Comparison of clinical and laboratory parameters of COVID-19 in diabetic patients using different glucose-lowering drugs: a retrospective study
et al., Current Research in Medical Sciences, doi:10.22088/crms.6.2.32, Dec 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
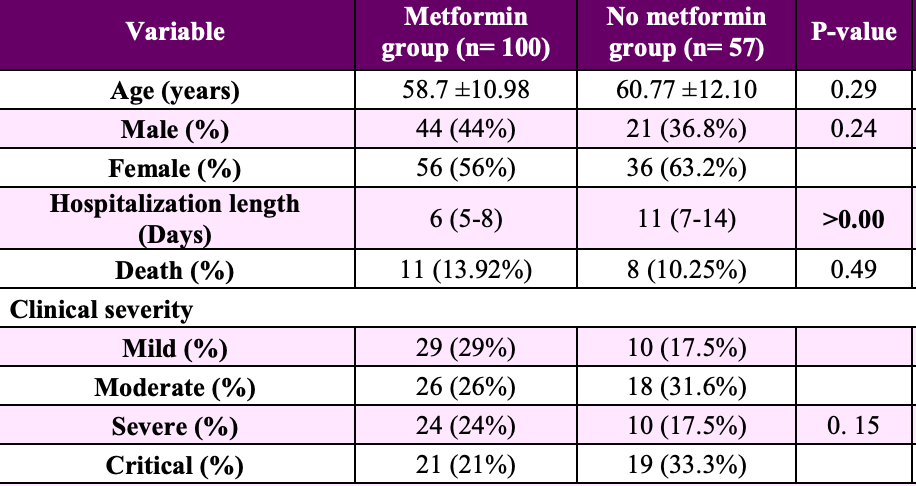
Retrospective 157 diabetic patients in Iran reporting shorter hospitalization with metformin, however numbers in this paper are inconsistent. The counts and percentages for death in Table 1 are not possible - 11 (13.92%) for metformin could indicate that the outcome was only known for 79/100 patients, however 8 (10.25%) for the no metformin group indicates 78 patients while the total group size is 57.
Khafri et al., 31 Dec 2022, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 20 April, 2020 - 21 July, 2020.
Contact: srostami.m@gmail.com.
Comparison of clinical and laboratory parameters of COVID-19 in diabetic patients using different glucose-lowering drugs: a retrospective study
doi:10.22088/crms.6.2.32
Background and Objective: Diabetes is a common metabolic disease that increases the risk of mortality of COVID-19. This study was done to compare the clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters of COVID-19 in diabetic patients using different glucose-lowering drugs to find out the proper predictors of disease severity. Methods: 157 diabetic patients with confirmed COVID-19 were enrolled in three groups according to the antidiabetic medications used before admission (metformin, insulin and sulfonylurea).
Findings: In 157 diabetic patients, the hospitalization length in the metformin group was lower than the no metformin group while duration of hospitalization and critical form of the disease in the insulin group were higher than the no insulin group. Furthermore, the levels of blood sugar, BUN, ALT and WBC were lower in the metformin group while ALP, ALT, BUN and creatinine levels were significantly higher in insulin group. In sulfonylurea group the levels of BUN and ALT were lower compared to the no sulfonylurea group. We also found that BUN and total bilirubin were the proper parameters to predict COVID-19 severity and mortality in metformin and insulin group respectively.
Conclusion: It seems that the outcomes of renal function test, bilirubin and O2 saturation are important parameters to predict COVID-19 severity in diabetic patients using different antidiabetic medications.
Current Research in Medical Sciences, 2022; 6(2): 32-49 The adjusted OR, crude OR, 95% CI, AUC, cut off, specificity and sensitivity are shown. P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. [ DOI: 10.22088
Discussion There is a strong association between diabetes and the mortality rate of COVID-19 (13, 14) . It seems that several disorders in diabetic patients, such as high expression of ACE2 receptors, chronic inflammation, hypertension, and nephropathy exacerbate the pathological processes of COVID-19 (15) . In the present retrospective study, we suggested important predictors of death and critical form of COVID-19 in diabetes patients taking different glucose-lowering medications. Our results revealed that despite matching age, gender, comorbidities, and use of ARBs and/or ACE inhibitors, some baseline characteristics differed significantly between the groups. The hospitalization length and the severity of COVID-19 were higher in insulin-group compared to no insulin group. This result is consistent with the result previously reported by Chen et al (12) . They reported that insulin usage was associated with a poor prognosis of COVID-19 in diabetic patients (12) . Another study showed that insulin therapy of diabetic patients after COVID-19 infection increased the mortality rate, induced systemic inflammation, and aggravated injuries of vital organs (9) . Therefore, they suggested that more attention is needed regarding diabetic patients with COVID-19..
References
Akbari, Emami, Javanmardi, Pirbonyeh, Fadakar, Early epidemiological analysis of CoVID-19: first report from South of Iran, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-19915/v1
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Weaver, Bradley et al., Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587
Bda, Ferreira, Diabetes and covid-19: more than the sum of two morbidities, Rev Saúde Pública, doi:10.11606/s1518-8787.2020054002577
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Dragon-Durey, Kirilovsky, Hamouda, Sissy, Russick, Differential association between inflammatory cytokines and multiorgan dysfunction in COVID-19 patients with obesity, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252026
Giannouchos, Sussman, Mier, Poulas, Farsalinos, Characteristics and risk factors for COVID-19 diagnosis and adverse outcomes in Mexico: an analysis of 89,756 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases, Eur Res J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02144-2020
Gong, Ou, Qiu, Jie, Chen et al., A tool for early prediction of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a multicenter study using the risk nomogram in Wuhan and Guangdong, China, Clin Infec Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa443
Kim, Jeon, Kim, Moon, Cho et al., The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in Daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Liu, Li, Long, Zeng, Gao et al., Bilirubin levels as potential indicators of disease severity in coronavirus disease patients: a retrospective cohort study, Current Research in Medical Sciences
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Liu, -L et al., Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Ttrop Med, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Marhl, Grubelnik, Magdič, Markovič, Diabetes and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.013
Mcgurnaghan, Weir, Bishop, Kennedy, Blackbourn et al., Risks of and risk factors for COVID-19 disease in people with diabetes: a cohort study of the total population of Scotland, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30405-8
Sachdeva, Desai, Gupta, Prakash, Jain et al., Admission hyperglycemia in non-diabetics predicts mortality and disease severity in COVID-19: a pooled analysis and meta-summary of literature, SN Compr Clin Med, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00575-8
Selvin, Parrinello, Daya, Bergenstal, Trends in insulin use and diabetes control in the US: 1988-1994 and 1999-2012, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc15-2229
Singh, Singh, Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268
Stoian, Banerjee, Rizvi, Rizzo, Diabetes and the COVID-19 pandemic: how insights from recent experience might guide future management, Metab Syndr Relat Disord, doi:10.1089/met.2020.0037
Thomson, COVID-19: Social distancing, ACE 2 receptors, protease inhibitors and beyond?, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13503
Van Buren, Toto, Hypertension in diabetic nephropathy: epidemiology, mechanisms, and management, Adv Chronic Kidney Dis, doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2010.10.003
Wang, Hu, Chen, Fu, Lei et al., Caution on kidney dysfunctions of 2019-nCoV patients, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.02.08.20021212
Wang, Yang, Dong, Yan, Zhang et al., Clinical characteristics of 28 patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Endocr Pract, doi:10.4158/EP-2020-0108
Ye, Wysocki, Naaz, Salabat, Lapointe et al., Increased ACE 2 and decreased ACE protein in renal tubules from diabetic mice: a renoprotective combination?, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000126192.27644.76
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes, Cell metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22088/crms.6.2.32",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22088/crms.6.2.32",
"author": [
{
"family": "Rostami-Mansoor",
"given": "S"
},
{
"family": "Khafri",
"given": "S"
},
{
"family": "Jalali",
"given": "S F"
},
{
"family": "Mohdenipoor",
"given": "F"
},
{
"family": "Parsian",
"given": "H"
},
{
"family": "Bayani",
"given": "M"
}
],
"container-title": "Current Research in Medical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "CRMS",
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"journalAbbreviation": "CRMS",
"language": "eng",
"publisher": "Babol University of Medical Sciences",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Comparison of clinical and laboratory parameters of COVID-19 in diabetic patients using different glucose-lowering drugs: a retrospective study",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "6"
}
