Protective Effect of Vitamin-D Supplementation in Patients of Acute Coronary Syndrome During COVID-19 Pandemic
et al., Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, doi:10.53350/pjmhs221631053, May 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 40 acute coronary syndrome patients in Pakistan, 20 given a single dose of 200,000IU vitamin D, showing lower incidence of COVID-19 in the following 2 months.
Bolus treatment is less effective.
Pharmacokinetics and the potential side effects of high bolus doses suggest
that ongoing treatment spread over time is more appropriate.
Research has confirmed that lower dose regular treatment with vitamin D is more
effective than intermittent high-dose bolus treatment for various conditions,
including rickets and acute respiratory infections1,2. The biological mechanisms supporting these
findings involve the induction of enzymes such as 24-hydroxylase and
fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) by high-dose bolus treatments. These
enzymes play roles in inactivating vitamin D, which can paradoxically reduce
levels of activated vitamin D and suppress its activation for extended periods
post-dosage. Evidence indicates that 24-hydroxylase activity may remain
elevated for several weeks following a bolus dose, leading to reduced levels
of the activated form of vitamin D. Additionally, FGF23 levels can increase
for at least three months after a large bolus dose, which also contributes to
the suppression of vitamin D activation1.
This is the 82nd of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
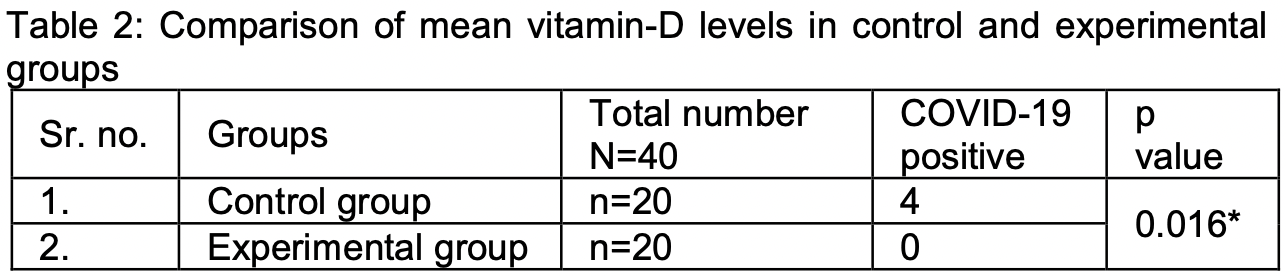
risk of symptomatic case, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 20 (0.0%), control 4 of 20 (20.0%), NNT 5.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jabeen et al., 11 May 2022, prospective, Pakistan, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, dosage 200,000IU single dose.
Contact: drsidraasad2011@gmail.com.
Protective Effect of Vitamin-D Supplementation in Patients of Acute Coronary Syndrome During COVID-19 Pandemic
Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, doi:10.53350/pjmhs221631053
Introduction: Objectives: To determine the effect of vitamin-D supplementation in patients of the acute coronary syndrome and its role if any in preventing COVID-19 infection.
Study design: Prospective clinical trial Place and duration: Armed Forces Institute of Cardiology in collaboration with Riphah International University Material and methods: The study was conducted by recruiting 40 patients, diagnosed with the acute coronary syndrome. After the PCI procedure during their hospital stay, 20 of them were given a single shot of vitamin-D supplement in a dose of 200000 IU while the rest of 20 were allocated as controls. Patients were instructed to follow the SOPs strictly and were followed up for incidence of coronavirus disease after 2 months. Detailed history regarding their stay during lockdown was taken. Independent sample t-test was used to compare the two groups with p≤0.05 considered as significant.
Results: The patients enrolled in the study were assessed for pre and post-intervention levels for vitamin-D. After the intervention the levels in the experimental group were increased to 30.74±18.40 ng/ml (p=0.000***) from a mean value of 18.27 ±8.98 ng/ml. Among the control group, eight out of 40 patients tested positive for COVID-19 while none among the experimental group got the disease (p=0.016*). The results of the follow-up interview showed that the patients followed the precautions for COVID protection during the pandemic. Conclusion: Vitamin-D supplementation during lockdown may prove beneficial in protection against COVID-19.
References
Ali, Elevated level of C-reactive protein may be an early marker to predict risk for severity of COVID-19, Journal of medical virology
Apaydin, Can, Kizilgul, Beysel, Kan et al., The effects of single high-dose or daily low-dosage oral colecalciferol treatment on vitamin D levels and muscle strength in postmenopausal women, BMC endocrine disorders
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad Med J
Choudry, Hamshere, Rathod, Akhtar, Archbold et al., High Thrombus Burden in Patients With COVID-19 Presenting With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction, J Am Coll Cardiol
Cuervo, Grandvaux, ACE2 : Evidence of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications in comorbidities, Elife
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System -Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin d supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and covid-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the Immune Response to Respiratory Viruses by Vitamin D, Nutrients
Gunville, Mourani, Ginde, The role of vitamin D in prevention and treatment of infection, Inflamm Allergy -Drug Targets
Jackson, Cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death : how are pharmacists getting involved ? Integrated pharmacy research & practice
Kearns, Alvarez, Tangpricha, Large, single-dose, oral vitamin D supplementation in adult populations: a systematic review, Endocr Pract
Metrio M De, Milazzo, Rubino, Cabiati, Moltrasio et al., Vitamin D Plasma Levels and In-Hospital and 1-Year Outcomes in Acute coronary syndromes A Prospective Study
Neve, Corrado, Francesco, Cantatore, Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D in peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Clinical and experimental medicine
Ohaegbulam, Swalih, Patel, Smith, Perrin, Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Case Series, Am J Ther
Orcid, Li, Orcid, Orcid, An Imperative Need for Research on the Role of Environmental Factors in Transmission of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19), Environ Sci Technol
Ranard, Fried, Abdalla, Anstey, Givens et al., Approach to Acute Cardiovascular Complications in COVID-19 Infection, Circ Hear Fail
Sandoval, Januzzi, Jaffe, Cardiac Troponin for Assessment of Myocardial Injury in COVID-19, Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Satilmis, Celik, Biyik, Ozturk, Celik et al., Association between serum vitamin D levels and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis and plaque burden / composition in young adult population, Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences
Sharifi, Vahedi, Nedjat, Rafiei, Hosseinzadeh-Attar, Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, APMIS, doi:10.1111/apm.12982
Vankadari, Wilce, Emerging COVID-19 coronavirus : glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerging microbes & infections
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama
Yılmaz, Şen, Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?, Pediatr Pulmonol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.53350/pjmhs221631053",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.53350/pjmhs221631053",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction: Objectives: To determine the effect of vitamin-D supplementation in patients of the acute coronary syndrome and its role if any in preventing COVID-19 infection. Study design: Prospective clinical trial Place and duration: Armed Forces Institute of Cardiology in collaboration with Riphah International University Material and methods: The study was conducted by recruiting 40 patients, diagnosed with the acute coronary syndrome. After the PCI procedure during their hospital stay, 20 of them were given a single shot of vitamin-D supplement in a dose of 200000 IU while the rest of 20 were allocated as controls. Patients were instructed to follow the SOPs strictly and were followed up for incidence of coronavirus disease after 2 months. Detailed history regarding their stay during lockdown was taken. Independent sample t-test was used to compare the two groups with p≤0.05 considered as significant. Results: The patients enrolled in the study were assessed for pre and post-intervention levels for vitamin-D. After the intervention the levels in the experimental group were increased to 30.74±18.40 ng/ml (p=0.000***) from a mean value of 18.27 ±8.98 ng/ml. Among the control group, eight out of 40 patients tested positive for COVID-19 while none among the experimental group got the disease (p=0.016*). The results of the follow-up interview showed that the patients followed the precautions for COVID protection during the pandemic. Conclusion: Vitamin-D supplementation during lockdown may prove beneficial in protection against COVID-19. Keywords: Vitamin-D, COVID-19, acute coronary syndrome</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jabeen",
"given": "Sidra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Humaira Fayyaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarwar",
"given": "Samia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashfaq",
"given": "Mehvish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafar",
"given": "Ayesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslam",
"given": "Ummara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamid",
"given": "Shmyla",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences",
"container-title-short": "PJMHS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-12T13:58:56Z",
"timestamp": 1652363936000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-12T13:59:01Z",
"timestamp": 1652363941000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T11:14:43Z",
"timestamp": 1652440483717
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
}
},
"member": "31137",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1053-1055",
"prefix": "10.53350",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Lahore Medical and Dental College",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://pjmhsonline.com/index.php/pjmhs/article/view/773"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Protective Effect of Vitamin-D Supplementation in Patients of Acute Coronary Syndrome During COVID-19 Pandemic",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}
