang, Zhang, Richards, Kestenbaum, Van Meurs et al., Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: a genome-wide association study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60588-0
Wessells, Brown, Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050568
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
Xiao, Li, Zheng, Qi, Wang et al., Targeting 7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase integrates cholesterol metabolism and irf3 activation to eliminate infection, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.015
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol Med Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7546
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.689419",
"ISSN": [
"2296-861X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.689419",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> COVID-19 pandemic has proved to be an unrelenting health threat for more than a year now. The emerging amount of data indicates that vitamin D, zinc and selenium could be important for clinical presentation of COVID-19. Here, we investigated association of genetic variants related to the altered level and bioavailability of vitamin D, zinc and selenium with clinical severity of COVID-19.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> We analyzed variants in genes significant for the status of vitamin D (<jats:italic>DHCR7</jats:italic>/<jats:italic>NADSYN1</jats:italic> rs12785878, GC rs2282679, <jats:italic>CYP2R1</jats:italic> rs10741657, and <jats:italic>VDR</jats:italic> rs2228570), zinc (<jats:italic>PPCDC</jats:italic> rs2120019) and selenium (<jats:italic>DMGDH</jats:italic> rs17823744) in 120 Serbian adult and pediatric COVID-19 patients using allelic discrimination. Furthermore, we carried out comparative population genetic analysis among European and other worldwide populations to investigate variation in allelic frequencies of selected variants.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> Study showed that <jats:italic>DHCR7/NADSYN</jats:italic> rs12785878 and <jats:italic>CYP2R1</jats:italic> rs10741657 variants were associated with severe COVID-19 in adults (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.017, respectively); carriers of <jats:italic>DHCR7/NADSYN</jats:italic> TG+GG and <jats:italic>CYP2R1</jats:italic> GG genotypes had 0.21 and 5.9 the odds for developing severe disease, OR 0.21 (0.05–0.9) and OR 5.9 (1.4–25.2), respectively. There were no associations between selected genetic variants and disease severity in pediatric patients. Comparative population genetic analysis revealed that Serbian population had the lowest frequency of <jats:italic>CYP2R1</jats:italic> rs10741657 G allele compared to other non-Finish Europeans (0.58 compared to 0.69 and 0.66 in Spanish and Italian population, respectively), suggesting that other populations should also investigate the relationship of <jats:italic>CYP2R1</jats:italic> variant and the COVID-19 disease course.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold> The results of the study indicated that vitamin D related genetic variants were implicated in severe COVID-19 in adults. This could direct prevention strategies based on population specific nutrigenetic profiles.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fnut.2021.689419"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kotur",
"given": "Nikola",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skakic",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klaassen",
"given": "Kristel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gasic",
"given": "Vladimir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zukic",
"given": "Branka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skodric-Trifunovic",
"given": "Vesna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stjepanovic",
"given": "Mihailo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zivkovic",
"given": "Zorica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ostojic",
"given": "Olivera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevanovic",
"given": "Goran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lavadinovic",
"given": "Lidija",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavlovic",
"given": "Sonja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stankovic",
"given": "Biljana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Front. Nutr.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-04T04:24:14Z",
"timestamp": 1622780654000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-04T04:24:17Z",
"timestamp": 1622780657000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-15T06:13:57Z",
"timestamp": 1676441637417
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1622764800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.689419/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26389",
"article-title": "The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Reddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1045",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2020283",
"article-title": "Genomewide association study of severe Covid-19 with respiratory failure",
"author": "Ellinghaus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1522",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.24.20200048",
"article-title": "Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19",
"author": "Pairo-Castineira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"article-title": "Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19",
"author": "Alexander",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2159",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Covid-19: from potential therapeutic effects to unanswered questions",
"author": "Teymoori-Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2159",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2019.101295",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: role of renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101295",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"article-title": "Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7432",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the covid-19 crisis",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831/a000693",
"article-title": "The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) - a supportive approach with selected micronutrients",
"author": "Gröber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Vitam Nutr Res.",
"key": "B10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.115.120873",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?",
"author": "Cashman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0050568",
"article-title": "Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting",
"author": "Wessells",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018",
"article-title": "Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Im",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "390",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077",
"article-title": "Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072098",
"article-title": "Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from COVID-19",
"author": "Moghaddam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab009",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "QJM An Int J Med.",
"key": "B17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"article-title": "Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1228",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-02662-2",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "260",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.113.080309",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D-binding protein",
"author": "Moy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1424",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60588-0",
"article-title": "Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: a genome-wide association study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "180",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.107920.110",
"author": "Ramagopalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1352",
"journal-title": "Genome Res.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/527488",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and the risk of acute lower respiratory tract infection in early childhood",
"author": "Roth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "197",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddx092",
"article-title": "Identification of genetic variants affecting vitamin D receptor binding and associations with autoimmune disease",
"author": "Gallone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2164",
"journal-title": "Hum Mol Genet.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cmi.2014.47",
"article-title": "Association between Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and multiple sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies",
"author": "Tizaoui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1028415X.2017.1352121",
"article-title": "Genetic predictors of celiac disease, lactose intolerance, and vitamin D function and presence of peptide morphins in urine of children with neurodevelopmental disorders",
"author": "Bojović",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "40",
"journal-title": "Nutr Neurosci.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddt239",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study identifies loci affecting blood copper, selenium and zinc",
"author": "Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3998",
"journal-title": "Hum Mol Genet.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddu546",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study of selenium concentrations",
"author": "Cornelis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1469",
"journal-title": "Hum Mol Genet.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa355",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study of response to selenium supplementation and circulating selenium concentrations in adults of European descent",
"author": "Batai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "J Nutr.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature15393",
"article-title": "A global reference for human genetic variation",
"author": "Auton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "68",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "526",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2308-7",
"article-title": "The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans",
"author": "Karczewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "434",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"article-title": "Current Vitamin D status in European and middle east countries and strategies to prevent Vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European calcified tissue society",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "P23",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10020225",
"article-title": "Impact of selenium addition to animal feeds on human selenium status in Serbia",
"author": "Pavlovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "225",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.plipres.2016.09.003",
"article-title": "DHCR7: a vital enzyme switch between cholesterol and vitamin D production",
"author": "Prabhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "Prog Lipid Res.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2148-13-144",
"article-title": "DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to Northern latitudes",
"author": "Kuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "144",
"journal-title": "BMC Evol Biol.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.015",
"article-title": "Targeting 7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase integrates cholesterol metabolism and irf3 activation to eliminate infection",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Immunity.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00014.2015",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: metabolism, molecular mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects",
"author": "Christakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddq155",
"article-title": "Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels",
"author": "Ahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2739",
"journal-title": "Hum Mol Genet.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2005-03-1029",
"article-title": "1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a potent suppressor of interferon γ-mediated macrophage activation",
"author": "Helming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4351",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092738",
"article-title": "Current state of evidence: influence of nutritional and nutrigenetic factors on immunity in the COVID-19 pandemic framework",
"author": "Galmés",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26409",
"article-title": "The role of DBP gene polymorphisms in the prevalence of new coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality rate",
"author": "Karcioglu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1409",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.22.21254032",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-related polymorphisms and vitamin D levels as risk biomarkers of COVID-19 infection severity",
"author": "Freitas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Medrxiv.",
"key": "B43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.08.20190975",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Covid-19 susceptibility and severity: a mendelian randomization study",
"author": "Butler-Laporte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Medrxiv [preprint]",
"key": "B44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000151",
"article-title": "No evidence that vitamin D is able to prevent or affect the severity of COVID-19 in individuals with European ancestry: a mendelian randomisation study of open data",
"author": "Amin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr Prev Heal.",
"key": "B45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2018.03.011",
"article-title": "Genetic variants in selenoprotein genes modulate biomarkers of selenium status in response to Brazil nut supplementation (the SU",
"author": "Donadio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "539",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr.",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511004715",
"article-title": "Differential responses to selenomethionine supplementation by sex and genotype in healthy adults",
"author": "Combs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1514",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1019",
"article-title": "Functional effects of a common single-nucleotide polymorphism (GPX4c718t) in the glutathione peroxidase 4 gene: interaction with sex",
"author": "Méplan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1019",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2008"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.689419/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of Vitamin D, Zinc and Selenium Related Genetic Variants With COVID-19 Disease Severity",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "8"
}
