Recent:Sevinç Gül Panatto Tazawa Boecker.
Mar 1 |
Meta-analysis of hypochlorous acid studies | |
| Meta-analysis of hypochlorous acid studies | ||
Sep 7 2025 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17091219 | Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) as a Promising Respiratory Antiseptic |
| Review of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a promising respiratory antiseptic for COVID-19 and other viral infections. Authors propose that aerosolized HOCl solutions up to 500 µM (≈26 ppm) could provide an effective early treatment strategy f.. | ||
Aug 1 2025 |
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina61081402 | Nasal Irrigations: A 360-Degree View in Clinical Practice |
| Review of nasal irrigation as a safe, effective, and low-cost treatment for various upper respiratory conditions. High-volume, low-pressure saline irrigations are effective for removing infectious agents, allergens, and inflammatory media.. | ||
Oct 19 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1284274 | Electrolyzed hypochlorous acid water exhibits potent disinfectant activity against various viruses through irreversible protein aggregation |
| In vitro study showing that highly purified slightly acidic hypochlorous acid water (Hp-SA-HAW) exhibits broad-spectrum antiviral activity against various viruses including SARS-CoV-2 through irreversible viral protein aggregation. | ||
Jun 12 2023 |
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11061694 | Preprocedural Viral Load Effects of Oral Antiseptics on SARS-CoV-2 in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review |
| Systematic review of 14 RCTs, showing significant reductions in short-term viral load with mouth rinses cetylpyridinium chloride, β-cyclodextrin and citrox, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine, hypochlorous acid, saline, and.. | ||
Mar 27 2023 |
et al., German Medical Science GMS Publishing House, doi:10.3205/dgkh000433 | Antimicrobial efficacy, mode of action and in vivo use of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) for prevention or therapeutic support of infections |
| Review of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) for in vivo antimicrobial applications including COVID-19. Authors describe HOCl as a naturally occurring component of the innate immune system produced by neutrophils, with broad-spectrum antimicrobial .. | ||
Feb 18 2023 |
et al., BMC Oral Health, doi:10.1186/s12903-023-02820-7 | Hypochlorous acid inactivates oral pathogens and a SARS-CoV-2-surrogate |
| In vitro study showing that hypochlorous acid (HOCl) effectively inactivates oral pathogens and a SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus (MHV-A59). | ||
Jul 31 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.3390/ijtm2030030 | The In Vitro Virucidal Effects of Mouthwashes on SARS-CoV-2 |
| Review of in vitro studies of mouthwashes, showing antiviral activity for SARS-CoV-2 with many compounds including PVP-I, cetylpyridinium chloride, chlorohexidine gluconate, dequalinium chloride, benzalkonium chloride, anionic phthalocyan.. | ||
Jul 29 2022 |
et al., Dental and Medical Problems, doi:10.17219/dmp/150831 | Effect of oral antiseptics on the viral load of SARS-CoV-2: A randomized controlled trial |
| RCT with 21 PVP-I, 20 HOCl, and 20 saline patients gargling for 30 seconds and testing PCR Ct after 30 minutes, showing greater improvement with PVP-I and HOCl, without statistical significance. Ct values differ across testing platforms, .. | ||
May 12 2022 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14051033 | Efficacy of the Sentinox Spray in Reducing Viral Load in Mild COVID-19 and Its Virucidal Activity against Other Respiratory Viruses: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial and an In Vitro Study |
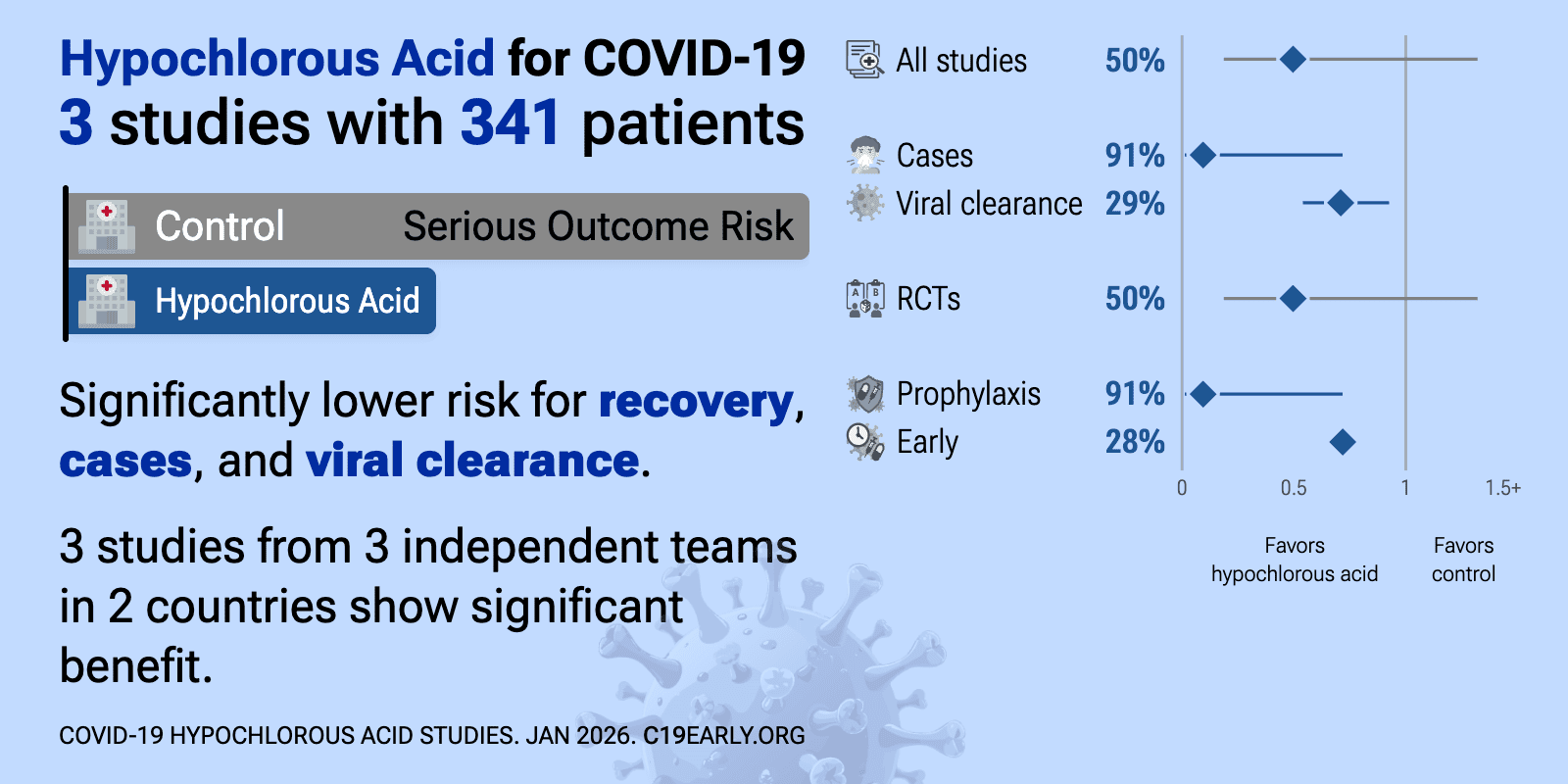
| 29% improved viral clearance (p=0.01). RCT 57 mild COVID-19 patients showing non-significant viral load reduction with Sentinox (STX), a hypochlorous acid nasal spray. The proportion of COVID negative patients by day 5 was significantly higher in the STX-3 group than controls... | ||
Dec 15 2021 |
et al., Biomedical Reports, doi:10.3892/br.2021.1494 | Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevents COVID‑19 in front‑line health professionals: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City |
| 91% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.004). RCT 170 front-line healthcare workers in Mexico showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases with neutral electrolyzed water (SES) nasal and oral rinses. Authors hypothesize that SES inactivates viral particles through its oxidizing potenti.. | ||
Jun 29 2021 |
et al., Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10347 | Safety and efficacy of a COVID‑19 treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed saline combined with usual medical care vs. usual medical care alone: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial |
| 28% improved recovery (p<0.0001). RCT 214 ambulatory COVID-19 patients showing significant benefit with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed saline. The treatment group had reduced risk of hospitalization, lower mortality, and faster time to an acceptable sym.. | ||