Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Who Required Oxygen Supplementation: Results of a Phase 3 Trial
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004, NCT04629703, Nov 2023
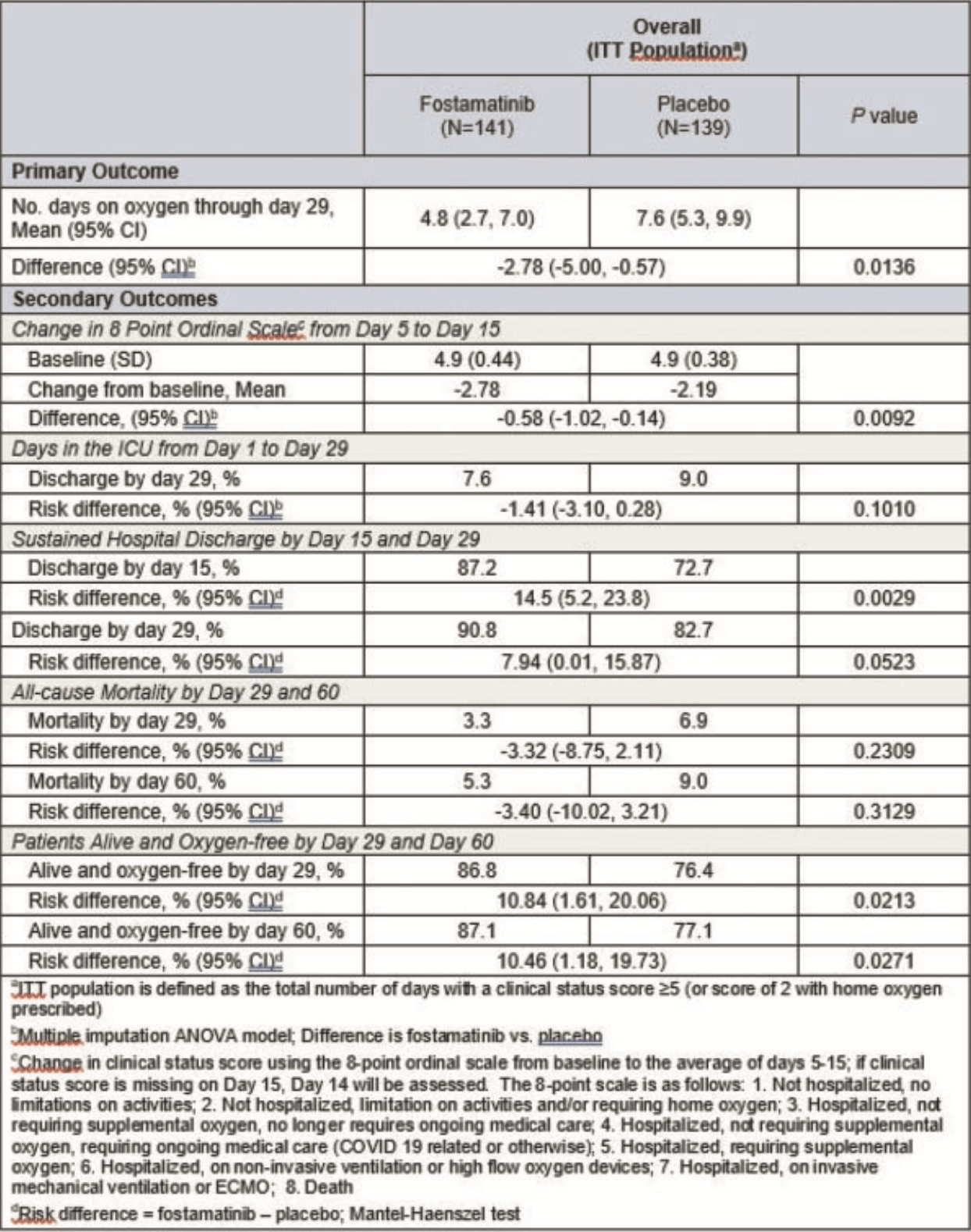
RCT 280 hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen supplementation, showing significantly fewer days on oxygen (4.8 vs. 7.6), improved 8-point ordinal scale score, and more patients alive and oxygen-free by day 60 with fostamatinib compared to placebo, in addition to standard care. Results are not clear, for example the reported mortality percentages do not match any number of the reported number of patients.
|
risk of death, 46.9% lower, RR 0.53, p = 0.17, treatment 7 of 141 (5.0%), control 13 of 139 (9.4%), NNT 23, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 50.7% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.20, treatment 5 of 141 (3.5%), control 10 of 139 (7.2%), NNT 27, day 29.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gotur et al., 27 Nov 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, trial NCT04629703 (history).
Abstract: 88. Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
Who Required Oxygen Supplementation: Results of a Phase 3 Trial
Deepa B. Gotur, MD, FCCP, FCCM1; Anuj Malik, MD, MS2; Vadim Markovtsov,
PhD3; Lucy Yan, MD, PhD4; Wolfgang Dummer, MD, PhD4; Ziad Mallat, MD, PhD5;
1
Weill Cornell Medical College and Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX;
2
Ascension St. John’s Medical Center, Tulsa, Oklahoma; 3Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
South San Francisco, California; 4Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco,
California; 5University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England, United Kingdom
Session: 31. Clinical Trials
Thursday, October 12, 2023: 11:15 AM
Background. Severe COVID-19 is linked to hyperactivation of the host immune
response involving signaling through multiple spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) pathways.
Fostamatinib is an orally administered potent and selective inhibitor of SYK that has
been approved in the US, Canada, Japan, and Europe for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
Methods. We conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase
3 trial of fostamatinib in adults hospitalized for COVID-19 who required oxygen supplementation (NCT04629703). Patients (pts) were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive
fostamatinib (150 mg BID administered orally) or placebo for 14 days. All pts additionally received standard of care at their hospital. The primary endpoint was days
on oxygen (days 1-29).
Results. A total of 280 pts underwent randomization (with 141 assigned to fostamatinib and 139 to placebo). The primary endpoint was met; those who received
fostamatinib had lower mean days on oxygen than those who received placebo (4.8
vs. 7.6 days, P=0.0136; Table 1).
Fostamatinib showed significance or trend towards significance in all secondary
endpoints of reducing mortality and morbidity compared to placebo. The mean
change in the 8-point ordinal score from baseline to the average of Day 5 to 15
was significantly improved in pts who received fostamatinib vs. placebo
(P=0.0092, Table 1). Furthermore, 6 pts were enrolled with a baseline ordinal
score of 6 (3 in each group). All patients in the fostamatinib group survived, and
all in the placebo group died by Day 30. A significantly higher proportion of pts
who received fostamatinib were discharged from the hospital by Day 15
compared to placebo (P=0.0029, Table 1). Significantly more patients were alive
and oxygen-free by Day 29 and Day 60 with fostamatinib treatment in
comparison to placebo (P=0.0213 and P=0.0271, respectively, Table 1).
Treatment-emergent adverse events were consistent with previous studies and
were similar between the 2 groups.
Conclusion. The addition of fostamatinib to standard of care treatment resulted
in significantly fewer days on oxygen, an improved 8-point ordinal scale score, and
significantly more patients alive and oxygen-free by Day 60 compared to placebo in
pts with COVID-19 requiring hospitalization and supplemental oxygen.
Disclosures. Deepa B. Gotur, MD, FCCP, FCCM, GSK: Advisor/Consultant|
GSK: Speaker at ATS|Moderna: Advisor/Consultant Vadim Markovtsov, PhD,
Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employee|Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Stocks/Bonds
Lucy Yan, MD, PhD, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employee|Rigel Pharmaceuticals,
Inc.: Stocks/Bonds Wolfgang Dummer, MD, PhD, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.:
Stocks/Bonds.
1
University of Southampton and University
Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust , Southampton, England, United
2
Kingdom..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe COVID-19 is linked to hyperactivation of the host immune response involving signaling through multiple spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) pathways. Fostamatinib is an orally administered potent and selective inhibitor of SYK that has been approved in the US, Canada, Japan, and Europe for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial of fostamatinib in adults hospitalized for COVID-19 who required oxygen supplementation (NCT04629703). Patients (pts) were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive fostamatinib (150 mg BID administered orally) or placebo for 14 days. All pts additionally received standard of care at their hospital. The primary endpoint was days on oxygen (days 1-29).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 280 pts underwent randomization (with 141 assigned to fostamatinib and 139 to placebo). The primary endpoint was met; those who received fostamatinib had lower mean days on oxygen than those who received placebo (4.8 vs. 7.6 days, P=0.0136; Table 1).</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Fostamatinib showed significance or trend towards significance in all secondary endpoints of reducing mortality and morbidity compared to placebo. The mean change in the 8-point ordinal score from baseline to the average of Day 5 to 15 was significantly improved in pts who received fostamatinib vs. placebo (P=0.0092,Table 1). Furthermore, 6 pts were enrolled with a baseline ordinal score of 6 (3 in each group). All patients in the fostamatinib group survived, and all in the placebo group died by Day 30. A significantly higher proportion of pts who received fostamatinib were discharged from the hospital by Day 15 compared to placebo (P=0.0029,Table 1). Significantly more patients were alive and oxygen-free by Day 29 and Day 60 with fostamatinib treatment in comparison to placebo (P=0.0213 and P=0.0271, respectively, Table 1). Treatment-emergent adverse events were consistent with previous studies and were similar between the 2 groups.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The addition of fostamatinib to standard of care treatment resulted in significantly fewer days on oxygen, an improved 8-point ordinal scale score, and significantly more patients alive and oxygen-free by Day 60 compared to placebo in pts with COVID-19 requiring hospitalization and supplemental oxygen.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Disclosures</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Deepa B. Gotur, MD, FCCP, FCCM, GSK: Advisor/Consultant|GSK: Speaker at ATS|Moderna: Advisor/Consultant Vadim Markovtsov, PhD, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employee|Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Stocks/Bonds Lucy Yan, MD, PhD, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employee|Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Stocks/Bonds Wolfgang Dummer, MD, PhD, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Stocks/Bonds.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Weill Cornell Medical College and Houston Methodist Hospital , Houston, TX"
}
],
"family": "Gotur",
"given": "Deepa B",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ascension St. John's Medical Center , Tulsa, Oklahoma"
}
],
"family": "Malik",
"given": "Anuj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , South San Francisco, California"
}
],
"family": "Markovtsov",
"given": "Vadim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Rigel Pharmaceuticals , South San Francisco, California"
}
],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Rigel Pharmaceuticals , South San Francisco, California"
}
],
"family": "Dummer",
"given": "Wolfgang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Cambridge , Cambridge, England , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Mallat",
"given": "Ziad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-27T02:19:01Z",
"timestamp": 1701051541000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-27T02:19:02Z",
"timestamp": 1701051542000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-27T05:18:01Z",
"timestamp": 1701062281664
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "Supplement_2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "Supplement_2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701043200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/10/Supplement_2/ofad500.004/53774994/ofad500.004.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/10/Supplement_2/ofad500.004/53774994/ofad500.004.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004/7448311"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "88. Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Who Required Oxygen Supplementation: Results of a Phase 3 Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "10"
}