Host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence within respiratory particles: a systematic review
et al., Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124, Oct 2025
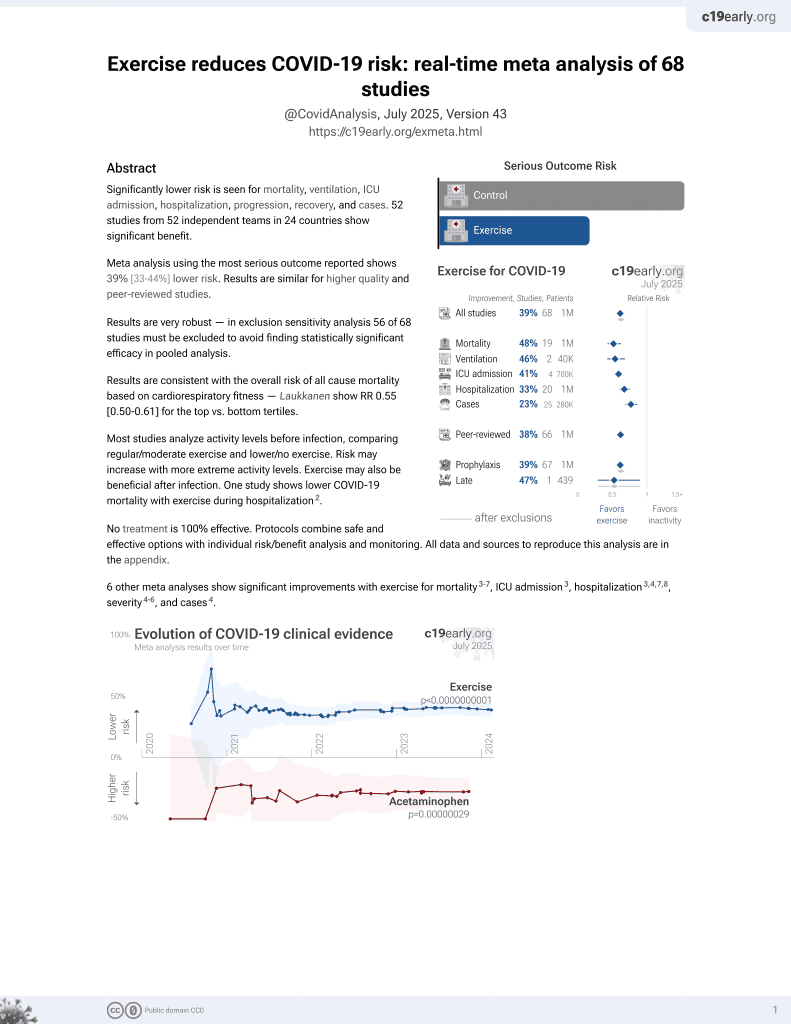
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
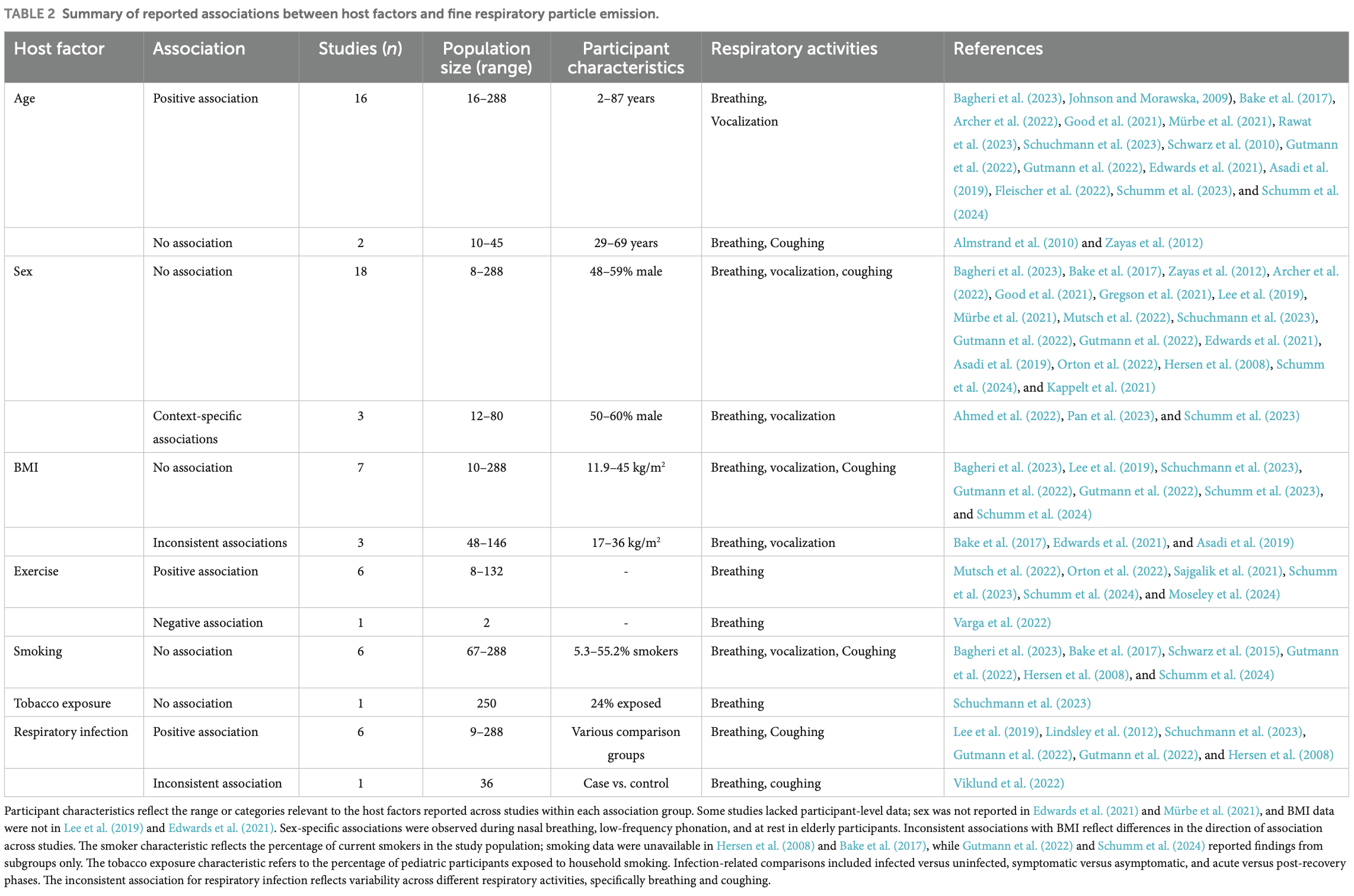
Systematic review of 44 studies examining host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence in exhaled particles. Fine respiratory particles (<5 μm) were consistently associated with older age (16 studies), physical exercise (6 studies), and active infection (6 studies). Authors hypothesize that physical exercise increases tidal volume and airflow velocities that amplify shear forces.
1.
Horstink et al., Host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence within respiratory particles: a systematic review, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124.
2.
Nindenshuti et al., Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, Alcohol Consumption, and Tobacco Use in Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review, INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, doi:10.1177/00469580231175780.
Horstink et al., 15 Oct 2025, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: m.lokate@umcg.nl.
Host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence within respiratory particles: a systematic review
Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124
Introduction: Understanding host factor-related mechanisms that drive variability in respiratory particle emission and virus presence in exhaled particles is essential to assess transmission risk and potentially identify individuals with elevated infectiousness. Methods: We conducted a systematic review of human observational studies examining associations between host factors and either respiratory particle emission or virus presence in exhaled particles. Searches in PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science covered studies up to September 2024. Risk of bias was assessed using STROBE-based criteria. Findings were synthesized narratively, grouped by host factor and outcome type. Results: Forty-four studies met inclusion criteria: 34 assessed host factors in relation to particle emission, and 11 examined viral presence in exhaled particles. Fine particle emission (<5 μm) was most consistently associated with older age (n = 16), physical exercise (n = 6), and active infection (n = 6). No consistent associations were found for sex (n = 21), body mass index (BMI; n = 10), or smoking (n = 6). Viral presence-mainly influenza and SARS-CoV-2-was more strongly associated with time since symptom onset (n = 8) and lower respiratory symptoms (n = 3), based largely on genomic detection. Associations with other factors, including upper respiratory symptoms (n = 6), swab viral load (n = 11), age (n = 6), sex (n = 6), and BMI (n = 2), were inconsistent or absent. Physical exercise was not evaluated in relation to viral presence. Discussion: Fine respiratory particles (<5 μm) were the predominant size fraction detected and often contained higher concentrations of viral RNA. Age, physical exercise, and active infection were consistently associated with increased emission of these particles. The presence of respiratory viruses in exhaled air was more strongly linked to infection-related factors such as early symptom onset and lower respiratory involvement. These patterns suggest distinct mechanisms contributing to airborne transmission. Interpretation was limited by methodological heterogeneity and predominant reliance on PCR. Still, consistent associations with host factors suggest their potential as indicators for transmission risk. As evidence focused mainly on influenza and SARS-CoV-2, generalizability is limited. Standardized methods and further research are needed to strengthen outbreak preparedness.
Frontiers in Microbiology 16 frontiersin.org
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors used OpenAI's ChatGPT model 4o to assist with language editing and sentence refinement during the preparation of this manuscript. All content was critically reviewed and finalized by the authors to ensure accuracy and integrity. Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124/ fulll#supplementary-material
References
Ahmed, Rawat, Ferro, Mofakham, Helenbrook et al., Characterizing respiratory aerosol emissions during sustained phonation, J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol, doi:10.1038/s41370-022-00430-z
Almstrand, Bake, Ljungström, Larsson, Bredberg et al., Effect of airway opening on production of exhaled particles, J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00873.2009
Alsved, Nygren, Thuresson, Fraenkel, Medstrand et al., Size distribution of exhaled aerosol particles containing SARS-CoV-2 RNA, Infect. Dis, doi:10.1080/23744235.2022.2140822
Archer, Mccarthy, Symons, Watson, Orton et al., Comparing aerosol number and mass exhalation rates from children and adults during breathing, speaking and singing, Interface Focus, doi:10.1098/rsfs.2021.0078
Asadi, Wexler, Cappa, Barreda, Bouvier et al., Aerosol emission and superemission during human speech increase with voice loudness, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-38808-z
Bagheri, Schlenczek, Turco, Thiede, Stieger et al., Size, concentration, and origin of human exhaled particles and their dependence on human factors with implications on infection transmission, J. Aerosol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2022.106102
Bake, Ljungström, Claesson, Carlsen, Holm, Exhaled particles after a standardized breathing maneuver, J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv, doi:10.1089/jamp.2016.1330
Bender, Sirota, Swetschinski, Dominguez, Novotney et al., Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00176-2
Chatterjee, Bhattacharya, Nag, Dhama, .-O et al., A detailed overview of SARS-CoV-2 omicron: its subvariants, mutations and pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, immunological landscape, immune escape, and therapies, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15010167
Chen, Bobrovitz, Premji, Koopmans, Fisman et al., Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.65774
Chow, Tay, Chen, Tang, Milton et al., Influenza A and B viruses in fine aerosols of exhaled breath samples from patients in tropical Singapore, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15102033
Clark, Glasziou, Del Mar, Bannach-Brown, Stehlik et al., A full systematic review was completed in 2 weeks using automation tools: a case study, J. Clin. Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.01.008
Coleman, Tay, Tan, Ong, Than et al., Viral load of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in respiratory aerosols emitted by patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) while breathing, talking, and singing, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab691
De Mesquita, Nguyen-Van-Tam, Killingley, Enstone, Lambkin-Williams et al., Influenza A (H3) illness and viral aerosol shedding from symptomatic naturally infected and experimentally infected cases, Influenza Other Respir. Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12790
Dixon, Peters, The effect of obesity on lung function, Expert Rev. Respir. Med, doi:10.1080/17476348.2018.1506331
Edwards, Ausiello, Salzman, Devlin, Langer et al., Exhaled aerosol increases with COVID-19 infection, age, and obesity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2021830118
Edwards, Man, Brand, Katstra, Sommerer et al., Inhaling to mitigate exhaled bioaerosols, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.0408159101
Fabian, Mcdevitt, Dehaan, Fung, Cowling et al., Influenza virus in human exhaled breath: an observational study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002691
Fleischer, Schumann, Hartmann, Walker, Ifrim et al., Pre-adolescent children exhibit lower aerosol particle volume emissions than adults for breathing, speaking, singing and shouting, J. R. Soc. Interface, doi:10.1098/rsif.2021.0833
Flerlage, Boyd, Meliopoulos, Thomas, Schultz-Cherry, Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2: pathogenesis and host responses in the respiratory tract, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00542-7
Forbes, Greenwood, Carter, Clark, Automation of duplicate record detection for systematic reviews: Deduplicator, Syst. Rev, doi:10.1186/s13643-024-02619-9
Good, Fedak, Goble, Keisling, L'orange et al., Respiratory aerosol emissions from vocalization: age and sex differences are explained by volume and exhaled CO2, Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett, doi:10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00760
Gregson, Watson, Orton, Haddrell, Mccarthy et al., Comparing aerosol concentrations and particle size distributions generated by singing, speaking and breathing, Aerosol Sci. Technol, doi:10.1080/02786826.2021.1883544
Guo, Zhao, Lee, Hung, Wong et al., A statistical framework for tracking the time-varying superspreading potential of COVID-19 epidemic, Epidemics, doi:10.1016/j.epidem.2023.100670
Gutmann, Donath, Herrlich, Lehmkuehler, Landeis et al., Exhaled aerosols in SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction-positive children and age-matched-negative controls, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2022.941785
Gutmann, Scheuch, Lehmkühler, Herrlich, Hutter et al., Aerosol measurement identifies SARS-CoV 2 PCR positive adults compared with healthy controls, Environ. Res, doi:10.1101/2022.01.21.22269423
Harrison, Saccente-Kennedy, Orton, Mccarthy, Archer et al., Emission rates, size distributions, and generation mechanism of oral respiratory droplets, Aerosol Sci. Technol, doi:10.1080/02786826.2022.2158778
Hersen, Moularat, Robine, Géhin, Corbet et al., Impact of health on particle size of exhaled respiratory aerosols: case-control study, Clean (Weinh), doi:10.1002/clen.200700189
Hu, Yuan, Gram, Yao, Sadrizadeh, Review of experimental measurements on particle size distribution and airflow behaviors during human respiration, Build. Environ, doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110994
Hussain-Alkhateeb, Bake, Holm, Emilsson, Mirgorodskaya, Novel non-invasive particles in exhaled air method to explore the lining fluid of small airways-a European population-based cohort study, BMJ Open Respir. Res, doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000804
Iannone, Cheng, Schloerke, Hughes, Lauer et al., Gt: easily create presentation-ready display tables
Igo, Geneva, The burden of influenza
Jaumdally, Tomasicchio, Pooran, Esmail, Kotze et al., Frequency, kinetics and determinants of viable SARS-CoV-2 in bioaerosols from ambulatory COVID-19 patients infected with the beta, delta or omicron variants, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45400-1
Johnson, Morawska, The mechanism of breath aerosol formation, J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv, doi:10.1089/jamp.2008.0720
Kappelt, Russell, Kwiatkowski, Afshari, Johnson, Correlation of respiratory aerosols and metabolic carbon dioxide, Sustainability, doi:10.3390/su132112203
Kutter, Spronken, Fraaij, Fouchier, Herfst, Transmission routes of respiratory viruses among humans, Curr. Opin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2018.01.001
Lai, Coleman, Tai, German, Hong et al., Exhaled breath aerosol shedding of highly transmissible versus prior severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 variants, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac846
Lee, Shih, Leu, Chang, Lin et al., Implications of age-related changes in anatomy for geriatric-focused difficult airways, Int. J. Gerontol, doi:10.1016/j.ijge.2016.11.003
Lee, Yoo, Ryu, Ham, Lee et al., Quantity, size distribution, and characteristics of cough-generated aerosol produced by patients with an upper respiratory tract infection, Aerosol Air Qual. Res, doi:10.4209/aaqr.2018.01.0031
Li, Tang, Abnormal airway mucus secretion induced by virus infection, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.701443
Lim, Cheong, Oh, Lee, So et al., Modeling the early temporal dynamics of viral load in respiratory tract specimens of COVID-19 patients in Incheon, the Republic of Korea, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.062
Lindsley, Blachere, Beezhold, Thewlis, Noorbakhsh et al., Viable influenza A virus in airborne particles expelled during coughs versus exhalations, Influenza Other Respir. Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12390
Lindsley, Blachere, Thewlis, Vishnu, Davis et al., Measurements of airborne influenza virus in aerosol particles from human coughs, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015100
Lindsley, Pearce, Hudnall, Davis, Davis et al., Quantity and size distribution of cough-generated aerosol particles produced by influenza patients during and after illness, J. Occup. Environ. Hyg, doi:10.1080/15459624.2012.684582
Lomauro, .-O, Aliverti, Sex differences in respiratory function, Breathe, doi:10.1183/20734735.000318
Marshall, Gibson, Romer, Illidi, Hull et al., Systemic but not local rehydration restores dehydration-induced changes in pulmonary function in healthy adults, J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00311.2020
Martins Rodrigues, Torres Pereira, De Castro Lopes, Massaroni, Baroni et al., Is age rating enough to investigate changes in breathing motion pattern associated with aging of physically active women?, J. Biomech, doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110582
Milton, Fabian, Cowling, Grantham, Mcdevitt, Influenza virus aerosols in human exhaled breath: particle size, culturability, and effect of surgical masks, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003205
Molgat-Seon, Peters, Sheel, Sex-differences in the human respiratory system and their impact on resting pulmonary function and the integrative response to exercise, Curr. Opin. Physio, doi:10.1016/j.cophys.2018.03.007
Morawska, Johnson, Ristovski, Hargreaves, Mengersen et al., Size distribution and sites of origin of droplets expelled from the human respiratory tract during expiratory activities, J. Aerosol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2008.11.002
Moseley, Archer, Orton, Symons, Watson et al., Relationship between exhaled aerosol and carbon dioxide emission across respiratory activities, Environ. Sci. Technol, doi:10.1021/acs.est.4c01717
Mutsch, Heiber, Grätz, Hain, Schönfelder et al., Aerosol particle emission increases exponentially above moderate exercise intensity resulting in superemission during maximal exercise, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2202521119
Mürbe, Kriegel, Lange, Rotheudt, Fleischer, Aerosol emission in professional singing of classical music, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-93281-x
Mürbe, Kriegel, Lange, Schumann, Hartmann et al., Aerosol emission of adolescents voices during speaking, singing and shouting, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246819
Nikolić, Sun, Rawlins, Human lung development: recent progress and new challenges, Development, doi:10.1242/dev.163485
Oh, Bu, Kikumoto, Ooka, Correlation between beverage consumption and droplet production during respiratory activity using interferometric Mie imaging experiment, J. Aerosol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2024.106458
Oldham, Moss, Pores of Kohn: forgotten alveolar structures and potential source of aerosols in exhaled breath, J. Breath Res, doi:10.1088/1752-7163/ab0524
Organization, Global technical consultation report on proposed terminology for pathogens that transmit through the air
Orton, Symons, Moseley, Archer, Watson et al., A comparison of respiratory particle emission rates at rest and while speaking or exercising, Commun Med, doi:10.1038/s43856-022-00103-w
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pan, Xu, Francis Yu, Liu, Characterization and size distribution of initial droplet concentration discharged from human breathing and speaking, Indoor and Built Environment, doi:10.1177/1420326X221110975
Puhach, Meyer, Eckerle, SARS-CoV-2 viral load and shedding kinetics, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00822-w
Pöhlker, Pöhlker, Krüger, Förster, Berkemeier et al., Respiratory aerosols and droplets in the transmission of infectious diseases, Rev. Mod. Phys, doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.95.045001
Rathnayake, Ditz, Van Nijnatten, Sadaf, Hansbro et al., Smoking induces shifts in cellular composition and transcriptome within the bronchial mucus barrier, Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.14401
Rawat, Agirsoy, Senarathna, Erath, Ahmed et al., Comparing respiratory aerosol emissions between children and adults during sustained phonation, Aerosol Sci. Technol, doi:10.1080/02786826.2023.2261715
Roman, Rossiter, Casaburi, Exercise, ageing and the lung, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00347-2016
Roth, Stiti, Frantz, Corber, Berrocal, Exhaled aerosols and saliva dropletsmeasured in time and 3D space: quantification of pathogens flow rate applied to SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Sci, doi:10.1002/ntls.20230007
Sajgalik, Garzona-Navas, Csécs, Askew, Lopez-Jimenez et al., Characterization of aerosol generation during various intensities of exercise, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.04.041
Schneider, Rowe, Garcia-De-Alba, Kim, Sharpe et al., The aging lung: physiology, disease, and immunity, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.005
Schuchmann, Scheuch, Naumann, Keute, Lücke et al., Exhaled aerosols among PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2-infected children, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2023.1156366
Schumm, Bremer, Knoedlseder, Schoenfelder, Hain et al., Indices of airway resistance and reactance from impulse oscillometry correlate with aerosol particle emission in different age groups, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-55117-2
Schumm, Bremer, Knödlseder, Schönfelder, Hain et al., Lung aerosol particle emission increases with age at rest and during exercise, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2301145120
Schwarz, Biller, Windt, Koch, Hohlfeld, Characterization of exhaled particles from the healthy human lung--a systematic analysis in relation to pulmonary function variables, J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv, doi:10.1089/jamp.2009.0809
Schwarz, Biller, Windt, Koch, Hohlfeld, Characterization of exhaled particles from the human lungs in airway obstruction, J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv, doi:10.1089/jamp.2013.1104
Sirota, Doxey, Dominguez, Bender, Vongpradith et al., Global, regional, and national burden of upper respiratory infections and otitis media, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00430-4
Sun, Zhang, Liu, Liu, Wu et al., Association between body mass index and respiratory symptoms in US adults: a national cross-sectional study, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-51637-z
Team, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Thomas, Guppy, Straus, Bell, Glasziou, Rate of normal lung function decline in ageing adults: a systematic review of prospective cohort studies, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028150
Tinglev, Ullah, Ljungkvist, Viklund, Olin et al., Characterization of exhaled breath particles collected by an electret filter technique, J. Breath Res, doi:10.1088/1752-7155/10/2/026001
Varga, Kwiatkowski, Pedro, Groepenhoff, Rose et al., Observation of aerosol generation by human subjects during cardiopulmonary exercise testing using a high-powered laser technique: A pilot project, J. Med. Biol. Eng, doi:10.1007/s40846-021-00675-3
Verreault, Moineau, Duchaine, Methods for sampling of airborne viruses, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev, doi:10.1128/mmbr.00002-08
Viklund, Kokelj, Larsson, Nordén, Andersson et al., Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 can be detected in exhaled aerosol sampled during a few minutes of breathing or coughing, Influenza Other Respir. Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12964
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, Pocock, Gøtzsche et al., The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X
Wang, Prather, Sznitman, Jimenez, Lakdawala et al., Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd9149
Wegehaupt, Endo, Vassall, Superspreading, overdispersion and their implications in the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic: a systematic review and metaanalysis of the literature, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-023-15915-1
Weston, Frieman, Respiratory viruses
Wickham, Averick, Bryan, Chang, Mcgowan et al., Welcome to the tidyverse, J. Open Source Softw, doi:10.21105/joss.01686
Xie, Li, Sun, Liu, Yan et al., Infectious virus in exhaled breath of symptomatic seasonal influenza cases from a college community, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1716561115
Zanin, Baviskar, Webster, Webby, The interaction between respiratory pathogens and mucus, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.01.001
Zayas, Chiang, Wong, Macdonald, Lange et al., Cough aerosol in healthy participants: fundamental knowledge to optimize droplet-spread infectious respiratory disease management, BMC Pulm. Med, doi:10.1186/1471-2466-12-11
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124",
"ISSN": [
"1664-302X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Understanding host factor-related mechanisms that drive variability in respiratory particle emission and virus presence in exhaled particles is essential to assess transmission risk and potentially identify individuals with elevated infectiousness.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a systematic review of human observational studies examining associations between host factors and either respiratory particle emission or virus presence in exhaled particles. Searches in PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science covered studies up to September 2024. Risk of bias was assessed using STROBE-based criteria. Findings were synthesized narratively, grouped by host factor and outcome type.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Forty-four studies met inclusion criteria: 34 assessed host factors in relation to particle emission, and 11 examined viral presence in exhaled particles. Fine particle emission (&lt;5 μm) was most consistently associated with older age (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 16), physical exercise (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6), and active infection (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6). No consistent associations were found for sex (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 21), body mass index (BMI; <jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 10), or smoking (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6). Viral presence—mainly influenza and SARS-CoV-2—was more strongly associated with time since symptom onset (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 8) and lower respiratory symptoms (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 3), based largely on genomic detection. Associations with other factors, including upper respiratory symptoms (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6), swab viral load (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 11), age (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6), sex (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 6), and BMI (<jats:italic>n =</jats:italic> 2), were inconsistent or absent. Physical exercise was not evaluated in relation to viral presence.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Discussion</jats:title><jats:p>Fine respiratory particles (&lt;5 μm) were the predominant size fraction detected and often contained higher concentrations of viral RNA. Age, physical exercise, and active infection were consistently associated with increased emission of these particles. The presence of respiratory viruses in exhaled air was more strongly linked to infection-related factors such as early symptom onset and lower respiratory involvement. These patterns suggest distinct mechanisms contributing to airborne transmission. Interpretation was limited by methodological heterogeneity and predominant reliance on PCR. Still, consistent associations with host factors suggest their potential as indicators for transmission risk. As evidence focused mainly on influenza and SARS-CoV-2, generalizability is limited. Standardized methods and further research are needed to strengthen outbreak preparedness.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124"
],
"article-number": "1652124",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horstink",
"given": "Nils",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lassing",
"given": "Kirsten",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knoester",
"given": "Marjolein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vermeulen",
"given": "Lucie C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rossen",
"given": "John W. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Voss",
"given": "Andreas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lokate",
"given": "Mariëtte",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Microbiol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-15T05:43:45Z",
"timestamp": 1760507025000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-15T05:43:46Z",
"timestamp": 1760507026000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-16T00:20:32Z",
"timestamp": 1760574032069,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1760486400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41370-022-00430-z",
"article-title": "Characterizing respiratory aerosol emissions during sustained phonation",
"author": "Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/japplphysiol.00873.2009",
"article-title": "Effect of airway opening on production of exhaled particles",
"author": "Almstrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "584",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2022.2140822",
"article-title": "Size distribution of exhaled aerosol particles containing SARS-CoV-2 RNA",
"author": "Alsved",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsfs.2021.0078",
"article-title": "Comparing aerosol number and mass exhalation rates from children and adults during breathing, speaking and singing",
"author": "Archer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20210078",
"journal-title": "Interface Focus",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-38808-z",
"article-title": "Aerosol emission and superemission during human speech increase with voice loudness",
"author": "Asadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2348",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaerosci.2022.106102",
"article-title": "Size, concentration, and origin of human exhaled particles and their dependence on human factors with implications on infection transmission",
"author": "Bagheri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106102",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Sci.",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2016.1330",
"article-title": "Exhaled particles after a standardized breathing maneuver",
"author": "Bake",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv.",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00176-2",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021",
"author": "Bender",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "974",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15010167",
"article-title": "A detailed overview of SARS-CoV-2 omicron: its sub-variants, mutations and pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, immunological landscape, immune escape, and therapies",
"author": "Chatterjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.65774",
"article-title": "Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65774",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15102033",
"article-title": "Influenza A and B viruses in fine aerosols of exhaled breath samples from patients in tropical Singapore",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2033",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.01.008",
"article-title": "A full systematic review was completed in 2 weeks using automation tools: a case study",
"author": "Clark",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab691",
"article-title": "Viral load of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in respiratory aerosols emitted by patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) while breathing, talking, and singing",
"author": "Coleman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1722",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12790",
"article-title": "Influenza A (H3) illness and viral aerosol shedding from symptomatic naturally infected and experimentally infected cases",
"author": "de Mesquita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir. Viruses",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2018.1506331",
"article-title": "The effect of obesity on lung function",
"author": "Dixon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2021830118",
"article-title": "Exhaled aerosol increases with COVID-19 infection, age, and obesity",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0408159101",
"article-title": "Inhaling to mitigate exhaled bioaerosols",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17383",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0002691",
"article-title": "Influenza virus in human exhaled breath: an observational study",
"author": "Fabian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2691",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsif.2021.0833",
"article-title": "Pre-adolescent children exhibit lower aerosol particle volume emissions than adults for breathing, speaking, singing and shouting",
"author": "Fleischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20210833",
"journal-title": "J. R. Soc. Interface",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00542-7",
"article-title": "Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2: pathogenesis and host responses in the respiratory tract",
"author": "Flerlage",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13643-024-02619-9",
"article-title": "Automation of duplicate record detection for systematic reviews: Deduplicator",
"author": "Forbes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Syst. Rev.",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00760",
"article-title": "Respiratory aerosol emissions from vocalization: age and sex differences are explained by volume and exhaled CO2",
"author": "Good",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett.",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02786826.2021.1883544",
"article-title": "Comparing aerosol concentrations and particle size distributions generated by singing, speaking and breathing",
"author": "Gregson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Aerosol Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.epidem.2023.100670",
"article-title": "A statistical framework for tracking the time-varying superspreading potential of COVID-19 epidemic",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100670",
"journal-title": "Epidemics",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2022.941785",
"article-title": "Exhaled aerosols in SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction-positive children and age-matched-negative controls",
"author": "Gutmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "941785",
"journal-title": "Front. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.01.21.22269423",
"article-title": "Aerosol measurement identifies SARS-CoV 2 PCR positive adults compared with healthy controls",
"author": "Gutmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "114417",
"journal-title": "Environ. Res.",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02786826.2022.2158778",
"article-title": "Emission rates, size distributions, and generation mechanism of oral respiratory droplets",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "187",
"journal-title": "Aerosol Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/clen.200700189",
"article-title": "Impact of health on particle size of exhaled respiratory aerosols: case-control study",
"author": "Hersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "572",
"journal-title": "Clean (Weinh)",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110994",
"article-title": "Review of experimental measurements on particle size distribution and airflow behaviors during human respiration",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110994",
"journal-title": "Build. Environ.",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "247",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000804",
"article-title": "Novel non-invasive particles in exhaled air method to explore the lining fluid of small airways-a European population-based cohort study",
"author": "Hussain-Alkhateeb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "804",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Respir. Res.",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Iannone",
"key": "ref31",
"volume-title": "Gt: easily create presentation-ready display tables",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-45400-1",
"article-title": "Frequency, kinetics and determinants of viable SARS-CoV-2 in bioaerosols from ambulatory COVID-19 patients infected with the beta, delta or omicron variants",
"author": "Jaumdally",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2003",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2008.0720",
"article-title": "The mechanism of breath aerosol formation",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv.",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/su132112203",
"article-title": "Correlation of respiratory aerosols and metabolic carbon dioxide",
"author": "Kappelt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2203",
"journal-title": "Sustainability",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2018.01.001",
"article-title": "Transmission routes of respiratory viruses among humans",
"author": "Kutter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Virol.",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac846",
"article-title": "Exhaled breath aerosol shedding of highly transmissible versus prior severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 variants",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "786",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijge.2016.11.003",
"article-title": "Implications of age-related changes in anatomy for geriatric-focused difficult airways",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gerontol.",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4209/aaqr.2018.01.0031",
"article-title": "Quantity, size distribution, and characteristics of cough-generated aerosol produced by patients with an upper respiratory tract infection",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "840",
"journal-title": "Aerosol Air Qual. Res.",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.701443",
"article-title": "Abnormal airway mucus secretion induced by virus infection",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "701443",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.062",
"article-title": "Modeling the early temporal dynamics of viral load in respiratory tract specimens of COVID-19 patients in Incheon, the Republic of Korea",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12390",
"article-title": "Viable influenza A virus in airborne particles expelled during coughs versus exhalations",
"author": "Lindsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "404",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir. Viruses",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0015100",
"article-title": "Measurements of airborne influenza virus in aerosol particles from human coughs",
"author": "Lindsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e15100",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15459624.2012.684582",
"article-title": "Quantity and size distribution of cough-generated aerosol particles produced by influenza patients during and after illness",
"author": "Lindsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "443",
"journal-title": "J. Occup. Environ. Hyg.",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/20734735.000318",
"article-title": "Sex differences in respiratory function",
"author": "LoMauro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "131",
"journal-title": "Breathe",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/japplphysiol.00311.2020",
"article-title": "Systemic but not local rehydration restores dehydration-induced changes in pulmonary function in healthy adults",
"author": "Marshall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110582",
"article-title": "Is age rating enough to investigate changes in breathing motion pattern associated with aging of physically active women?",
"author": "Martins Rodrigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110582",
"journal-title": "J. Biomech.",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1003205",
"article-title": "Influenza virus aerosols in human exhaled breath: particle size, culturability, and effect of surgical masks",
"author": "Milton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1003205",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cophys.2018.03.007",
"article-title": "Sex-differences in the human respiratory system and their impact on resting pulmonary function and the integrative response to exercise",
"author": "Molgat-Seon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Physio.",
"key": "ref48",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaerosci.2008.11.002",
"article-title": "Size distribution and sites of origin of droplets expelled from the human respiratory tract during expiratory activities",
"author": "Morawska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "256",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Sci.",
"key": "ref49",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.est.4c01717",
"article-title": "Relationship between exhaled aerosol and carbon dioxide emission across respiratory activities",
"author": "Moseley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15120",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-93281-x",
"article-title": "Aerosol emission in professional singing of classical music",
"author": "Mürbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14861",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref51",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246819",
"article-title": "Aerosol emission of adolescents voices during speaking, singing and shouting",
"author": "Mürbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0246819",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2202521119",
"article-title": "Aerosol particle emission increases exponentially above moderate exercise intensity resulting in superemission during maximal exercise",
"author": "Mutsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2202521119",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref53",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1242/dev.163485",
"article-title": "Human lung development: recent progress and new challenges",
"author": "Nikolić",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "163485",
"journal-title": "Development",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaerosci.2024.106458",
"article-title": "Correlation between beverage consumption and droplet production during respiratory activity using interferometric Mie imaging experiment",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106458",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Sci.",
"key": "ref55",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1088/1752-7163/ab0524",
"article-title": "Pores of Kohn: forgotten alveolar structures and potential source of aerosols in exhaled breath",
"author": "Oldham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "021003",
"journal-title": "J. Breath Res.",
"key": "ref56",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "ref57",
"volume-title": "Global technical consultation report on proposed terminology for pathogens that transmit through the air;. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "ref58",
"volume-title": "The burden of influenza",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43856-022-00103-w",
"article-title": "A comparison of respiratory particle emission rates at rest and while speaking or exercising",
"author": "Orton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Commun Med",
"key": "ref59",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n71",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref60",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1420326X221110975",
"article-title": "Characterization and size distribution of initial droplet concentration discharged from human breathing and speaking",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2020",
"journal-title": "Indoor and Built Environment.",
"key": "ref61",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1103/RevModPhys.95.045001",
"article-title": "Respiratory aerosols and droplets in the transmission of infectious diseases",
"author": "Pöhlker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "045001",
"journal-title": "Rev. Mod. Phys.",
"key": "ref62",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00822-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load and shedding kinetics",
"author": "Puhach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref63",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.14401",
"article-title": "Smoking induces shifts in cellular composition and transcriptome within the bronchial mucus barrier",
"author": "Rathnayake",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "ref64",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02786826.2023.2261715",
"article-title": "Comparing respiratory aerosol emissions between children and adults during sustained phonation",
"author": "Rawat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "Aerosol Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref65",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00347-2016",
"article-title": "Exercise, ageing and the lung",
"author": "Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1471",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref66",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ntls.20230007",
"article-title": "Exhaled aerosols and saliva dropletsmeasured in time and 3D space: quantification of pathogens flow rate applied to SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Roth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat. Sci.",
"key": "ref67",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2021.04.041",
"article-title": "Characterization of aerosol generation during various intensities of exercise",
"author": "Sajgalik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref68",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.005",
"article-title": "The aging lung: physiology, disease, and immunity",
"author": "Schneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1990",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref69",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2023.1156366",
"article-title": "Exhaled aerosols among PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2-infected children",
"author": "Schuchmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1156366",
"journal-title": "Front. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref70",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2301145120",
"article-title": "Lung aerosol particle emission increases with age at rest and during exercise",
"author": "Schumm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2301145120",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref71",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-55117-2",
"article-title": "Indices of airway resistance and reactance from impulse oscillometry correlate with aerosol particle emission in different age groups",
"author": "Schumm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4644",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref72",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2009.0809",
"article-title": "Characterization of exhaled particles from the healthy human lung--a systematic analysis in relation to pulmonary function variables",
"author": "Schwarz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "371",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv.",
"key": "ref73",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2013.1104",
"article-title": "Characterization of exhaled particles from the human lungs in airway obstruction",
"author": "Schwarz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv.",
"key": "ref74",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00430-4",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national burden of upper respiratory infections and otitis media, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021",
"author": "Sirota",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref75",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-51637-z",
"article-title": "Association between body mass index and respiratory symptoms in US adults: a national cross-sectional study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "940",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref76",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "ref77",
"volume-title": "R: A language and environment for statistical computing",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028150",
"article-title": "Rate of normal lung function decline in ageing adults: a systematic review of prospective cohort studies",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e028150",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "ref78",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1088/1752-7155/10/2/026001",
"article-title": "Characterization of exhaled breath particles collected by an electret filter technique",
"author": "Tinglev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "026001",
"journal-title": "J. Breath Res.",
"key": "ref79",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40846-021-00675-3",
"article-title": "Observation of aerosol generation by human subjects during cardiopulmonary exercise testing using a high-powered laser technique: A pilot project",
"author": "Varga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Biol. Eng.",
"key": "ref80",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mmbr.00002-08",
"article-title": "Methods for sampling of airborne viruses",
"author": "Verreault",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev.",
"key": "ref81",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12964",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 can be detected in exhaled aerosol sampled during a few minutes of breathing or coughing",
"author": "Viklund",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "402",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir. Viruses",
"key": "ref82",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X",
"article-title": "The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies",
"author": "von Elm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1453",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref83",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd9149",
"article-title": "Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabd9149",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref84",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-023-15915-1",
"article-title": "Superspreading, overdispersion and their implications in the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature",
"author": "Wegehaupt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1003",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "ref85",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Respiratory viruses",
"author": "Weston",
"first-page": "85",
"key": "ref86",
"volume-title": "Encyclopedia of microbiology",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21105/joss.01686",
"article-title": "Welcome to the tidyverse",
"author": "Wickham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1686",
"journal-title": "J. Open Source Softw.",
"key": "ref87",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsif.2009.0388.focus",
"article-title": "Exhaled droplets due to talking and coughing",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S703",
"journal-title": "J. R. Soc. Interface",
"key": "ref88",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1716561115",
"article-title": "Infectious virus in exhaled breath of symptomatic seasonal influenza cases from a college community",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1081",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref89",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2016.01.001",
"article-title": "The interaction between respiratory pathogens and mucus",
"author": "Zanin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref90",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2466-12-11",
"article-title": "Cough aerosol in healthy participants: fundamental knowledge to optimize droplet-spread infectious respiratory disease management",
"author": "Zayas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "BMC Pulm. Med.",
"key": "ref91",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2012"
}
],
"reference-count": 91,
"references-count": 91,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence within respiratory particles: a systematic review",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}