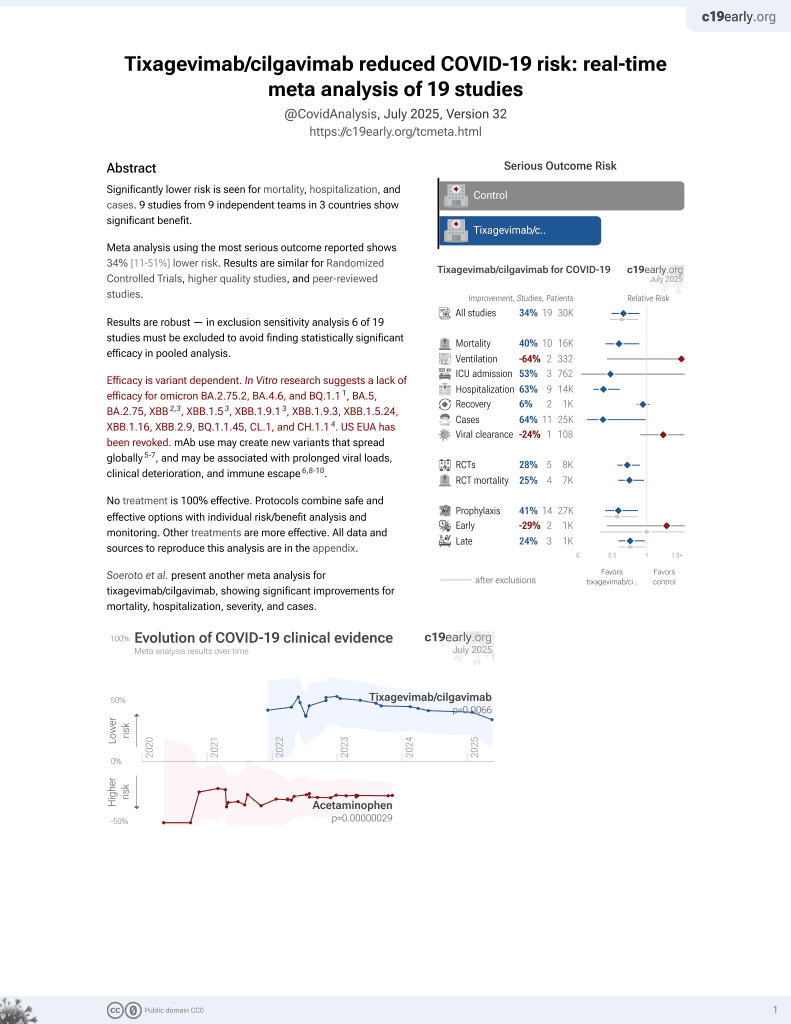
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
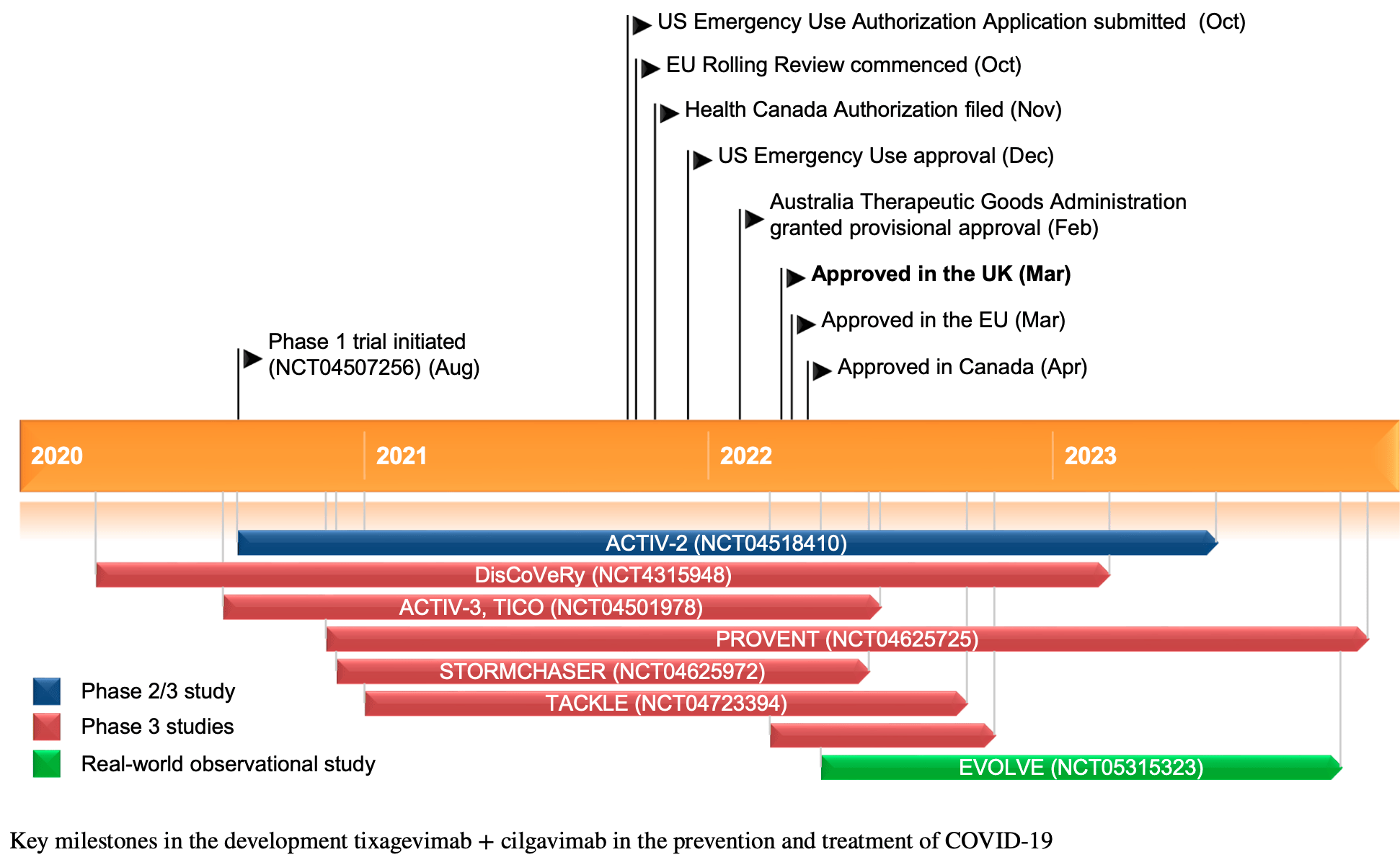
Review of tixagevimab + cilgavimab for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Tixagevimab and cilgavimab are long-acting monoclonal antibodies that bind to distinct sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. In March 2022, the combination received its first approval in the UK for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in adults unlikely to mount an adequate immune response to vaccination or for whom vaccination is not recommended. The phase 3 PROVENT trial showed that a single 300mg intramuscular dose significantly reduced the risk of symptomatic COVID-19 compared to placebo in this population. Treatment also reduced the risk of severe COVID-19 or death compared to placebo in non-hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate disease in the phase 3 TACKLE trial.
1.
Focosi et al., The Emergence of Escape Mutations in COVID-19 Following Anti-Spike Monoclonal Antibody Treatment: How Do We Tackle It?, Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S540928.
2.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
3.
Focosi (B), D., Monoclonal Antibody Therapies Against SARS-CoV-2: Promises and Realities, Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1007/82_2024_268.
4.
Enyeji et al., Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports, Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034.
Keam et al., 21 Jun 2022, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: dru@adis.com.
Tixagevimab + Cilgavimab: First Approval
Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1
Tixagevimab 150 mg and cilgavimab 150 mg (EVUSHELD TM 150 mg + 150 mg solution for injection; tixagevimab + cilgavimab) is an intramuscular (IM) long-acting monoclonal antibody combination developed by AstraZeneca for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. In March 2022, tixagevimab + cilgavimab was approved in the UK for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in adults who are not currently infected with SARS-CoV-2 and who have not had a known recent exposure to an individual infected with SARS-CoV-2 and who are unlikely to mount an adequate immune response to COVID-19 vaccination or for whom COVID-19 vaccination is not recommended, and in the EU for the prevention of COVID-19 in adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years and weighing ≥40 kg. In December 2021, tixagevimab + cilgavimab was granted Emergency Use Authorization by the US FDA for the pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in adults and paediatric individuals (≥ 12 years of age and weighing ≥ 40 kg). This article summarizes the milestones in the development of tixagevimab + cilgavimab leading to this first approval for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in individuals who are not currently infected with SARS-CoV-2. This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s40265-022-01731-1.
Declarations Funding The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Susan J. Keam is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content. Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability Not applicable.
Authors and Affiliations Susan J. Keam 1 1 Springer Nature, Mairangi Bay, Private Bag 65901, Auckland 0754, New Zealand
References
Astrazeneca, AZD7442 request for Emergency Use Authorization for COVID-19 prophylaxis filed in US
Astrazeneca, Advancing our discovery of novel coronavirus-neutralising antibodies against COVID-19
Astrazeneca, AstraZeneca's Evusheld™ (tixagevimab and cilgavimab) granted provisional approval for pre-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) of COVID-19 in Australia's most at-risk [media release
Astrazeneca, COVID-19 Long-Acting AntiBody (LAAB) combination AZD7442 rapidly advances into Phase III clinical trials
Astrazeneca, Evusheld long-acting antibody combination approved in the EU for pre-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) of COVID-19 in a broad population [media release
Astrazeneca, Researching antibodies to target COVID-19
Astrazeneca, Samsung Biologics and AstraZeneca expand strategic manufacturing partnership to include COVID-19 and cancer therapy
Astrazeneca, Update on AZD7442 STORM CHASER trial in post-exposure prevention of symptomatic COVID-19
Boggiano, Eisinger, Lerner, Update on and future directions for use of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: National Institutes of Health Summit on Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19, Ann Intern Med
Case, Mackin, Errico, Resilience of S309 and AZD7442 monoclonal antibody treatments against infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineage strains, bioRxiv
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell
Dejnirattisai, Shaw, Supasa, Reduced neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 omicron B.1.1.529 variant by post-immunisation serum, Lancet
Dong, Zost, Greaney, Genetic and structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 variant neutralization by a two-antibody cocktail, Nat Microbiol
Driouich, Lingas, Luciani, Activity of tixagevimab/ cilgavimab against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 in a hamster model, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1399448/v1
Holland, Ginde, Paredes, Tixagevimab/cilgavimab for treatment of hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial, Lancet, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4087355
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116620
Lonza, Lonza announces agreement to manufacture AstraZeneca's COVID-19 long-acting antibody combination
Loo, Mctamney, Arends, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans, Sci Transl Med
Montgomery, Hobbs, Padilla, Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab-cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1
Neerukonda, Vassell, Herrup, Establishment of a well-characterized SARS-CoV-2 lentiviral pseudovirus neutralization assay using 293T cells with stable expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, PLoS ONE
Oganesyan, Gao, Shirinian, Structural characterization of a human Fc fragment engineered for lack of effector functions, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
Robbie, Criste, Dall, Wf, A novel investigational Fc-modified humanized monoclonal antibody, motavizumab-YTE, has an extended half-life in healthy adults, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Touret, Baronti, Bouzidi, In vitro evaluation of therapeutic antibodies against a SARS-CoV-2 Omicron B.1.1.529 isolate, Sci Rep
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med
Zost, Gilchuk, Case, Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1",
"ISSN": [
"0012-6667",
"1179-1950"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1",
"alternative-id": [
"1731"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 1,
"value": "21 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Funding",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Authorship and Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Susan J. Keam is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keam",
"given": "Susan J.",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Drugs",
"container-title-short": "Drugs",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-21T15:03:13Z",
"timestamp": 1655823793000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-12T21:04:09Z",
"timestamp": 1657659849000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-09T02:56:46Z",
"timestamp": 1723172206951
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 35,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654041600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654041600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1001-1010",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "1731_CR1",
"unstructured": "UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Evusheld approved to prevent COVID-19 in people whose immune response is poor [media release]. 17 Mar 2022. https://www.gov.uk/government/news/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"author": "MJ Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1731_CR2",
"unstructured": "Levin MJ, Ustianowski A, De Wit S, et al. Intramuscular AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116620.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1731_CR3",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. Evusheld: EPAR—assessment report. 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/evusheld. Accessed 4 May 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-3669",
"author": "CP Boggiano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "1731_CR4",
"unstructured": "Boggiano CP, Eisinger RWP, Lerner AMMD, et al. Update on and future directions for use of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: National Institutes of Health Summit on Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2022;175(1):119–26.",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1731_CR5",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. Advancing our discovery of novel coronavirus-neutralising antibodies against COVID-19 [media release]. 9 June 2020. http://www.astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR6",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. AZD7442 request for Emergency Use Authorization for COVID-19 prophylaxis filed in US [media release]. 5 Oct 2021. http://www.astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR7",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. COVID-19 Long-Acting AntiBody (LAAB) combination AZD7442 rapidly advances into Phase III clinical trials [media release]. 9 Oct 2020. http://www.astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2548-6",
"author": "SJ Zost",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "443",
"issue": "7821",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1731_CR8",
"unstructured": "Zost SJ, Gilchuk P, Case JB, et al. Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2020;584(7821):443–9.",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1731_CR9",
"unstructured": "UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. EVUSHELD: UK summary of product characteristics. 2022. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/regulatory-approval-of-evusheld-tixagevimabcilgavimab/summary-of-product-characteristics-for-evusheld. Accessed 6 May 2022."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR10",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. EVUSHELD: Emergency Use Authorization (EAU)—full fact sheet for healthcare providers. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/154701/download. Accessed 6 May 2022."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR11",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. Evusheld long-acting antibody combination approved in the EU for pre-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) of COVID-19 in a broad population [media release]. 28 Mar 2022. https://www.astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR12",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. EVUSHELD 150 mg + 150 mg solution for injection: EU summary of product characteristics. 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/. Accessed 2 May 2022."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR13",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca Canada Inc. EVUSHELDTM (tixagevimab and cilgavimab injection): Canadian product monograph. 2022. https://covid-vaccine.canada.ca/info/pdf/evusheld-pm-en.pdf. Accessed 11 May 2022"
},
{
"key": "1731_CR14",
"unstructured": "Department of Health Abu Dhabi. Abu Dhabi receives the first global shipment of the new AstraZeneca “Evusheld” COVID-19 medication [media release]. 20 Dec 2021. https://www.doh.gov.ae/en/news/."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR15",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca’s Evusheld™ (tixagevimab and cilgavimab) granted provisional approval for pre-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) of COVID-19 in Australia’s most at-risk [media release]. 25 Feb 2022. https://www.astrazeneca.com.au."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR16",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. Samsung Biologics and AstraZeneca expand strategic manufacturing partnership to include COVID-19 and cancer therapy [media release]. 13 Dec 2021. http://astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR17",
"unstructured": "Lonza. Lonza announces agreement to manufacture AstraZeneca's COVID-19 long-acting antibody combination [media release]. 30 Oct 2020. http://www.lonza.com."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR18",
"unstructured": "Vanderbilt University. Vanderbilt University Medical Center and AstraZeneca join forces to identify potential COVID-19 treatments [media release]. 8 Apr 2020. http://www.vsumc.org."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR19",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. Researching antibodies to target COVID-19. 2020. https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/articles/2020/researching-antibodies-to-target-covid-19.html#. Accessed 5 May 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01285-13",
"author": "GJ Robbie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6147",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "1731_CR20",
"unstructured": "Robbie GJ, Criste R, Dall’acqua WF, et al. A novel investigational Fc-modified humanized monoclonal antibody, motavizumab-YTE, has an extended half-life in healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(12):6147–53.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124",
"author": "YM Loo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabl8124",
"issue": "635",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med.",
"key": "1731_CR21",
"unstructured": "Loo YM, McTamney PM, Arends RH, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(635):eabl8124.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444908007877",
"author": "V Oganesyan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "700",
"issue": "Pt 6",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr",
"key": "1731_CR22",
"unstructured": "Oganesyan V, Gao C, Shirinian L, et al. Structural characterization of a human Fc fragment engineered for lack of effector functions. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008;64(Pt 6):700–4.",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-00972-2",
"author": "J Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1233",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "1731_CR23",
"unstructured": "Dong J, Zost SJ, Greaney AJ, et al. Genetic and structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 variant neutralization by a two-antibody cocktail. Nat Microbiol. 2021;6(10):1233–44.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"author": "W Dejnirattisai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "467",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "1731_CR24",
"unstructured": "Dejnirattisai W, Huo J, Zhou D, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses. Cell. 2022;185(3):467-84 e15.",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-08559-5",
"author": "F Touret",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4683",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "1731_CR25",
"unstructured": "Touret F, Baronti C, Bouzidi HS, et al. In vitro evaluation of therapeutic antibodies against a SARS-CoV-2 Omicron B.1.1.529 isolate. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4683.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02844-0",
"author": "W Dejnirattisai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "234",
"issue": "10321",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1731_CR26",
"unstructured": "Dejnirattisai W, Shaw RH, Supasa P, et al. Reduced neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 omicron B.1.1.529 variant by post-immunisation serum. Lancet. 2022;399(10321):234–6.",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"author": "LA VanBlargan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "1731_CR27",
"unstructured": "VanBlargan LA, Errico JM, Halfmann PJ, et al. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat Med. 2022;28(3):490–5.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1731_CR28",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Open data portal | SARS-CoV-2 variants and therapeutics: therapeutic activity explorer. 2022. https://opendata.ncats.nih.gov/variant/activity. Accessed 6 May 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-31615-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1731_CR29",
"unstructured": "Case JB, Mackin S, Errico J, et al. Resilience of S309 and AZD7442 monoclonal antibody treatments against infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineage strains. bioRxiv. 2022(PPR469910):1–33."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0248348",
"author": "SN Neerukonda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1731_CR30",
"unstructured": "Neerukonda SN, Vassell R, Herrup R, et al. Establishment of a well-characterized SARS-CoV-2 lentiviral pseudovirus neutralization assay using 293T cells with stable expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(3): e0248348.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1399448/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1731_CR31",
"unstructured": "Driouich J-S, Lingas G, Luciani L, et al. Activity of tixagevimab/cilgavimab against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 in a hamster model. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1399448/v1. Accessed 10 May 2022."
},
{
"key": "1731_CR32",
"unstructured": "AstraZeneca. Update on AZD7442 STORM CHASER trial in post-exposure prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 [media release]. 15 June 2021. https://www.astrazeneca.com."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1731_CR33",
"unstructured": "Montgomery H, Hobbs FDR, Padilla F, et al. Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab-cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.4087355",
"author": "TL Holland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1731_CR34",
"unstructured": "Holland TL, Ginde AA, Paredes R, et al. Tixagevimab/cilgavimab for treatment of hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4087355.",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40265-022-01731-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tixagevimab + Cilgavimab: First Approval",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "82"
}