Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, Alcohol Consumption, and Tobacco Use in Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review
et al., INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, doi:10.1177/00469580231175780, May 2023
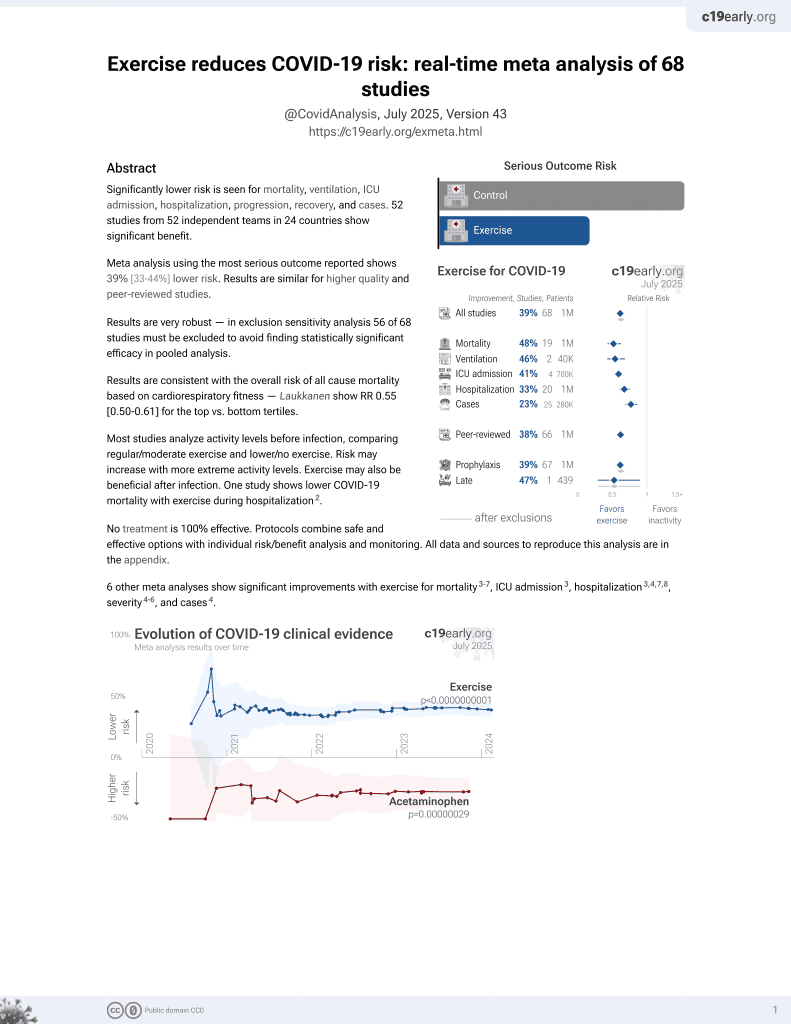
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
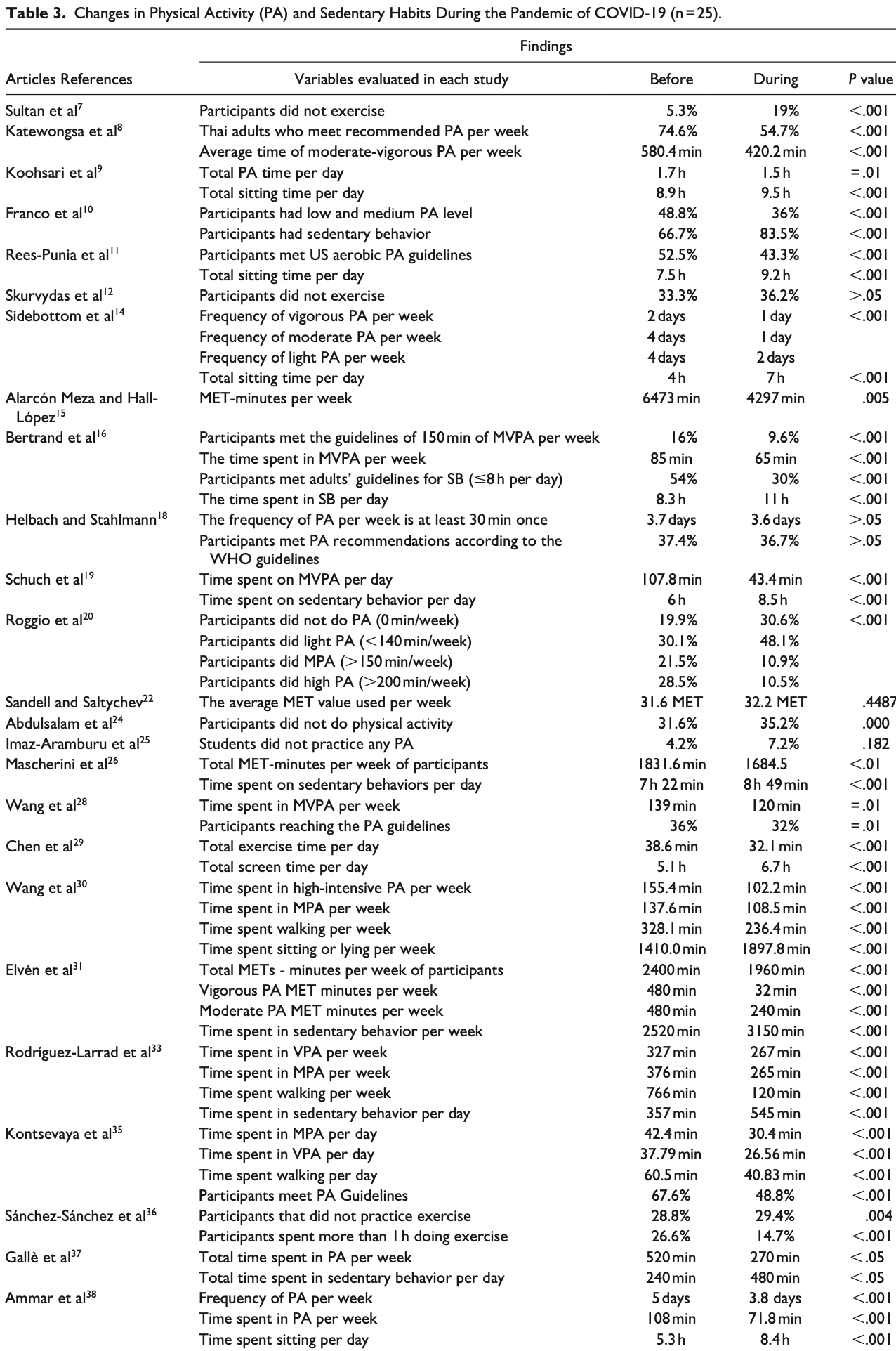
Systematic review showing 25 of 25 studies reported a decrease in physical activity and 13 of 13 studies reported an increase in sedentary behavior during the pandemic.
1.
Horstink et al., Host factors associated with respiratory particle emission and virus presence within respiratory particles: a systematic review, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2025.1652124.
2.
Nindenshuti et al., Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, Alcohol Consumption, and Tobacco Use in Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review, INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, doi:10.1177/00469580231175780.
Nindenshuti et al., 23 May 2023, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Contact: nshutimarcel@gmail.com.
Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, Alcohol Consumption, and Tobacco Use in Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, doi:10.1177/00469580231175780
The COVID-19 pandemic changed various lifestyle habits worldwide due to the prevention measures implemented in each country, these changes may affect or benefit people's health. We aimed to systematically review changes in diet, physical activity (PA), alcohol consumption, and tobacco use habits during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults. Two databases: PubMed and ScienceDirect, were used for this systematic review. The research was limited to open-access, peer-reviewed original articles published in English, French, or Spanish from January 2020 to December 2022 and investigated diet, PA, alcohol consumption, and tobacco use habits before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults. Excluded studies were review studies, intervention studies with a sample size of fewer than 30 participants, and poorquality articles. This review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines (PROSPERO: CRD42023406524), whereas to assess the quality of the studies, we used the quality assessment tools developed by the BSA Medical Sociology Group for crosssectional studies and the QATSO for the longitudinal studies. Thirty-two studies were included. Some studies reported changes to promote healthy lifestyles; 13 out of 15 articles reported an increase in healthy diet consumption habits, 5 out of 7 studies reported a decrease in alcohol consumption, and 2 out of 3 studies reported a decrease in tobacco use. On the other hand, the other studies reported changes to promote unhealthy lifestyles: 9 out of 15, and 2 out of 7 studies reported an increase in unhealthy diet and alcohol consumption habits respectively, 25 out of 25 reported a decrease in physical activity, and 13 out of 13 reported an increase in sedentary behavior. During the COVID-19 pandemic, there have been changes to promote a healthy and unhealthy lifestyle; the latter can affect people's health. Therefore, effective responses are needed to mitigate the consequences.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics Declaration Our study did not require ethical board approval because our study is a systematic review.
Informed Consent Our study did not require informed consent for participants because our study is a systematic review.
Presence of Declarations, and Ethics and Consent Statements For this systematic review, no ethical/consent concerns were needed. We only checked the available literature in two databases.
ORCID iD Paul Marcel Nindenshuti https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9487-140X
Supplemental Material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
Abdulsalam, Khateeb, Aljerbi, Assessment of dietary habits and physical activity changes during the full COVID-19 curfew period and its effect on weight among adults in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18168580
Ammar, Brach, Trabelsi, Effects of COVID-19 home confinement on eating behaviour and physical activity: results of the ECLB-COVID19 International Online Survey, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061583
Andrade-Chauvín, Stress and alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, Retos De la Cienc
Assessed, None
Balanzá-Martínez, Kapczinski, De Azevedo Cardoso, The assessment of lifestyle changes during the COVID-19 pandemic using a multidimensional scale, Revista Revista Psiquiatr Y Salud Ment, doi:10.1016/j.rps-men.2020.07.005
Barbosa, Cowell, Dowd, Alcohol consumption in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, J Addict Med, doi:10.1097/adm.0000000000000767
Bağcı, Kanadıkırık, Somyürek, Impact of COVID-19 on eating habits, sleeping behaviour and physical activity status of final-year medical students in Ankara, Turkey. Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980021003906
Bennett, Young, Butler, Coe, The impact of lockdown during the COVID-19 outbreak on dietary habits in various population groups: a scoping review, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.626432
Bertrand, Shaw, Ko, Deprez, Chilibeck et al., The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on university students' dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour, Appl Physiol Nutr Metab, doi:10.1139/apnm-2020-0990
Brancaccio, Mennitti, Gentile, Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on job activity, dietary behaviours and physical activity habits of University population of Naples, Federico II-Italy, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18041502
Callinan, Mojica-Perez, Wright, Purchasing, consumption, demographic and socioeconomic variables associated with shifts in alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, Drug Alcohol Rev, doi:10.1111/dar.13200
Castaldelli-Maia, Segura, Martins, The concerning increasing trend of alcohol beverage sales in the U.S. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Alcohol, doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2021.06.004
Chen, Li, Xia, Changes of exercise, screen time, fast food consumption, alcohol, and cigarette smoking during the COVID-19 pandemic among adults in the United States, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103359
Clift, Von Ende, Tan, Smoking and COVID-19 outcomes: an observational and Mendelian randomisation study using the UK Biobank cohort, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217080
De Luis Román, Izaola, Martín, Hoyos, Torres et al., Effect of lockdown for COVID-19 on self-reported body weight gain in a sample of obese patients, Nutr Hosp, doi:10.20960/nh.03307
Diana, Pineda, Alcoholismo, tabaquismo y sustancias psicoactivas, Revista De Salud Pública
Dicken, Mitchell, Newberry, Vay, Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on diet behaviour among UK adults: a longitudinal analysis of the HEBECO study, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.788043
Elvén, Kerstis, Stier, Changes in physical activity and sedentary behavior before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a Swedish population study, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19052558
Franco, Urosa, Barakat, Refoyo, Physical activity and adherence to the Mediterranean diet among Spanish employees in a health-promotion program before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: the Sanitas-Healthy Cities challenge, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18052735
Gallè, Sabella, Ferracuti, Giglio, Caggiano et al., Italian undergraduate students' sedentary behaviors and physical activity during lockdown at the time of the CoViD-19 pandemic, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17176171
Gaona-Pineda, Martínez-Tapia, Arango-Angarita, Consumo de grupos de alimentos y factores sociodemográficos en población mexicana, Salud Pública de México, doi:10.21149/8803
Helbach, Stahlmann, Changes in digital media use and physical activity in German young adults under the covid-19 pandemic -a cross-sectional study, J Sports Sci Med, doi:10.52082/jssm.2021.642
Hu, Quigley, Taylor, Human mobility data and machine learning reveal geographic differences in alcohol sales and alcohol outlet visits across U.S. States during COVID-19, PLoS One
Imaz-Aramburu, Gamboa, Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the lifestyles of health sciences university students in Spain: a longitudinal study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061958
Katewongsa, Widyastari, Saonuam, Haemathulin, Wongsingha, The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the physical activity of the Thai population: evidence from Thailand's surveillance on Physical Activity 2020, J Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2020.10.001
Kent, Murray, Penrose, Food insecure households faced greater challenges putting healthy food on the table during the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia, Appetite, doi:10.1016/j.appet.2021.105815
Kontsevaya, Mukaneeva, Myrzamatova, Okely, Drapkina, Changes in physical activity and sleep habits among adults in Russian Federation during COVID-19: a cross-sectional study, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-021-10946-y
Koohsari, Nakaya, Mccormack, Shibata, Ishii et al., Changes in workers' sedentary and physical activity behaviors in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and their relationships with fatigue: longitudinal online study, doi:10.2196/26293
Lakka, Bouchard, Physical activity, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, doi:10.1007/3-540-27661-0_4
Maestre, Sospedra, Martínez-Sanz, Assessment of Spanish food consumption patterns during COVID-19 home confinement, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114122
Mascherini, Catelan, Pellegrini-Giampietro, Petri, Scaletti et al., Changes in physical activity levels, eating habits and psychological well-being during the Italian COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: impact of socio-demographic factors on the Florentine academic population, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252395
Meza, López, Physical activity in university student athletes, prior and in confinement due to pandemic associated with COVID-19 (Actividad física en estudiantes deportistas universitarios, previo y en el confinamiento por pandemia asociada al COVID-19), doi:10.47197/retos.v0i39.81293
Morton, Alcohol sales during COVID-19 social restrictions: initial evidence from alcoholic beverage control states, Subst Abuse, doi:10.1080/08897077.2020.1856293
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/jour-nal.pmed.1003583
Ramón-Arbués, Abadía, López, Eating behavior and relationships with stress, anxiety, depression, and insomnia in university students, Nutr Hosp, doi:10.20960/nh.02641
Rao, Mueller, Broadbent, Risky alcohol consumption in older people before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom, J Subst Use, doi:10.1080/14659891.2021.1916851
Rees-Punia, Newton, Rittase, Prospective changes in physical activity, sedentary time, and sleep during the COVID-19 pandemic in a US-based cohort study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053817
Rodríguez-Larrad, Mañas, Labayen, Impact of COVID-19 confinement on physical activity and sedentary behaviour in Spanish university students: role of gender, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18020369
Roggio, Trovato, Ravalli, One year of COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: effect of sedentary behavior on physical activity levels and musculoskeletal pain among university students, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18168680
Rosenheck, Fast food consumption and increased caloric intake: a systematic review of a trajectory towards weight gain and obesity risk, Obes Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1467-789x.2008.00477.x
Rouhani, Salehi-Abargouei, Surkan, Azadbakht, Is there a relationship between red or processed meat intake and obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies: red or processed meat and obesity, Obes Rev, doi:10.1111/obr.12172
Sandell, Saltychev, Change in alcohol consumption and physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic amongst 76 medical students, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.12580
Schuch, Bulzing, Meyer, Moderate to vigorous physical activity and sedentary behavior changes in selfisolating adults during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil: a cross-sectional survey exploring correlates, Sport Sci Health, doi:10.1007/s11332-021-00788-x
Sidebottom, Ullevig, Cheever, Zhang, Effects of COVID-19 pandemic and quarantine period on physical activity and dietary habits of college-aged students, Sports Med Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.smhs.2021.08.005
Skurvydas, Lisinskiene, Lochbaum, Did COVID-19 pandemic change people's physical activity distribution, eating, and alcohol consumption habits as well as body mass index?, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph182312405
Sultan, Alobaidi, Sewaid, Bader, Almuwallad et al., Assessment of the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the lifestyle of the population in Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional online survey study, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.19796
Sánchez-Sánchez, Vargas, Avellaneda-López, Orellana-Pecino, García-Marín et al., Eating habits and physical activity of the Spanish population during the COVID-19 pandemic period, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092826
Vayr, Martin-Blondel, Savall, Occupational exposure to human mycobacterium bovis infection: A systematic review, PLoS Negl Trop Dis, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0006208
Wang, Feng, Zhang, Changes in Chinese adults' physical activity behavior and determinants before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10143069
Wang, Yeoh, Yung, Change in eating habits and physical activities before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong: a cross-sectional study via random telephone survey, J Int Soc Sports Nutr, doi:10.1186/s12970-021-00431-7
Wong, Cheung, Hart, Development of a quality assessment tool for systematic reviews of observational studies (QATSO) of HIV prevalence in men having sex with men and associated risk behaviours, Emerg Themes Epidemiol, doi:10.1186/1742-7622-5-23
Yang, Ma, How the COVID-19 pandemic impacts tobacco addiction: changes in smoking behavior and associations with well-being, Addict Behav, doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106917
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00469580231175780",
"ISSN": [
"0046-9580",
"1945-7243"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/00469580231175780",
"abstract": "<jats:p> The COVID-19 pandemic changed various lifestyle habits worldwide due to the prevention measures implemented in each country, these changes may affect or benefit people’s health. We aimed to systematically review changes in diet, physical activity (PA), alcohol consumption, and tobacco use habits during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults. Two databases: PubMed and ScienceDirect, were used for this systematic review. The research was limited to open-access, peer-reviewed original articles published in English, French, or Spanish from January 2020 to December 2022 and investigated diet, PA, alcohol consumption, and tobacco use habits before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults. Excluded studies were review studies, intervention studies with a sample size of fewer than 30 participants, and poor-quality articles. This review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines (PROSPERO: CRD42023406524), whereas to assess the quality of the studies, we used the quality assessment tools developed by the BSA Medical Sociology Group for cross-sectional studies and the QATSO for the longitudinal studies. Thirty-two studies were included. Some studies reported changes to promote healthy lifestyles; 13 out of 15 articles reported an increase in healthy diet consumption habits, 5 out of 7 studies reported a decrease in alcohol consumption, and 2 out of 3 studies reported a decrease in tobacco use. On the other hand, the other studies reported changes to promote unhealthy lifestyles: 9 out of 15, and 2 out of 7 studies reported an increase in unhealthy diet and alcohol consumption habits respectively, 25 out of 25 reported a decrease in physical activity, and 13 out of 13 reported an increase in sedentary behavior. During the COVID-19 pandemic, there have been changes to promote a healthy and unhealthy lifestyle; the latter can affect people’s health. Therefore, effective responses are needed to mitigate the consequences. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/00469580231175780"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9487-140X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación en Alimentación y Desarrollo, A.C, Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nindenshuti",
"given": "Paul Marcel",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación en Alimentación y Desarrollo, A.C, Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Caire-Juvera",
"given": "Graciela",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing",
"container-title-short": "INQUIRY",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-23T12:48:57Z",
"timestamp": 1684846137000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-23T12:49:01Z",
"timestamp": 1684846141000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-24T04:48:01Z",
"timestamp": 1684903681623
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/00469580231175780",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/00469580231175780",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/00469580231175780",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "004695802311757",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"key": "bibr1-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Listings of WHO’s response to COVID-19 [Internet]. 2020. Accessed September 21, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline"
},
{
"key": "bibr2-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic [Internet]. 2020. Accessed September 21, 2022. https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rpsmen.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20960/nh.02641",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.53877/rc.5.11.20210701.0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.19796",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jshs.2020.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/26293",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18052735",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053817",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph182312405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106917",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.smhs.2021.08.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47197/retos.v0i39.81293",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1139/apnm-2020-0990",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14659891.2021.1916851",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52082/jssm.2021.642",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11332-021-00788-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18168680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dar.13200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj.12580",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980021003906.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18168580",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061958",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0252395",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/adm.0000000000000767",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10143069",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12970-021-00431-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19052558",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.788043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18020369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114122",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-021-10946-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092826",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17176171",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr37-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21149/8803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.12172",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1467-789x.2008.00477.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.626432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr42-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20960/nh.03307",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr43-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.appet.2021.105815",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr44-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/3-540-27661-0_4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr45-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18041502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr46-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217080",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr47-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0006208",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr48-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1742-7622-5-23",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr49-00469580231175780"
},
{
"key": "bibr50-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Healthy diet. [Internet]. 2023. Accessed February 27, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet"
},
{
"key": "bibr51-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. #HealthyAtHome – Physical activity. [Internet]. 2023. Accessed February 27, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/campaigns/connecting-the-world-to-combat-coronavirus/healthyathome/healthyathome—physical-activity"
},
{
"key": "bibr52-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Highlights glaring gaps in the regulation of alcohol marketing across borders [Internet]. 2023. Accessed February 27, 2023. https://www.who.int/news/item/10-05-2022-who-highlights-glaring-gaps-in-regulation-of-alcohol-marketing-across-borders"
},
{
"key": "bibr53-00469580231175780",
"unstructured": "Diana R, Pineda V. Alcoholismo, tabaquismo y sustancias psicoactivas. Revista De Salud Pública. 2001;3(1):74-88. Assessed February 27, 2023. http://www.scielo.org.co/pdf/rsap/v3n1/v3n1a06.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.alcohol.2021.06.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr54-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0255757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr55-00469580231175780"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08897077.2020.1856293",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr56-00469580231175780"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00469580231175780"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health Policy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, Alcohol Consumption, and Tobacco Use in Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "60"
}